New Mastoparan Peptides in the Venom of the Solitary Eumenine Wasp Eumenes micado
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
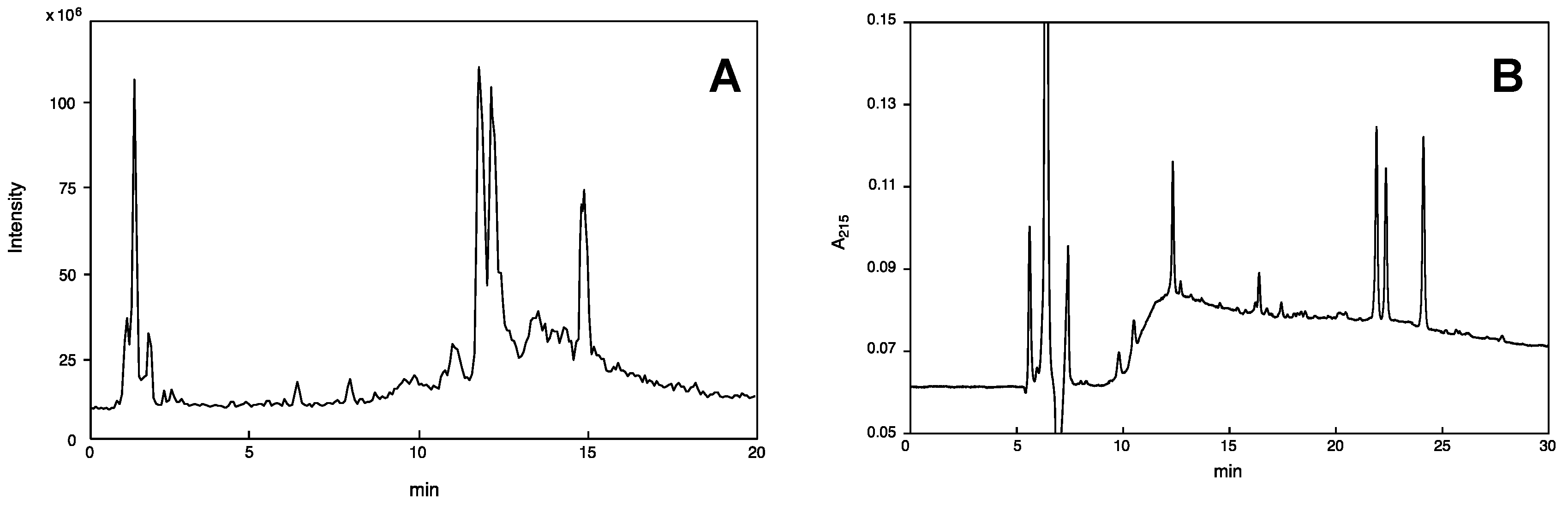
2.1. On-Line Mass Fingerprinting by LC-MS
2.2. Identification of Small Molecules (Amino Acids, Biogenic Amines, and Nucleic Acids)
2.3. Peptide Sequencing by MS/MS Analysis
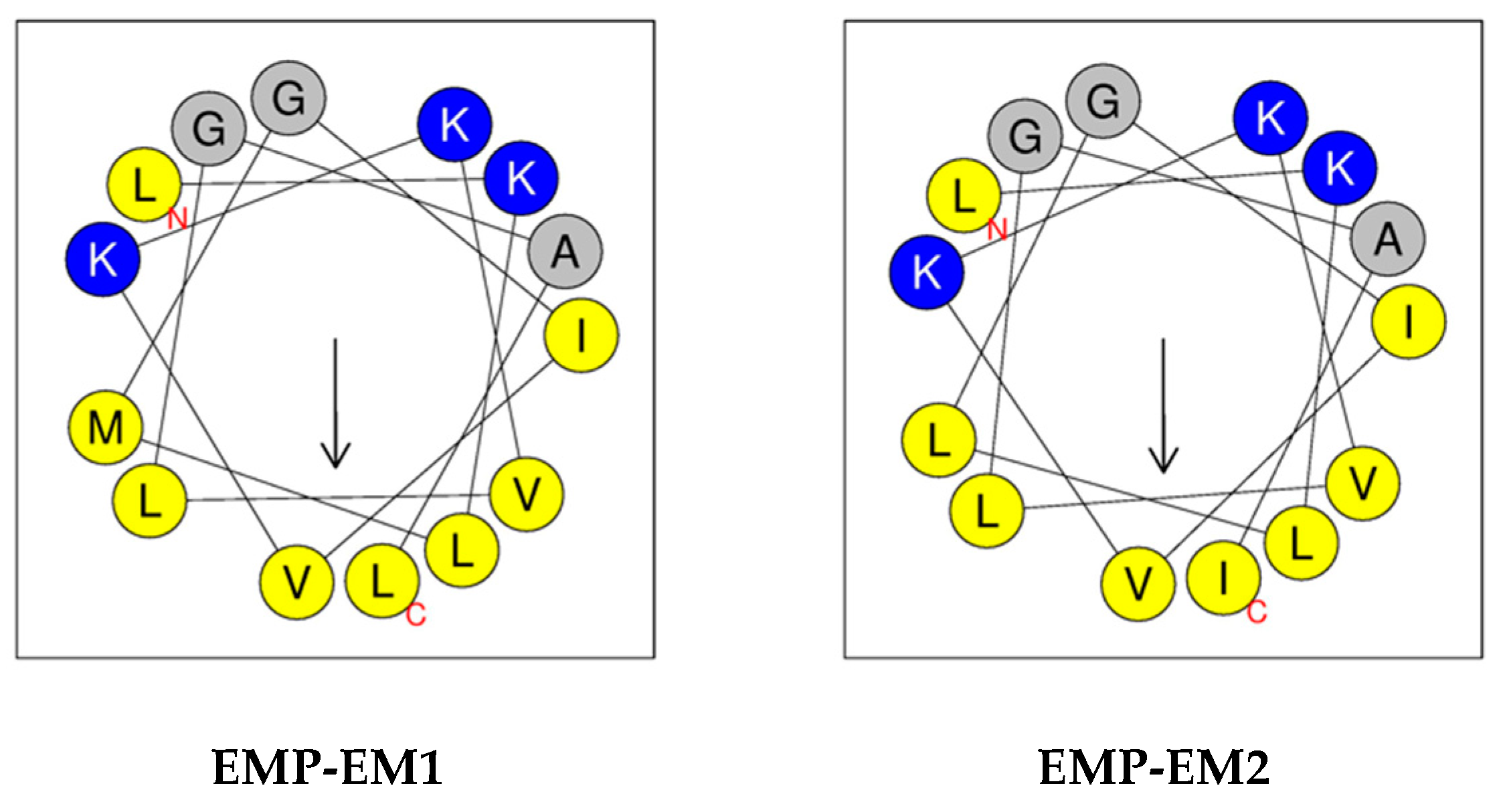
2.4. Purification and Sequence Determination of Mastoparan Peptides
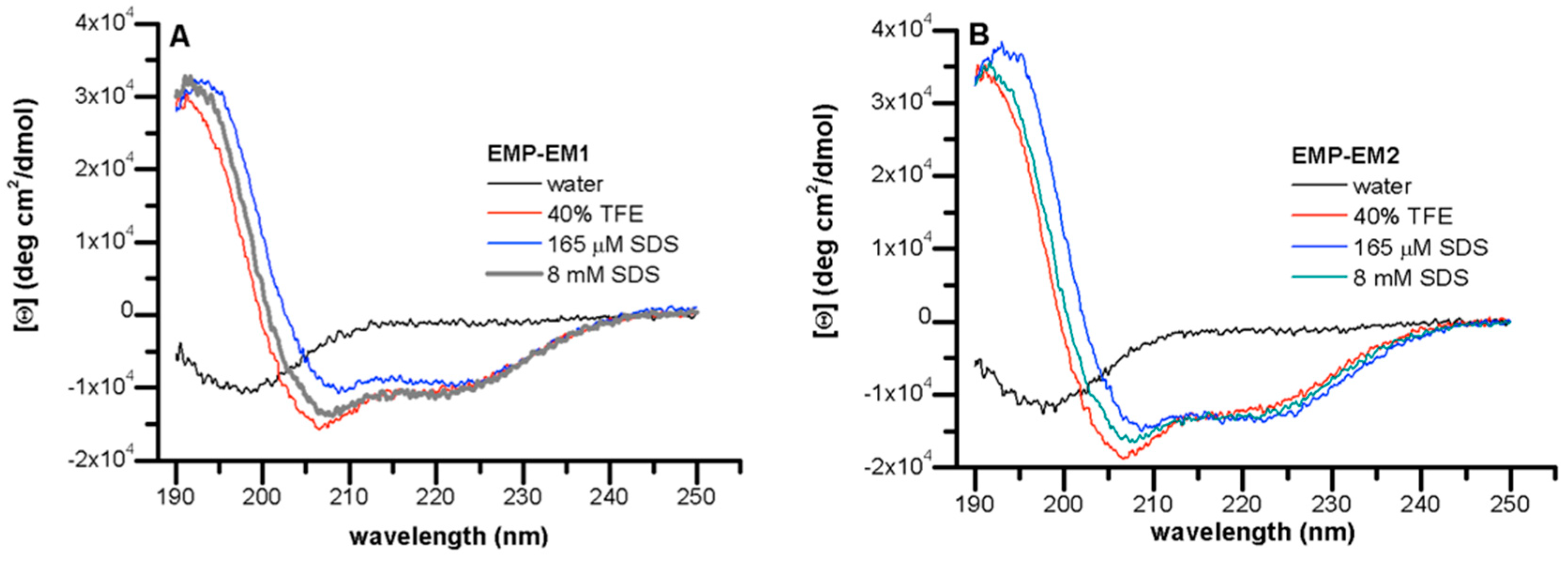
2.5. CD Spectroscopy
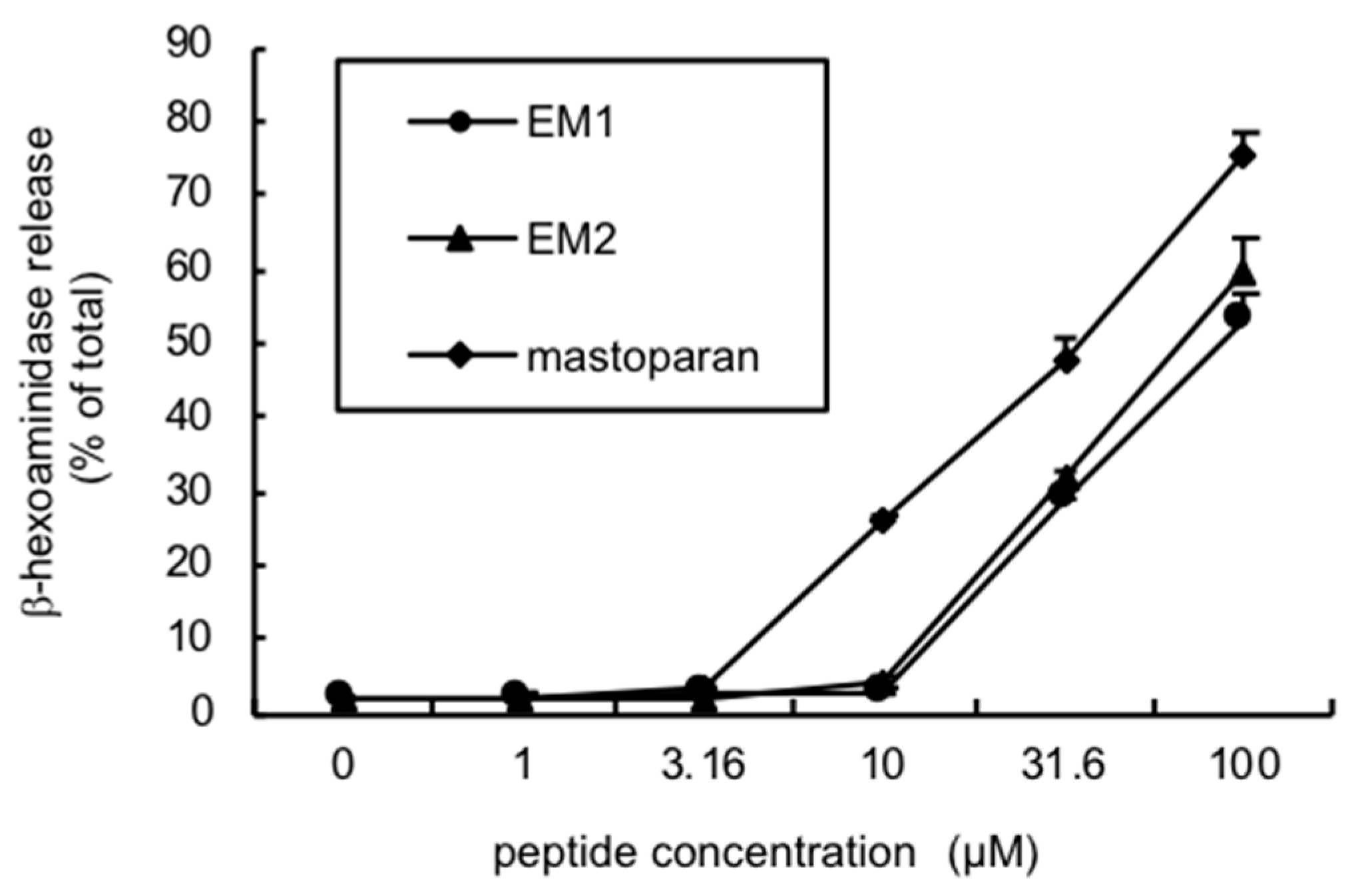
2.6. Biological Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Wasp Collection
4.2. LC-ESI-MS (Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry)
4.3. Purification of Mastoparan Peptides
4.4. Amino Acid Sequencing
4.5. Peptide Synthesis
4.6. Circular Dichroism (CD) measurements
4.7. Mast Cell Degranulation Activity (β-Hexosaminidase Assay)
4.8. Hemolytic Assay
4.9. Antimicrobial Activity (Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration, MIC)
4.10. Leishmanicidal Activity
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirai, Y.; Yasuhara, T.; Yoshida, H.; Nakajima, T.; Fujino, M.; Kitada, C. A new mast cell degranulating peptide “mastoparan” in the venom of Vespula lewisii. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1979, 27, 1942–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T. Pharmacological biochemistry of vespid venoms. In Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects; Piek, T., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1986; pp. 309–327. ISBN 0-12-554771-4. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, K.; Shinada, T.; Ohfune, Y.; Hisada, M.; Yasuda, A.; Naoki, H.; Nakajima, T. Novel biologically active peptides from the venom of Polistes rothneyi iwatai. