A Hylarana latouchii Skin Secretion-Derived Novel Bombesin-Related Pentadecapeptide (Ranatensin-HLa) Evoke Myotropic Effects on the in vitro Rat Smooth Muscles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
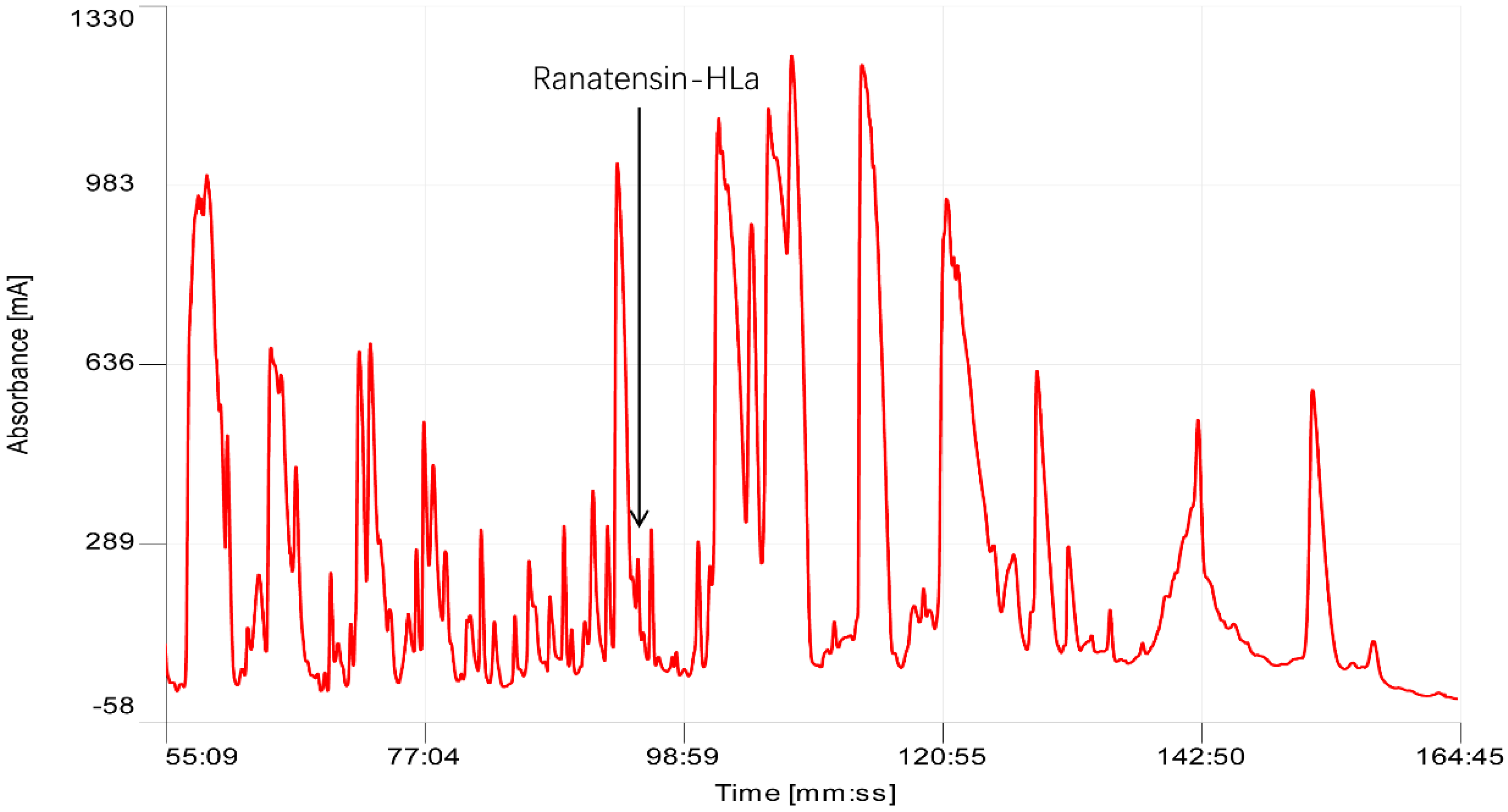
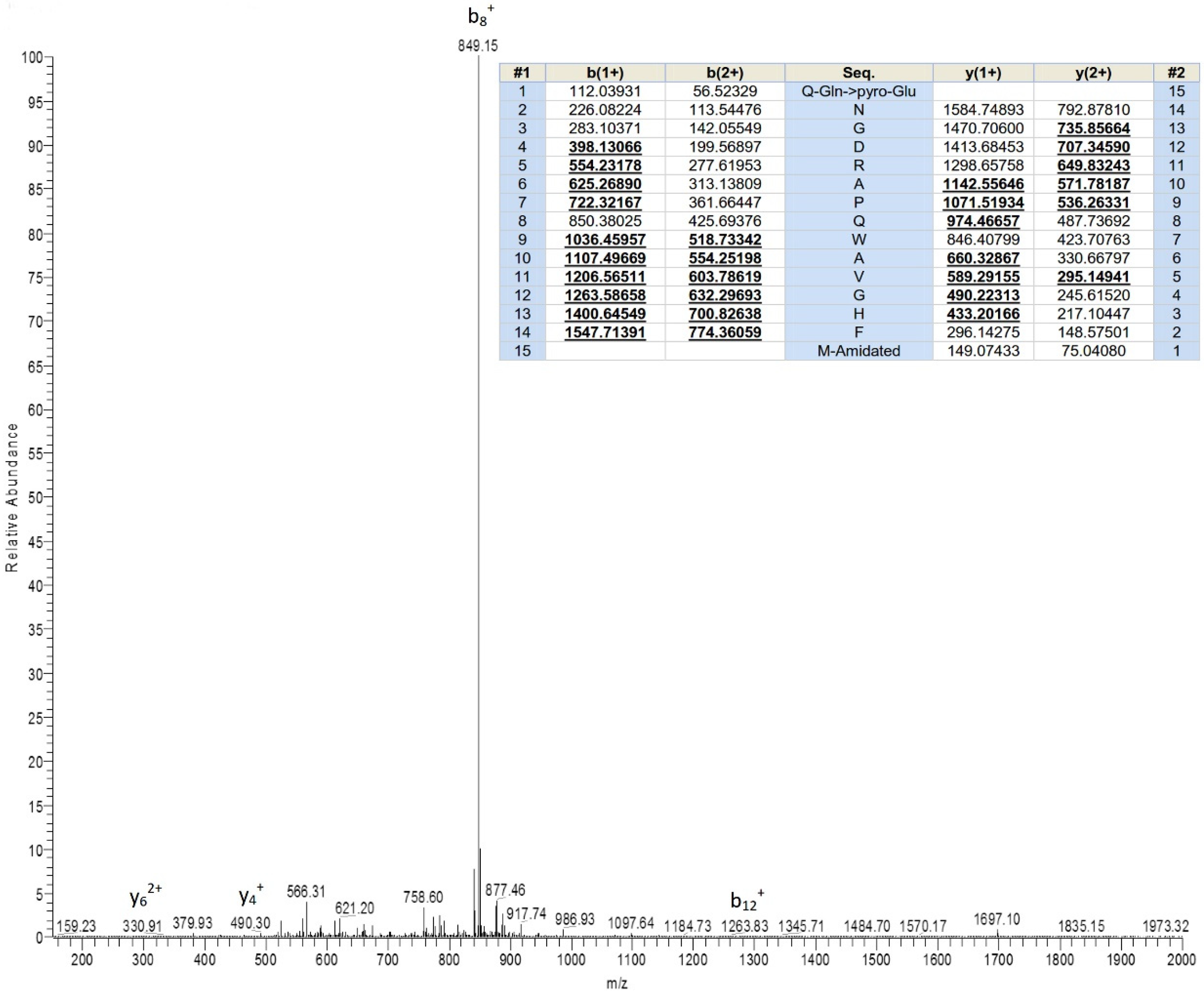
2.1. Bioactivity Screening Resulted in Discovery of Ranatensin-HLa
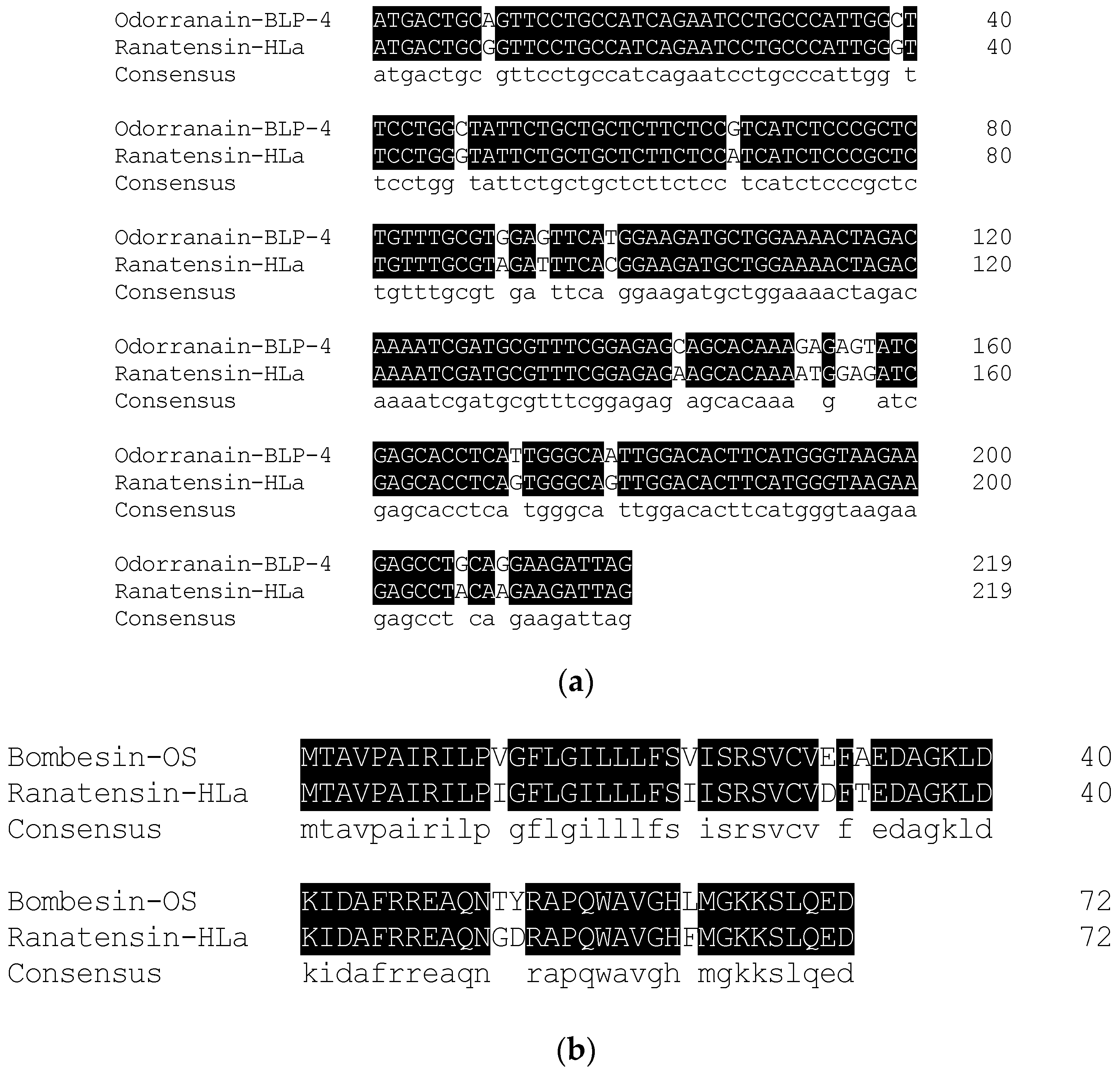
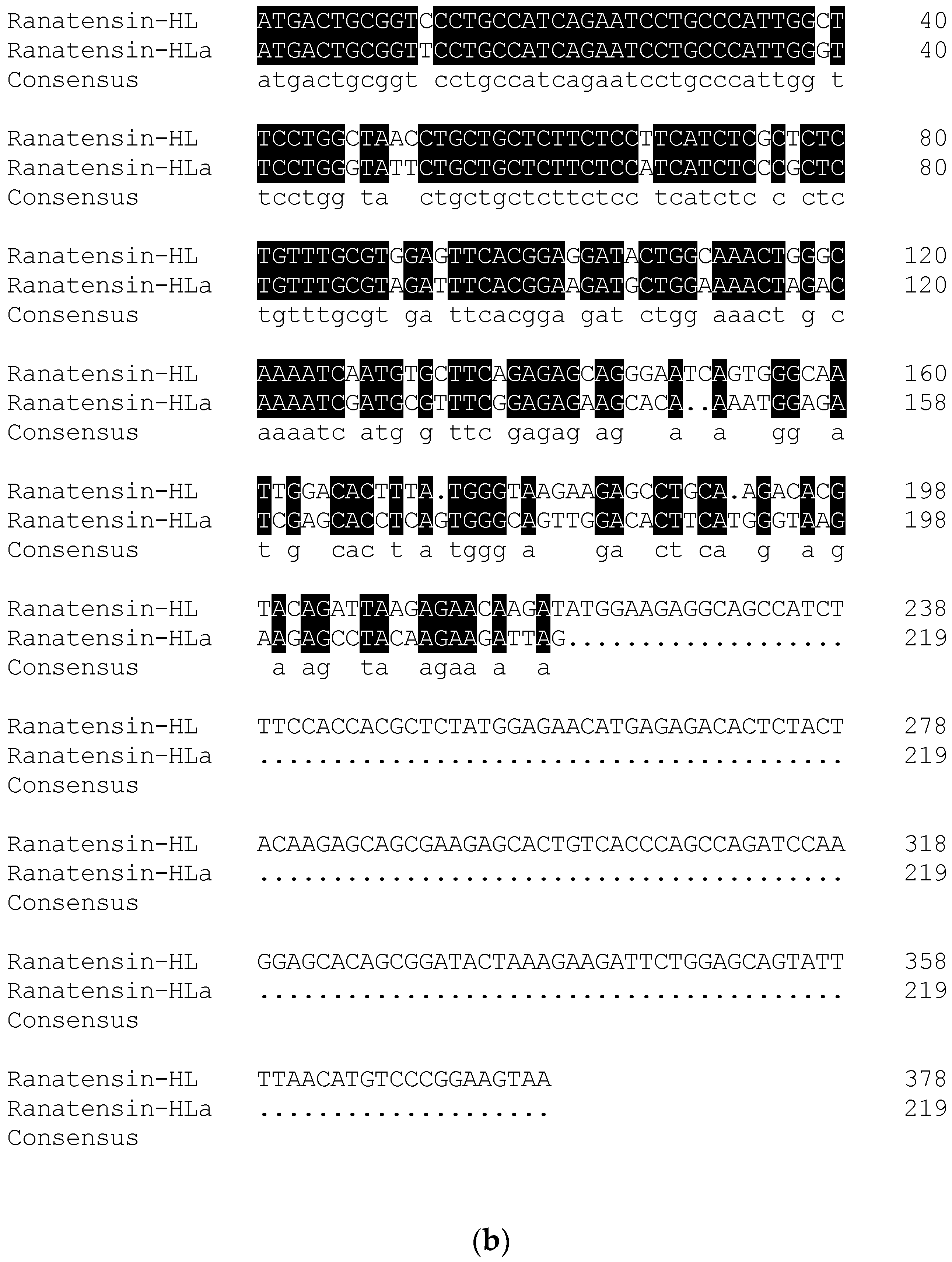
2.2. Molecular Cloning of the cDNA Encoding the Biosynthetic Precursor of Ranatensin-HLa
2.3. Pharmacological Effects of Ranatensin-HLa on Rat Smooth Muscles
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Specimen Biodata and Skin Secretion Acquisition
5.2. Chromatographic Fractionation of H. latouchii Skin Secretion with Reverse Phase HPLC
5.3. Myoactivity Screening of Chromatographic Fractions
5.4. Structural Characterization of Peptide Possessing Bioactivity
5.5. Molecular Cloning of the cDNA Encoding the Peptide Biosynthetic Precursor of Ranatensin-HLa
5.6. Fmoc Chemistry Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis of Ranatensin-HLa
5.7. The Effects of Synthetic Peptide on Rat Smooth Muscles Tension
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pough, F.H. Amphibian biology and husbandry. Inst. Lab. Anim. Resour. 2007, 48, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, M.L. Amphibian diversity and life history. In Amphibian Ecology and Conservation: A Handbook of Techniques; Dodd, C.K., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, D.R. Amphibian Species of the World: An Online Reference. Version 6.0. Available online: http://research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html (accessed on 20 February 2019).
