Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Proteinase Activity Measurements Confirm Known Targets and Reveal New Substrate Sequences
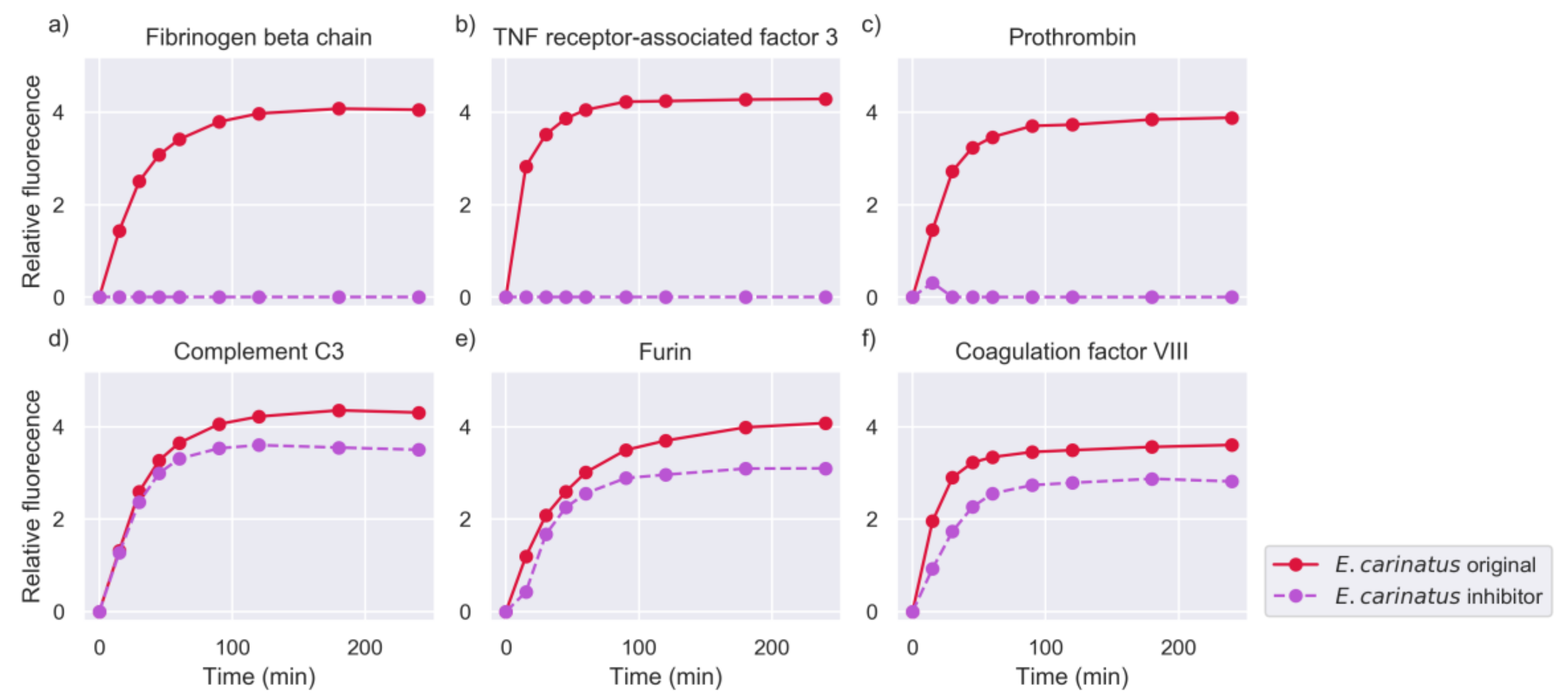
2.2. Inhibition of Metalloproteinase Activity Provides Insights on Targets of Both Proteinase Families
2.3. Models of Proteinase Activity
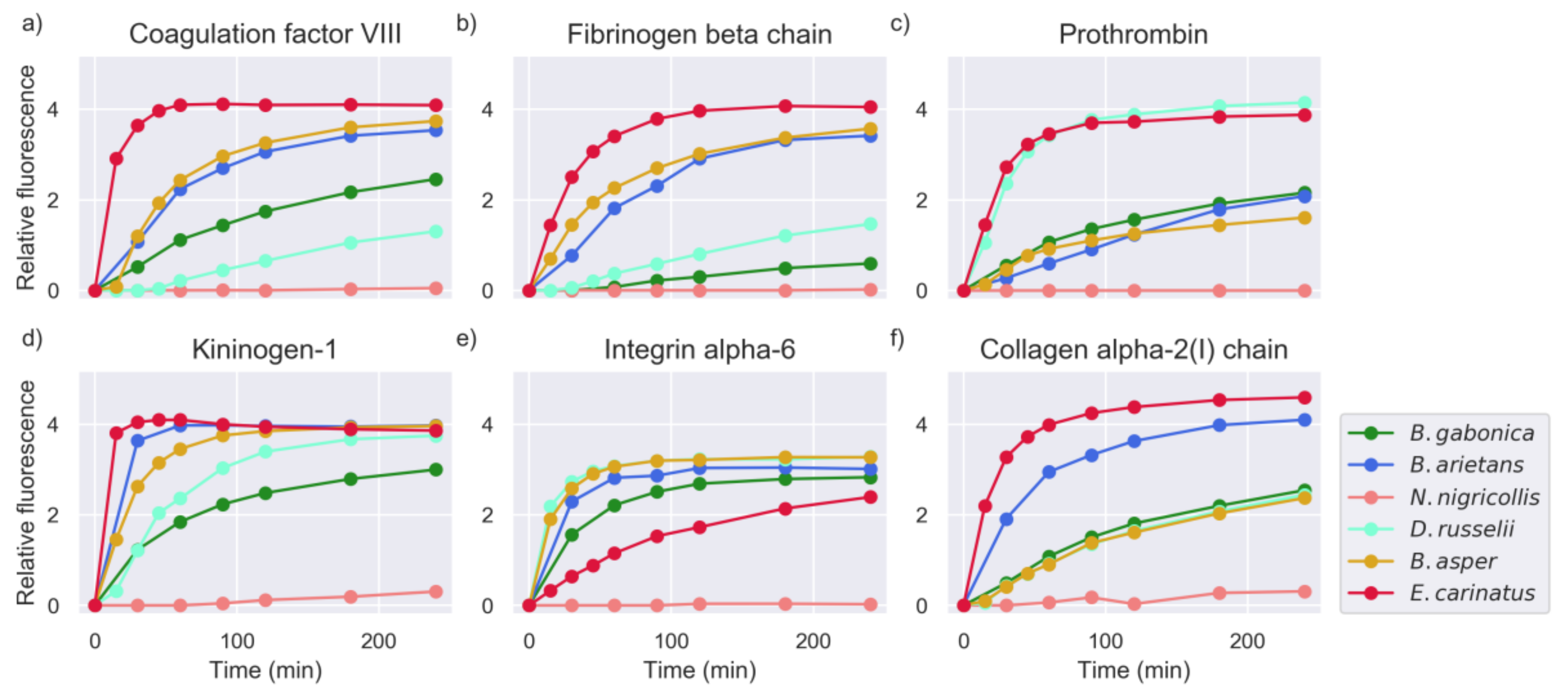
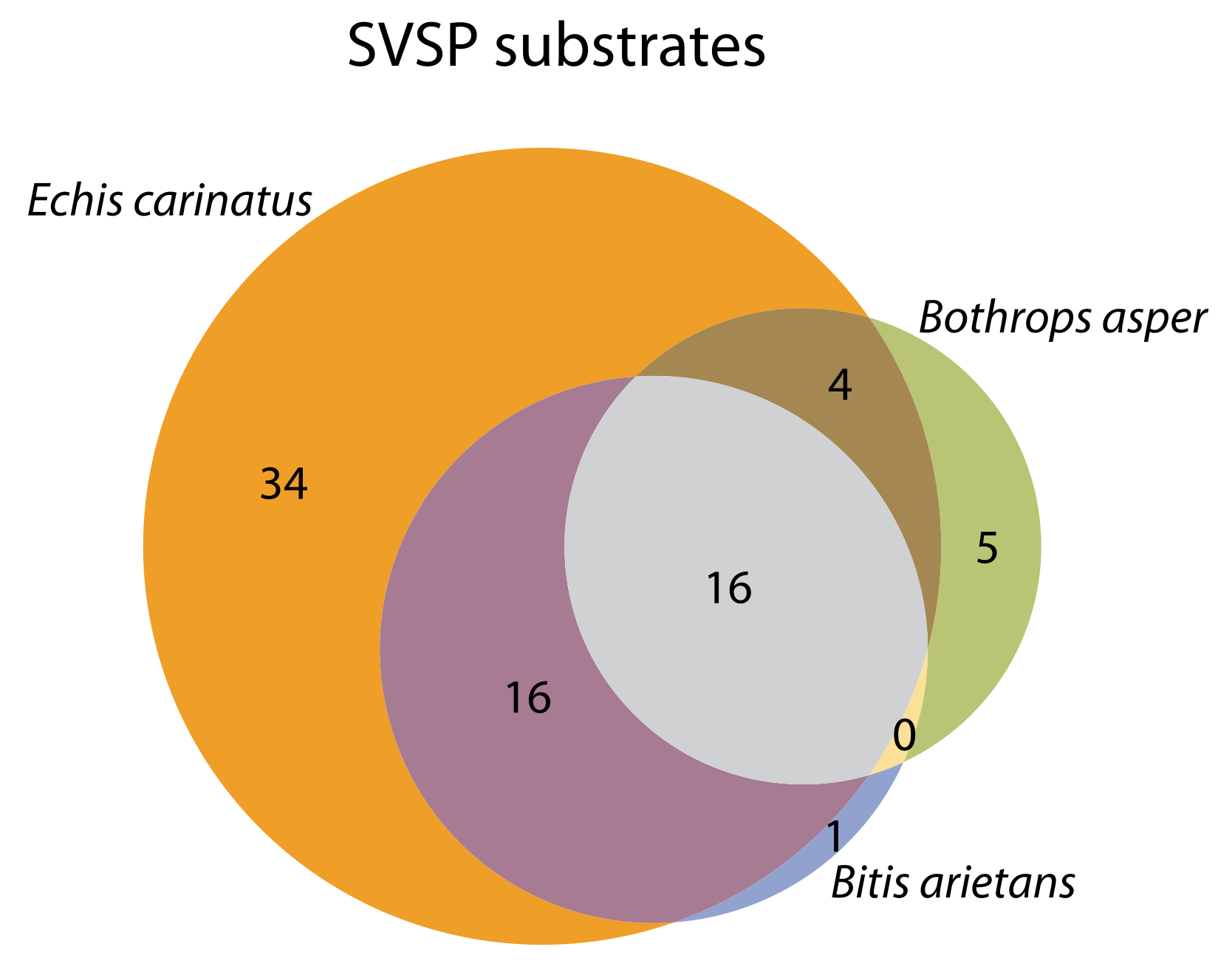
2.4. Substrate Cleavage Determination of Studied Venoms
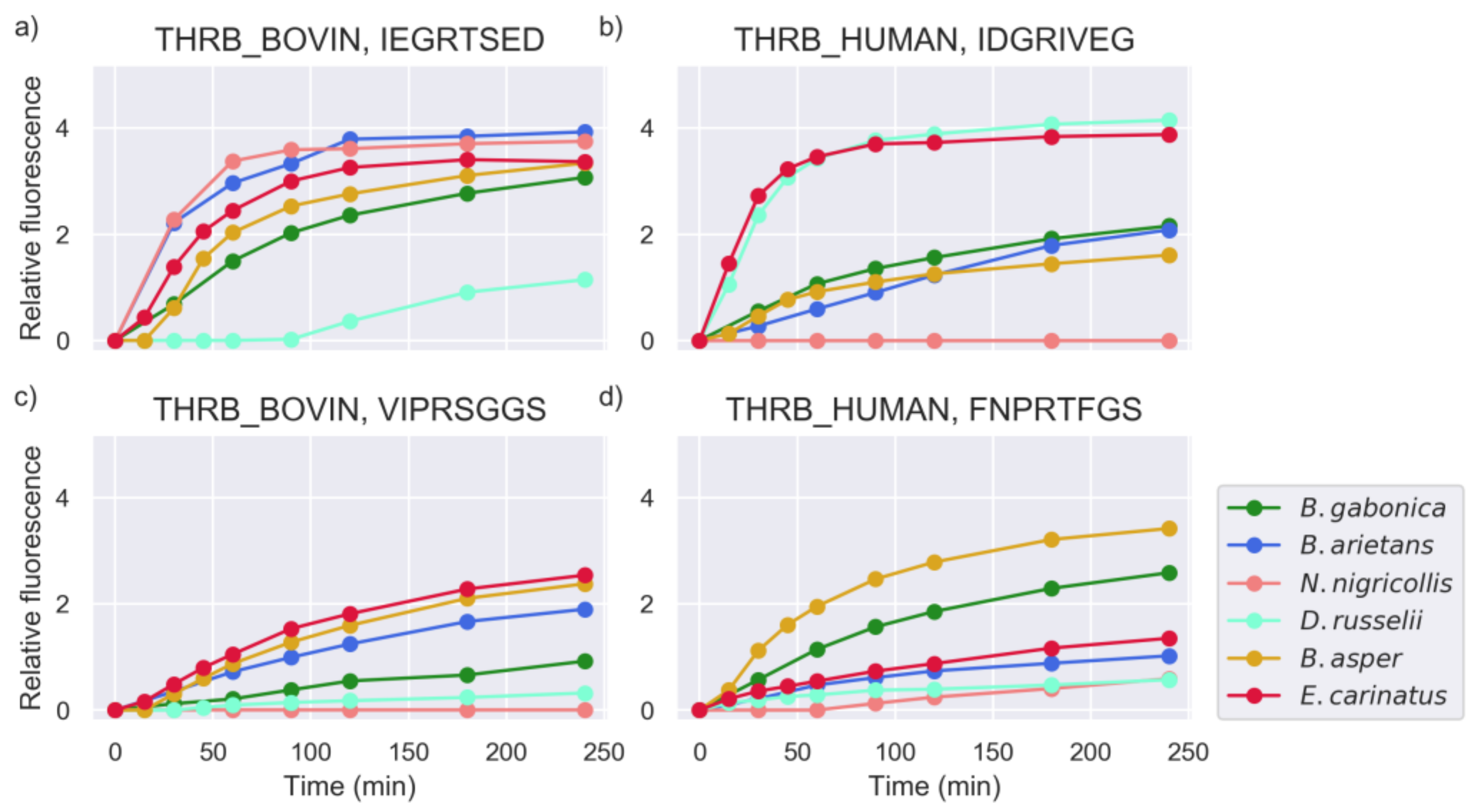
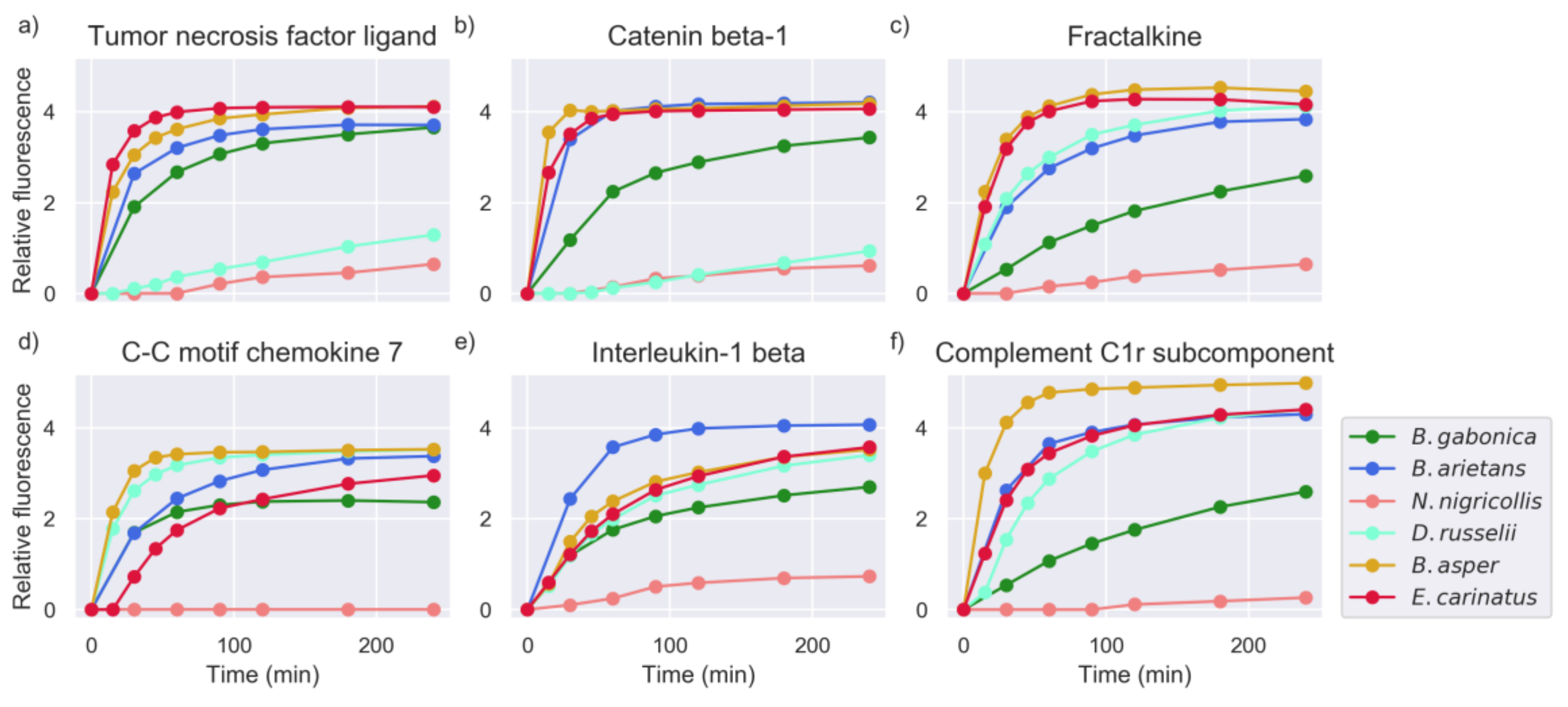
2.5. Investigation of Relevant Targets for Human Snakebite Envenoming
2.6. Comparison of Activities Reveals Phylogeny-Related Differences
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Snake Venoms
4.2. Proteinase Activity and Inhibition Experiments
4.3. Data Analysis and Modeling
4.4. Substrate Cleavage
4.5. Jaccard Similarity Coefficient and Phylogeny
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, T.S.; Georgieva, D.; Genov, N.; Murakami, M.T.; Sinha, M.; Kumar, R.P.; Kaur, P.; Kumar, S.; Dey, S.; Sharma, S.; et al. Enzymatic toxins from snake venom: Structural characterization and mechanism of catalysis. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4544–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleary, R.J.R.; Kini, R.M. Non-enzymatic proteins from snake venoms: A gold mine of pharmacological tools and drug leads. Toxicon 2013, 62, 56–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Fernández, J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Venomous snakes of Costa Rica: Biological and medical implications of their venom proteomic profiles analyzed through the strategy of snake venomics. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, L.F.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Nishiyama-Jr, M.Y.; Amazonas, D.R.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Mourão, R.H.