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; Giralt, E. Three valuable peptides from bee and wasp venoms for therapeutic and biotechnological use. Toxins 2015, 7, 1126–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Bininda-Emonds, O.R.P.; Shaw, C.; Chen, T.; Zhou, M. Evaluation of the bioactivity of a mastoparan peptide from wasp venom and of its analogues designed through targeted engineering. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howl, J.; Howl, L.; Jones, S. The cationic tetradecapeptide mastoparan as a privileged structure for drug discovery: Enhanced antimicrobial properties of mitoparan analogues modified at position-14. Peptides 2018, 101, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, K.; Kazuma, K.; Nihei, K. Peptide toxins in solitary wasp venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, K.; Hisada, M.; Naoki, H.; Itagaki, Y.; Kawai, N.; Miwa, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Morimoto, Y.; Nakata, Y. Structure and biological activities of eumenine mastoparan-AF (EMP-AF), a novel mast cell degranulating peptide in the venom of the solitary wasp (Anterhynchium flavomarginatum micado). Toxicon 2000, 38, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, M.P.S.; Souza, B.M.; Fontana, R.; Konno, K.; Palma, M.S.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr.; Ruggiero Neto, J. Conformation and lytic activity of eumenine mastoparan: A new antimicrobial peptide from wasp venom. J. Peptide Res. 2004, 64, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforça, M.L.; Oyama, S., Jr.; Canduri, F.; Lorenzi, C.C.B.; Pertinez, T.A.; Konno, K.; Souza, B.M.; Palma, M.S.; Ruggiero Neto, J.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr.; et al. How C-terminal carboxyamidation alters the mast cell degranulating activity of peptides from the venom of the eumenine solitary wasp. