A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance
2.2. Apparent Metabolic Rate
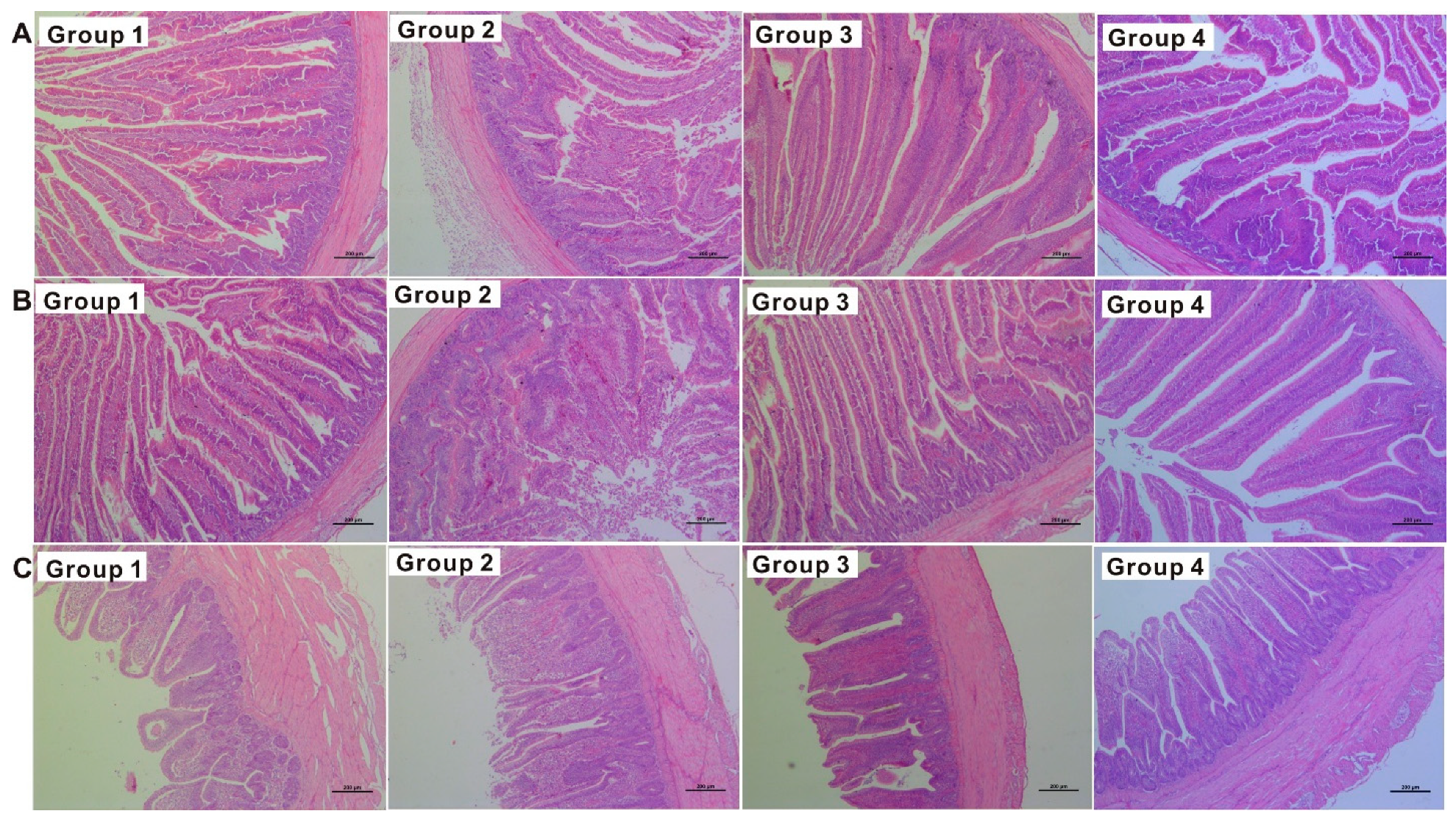
2.3. Serum Biochemistry and Histopathology
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Birds, Treatment, and Growth Performance
5.2. Serum Biochemistry and Histopathology
5.3. Apparent Metabolic Rate
5.4. Statistical Analysis
5.5. Ethical
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Nepovimova, E.; Miron, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Su, D.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Kuca, K. Trichothecenes: Immunomodulatory effects, mechanisms, and anti-cancer potential. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3737–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareis, M.; Zimmermann, C.; Schothorst, R.C. Collection of Occurrence Data of Fusarium Toxin in Food and Assessment of Dietary Intake by the Population of EU Member States. 2003. Available online: https://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/20001046845/ (accessed on 2 April 2019).