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Valente, R.H.; et al. Functional proteomic analyses of Bothrops atrox venom reveals phenotypes associated with habitat variation in the Amazon. J. Proteom. 2017, 159, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Sasa, M.; Acevedo, M.E.; Dwyer, Q.; Durban, J.; Pérez, A.; Rodriguez, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Calvete, J.J. Proteomic analysis of venom variability and ontogeny across the arboreal palm-pitvipers (genus Bothriechis). J. Proteom. 2017, 152, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durban, J.; Sanz, L.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Neri-Castro, E.; Alagón, A.; Calvete, J.J. Integrated Venomics and Venom Gland Transcriptome Analysis of Juvenile and Adult Mexican Rattlesnakes Crotalus simus, C. tzabcan, and C. culminatus Revealed miRNA-modulated Ontogenetic Shifts. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3370–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaz Florea, S.A.; Gaz Florea, A.; Kelemen, H.; Daniela-Lucia, M. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. Acta Medica Marisiensis 2016, 62, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, H.C.; Abreu, P.A.; Geraldo, R.B.; Martins, R.C.A.; Dos Santos, R.; Loureiro, N.I.V.; Cabral, L.M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Looking at the proteases from a simple perspective. J. Mol. Recognit. 2011, 24, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A.; Escalante, T. Snake venom metalloproteinases. Biological roles and participation in the pathophysiology of envenomation. In Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; Mackessy, S.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S. ADAM and ADAMTS family proteins and snake venom metalloproteinases: A structural overview. Toxins 2016, 8, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaqueo, K.D.; Kayano, A.M.; Simões-Silva, R.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Fernandes, C.F.C.; Fuly, A.L.