Ankle and Foot Spasticity Patterns in Chronic Stroke Survivors with Abnormal Gait
Abstract
1. Introduction
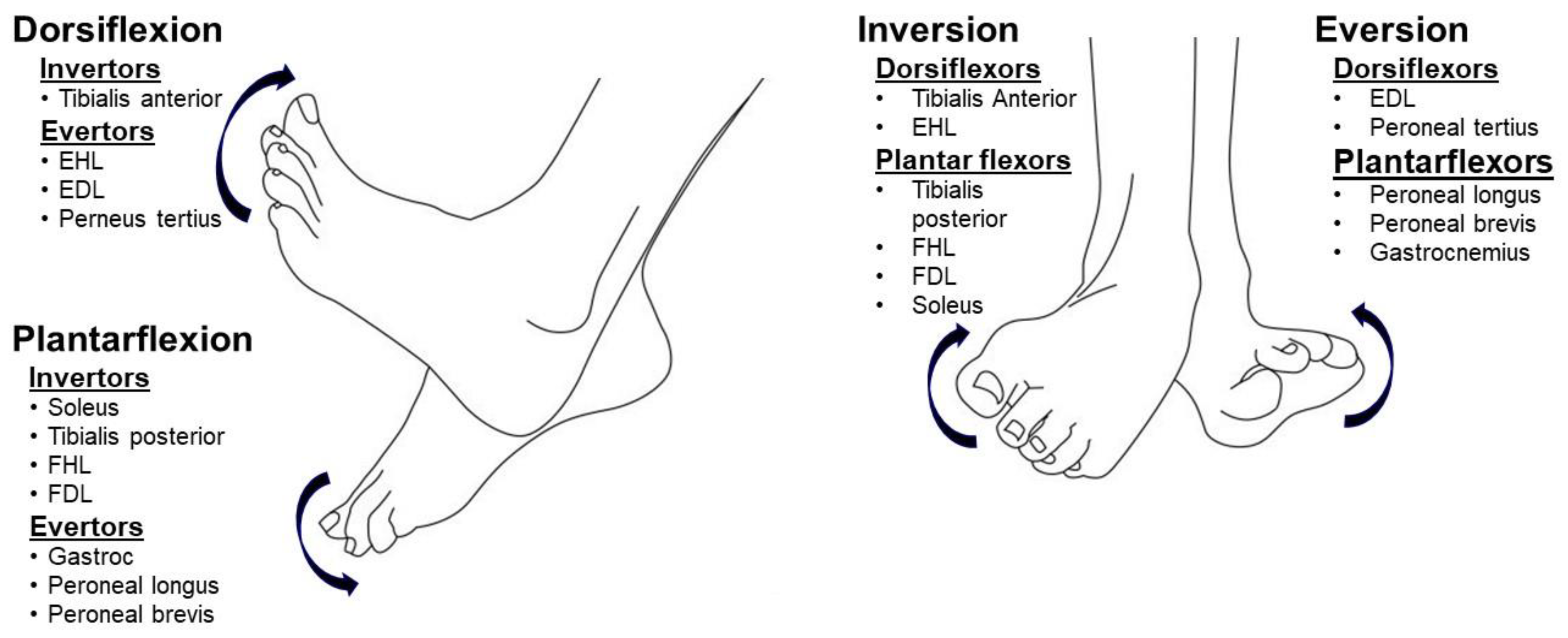
2. Common Deformities
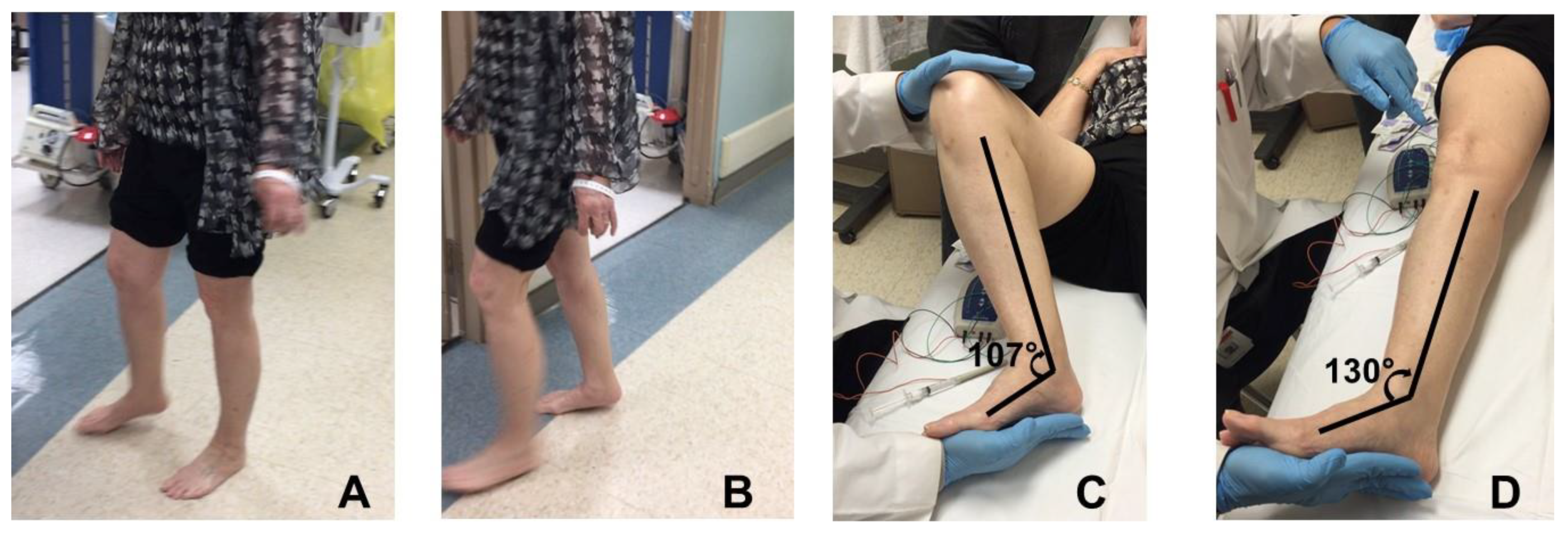
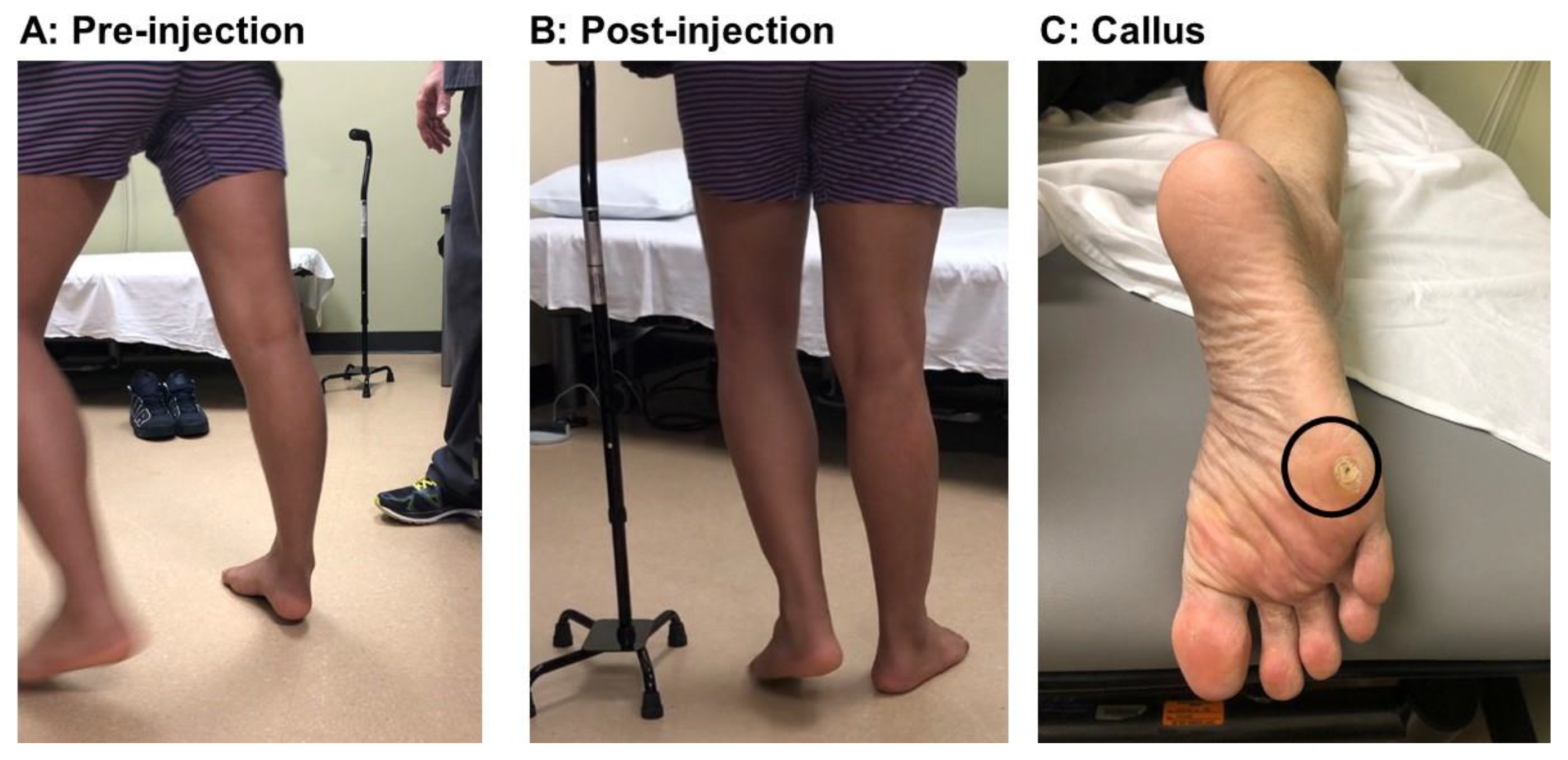
2.1. Equinus (Plantar Flexion)
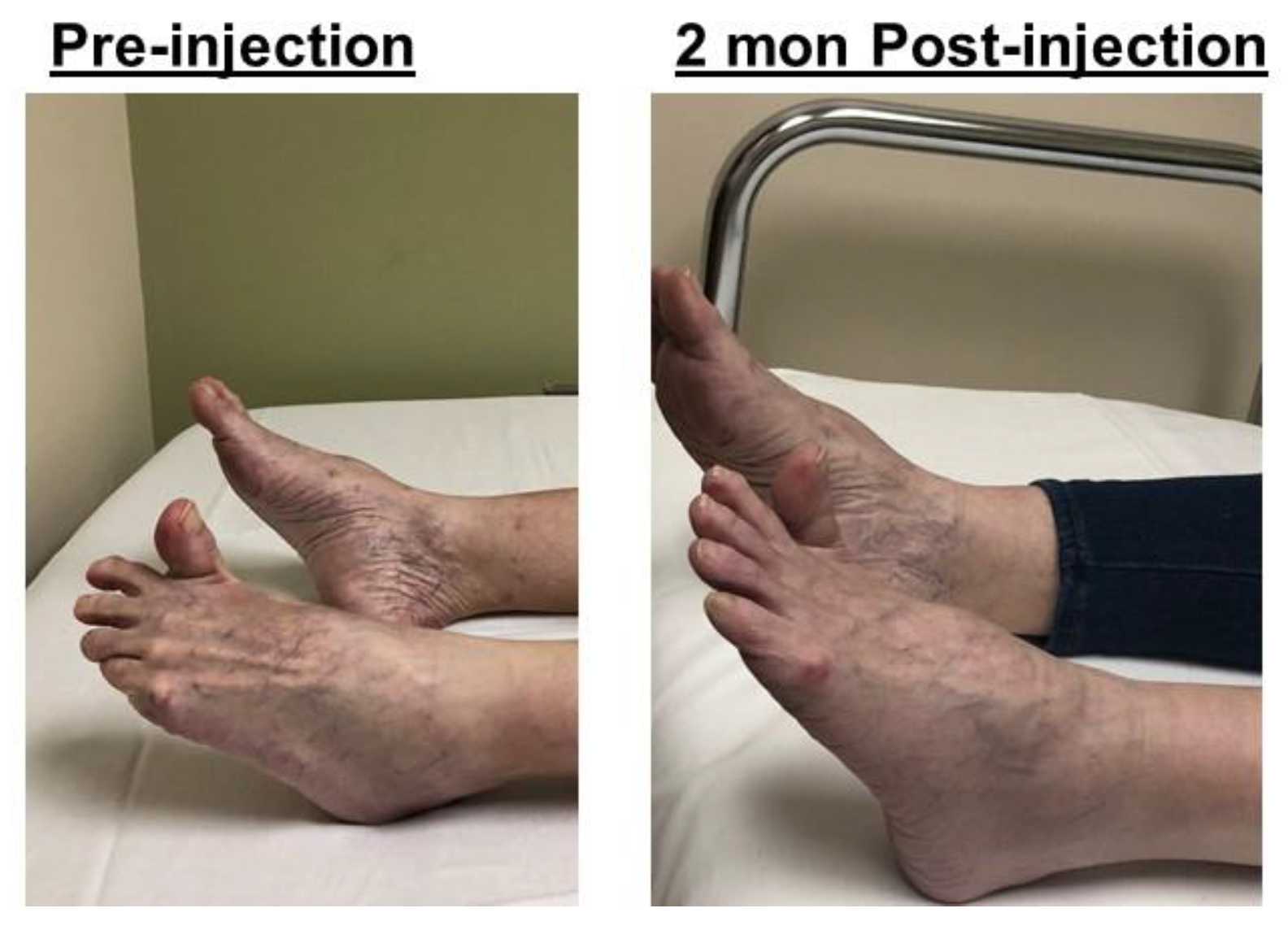
2.2. Varus (Inversion)
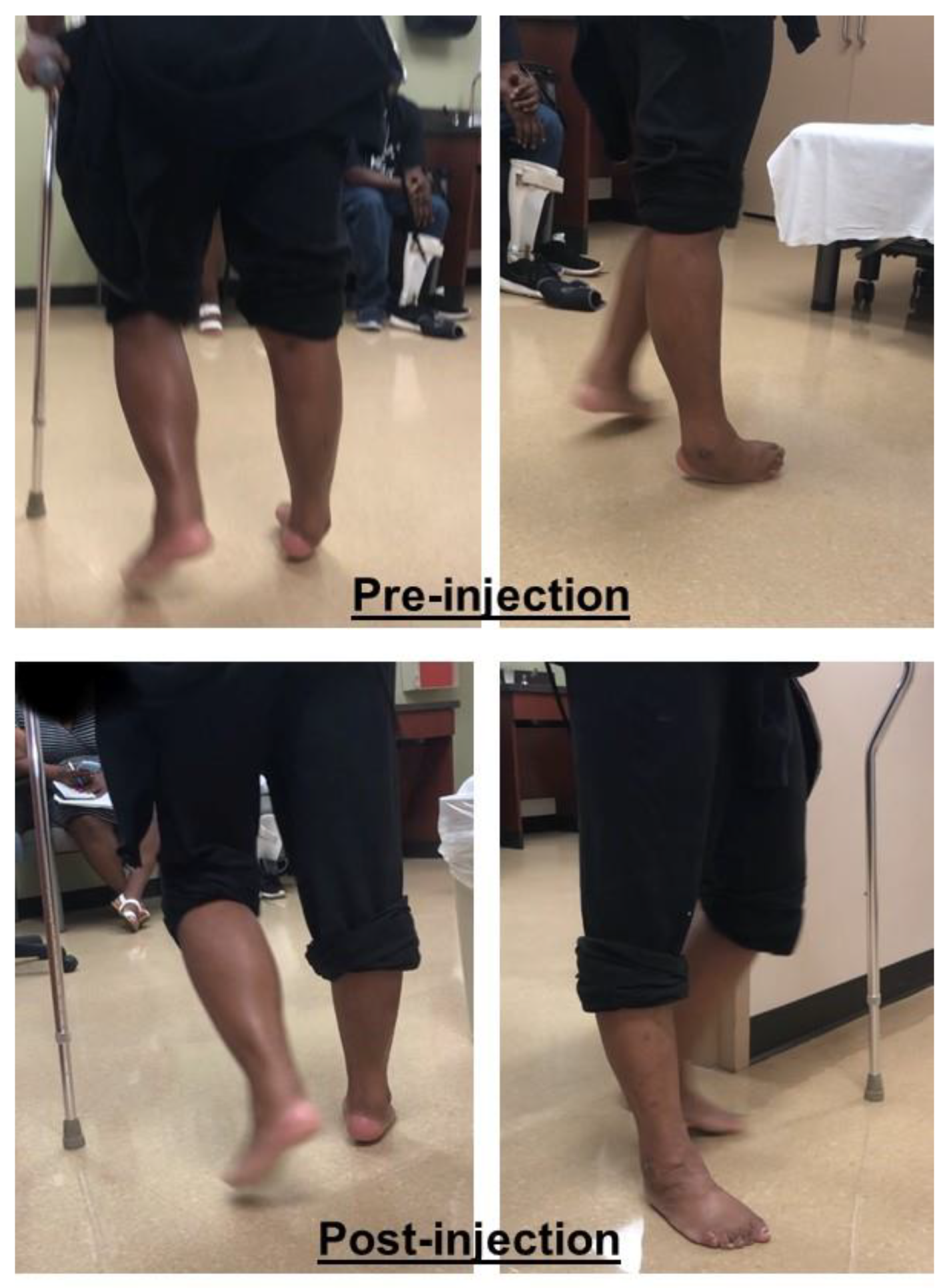
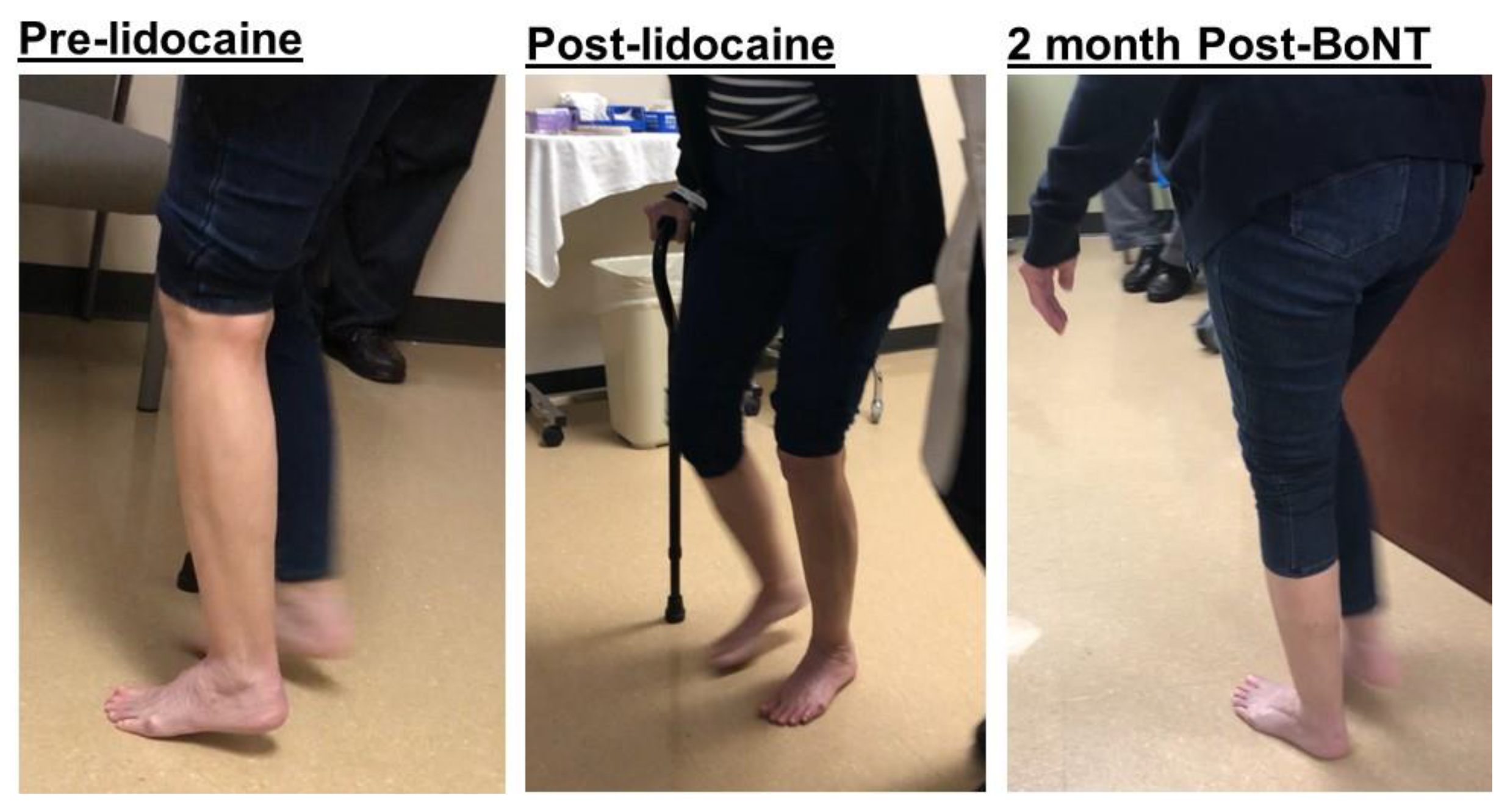
2.3. Equinovarus
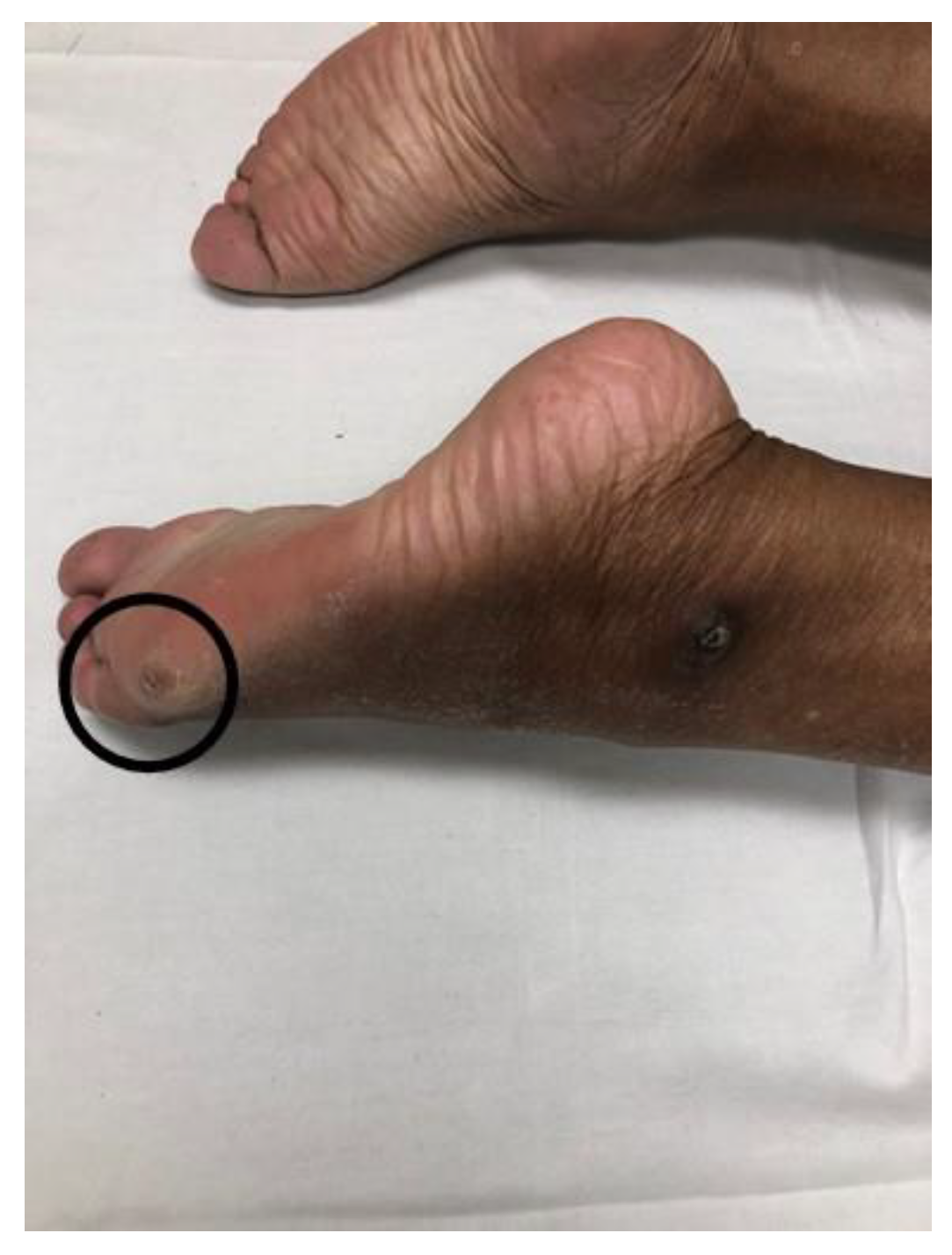
2.4. Striatal Toe
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Nakayama, H.; Raaschou, H.O.; Olsen, T.S. Recovery of walking function in stroke patients: The copenhagen stroke study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1995, 76, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltombe, T.; Wautier, D.; De