- Rasmussen, P.H.; Ghorbani, F.; Berg, T. Deoxynivalenol and other Fusarium toxins in wheat and rye flours on the Danish market. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Gonkowski, S. The impact of T-2 toxin on vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive (VIP-LI) nerve structures in the wall of the porcine stomach and duodenum. Toxins 2018, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowska, K.; Obremski, K.; Zielonka, L.; Gonkowski, S. The influence of low doses of zearalenone and t-2 toxin on calcitonin gene related peptide-like immunoreactive (CGRP-LI) neurons in the ens of the porcine descending colon. Toxins 2017, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Zhang, H. Comparison of anorectic potencies of type A trichothecenes T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, Diacetoxyscirpenol, and Neosolaniol. Toxins 2018, 10, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, M.S.; Mirocha, C.J.; Kurtz, H.J.; Weaver, G.; Bates, F.; Shimoda, W. Subacute toxicity of T-2 toxin in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1977, 56, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissonnier, G.M.; Laffitte, J.; Raymond, I.; Benoit, E.; Cossalter, A.M.; Pinton, P.; Bertin, G.; Oswald, I.P.; Galtier, P. Subclinical doses of T-2 toxin impair acquired immune response and liver cytochrome P450 in pigs. Toxicology 2008, 247, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubena, L.F.; Edrington, T.S.; Harvey, R.B.; Buckley, S.A.; Phillips, T.D.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Casper, H.H. Individual and combined effects of fumonisin B1 present in Fusarium moniliforme culture material and T-2 toxin or deoxynivalenol in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1997, 76, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafi, M.; Mohan, K.; Ali, M.N. Effect of ochratoxin A on coccidiosis-challenged broiler chicks. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Yi, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, N.; Tian, Y. Autophagy and apoptosis interact to modulate T-2 toxin-induced toxicity in liver cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshmand, H.; Klopfenstein, C.F. Effects of gamma irradiation on mycotoxin disappearance and amino acid contents of corn, wheat, and soybeans with different moisture contents. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1995, 47, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faifer, G.C.; Velazco, V.; Godoy, H.M. Adjustment of the conditions required for complete decontamination of T-2 toxin residues with alkaline sodium hypochlorite. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 52, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, G.J.; Cortes, A.; Roldan, L. Evaluation of the efficacy of four feed additives against the adverse effects of T-2 toxin in growing broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2005, 14, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, A.; Galvano, F. Nutritional approaches to reduce the impact of mycotoxins. In Biotechnology in the Feed Industry; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huwig, A.; Freimund, S.; Käppeli, O.; Dutler, H. Mycotoxin detoxication of animal feed by different adsorbents. Toxicol. Lett. 2001, 122, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerez, J.; Buck, L.; Marutani, V.; Calliari, C.; Bracarense, A. Low levels of chito-oligosaccharides are not effective in reducing deoxynivalenol toxicity in swine jejunal explants. Toxins 2018, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santurio, J.M.; Mallmann, C.A.; Rosa, A.P.; Appel, G.; Heer, A.; Dageforde, S.; Bottcher, M. Effect of sodium bentonite on the performance and blood variables of broiler chickens intoxicated with aflatoxins. Br. Poult. Sci. 