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honório, K.M.; da Silva, S.L.; Acosta, G.; et al. Isolation and biochemical characterization of a new thrombin-like serine protease from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 595186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M.T.; Maroun, R.C. Snake venom serine proteinases: Sequence homology vs. substrate specificity, a paradox to be solved. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaldo, D.L.; Bernardes, C.P.; Santos-Filho, N.A.; Moura, L.D.A.; Fuly, A.L.; Arantes, E.C.; Sampaio, S.V. Biochemical characterization and comparative analysis of two distinct serine proteases from Bothrops pirajai snake venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2545–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Takeya, H.; Iwanaga, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases: Structure, function and relevance to the mammalian ADAM/ADAMTS family proteins. BBA-Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M.T. Structural considerations of the snake venom metalloproteinases, key members of the M12 reprolysin family of metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2005, 45, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.M.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z.Z.; Pei, J.Z.; Yang, Y.E.; Yan, S.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, W.-L; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, Y.M.; et al. Serine protease isoforms in Gloydius intermedius venom: Full sequences, molecular phylogeny and evolutionary implications. J. Proteom. 2017, 164, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Shih, C.H.; Huang, T.F. A novel P-I class metalloproteinase with broad substrate-cleaving activity, agkislysin, from Agkistrodon acutus venom. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezotto-Neto, J.P.; Kimura, L.F.; Alves, A.