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 5608–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Shinada, T.; Ohfune, Y.; Hisada, M.; Yasuda, A.; Naoki, H.; Nakajima, T. Novel mastoparan and protonectin analogs isolated from a solitary wasp, Orancistrocerus drewseni drewseni. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Isolation and molecular cloning of venom peptides from Orancistrocerus drewseni (Hymenoptera: Eumenidae). Toxicon 2010, 55, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, M.; Cabrera, M.P.S.; Kazuma, K.; Ando, K.; Wang, X.; Kato, M.; Nihei, K.; Hirata, I.Y.; Cross, T.; Garcia, A.N.; et al. Chemical and biological characterization of four new antimicrobial and α-helical peptides from the venoms of two solitary eumenine wasps. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Differential gene expression profiles in the venom gland/sac of Eumenes pomiformis (Hymenoptera: Eumenidae). Toxicon 2010, 55, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn-Nentwig, L. Antimicrobial and cytolytic peptides of venomous arthropods. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2003, 60, 2651–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, T.; Yasuhara, T.; Yoshida, N.; Takemoto, Y.; Shinonaga, S.; Kano, R.; Yoshida, H. The pattern analysis of biologically active amines in some Hymenopteran venoms by high performance liquid chromatography. Jpn. J. Sanit. Zool. 1983, 34, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, M.; Satake, H.; Masuda, K.; Aoyama, M.; Murata, K.; Shinada, T.; Iwashita, T.; Ohfune, Y.; Nakajima, T. Molecular components and toxicity of the venom of the solitary wasp, Anoplius samariensis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 330, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.L.; Arvidson, R.; Banks, C.; Urenda, J.P.; Duong, E.; Mohammed, H.; Adams, M.E. Ampulexins: A new family of peptides in venom of the emerald jewel wasp, Ampulex compressa. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, K.; Hisada, M.; Naoki, H.; Itagaki, Y.; Yasuhara, T.; Juliano, M.A.; Juliano, L.; Palma, M.S.; Nakajima, T. Isolation and sequence determination of peptides in the venom of the spider wasp Cyphononyx dorsalis guided by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Okada, A.; Miyazawa, T.; Ohya, M.; Higashijima, T. Membrane-bound conformation of Mastoparan-X, a G protein-activating peptide. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 5654–5660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, Y.; Demura, M.; Iwadate, M.; Ulrich, A.S.; Niidome, T.; Aoyagi, H.; Asakura, T. Interaction of mastoparan with membranes studied by 1H-NMR spectroscopy in detergent micelles and by solid-state 2H-NMR and 15N-NMR spectroscopy in oriented lipid bilayers. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todokoro, Y.; Yumen, I.; Fukushima, K.; Kang, S.W.; Park, J.S.; Kohno, T.; Wakamatsu, K.; Akutsu, H.; Fujiwara, T. Structure of tightly membrane-bound Mastoparan-X, a G-protein-activating peptide, determined by solid-state NMR. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimley, W.C. Describing the mechanism of antimicrobial peptide action with the interfacial activity model. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.G.; Yamato, Y.; Lee, S.; Sugihara, G. Interaction of mastoparan-B from venom of a hornet in Taiwan with phospholipid bilayers and its antimicrobial activity. Biopolymers 1995, 36, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondelle, S.E.; Forood, B.; Houghten, R.A.; Pérez-Payá, E. Secondary