1999, 40, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desheng, Q.; Fan, L.; Yanhu, Y.; Niya, Z. Adsorption of aflatoxin B1 on montmorillonite. Poult. Sci. 2005, 84, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miazzo, R.; Rosa, C.A.; De Queiroz, C.E.; Magnoli, C.; Chiacchiera, S.M.; Palacio, G.; Saenz, M.; Kikot, A.; Basaldella, E.; Dalcero, A. Efficacy of synthetic zeolite to reduce the toxicity of aflatoxin in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 2000, 79, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbes, S.; Salah-Abbes, J.B.; Ouanes, Z.; Houas, Z.; Othman, O.; Bacha, H.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A.; Oueslati, R. Preventive role of phyllosilicate clay on the immunological and biochemical toxicity of zearalenone in Balb/c mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, N.J.; Xue, K.S.; Lin, S.; Marroquin-Cardona, A.; Brown, K.A.; Elmore, S.E.; Tang, L.; Romoser, A.; Gelderblom, W.C.; Wang, J.S.; et al. Calcium montmorillonite clay reduces AFB1 and FB1 biomarkers in rats exposed to single and co-exposures of aflatoxin and fumonisin. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish, C.K.; Devegowda, G. Efficacy of Glucomannan-containing Yeast Product (Mycosorb 짰) and Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate in Preventing the Individual and Combined Toxicity of Aflatoxin and T-2 Toxin in Commercial Broilers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danicke, S.; Matthes, S.; Halle, I.; Ueberschar, K.H.; Doll, S.; Valenta, H. Effects of graded levels of Fusarium toxin-contaminated wheat and of a detoxifying agent in broiler diets on performance, nutrient digestibility and blood chemical parameters. Br. Poult. Sci. 2003, 44, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.J.; Huff, W.E.; Hamilton, P.B.; Burmeister, H.R. Comparison of ochratoxin, aflatoxin, and T-2 toxin for their effects on selected parameters related to digestion and evidence for specific metabolism of carotenoids in chickens. Poult. Sci. 1982, 61, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, B.; Backer, P.D.; Remon, J.P. Drug administration to poultry. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Han, W.; Zhao, Z.H.; Sun, Z.Z.; Guo, W.B. Influence of T-2 toxin on nutrient apparent digestibility and small intestinal morphology in BALB/c Mice. Chin. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 46, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.H.; Lei, M.Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Zhao, L.; Krumm, C.S.; Qi, D.S. Hepatotoxic effects of mycotoxin combinations in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shareef, A.M. Ineffectiveness of different adsorbents in alleviation of oral lesions induced by feeding T-2 toxin in broiler chickens. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2007, 21, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivashankar, B.P.; Narayanaswamy, H.D.; Satyanarayana, M.L.; Rao, S.; Rathnamma, D.; Rathnamma, H.K.; Sridhar, N.B. Effect of diatomaceous earth on performance, internalorgans and biochemical alterations in T-2 toxicosis of broiler chickens. J. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 15, 4983–4988. [Google Scholar]