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Otero, R.; Suárez, A.M.; Santoro, M.L.; Barbaro, K.C. Biochemical and biological characterization of Bothriechis schlegelii snake venoms from Colombia and Costa Rica. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 2075–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshenko, V.; Platonova, T.; Makogonenko, Y.; Rebriev, A.; Mikhalovska, L.; Chernyshenko, T.; Komisarenko, S. Fibrin(ogen)olytic and platelet modulating activity of a novel protease from the Echis multisquamatis snake venom. Biochimie 2014, 105, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Park, J.E.; Park, J.W.; Lee, J.S. Purification and biochemical characterization of a fibrin(ogen)olytic metalloprotease from Macrovipera mauritanica snake venom which induces vascular permeability. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1180–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes Leme, A.F.; Escalante, T.; Pereira, J.G.C.; Oliveira, A.K.; Sanchez, E.F.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Fox, J.W. High resolution analysis of snake venom metalloproteinase (SVMP) peptide bond cleavage specificity using proteome based peptide libraries and mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelanis, A.; Huesgen, P.F.; Oliveira, A.K.; Tashima, A.K.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Overall, C.M. Snake venom serine proteinases specificity mapping by proteomic identification of cleavage sites. J. Proteom. 2015, 113, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Saavedra, A.N.; Pan, S.; Xiang, W.; Liao, J. Internal calibration förster resonance energy transfer assay: A real-time approach for determining protease kinetics. Sensors 2013, 13, 4553–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G. Protease Assays. In Assay Guidance Manual; 2012; pp. 1–14. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92006/ (accessed on 6 July 2018).
