Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Composition in Mice with CKD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
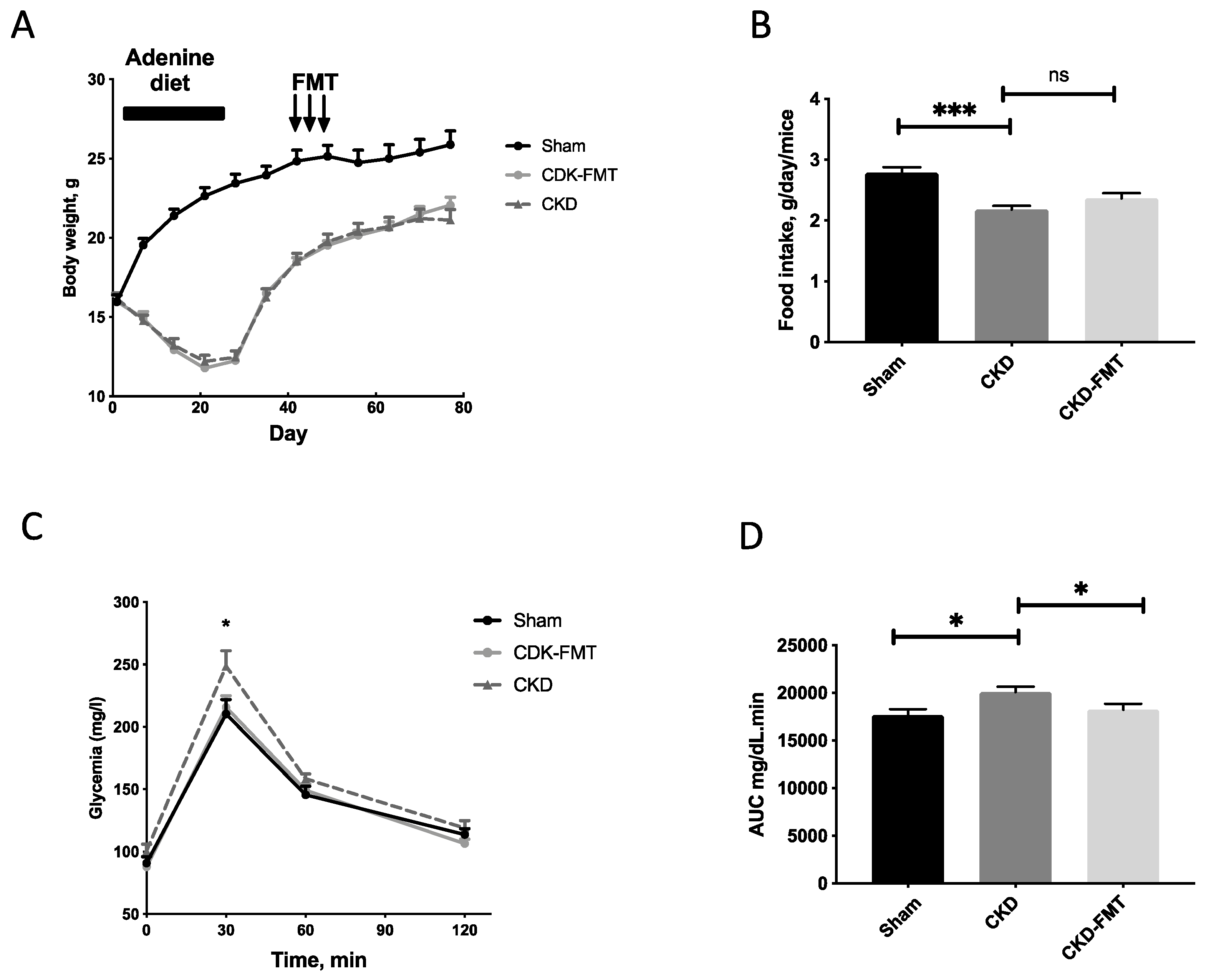
2.1. Characteristics of the CKD Mice
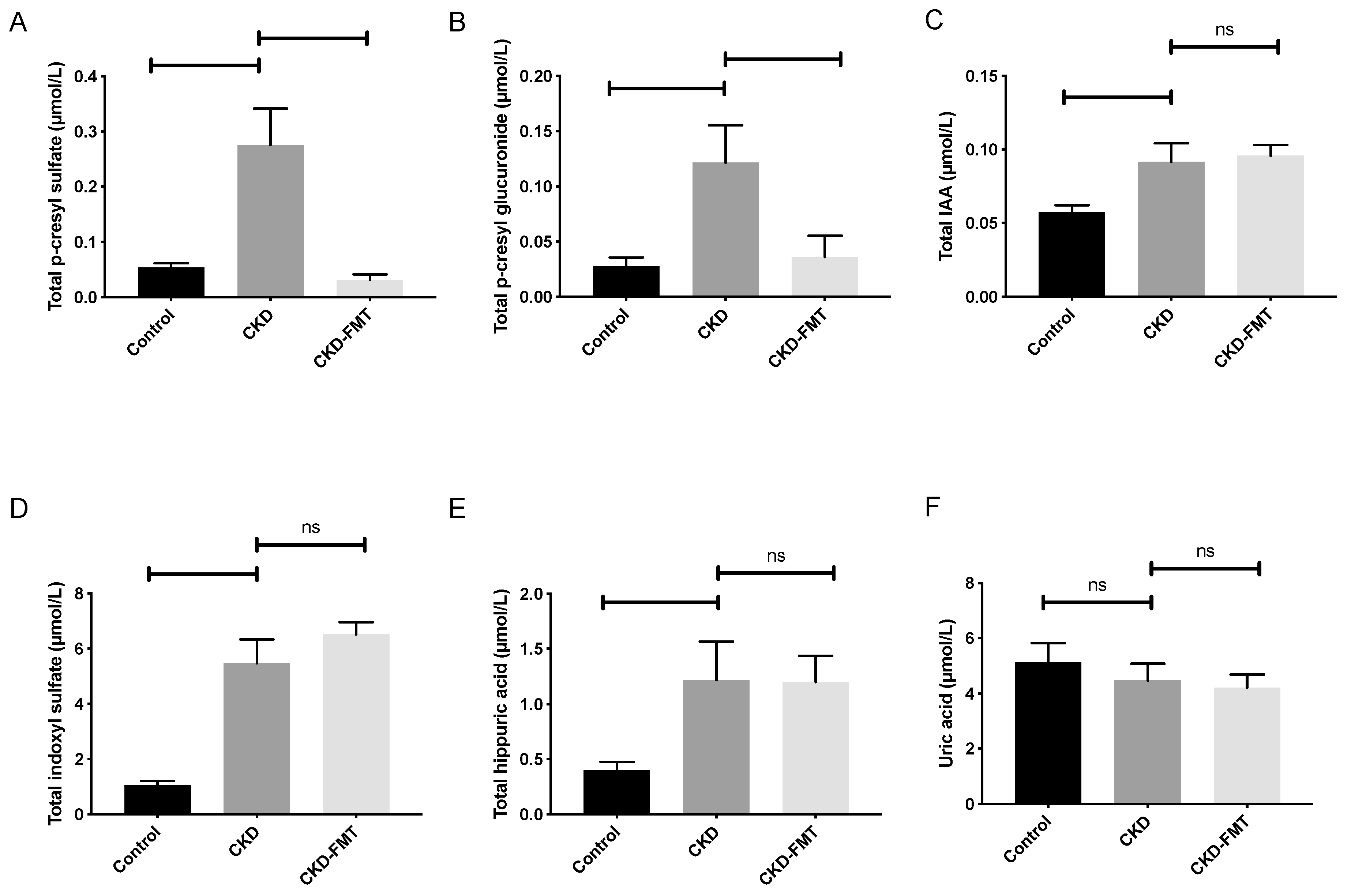
2.2. Effect of FMT on Microbiota-Derived Uremic Toxins
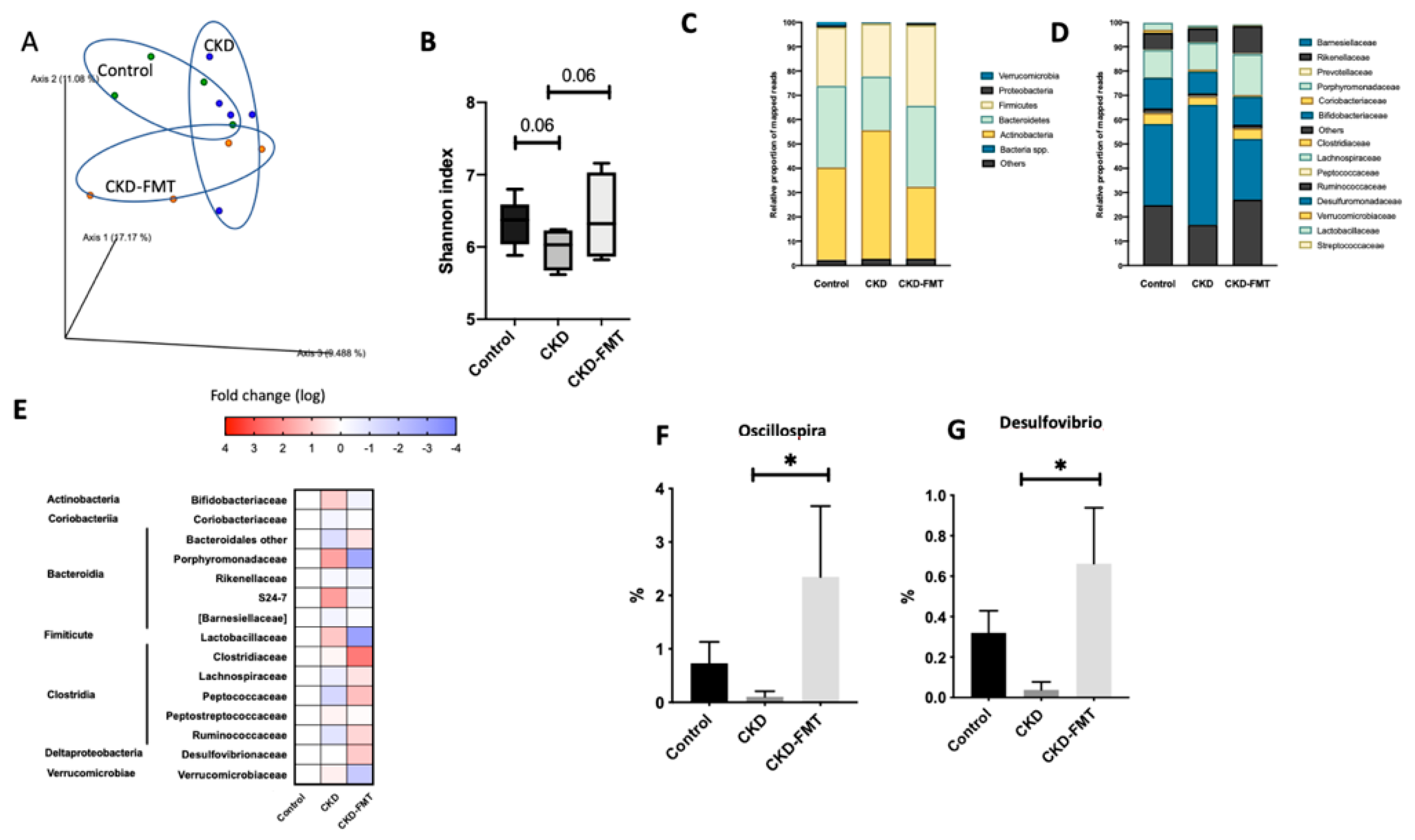
2.3. Gut Effects of FMT on Microbiota Composition
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
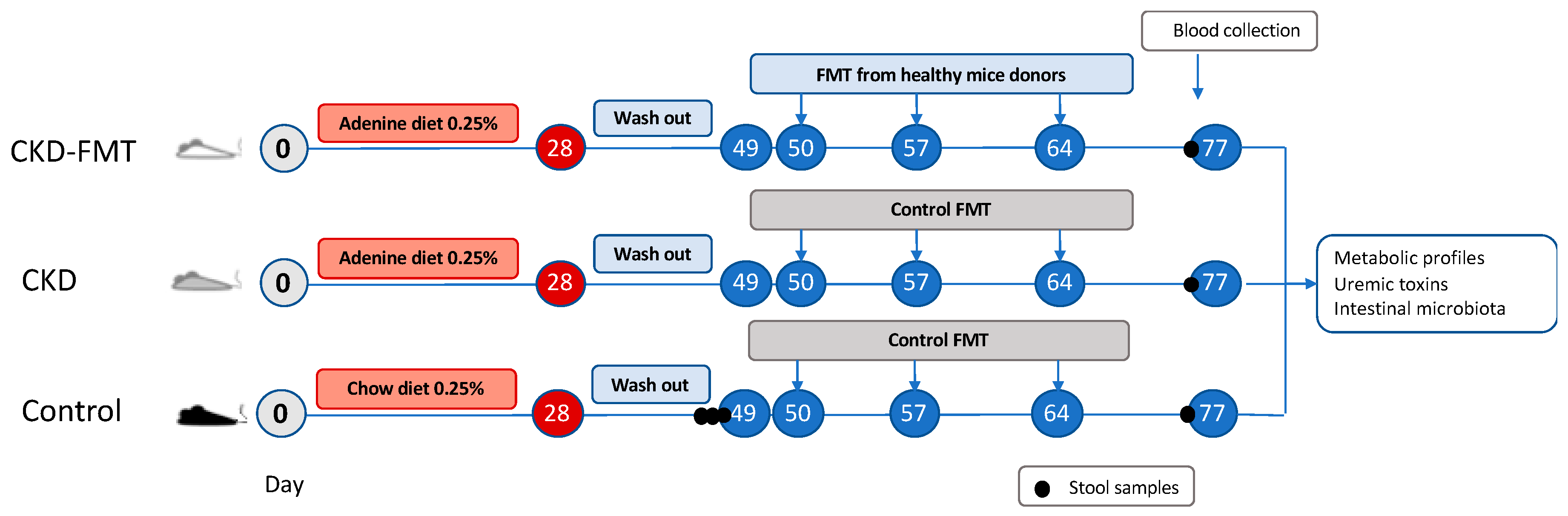
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
5.3. Diuresis and 24-h Proteinuria
5.4. Euthanasia and Necropsy
5.5. Biochemical Analysis and Glucose Challenge
5.6. Analysis of Gene Expression
5.7. Renal Histology
5.8. Measurement of Uremic Toxins
5.9. Fecal Microbiota Analysis by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
5.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2020, 395, 709–733. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Zhao, L.; Hao, Y.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Bian, W.; Zuo, L.; et al. Aberrant gut microbiota alters host metabolome and impacts renal failure in humans and rodents. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Schepers, E.; Pletinck, A.; Nagler, E.V.; Glorieux, G. The uremic toxicity of indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate: A systematic review. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2014, 25, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppe, L.; Fouque, D.; Soulage, C.O. The Role of Gut Microbiota and Diet on Uremic Retention Solutes Production in the Context of Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2018, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masereeuw, R.; Verhaar, M.C. Innovations in approaches to remove uraemic toxins. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 552–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, L.; Roberts, J.; Singh, P.; Jhawar, S.; Matalon, A.; Gao, Z.; Holzman, R.; Liebes, L.; Blaser, M.J.; Lowenstein, J. Microbiome perturbation by oral vancomycin reduces plasma concentration of two gut-derived uremic solutes, indoxyl sulfate and p-cresyl sulfate, in end-stage renal disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2017, 32, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppe, L.; Mafra, D.; Fouque, D. Probiotics and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koppe, L.; Fouque, D. Microbiota and prebiotics modulation of uremic toxin generation. Panminerva Med. 2017, 59, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, G.; Cosola, C.; Di Leo, V.; Gesualdo, M.; Gesualdo, L. Microbiome modulation to correct uremic toxins and to preserve kidney functions. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G.; Tilg, H.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Kump, P.; Satokari, R.; Sokol, H.; Arkkila, P.; Pintus, C.; Hart, A.; et al. European consensus conference on faecal microbiota transplantation in clinical practice. Gut 2017, 66, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.P. Fecal microbiota transplantation—An old therapy comes of age. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 474–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kootte, R.S.; Levin, E.; Salojärvi, J.; Smits, L.P.; Hartstra, A.V.; Udayappan, S.D.; Hermes, G.; Bouter, K.E.; Koopen, A.M.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity after Lean Donor Feces in Metabolic Syndrome Is Driven by Baseline Intestinal Microbiota Composition. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 611–619.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossen, N.G.; Fuentes, S.; van der Spek, M.J.; Tijssen, J.G.; Hartman, J.H.A.; Duflou, A.; Löwenberg, M.; van den Brink, G.R.; Mathus-Vliegen, E.M.H.; de Vos, W.M.; et al. Findings From a Randomized Controlled Trial of Fecal Transplantation for Patients With Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 110–118.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Wakino, S.; Irie, J.; Miyamoto, J.; Matsui, A.; Tajima, T.; Itoh, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yoshifuji, A.; Kimura, I.; et al. Contribution of uremic dysbiosis to insulin resistance and sarcopenia. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2020, 35, 1501–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruppen, E.G.; Garcia, E.; Connelly, M.A.; Jeyarajah, E.J.; Otvos, J.D.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Dullaart, R.P.F. TMAO is Associated with Mortality: Impact of Modestly Impaired Renal Function. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppe, L.; Pillon, N.J.; Vella, R.E.; Croze, M.L.; Pelletier, C.C.; Chambert, S.; Massy, Z.; Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Dugenet, Y.; et al. p-Cresyl Sulfate Promotes Insulin Resistance Associated with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2013, 24, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joossens, M.; Faust, K.; Gryp, T.; Nguyen, A.T.L.; Wang, J.; Eloot, S.; Schepers, E.; Dhondt, A.; Pletinck, A.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Gut microbiota dynamics and uraemic toxins: One size does not fit all. Gut 2019, 68, 2257–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryp, T.; Huys, G.R.B.; Joossens, M.; Van Biesen, W.; Glorieux, G.; Vaneechoutte, M. Isolation and Quantification of Uremic Toxin Precursor-Generating Gut Bacteria in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, L.F.; Stabler, R.A.; Wren, B.W. Assessing the role of p-cresol tolerance in Clostridium difficile. J. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 57, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devlin, A.S.; Marcobal, A.; Dodd, D.; Nayfach, S.; Plummer, N.; Meyer, T.; Pollard, K.S.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Fischbach, M.A. Modulation of a Circulating Uremic Solute via Rational Genetic Manipulation of the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kieffer, D.A.; Piccolo, B.D.; Vaziri, N.D.; Liu, S.; Lau, W.L.; Khazaeli, M.; Nazertehrani, S.; Moore, M.E.; Marco, M.L.; Martin, R.J.; et al. Resistant starch alters gut microbiome and metabolomic profiles concurrent with amelioration of chronic kidney disease in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2016, 310, F857–F871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaziri, N.D.; Wong, J.; Pahl, M.; Piceno, Y.M.; Yuan, J.; Desantis, T.Z.; Ni, Z.