- Kutasi, J.; Papp, Z.; Jakab, L.; Brydl, E.; Rafai, P. Deactivation of T-2 toxin in broiler ducks by biotransformation. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2012, 21, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankič, T.; Salobir, J.; Rezar, V. The effect of vitamin E supplementation on reduction of lymphocyte DNA damage induced by T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in weaned pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 141, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmon, R.; Sedmikova, M.; Jilek, F.; Koubkova, M.; Barta, I.; Smerak, P. Combined effects of repeated low doses of aflatoxin B1 and T-2 toxin on the Chinese hamster. Vet. Med. 2001, 46, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Li, Y.H.; Lin, M.F. Chronic exposure to the Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol: Impact on performance, immune organ, and intestinal integrity of slow-growing chickens. Toxins 2017, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.G.; Phillips, T.D. Isothermal adsorption of aflatoxin B1 on HSCAS clay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.H.; Kubena, L.F.; Harvey, R.B.; Buckley, S.A.; Rottinghaus, G.E. Efficacy of various inorganic sorbents to reduce the toxicity of aflatoxin and T-2 toxin in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 1623–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.; Young, L.G. Efficacy of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate, screening and dilution in reducing the effects of mold contaminated corn in pigs. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 73, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomašević-Čanović, M.; Daković, A.; Rottinghaus, G.; Matijašević, S.; Đuričić, M. Surfactant modified zeolites–new efficient adsorbents for mycotoxins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.B.; Devegowda, G.; Shashidhara, R.G. Ability of modified glucomannan to sequestrate T-2 toxin in the gastrointestinal tract of chicken. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 17, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, S.L.; Mayura, K.; Reeves, W.R.; Wang, N.; Fickey, C.; Phillips, T.D. Investigation of organophilic montmorillonite clay inclusion in zearalenone-contaminated diets using the mouse uterine weight bioassay. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 2001, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, B.; Tóthné Hajdu, E.; Tanyi, J. Effect of Myco-ad on experimental T-2 toxicosis in broiler chickens. Magyar Állatorvosok Lapja 2000, 122, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Meissonnier, G.M.; Raymond, I.; Laffitte, J.; Cossalter, A.M.; Pinton, P.; Benoit, E.; Bertin, G.; Galtier, P.; Oswald, I.P. Dietary glucomannan improves the vaccinal response in pigs exposed to aflatoxin B1 or T-2 toxin. World Mycotoxin J. 2009, 2, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbes, S.; Ouanes, Z.S.J.; Houas, Z.; Oueslati, R.; Bacha, H.; Othman, O. The protective effect of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate against haematological, biochemical and pathological changes induced by Zearalenone in mice. Toxicon 2006, 47, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Z.H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Khalil, M.M.; Gu, C.Q.; Qi, D.S.; Sun, L.H. Dietary Silymarin Supplementation Alleviates Zearalenone-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Reproductive Toxicity in Rats. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.H.; Zhang, N.Y.; Zhu, M.K.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J.C.; Qi, D.S. Prevention of aflatoxin B1 hepatoxicity by dietary selenium is associated with inhibition of cytochrome P450 isozymes and up-regulation of 6 selenoprotein genes in chick liver. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denli, M.; Blandon, J.C.; Guynot, M.E.; Salado, S.; Perez, J.F. Effects of dietary AflaDetox on performance, serum biochemistry, histopathological changes, and aflatoxin residues in broilers exposed to aflatoxin B1. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkung, H.; Leeson, S. Effect of phytase enzyme on dietary nitrogen-corrected apparent metabolizable energy and the ileal digestibility of nitrogen and amino acids in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 1999, 78, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.Y.; Pan, Y.X.; Zhu, L.Y.; Batonon-Alavo, D.I.; Ma, L.B.; Khalil, M.M.; Qi, D.S.; Sun, L.H. Efficacy of 2-hydroxy-4-methylthiobutanoic acid compared to DL-Methionine on growth performance, carcass traits, feather growth, and redox status of Cherry Valley ducks. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3166–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight, g/bird | 54.3 ± 0.4 | 54.4 ± 0.7 | 54.5 ± 0.7 | 54.0 ± 0.2 |