- Sharkov, N.A.; Davis, R.M.; Reidhaar-Olson, J.F.; Navre, M.; Cai, D. Reaction kinetics of protease with substrate phage: Kinetic model developed using stromelysin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10788–10793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liao, J. Quantitative Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Analysis for SENP1 Protease Kinetics Determination. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 28, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, D.; Sanz, L.; Segura, Á.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Solano, D.; Vargas, M.; León, G.; Warrell, D.A.; Theakston, R.D.G.; et al. Snake Venomics of African Spitting Cobras: Toxin Composition and Assessment of Congeneric Cross-Reactivity of the Pan-African EchiTAb-Plus-ICP Antivenom by Antivenomics and Neutralization Approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1266–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, A.; McKelvy, A.D.; Grismer, L.L.; Bell, C.D.; Lailvaux, S.P. A species-level phylogeny of extant snakes with description of a new colubrid subfamily and genus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn-Dantona, E.A.; Aimes, R.T.; Quigley, J.P. The isolation, characterization, and molecular cloning of a 75-kDa gelatinase B-like enzyme, a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family: An avian enzyme that is MMP-9-like in its cell expression pattern but diverges from mammalian gelatinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40827–40838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, C.L.; MacKessy, S.P. Alsophinase, a new P-III metalloproteinase with α-fibrinogenolytic and hemorrhagic activity from the venom of the rear-fanged Puerto Rican Racer Alsophis portoricensis (Serpentes: Dipsadidae). Biochimie 2012, 94, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ami, A.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Biochemical and biological characterization of a dermonecrotic metalloproteinase isolated from Cerastes cerastes snake venom. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegemann, C.; Didangelos, A.; Barallobre-Barreiro, J.; Langley, S.R.; Mandal, K.; Jahangiri, M.; Mayr, M. Proteomic identification of matrix metalloproteinase substrates in the human vasculature. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertholim, L.; Zelanis, A.; Oliveira, A.K.; Serrano, S.M.T. Proteome-derived peptide library for the elucidation of the cleavage specificity of HF3, a snake venom metalloproteinase. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Lee, P.Y.; Son, W.C.; Chi, S.W.; Park, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.G. Identification of the novel substrates for caspase-6 in apoptosis using proteomic approaches. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, L.; Qi, S.; Mi, Y.; Liu, D.; Tian, Q. Identification of candidate substrates of ubiquitin-specific protease 13 using 2D-DiGE. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, I.R.F.; Lorenzetti, R.; Rennó, A.L.; Baldissera, L.; Zelanis, A.; Serrano, S.M.D.T.; Hyslop, S. BJ-PI2, A non-hemorrhagic metalloproteinase from Bothrops jararaca snake venom. BBA-Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlage, P.; Egli, F.E.; auf dem Keller, U. Time-Resolved Analysis of Matrix Metalloproteinase Substrates in Complex Samples. In Matrix Metalloproteases: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1579, pp. 185–198. ISBN 978-1-4939-6861-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Ye, M.; Wei, X.; Bian, Y.; Cheng, K.; Zou, H. A bead-based cleavage method for large-scale identification of protease substrates. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, O.; Overall, C.M. Proteome-derived, database-searchable peptide libraries for identifying protease cleavage sites. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.M.T. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Berndt, M.C.; Andrews, R.K. Snake venom probes of platelet adhesion receptors and their ligands. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; Jia, R.