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Andersen, G.L. Chronic kidney disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Huang, M.; You, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y. Gut microbiota mediates the anti-obesity effect of calorie restriction in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burrello, C.; Garavaglia, F.; Cribiù, F.M.; Ercoli, G.; Lopez, G.; Troisi, J.; Colucci, A.; Guglietta, S.; Carloni, S.; Guglielmetti, S.; et al. Therapeutic faecal microbiota transplantation controls intestinal inflammation through IL10 secretion by immune cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunc, F.; Schleicher, E.; Weigert, C.; Fritsche, A.; Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U. The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 721–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Hashimoto, N.; Hayashi, H.; Ise, M.; Uehara, Y.; Maeda, K. Suppressed serum and urine levels of indoxyl sulfate by oral sorbent in experimental uremic rats. Am. J. Nephrol. 1992, 12, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Roy, T.; Debédat, J.; Marquet, F.; Da-Cunha, C.; Ichou, F.; Guerre-Millo, M.; Kapel, N.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Clément, K. Comparative Evaluation of Microbiota Engraftment Following Fecal Microbiota Transfer in Mice Models: Age, Kinetic and Microbial Status Matter. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, R.; Toft, M.F.; August, B.; Hansen, A.K.; Hansen, C.H.F. Antibiotic-treated versus germ-free rodents for microbiota transplantation studies. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoop, K.A.; McDonald, K.G.