| d 1 to 7 | ||||
| Body weight gain, g/bird | 138.9 ± 6.2 a | 117.6 ± 5.4 b | 115.9 ± 8.7 b | 136.2 ± 18.4 a |
| Feed intake, g/bird | 167.6 ± 3.8 a | 146.9 ± 4.8 b | 149.1 ± 5.3 b | 166.3 ± 1.8 a |
| Feed/gain, g/g | 1.21 ± 0.05 | 1.25 ± 0.08 | 1.29 ± 0.06 | 1.24 ± 0.17 |
| d 8 to 14 | ||||
| Body weight gain, g/bird | 280.2 ± 17.0 a | 191.1 ± 10.1 c | 232.6 ± 11.9 b | 289.8 ± 22.7 a |
| Feed intake, g/bird | 385.2 ± 11.9 a | 305.8 ± 10.7 c | 334.4 ± 28.9 b | 376.3 ± 18.8 a |
| Feed/gain, g/g | 1.38 ± 0.05 b | 1.60 ± 0.07 a | 1.44 ± 0.05 b | 1.30 ± 0.06 b |
| d 1 to 14 | ||||
| Body weight gain, g/bird | 419.2 ± 21.7 a | 308.7 ± 8.1 c | 351.3 ± 11.6 b | 426.0 ± 9.1 a |
| Feed intake, g/bird | 552.8 ± 11.9 a | 452.7 ± 14.5 b | 485.7 ± 30.7 b | 542.9 ± 17.9 a |
| Feed/gain, g/g | 1.32 ± 0.05 b | 1.47 ± 0.02 a | 1.38 ± 0.05 b | 1.27 ± 0.02 b |
| Item | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross energy, % | 67.1 ± 3.0 | 64.1 ± 2.8 | 67.0 ± 3.6 | 66.1 ± 2.6 |
| Crude protein, % | 57.6 ± 2.5 a | 49.0 ± 5.0 b | 52.5 ± 6.9 ab | 55.3 ± 1.7 a |
| Calcium, % | 40.5 ± 5.2 a | 33.2 ± 4.9 b | 30.6 ± 1.1 b | 34.9 ± 10.9 ab |
| Total phosphorus, % | 52.7 ± 6.9 a | 44.2 ± 4.8 b | 48.4 ± 8.1 ab | 49.3 ± 7.8 ab |
| Item | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT/(U/L) | 2.68 ± 0.12 | 2.85 ± 0.34 | 2.47 ± 0.27 | 2.80 ± 0.19 |
| AST/(U/L) | 196.7 ± 6.0 b | 231.5 ± 5.2 a | 203.0 ± 3.4 b | 200.6 ± 7.9 b |
| TP/(g/L) | 25.7 ± 1.6 | 27.2 ± 1.2 | 28.4 ± 1.0 | 27.4 ± 1.9 |
| ALB/(g/L) | 12.7 ± 1.0 | 13.1 ± 0.8 | 13.3 ± 0.6 | 13.7 ± 1.3 |
| Ingredients (%) | Quantity (%) |
|---|---|
| Corn | 54.5 |
| Soybean meal (48%) | 30.4 |
| Fish meal (64.5%) | 5.6 |
| Soybean oil | 5.9 |
| Calcium hydrophosphate | 1.2 |
| Limestone | 1.0 |
| Salt | 0.2 |
| DL-methionine | 0.2 |
| Premix 1 | 1.0 |
| Approximate composition of the test diets 2 | |
| Crude protein | 23.00 |
| Metabolisable energy, (MJ/kg) | 13.38 |
| Lysine | 1.40 |
| Methionine | 0.58 |
| Methionine + cysteine | 0.94 |
| Calcium | 1.02 |
| Available phosphorus | 0.47 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.-T.; Wu, K.-T.; Sun, H.; Khalil, M.M.; Dai, J.-F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.-Y.; Qi, D.-S.; Sun, L.-H. A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks. Toxins 2019, 11, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040199
Wei J-T, Wu K-T, Sun H, Khalil MM, Dai J-F, Liu Y, Liu Q, Zhang N-Y, Qi D-S, Sun L-H. A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks. Toxins. 2019; 11(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jin-Tao, Kun-Tan Wu, Hua Sun, Mahmoud Mohamed Khalil, Jie-Fan Dai, Ying Liu, Qiang Liu, Ni-Ya Zhang, De-Sheng Qi, and Lv-Hui Sun. 2019. "A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks" Toxins 11, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040199
APA StyleWei, J.-T., Wu, K.-T., Sun, H., Khalil, M. M., Dai, J.-F., Liu, Y., Liu, Q., Zhang, N.-Y., Qi, D.-S., & Sun, L.-H. (2019). A Novel Modified Hydrated Sodium Calcium Aluminosilicate (HSCAS) Adsorbent Can Effectively Reduce T-2 Toxin-Induced Toxicity in Growth Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, Serum Biochemistry, and Small Intestinal Morphology in Chicks. Toxins, 11(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040199