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J. Integrin β4 is a target of rattlesnake venom during inducing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2004, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Ghosh, S.S.; Mukherjee, A.K. Elucidation of procoagulant mechanism and pathophysiological significance of a new prothrombin activating metalloprotease purified from Daboia russelii russelii venom. Toxicon 2015, 100, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidde-Queiroz, G.; de Fátima Furtado, M.; Filgueiras, C.F.; Pessoa, L.A.; Spadafora-Ferreira, M.; van den Berg, C.W.; Tambourgi, D.V. Human complement activation and anaphylatoxins generation induced by snake venom toxins from Bothrops genus. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsky, S.H.P.; Gonçalves, L.R.C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Correa, A.P.; Rucavado, A.; Gasque, P.; Tambourgi, D.V. Bothrops asper snake venom and its metalloproteinase BaP-1 activate the complement system. Role in leucocyte recruitment. Mediators Inflamm. 2000, 9, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Wüster, W.; Wagstaff, S.C. Comparative venom gland transcriptome surveys of the saw-scaled vipers (Viperidae: Echis) reveal substantial intra-family gene diversity and novel venom transcripts. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalta, M.; Sánchez, A.; Herrera, M.; Vargas, M.; Segura, Á.; Cerdas, M.; Estrada, R.; Gawarammana, I.; Keyler, D.E.; McWhorter, K.; et al. Development of a new polyspecific antivenom for snakebite envenoming in Sri Lanka: Analysis of its preclinical efficacy as compared to a currently available antivenom. Toxicon 2016, 122, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alape-Girón, A.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Sanz, L.; Madrigal, M.; Escolano, J.; Sasa, M.; Calvete, J.J. Studies on the venom proteome of Bothrops asper: Perspectives and applications. Toxicon 2009, 54, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, A.; Castillo, M.C.; Núñez, V.; Yarlequé, A.; Gonçalves, L.R.C.; Villalta, M.; Bonilla, C.; Herrera, M.; Vargas, M.; Fernández, M.; et al. Preclinical assessment of the neutralizing capacity of antivenoms produced in six Latin American countries against medically-relevant Bothrops snake venoms. Toxicon 2010, 56, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez, P.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Oliver, J.; Sanz, L.; Harrison, R.A.; Calvete, J.J. Molecular cloning of disintegrin-like transcript BA-5A from a Bitis arietans venom gland cDNA library: A putative intermediate in the evolution of the long-chain disintegrin bitistatin. J. Mol. Evol. 2006, 63, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, Á.; Villalta, M.; Herrera, M.; León, G.; Harrison, R.; Durfa, N.; Nasidi, A.; Calvete, J.J.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Warrell, D.A.; et al. Preclinical assessment of the efficacy of a new antivenom (EchiTAb-Plus-ICP®) for the treatment of viper envenoming in sub-Saharan Africa. Toxicon 2010, 55, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Escolano, J.; Sanz, L. Snake Venomics of Bitis Species Reveals Large Intragenus Venom Toxin Composition Variation: Application to Taxonomy of Congeneric Taxa. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K.; Kalita, B.; Mackessy, S.P. A proteomic analysis of Pakistan Daboia russelii russelii venom and assessment of potency of Indian polyvalent and monovalent antivenom. J. Proteom. 2016, 144, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rojas, E.; Quesada, L.; León, G.; Núñez, J.; Laing, G.D.; Sasa, M.; Renjifo, J.M.; Nasidi, A.; Warrell, D.A.; et al. Pan-African polyspecific antivenom produced by caprylic acid purification of horse IgG: An alternative to the antivenom crisis in Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 99, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alape-Girón, A.; Sanz, L.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Madrigal, M.; Sasa, M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics of the Lancehead Pitviper Bothrops asper: Geographic, Individual, and Ontogenetic Variations research articles. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 3556–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, E.N.; Lomonte, B.; del Carmen Gutiérrez, M.; Alagón, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Intraspecies variation in the venom of the rattlesnake Crotalus simus from Mexico: Different expression of crotoxin results in highly variable toxicity in the venoms of three subspecies. J. Proteom. 