- König, E.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Shaw, C. The diversity and evolution of anuran skin peptides. Peptides 2015, 63, 96–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, C.; Navas, P.; Aijon, J.; Lopez-Campos, J.L. Glycoconjugates in the epidermis of Pleurodeles waltlii. J. Ultrasructure Res. 1981, 77, 354–359. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, R.C.; Jared, C. Cutaneous granular glands and amphibian venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part Physiol. 1995, 111, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, L.H.; Attila, M. The toad, ugly and venomous, wears yet a precious jewel in his skin. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 41, 473–507. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.T. The natural history of amphibian skin secretions, their normal functioning and potential medical applications. Biol. Rev. 1997, 72, 365–379. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes, A.; Giri, B.; Saha, A.; Mishra, R.; Dasgupta, S.C.; Debnath, A.; Gomes, A. Bioactive molecules from amphibian skin: Their biological activities with reference to therapeutic potentials for possible drug development. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 45, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevins, C.; Zasloff, M. Peptides from frog skin. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 395–414. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, A.; Pirri, G.; Nicoletto, S.F. Antimicrobial peptides: An overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2007, 2, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Samgina, T.Y.; Artemenko, K.A.; Gorshkov, V.A.; Lebedev, A.T. Bioactive peptides from the skin of ranid frogs: Modern approaches to the mass spectrometric de novo sequencing. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Calderon, L.; Stabeli, R. Anuran Amphibians: A huge and threatened factory of a variety of active peptides with potential nanobiotechnological applications in the face of amphibian decline. Chang. Divers. Chang. Environ. Oscar Grillo Gianfranco Venora 2011, 7, 211–242. [Google Scholar]
- Simmaco, M.; Mignogna, G.; Barra, D. Antimicrobial peptides from amphibian skin: What do they tell us? Biopolym. (Peptide Sci.) 1998, 47, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, A.; Erspamer, V.; Bucci, M. Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytesin, two analogous active peptides from the skin of the european amphibians Bombina and Alytes. Experientia 1971, 27, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, T.J.; Jörnvall, H.; Nilsson, G.; Vagne, M.; Ghatei, M.; Bloom, S.R.; Mutt, V. Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 90, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Neuromedin B: A novel bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 114, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erspamer, V.; Erspamer, G.F.; Inselvini, M. Some pharmacological actions of alytesin and bombesin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1970, 22, 875–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalla, S.R.; Barry, B.J.; Falick, A.M.; Gibson, B.W.; Taylor, J.E.; Dong, J.Z.; Spindel, E.R. There are three distinct forms of bombesin: identification of [Leu13] bombesin, [Phe13] bombesin, and [Ser3, Arg10, Phe13] bombesin in the frog Bombina orientalis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7731–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, R.; Liu, H.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. A novel proline rich bombesin-related peptide (PR-bombesin) from toad Bombina maxima. Peptides 2002, 23, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.T.; Battey, J.F.; Spindel, E.R.; Benya, R.V. International Union of Pharmacology. LXVIII. Mammalian Bombesin Receptors: Nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, signaling, and functions in normal and disease states. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krane, I.M.; Naylor, S.L.; Helin-Davis, D.; Chin, W.W.; Spindel, E.R. Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding the human bombesin-like peptide neuromedin B. Chromosomal localization and comparison to cDNAs encoding its amphibian homolog ranatensin. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13317–13323. [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi, M.; Ui-Tei, K.; Yamada, K.; Matsuda, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Ohki-Hamazaki, H. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian bombesin-like peptide receptors: New tools for investigating molecular basis for ligand selectivity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagalla, S.R.; Barry, B.J.; Creswick, K.C.; Eden, P.; Taylor, J.T.; Spindel, E.R. Cloning of a receptor for amphibian [Phe13] bombesin distinct from the receptor for gastrin-releasing peptide: Identification of a fourth bombesin receptor subtype (BB4). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1995, 92, 6205–6209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, T.; Pradhan, T.K.; Ryan, R.R.; Mantey, S.A.; Jensen, R.T. Pharmacology and cell biology of the bombesin receptor subtype 4 (BB4-R). Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7307–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippe, G.; Angenot, L. Recent developments in the field of arrow and dart poisons. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumbacher, J.P.; Wako, A.; Derrickson, S.R.; Samuelson, A.; Spande, T.F.; Daly, J.W. Melyrid beetles (Choresine): A putative source for the batrachotoxin alkaloids found in poison-dart frogs and toxic passerine birds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15857–15860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, F.; Li, A.; Inagaki, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Kokudo, N.; Li, X.K.; Tang, W. Chinese herbal medicines as adjuvant treatment during chemo- or radio-therapy for cancer. Biosci. Trends 2010, 4, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Raju, U.; Milas, L.; Molkentine, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, P.; Cohen, L.; Meng, Z.; Liao, Z. Huachansu, containing cardiac glycosides, enhances radiosensitivity of human lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takai, N.; Kira, N.; Ishii, T.; Yoshida, T.; Nishida, M.; Nishida, Y.; Nasu, K.; Narahara, H. Bufalin, a traditional oriental medicine, induces apoptosis in human cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Q. Preparative separation and purification of bufadienolides from chansu by high-speed counter-current chromatography combined with preparative HPLC. Quimica Nova 2013, 36, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, D.; Simmaco, M. Amphibian skin: A promising resource for antimicrobial peptides. Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Su, S.; Shaw, C. Ranatensin-HL: A bombesin-related tridecapeptide from the skin secretion of the broad-folded frog, Hylarana latouchii. Molecules 2017, 22, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, J.M.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N. Antimicrobial peptides from ranid frogs: Taxonomic and phylogenetic markers and a potential source of new therapeutic agents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteomics 2004, 1696, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, T.F.; Vanhoye, D.; Nicolas, P. Roles of diversifying selection and coordinated evolution in the evolution of amphibian antimicrobial peptides. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoye, D.; Bruston, F.; Nicolas, P.; Amiche, M. Antimicrobial peptides from hylid and ranin frogs originated from a 150-million-year-old ancestral precursor with a conserved signal peptide but a hypermutable antimicrobial domain. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelants, K.; Fry, B.G.; Norman, J.A.; Clynen, E.; Schoofs, L.; Bossuyt, F. Identical skin toxins by convergent molecular adaptation in frogs. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortezova, N.; Mizhorkova, Z.; Milusheva, E.; Coy, D.H.; Vizi, E.S.; Varga, G. GRP-preferring bombesin receptor subtype mediates contractile activity in cat terminal ileum. Peptides 1994, 15, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgore, W.R.; Mantyh, P.W.; Mantyh, C.R.; McVey, D.C.; Vigna, S.R. Bombesin/GRP-preferring and neuromedin B-preferring receptors in the rat urogenital system. Neuropeptides 1993, 24, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erspamer, G.F.; Severini, C.; Erspamer, V.; Melchiorri, P.; Delle Fave, G.; Nakajima, T. Parallel bioassay of 27 bombesin-like peptides on 9 smooth muscle preparations. Structure-activity relationships and bombesin receptor subtypes. Regul. Pept. 1988, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ma, C.