Cloedt, P.; Fostier, M.; Gustin, T. Assessment and treatment of spastic equinovarus foot after stroke: Guidance from the mont-godinne interdisciplinary group. J. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 49, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioni, M.; Esquenazi, A.; Hirai, B. Effects of Botulinum Toxin-A on Gait Velocity, Step Length, and Base of Support of Patients with Dynamic Equinovarus Foot. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 85, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, N.; Murie-Fernandez, M.; Speechley, M.; Salter, K.; Sequeira, K.; Teasell, R. Does the treatment of spastic equinovarus deformity following stroke with botulinum toxin increase gait velocity? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensoussan, L.; Mesure, S.; Viton, J.M.; Delarque, A. Kinematic and kinetic asymmetries in hemiplegic patients’ gait initiation patterns. J. Rehabil. Med. 2006, 38, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Francisco, G.E.; Zhou, P. Post-stroke Hemiplegic Gait: New Perspective and Insights. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Francisco, G.E. New insights into the pathophysiology of post-stroke spasticity. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chen, Y.T.; Francisco, G.E.; Zhou, P.; Rymer, W.Z. A Unifying Pathophysiological Account for Post-stroke Spasticity and Disordered Motor Control. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, A.; Brüggemann, G.P.; Koebke, J.; Segesser, B. Asymmetrical loading of the human triceps surae: I. Mediolateral force differences in the Achilles tendon. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojsen-Møller, J.; Magnusson, S.P. Heterogeneous Loading of the Human Achilles Tendon In Vivo. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2015, 43, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnekes, J.; Benda, N.; Van Duijnhoven, H.; Lem, F.; Keijsers, N.; Louwerens, J.W.K.; Pieterse, A.; Renzenbrink, B.; Weerdesteyn, V.; Buurke, J.; et al. Management of gait impairments in chronic unilateral upper motor neuron lesions a review. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picelli, A.; Tamburin, S.; Bonetti, P.; Fontana, C.; Barausse, M.; Dambruoso, F.; Gajofatto, F.; Santilli, V.; Smania, N. Botulinum toxin type A injection into the gastrocnemius muscle for spastic equinus in adults with stroke: A randomized controlled trial comparing manual needle placement, electrical stimulation and ultrasonography-guided injection techniques. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, L.; Lisco, G.; Pastorelli, S.; Dimanico, U. Effects of botulinum neurotoxin on spatio-temporal gait parameters of patients with chronic stroke: A prospective open-label study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esquenazi, A.; Moon, D.; Wikoff, A.; Sale, P. Hemiparetic gait and changes in functional performance due to OnabotulinumtoxinA injection to lower limb muscles. Toxicon 2015, 107, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, M.; Rabuffetti, M.; Bacchini, M.; Casiraghi, A.; Castagna, A.; Pizzi, A.; Montesano, A. Does gait analysis change clinical decision-making in poststroke patients? Results from a pragmatic prospective observational