2013, 87, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rasmussen, A.R.; Engmark, M.; Gravlund, P.; Sanders, K.L.; Lohse, B.; Lomonte, B. Danger in the reef: Proteome, toxicity, and neutralization of the venom of the olive sea snake, Aipysurus laevis. Toxicon 2015, 107, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, S.H.; Friis, R.U.W.; Petersen, S.D.; Martos-Esteban, A.; Laustsen, A.H. Snake Venomics Display: An online toolbox for visualization of snake venomics data. Toxicon 2018, 152, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S. Snake venoms and the hemostatic system. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1749–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, M.J.I.; Liang, G. Ecarin. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Barrett, A.J., Rawlings, N.D., Woessner, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 689–691. ISBN 9780080984155. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, D.; Sekiya, F.; Morita, T. Isolation and characterization of carinactivase, a novel prothrombin activator in Echis carinatus venom with a unique catalytic mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5200–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trummal, K.; Vija, K.; Subbi, J.; Siigur, J. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry analysis of substrate specificity of lebetase, a direct-acting fibrinolytic metalloproteinase from Vipera lebetina snake venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000, 1476, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría, G.D.; Rucavado, A.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Fox, J.W.; Alape, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Characterization of “basparin A,” a prothrombin-activating metalloproteinase, from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper that inhibits platelet aggregation and induces defibrination and thrombosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 418, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, A.; Rucavado, A.; Mora, N.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Purification and characterization of BaH4, a hemorrhagic metalloproteinase from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper. Toxicon 2000, 38, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Venombin AB. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Barrett, A.J., Rawlings, N.D., Woessner, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 1723–1724. ISBN 9780080984155. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, S.; Iwanaga, S. Russelysin. In Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes; Barrett, A.J., Rawlings, N.D., Woessner, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 683–684. ISBN 9780080984155. [Google Scholar]
- White, J. Snake venoms and coagulopathy. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Laing, G.D.; Paine, M.J.I.; Dennison, J.M.T.J.; Politi, V.; Crampton, J.M.; Theakston, R.D.G. Processing of pro-tumor necrosis factor-α by venom metalloproteinases: A hypothesis explaining local tissue damage following snake bite. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 2000–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambourgi, D.V.; van den Berg, C.W. Animal venoms/toxins and the complement system. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Herrera, C.; Fox, J.W. A comprehensive view of the structural and functional alterations of extracellular matrix by snake venom metalloproteinases (SVMPs): Novel perspectives on the pathophysiology of envenoming. Toxins 2016, 8, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, N.; Escalante, T.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rucavado, A. Skin pathology induced by snake venom metalloproteinase: Acute damage, revascularization, and re-epithelization in a mouse ear model. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucavado, A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Escalante, T.; Kim, J.; Herrera, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Fox, J.W. Viperid envenomation wound exudate contributes to increased vascular permeability via a DAMPs/TLR-4 mediated pathway. Toxins 2016, 8, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, E.F.; Flores-Ortiz, R.J.; Alvarenga, V.G.; Eble, J.A. Direct fibrinolytic snake venom metalloproteinases affecting hemostasis: Structural, biochemical features and therapeutic potential. Toxins 2017, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.C.I.; Armugam, A.; Jeyaseelan, K. Snake venom components and their applications in biomedicine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 3030–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Python Software Foundation. Python Language Reference. Available online: https://www.python.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2018).