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, X.; Zhong, R.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Wang, L. Pharmacological effects of two novel bombesin-like peptides from the skin secretions of Chinese piebald odorous frog (odorrana schmackeri) and European edible frog (Pelophylax kl. esculentus) on smooth muscle. Molecules 2017, 22, 1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukala, T.L.; Bowie, J.H.; Maselli, V.M.; Musgrave, I.F.; Tyler, M.J. Host-defence peptides from the glandular secretions of amphibians: Structure and activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 368–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, M.J.; Stone, D.J.M.; Bowie, J.H. A novel method for the release and collection of dermal, glandular secretions from the skin of frogs. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1992, 28, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
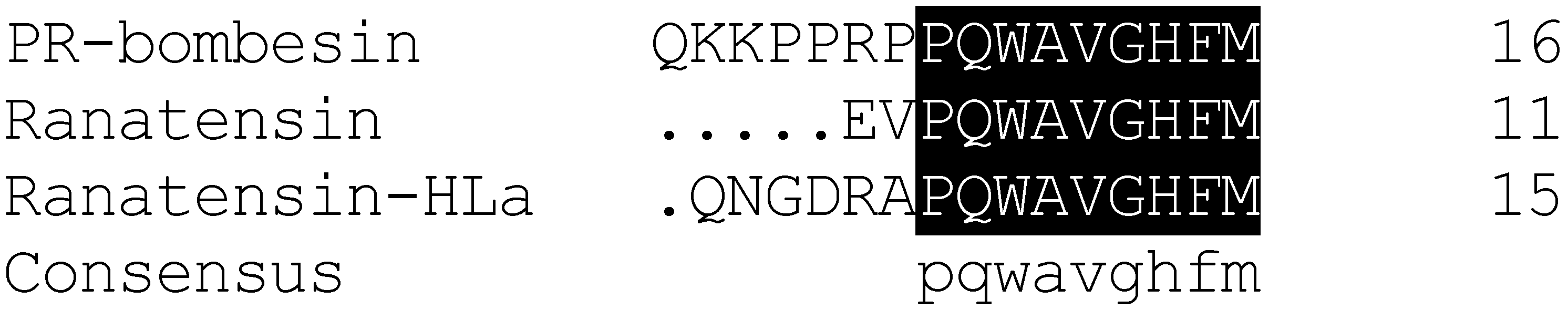

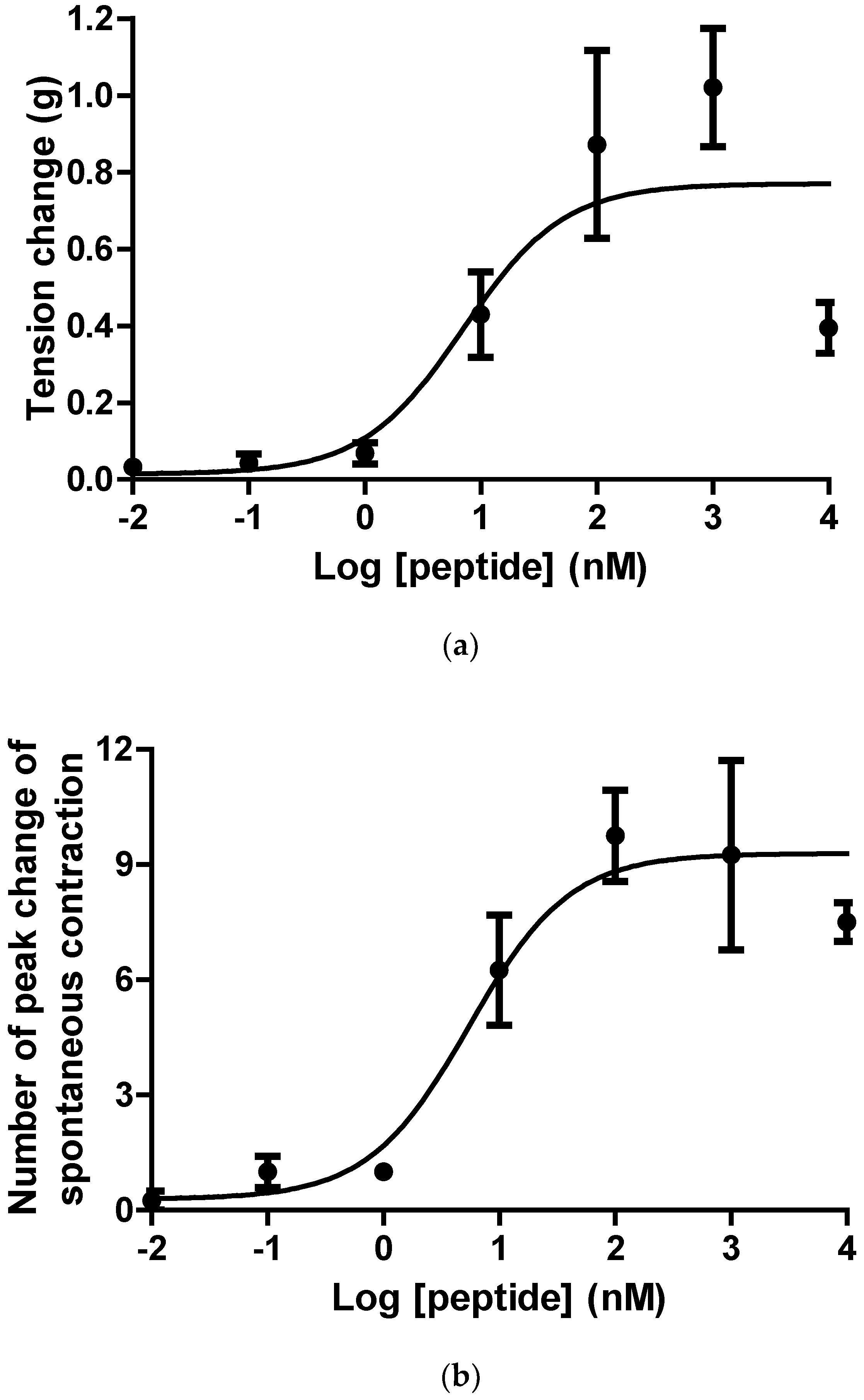

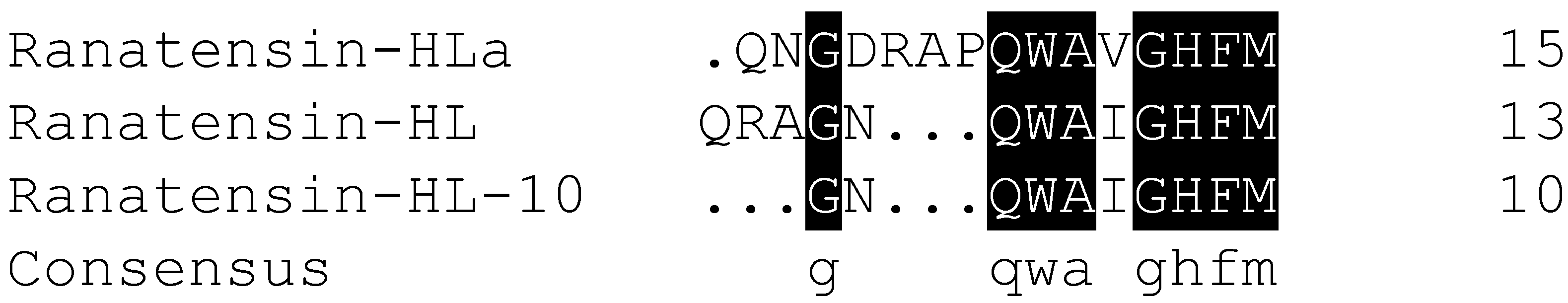
| Peptides | Bladder (EC50, nM) | Uterus (EC50, nM) |
|---|---|---|
| Ranatensin-HLa | 7.1 | 5.5 |
| Ranatensin-HL | 19.2 | 5.4 |
| Ranatensin-HL-10 | 63.8 | 70.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Hu, N.; He, H.; Ma, C.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, T. A Hylarana latouchii Skin Secretion-Derived Novel Bombesin-Related Pentadecapeptide (Ranatensin-HLa) Evoke Myotropic Effects on the in vitro Rat Smooth Muscles. Toxins 2019, 11, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040204
Lin Y, Hu N, He H, Ma C, Zhou M, Wang L, Chen T. A Hylarana latouchii Skin Secretion-Derived Novel Bombesin-Related Pentadecapeptide (Ranatensin-HLa) Evoke Myotropic Effects on the in vitro Rat Smooth Muscles. Toxins. 2019; 11(4):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yan, Nan Hu, Haoyang He, Chengbang Ma, Mei Zhou, Lei Wang, and Tianbao Chen. 2019. "A Hylarana latouchii Skin Secretion-Derived Novel Bombesin-Related Pentadecapeptide (Ranatensin-HLa) Evoke Myotropic Effects on the in vitro Rat Smooth Muscles" Toxins 11, no. 4: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040204
APA StyleLin, Y., Hu, N., He, H., Ma, C., Zhou, M., Wang, L., & Chen, T. (2019). A Hylarana latouchii Skin Secretion-Derived Novel Bombesin-Related Pentadecapeptide (Ranatensin-HLa) Evoke Myotropic Effects on the in vitro Rat Smooth Muscles. Toxins, 11(4), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040204