study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Mottram, C.J.; Suresh, N.L.; Heckman, C.J.; Gorassini, M.A.; Rymer, W.Z. Origins of abnormal excitability in biceps brachii motoneurons of spastic-paretic stroke survivors. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 102, 2026–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottram, C.J.; Wallace, C.L.; Chikando, C.N.; Rymer, W.Z. Origins of spontaneous firing of motor units in the spastic-paretic biceps brachii muscle of stroke survivors. J. Neurophysiol. 2010, 104, 3168–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Francisco, G.E.; Zhou, P.; Rymer, W.Z.; Li, S. Spasticity, weakness, force variability, and sustained spontaneous motor unit discharges of resting spastic-paretic biceps brachii muscles in chronic stroke. Muscle Nerve 2013, 48, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suputtitada, A. Local botulinum toxin type A injections in the treatment of spastic toes. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 81, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtis, M.M.; Floyd, A.G.; Yu, Q.P.; Pullman, S.L. High doses of botulinum toxin effectively treat disabling up-going toe. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 264, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, A.P.; Keenan, M.A.E.; Smith, C.W.; Garland, D.E. Intrinsic Toe Flexion Deformity Following Correction of Spastic Equinovarus Deformity in Adults. Foot Ankle Int. 1987, 7, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Tanikawa, H.; Kagaya, H.; Saitoh, E.; Ozaki, K.; Hirano, S.; Itoh, N.; Yamada, J.; Kanada, Y. Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin A Treatment for Pes Varus during Gait. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2416–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S. Ankle and Foot Spasticity Patterns in Chronic Stroke Survivors with Abnormal Gait. Toxins 2020, 12, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100646
Li S. Ankle and Foot Spasticity Patterns in Chronic Stroke Survivors with Abnormal Gait. Toxins. 2020; 12(10):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Sheng. 2020. "Ankle and Foot Spasticity Patterns in Chronic Stroke Survivors with Abnormal Gait" Toxins 12, no. 10: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100646
APA StyleLi, S. (2020). Ankle and Foot Spasticity Patterns in Chronic Stroke Survivors with Abnormal Gait. Toxins, 12(10), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12100646