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Newberry, R.D. Antibiotics Promote Inflammation Through the Translocation of Native Commensal Colonic Bacteria. Gut 2016, 65, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baym, M.; Stone, L.K.; Kishony, R. Multidrug evolutionary strategies to reverse antibiotic resistance. Science 2016, 351, aad3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, E.; Fukuda, S.; Mukawa, C.; Yuri, A.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Fukuda, N.N.; Tsukamoto, H.; Asaji, K.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of gut microbiota on uremic solute accumulation by a CE-TOFMS-based metabolomics approach. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 634–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, H.R.; Gandolfo, M.T.; Ko, G.J.; Satpute, S.; Racusen, L.; Rabb, H. Early exposure to germs modifies kidney damage and inflammation after experimental ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 297, F1457–F1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freitag, T.L.; Hartikainen, A.; Jouhten, H.; Sahl, C.; Meri, S.; Anttila, V.-J.; Mattila, E.; Arkkila, P.; Jalanka, J.; Satokari, R. Minor Effect of Antibiotic Pre-treatment on the Engraftment of Donor Microbiota in Fecal Transplantation in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deltombe, O.; Dhondt, A.; Biesen, W.V.; Glorieux, G.; Eloot, S. Effect of sample temperature, pH, and matrix on the percentage protein binding of protein-bound uraemic toxins. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1935–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albouery, M.; Buteau, B.; Grégoire, S.; Cherbuy, C.; Pais de Barros, J.-P.; Martine, L.; Chain, F.; Cabaret, S.; Berdeaux, O.; Bron, A.M.; et al. Age-Related Changes in the Gut Microbiota Modify Brain Lipid Composition. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Control | CKD | CKD-FMT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 10 | 10 | 9 | ||||||
| Biometric data | |||||||||
| BW (g) | 26 | ± | 1a | 21 | ± | 1b | 22 | ± | 1b |
| BL (cm) | 9.5 | ± | 0.1a | 8.9 | ± | 0.1b | 8.9 | ± | 0.1b |
| Lee index (×103) | 312 | ± | 2a | 312 | ± | 2a | 317 | ± | 4a |
| Adipose tissue weight | |||||||||