- Oliphant, T.E. A guide to NumPy, 1st ed.; Trelgol Publishing: Spanish Fork, UT, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, W. Data Structures for Statistical Computing in Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; Volume 445, pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D Graphics Environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.; Botvinnik, O.; O’Kane, D.; Hobson, P.; Lukauskas, S.; Gemperline, D.C.; Augspurger, T.; Halchenko, Y.; Cole, J.B.; Warmenhoven, J.; et al. mwaskom/seaborn: v0.8.0 (July 2017). 2017. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/824567#.XItk_poRWUk (accessed on 15 December 2018). [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Oliphant, T.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open source scientific tools for Python. Available online: https://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 6 July 2018).
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and Statistical Modeling with Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June–3 July 2010; pp. 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, I.E.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Makeev, V.J. Jaccard index based similarity measure to compare transcription factor binding site models. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2013, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, R.; VanderSluis, B.; Myers, C.L. Comparison of Profile Similarity Measures for Genetic Interaction Networks. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Dopazo, J.; Gabaldón, T. ETE: A python Environment for Tree Exploration. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

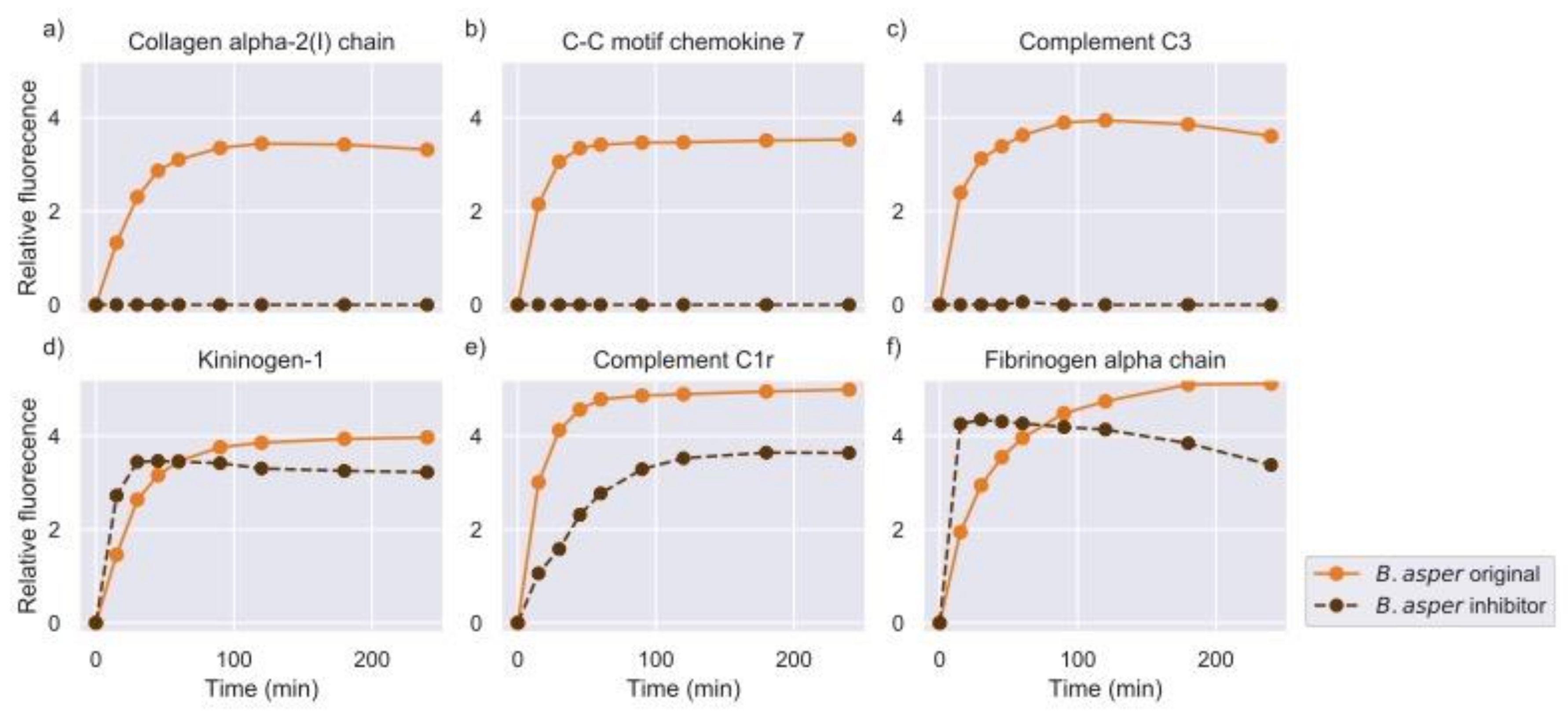
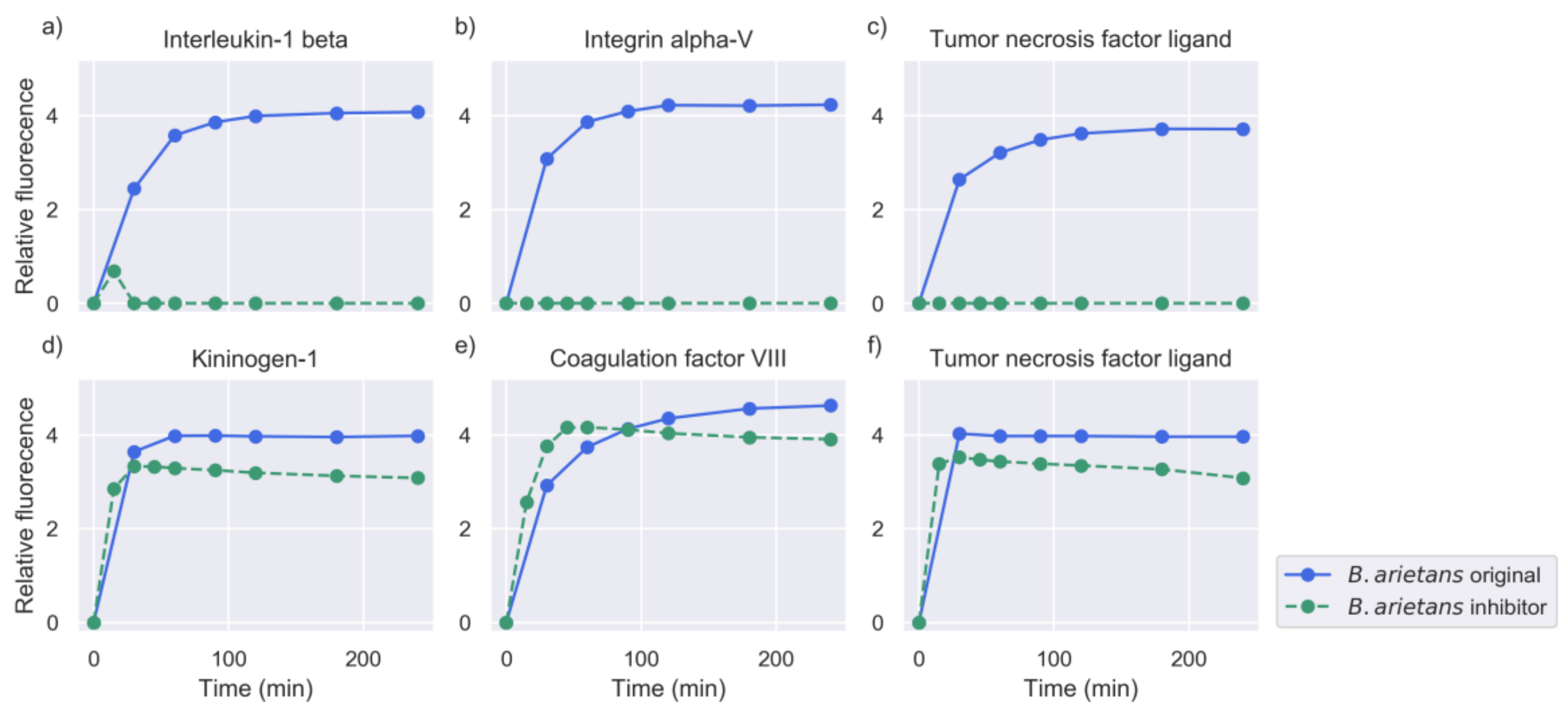
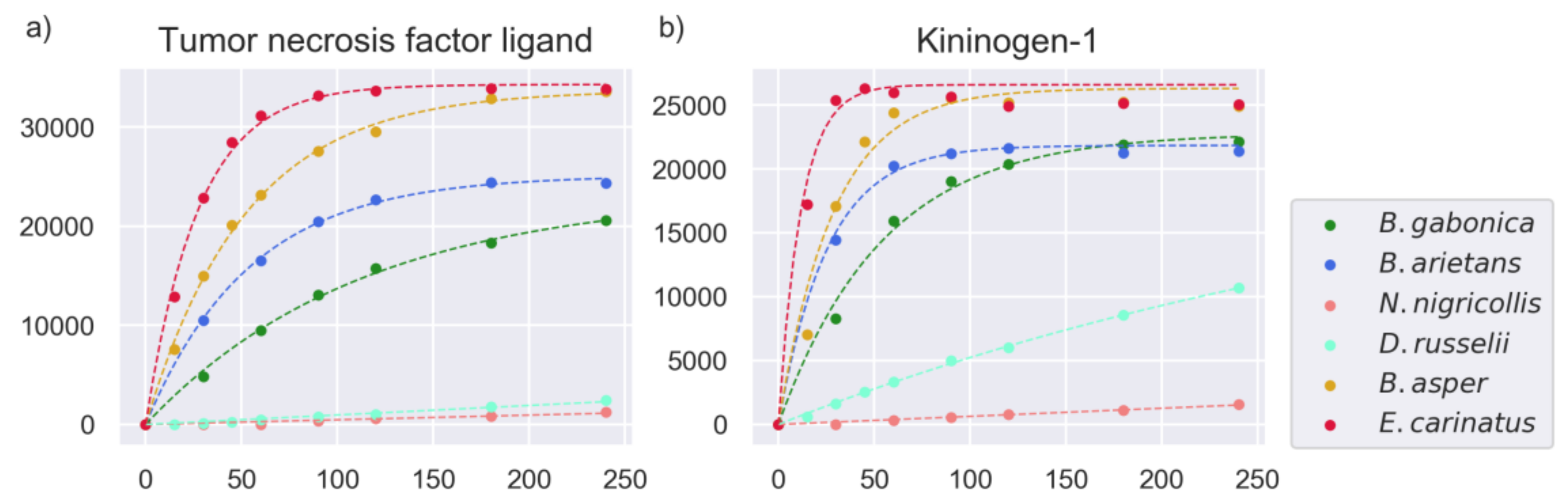
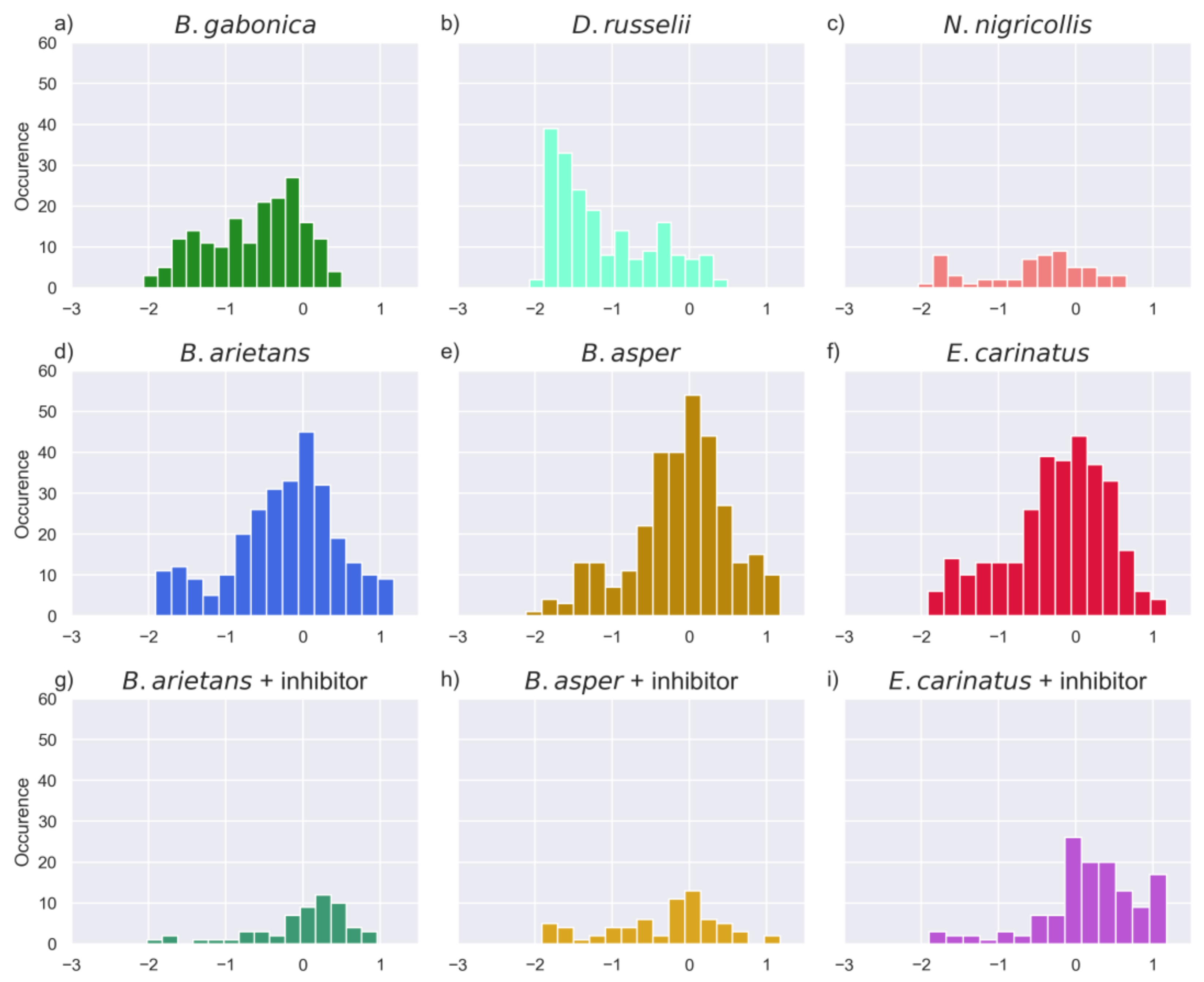


| Venom | Substrates Venom | % of Substrates | Substrates Venom + PT | % of Substrates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. asper | 98 | 27.2 | 21 | 5.8 |
| E. carinatus | 95 | 26.3 | 70 | 19.4 |
| B. arietans | 76 | 21.1 | 32 | 8.8 |
| B. gabonica | 15 | 4.1 | ||
| D. russelii | 8 | 2.2 | ||
| N. nigricollis | 13 | 3.6 |
| Venom | Proteinase% | SVMPs% | SVSPs% | Min. Hemorrhagic Dose (μg) | Min. Coagulant Dose (μg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. carinatus | 61.2 [49] | 56.6 | 4.6 | 0.30 [50] | 3.30 [50] |
| B. asper | 59.2 [51] | 41.0 | 18.2 | 1.50 [52] | 0.32 [52] |
| B. arietans | 57.9 [53] | 38.5 | 19.5 | 0.15 [54] | Non-coagulant |
| B. gabonica | 54.7 [55] | 30.8 | 23.9 | 0.38 [54] | Non-coagulant |
| D. russelii | 25.0 [56] | 21.8 | 3.2 | 4.30 [50] | 4.00 [50] |
| N. nigricollis | 2.4 [29] | 2.4 | - | Non-hemorrhagic [57] | Non-coagulant |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalogeropoulos, K.; Treschow, A.F.; auf dem Keller, U.; Escalante, T.; Rucavado, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Laustsen, A.H.; Workman, C.T. Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening. Toxins 2019, 11, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030170
Kalogeropoulos K, Treschow AF, auf dem Keller U, Escalante T, Rucavado A, Gutiérrez JM, Laustsen AH, Workman CT. Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening. Toxins. 2019; 11(3):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030170
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalogeropoulos, Konstantinos, Andreas Frederik Treschow, Ulrich auf dem Keller, Teresa Escalante, Alexandra Rucavado, José María Gutiérrez, Andreas Hougaard Laustsen, and Christopher T. Workman. 2019. "Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening" Toxins 11, no. 3: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030170
APA StyleKalogeropoulos, K., Treschow, A. F., auf dem Keller, U., Escalante, T., Rucavado, A., Gutiérrez, J. M., Laustsen, A. H., & Workman, C. T. (2019). Protease Activity Profiling of Snake Venoms Using High-Throughput Peptide Screening. Toxins, 11(3), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030170