| Intra-abdoWAT (mg/10 g BW) | 167 | ± | 14a | 130 | ± | 9a | 131 | ± | 5a |
| rWAT (mg/10 g BW) | 36 | ± | 5a | 18 | ± | 2b | 22 | ± | 1b,c |
| eWAT (mg/10 g BW) | 131 | ± | 9a | 112 | ± | 8ab | 70 | ± | 17b |
| Organ weight | |||||||||
| Heart (mg/10 g BW) | 50 | ± | 2a | 54 | ± | 1a | 53 | ± | 1a |
| Gastrocnemius (mg/10 g BW) | 56 | ± | 3a | 56 | ± | 2a | 55 | ± | 1a |
| Liver (mg/10 g BW) | 452 | ± | 8a | 405 | ± | 8b | 467 | ± | 9a |
| Kidneys (mg/10 g BW) | 114 | ± | 3a | 77 | ± | 1b | 78 | ± | 2b |
| Variable n | Control | CKD | CKD-FMT | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | 9 | |||||||
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 5.0 | ± | 0.3a | 5.5 | ± | 0.3a | 4.8 | ± | 0.2a |
| Serum creatinine (µmol/L) | 8.52 | ± | 0.4a | 16.0 | ± | 1.1b | 17.2 | ± | 0.5b |
| Urinary output (mL/24 h) | 0.3 | ± | 0.1a | 2.1 | ± | 0.4a | 1.9 | ± | 0.8a |
| Urinary protein (mg/24 h) | 0.5 | ± | 0.2a | 0.5 | ± | 0.2a | 0.6 | ± | 0.3a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barba, C.; Soulage, C.O.; Caggiano, G.; Glorieux, G.; Fouque, D.; Koppe, L. Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Composition in Mice with CKD. Toxins 2020, 12, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120741
Barba C, Soulage CO, Caggiano G, Glorieux G, Fouque D, Koppe L. Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Composition in Mice with CKD. Toxins. 2020; 12(12):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120741
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarba, Christophe, Christophe O. Soulage, Gianvito Caggiano, Griet Glorieux, Denis Fouque, and Laetitia Koppe. 2020. "Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Composition in Mice with CKD" Toxins 12, no. 12: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120741
APA StyleBarba, C., Soulage, C. O., Caggiano, G., Glorieux, G., Fouque, D., & Koppe, L. (2020). Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Composition in Mice with CKD. Toxins, 12(12), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12120741