structure induction in aqueous vs. membrane-like environments. Biopolymers 1997, 42, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Schwarz, E.; Komaromy, M.; Wall, R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 179, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Identification and characterization of venom protein of two solitary wasps, Eumenes pomiformis and Orancistrocerus drewseni. Toxicon 2010, 56, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Baek, J.H.; Yoon, K.A. Differential properties of venom peptides and proteins in solitary vs. social hunting wasps. Toxins 2016, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marle, J.V.; Piek, T. Morphology of the venom apparatus. In Venoms of the Hymenoptera: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Behavioural Aspects; Piek, T., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1986; pp. 17–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rohl, C.A.; Baldwin, R.L. Deciphering rules of helix stability in peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1998, 295, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hide, I.; Bennett, J.P.; Pizzey, A.; Boonen, G.M.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Gomperts, B.D.; Tatham, P.E.R. Degranulation of individual mast cells in response to Ca2+ and guanine nucleotides: An all-or-none event. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, K.C.; Andrade, R.M.A.; Piazza, R.M.F.; Ferreira, J.M.C., Jr.; Berg, C.W.; Tambourgi, D.V. Variations in Loxosceles spider venom composition and toxicity contribute to the severity of envenomation. Toxicon 2005, 45, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, M.; Malpezzi, E.L.A.; Susini, S.M.M.; Freitas, J.C. Hemolytic activity in extracts of the diatom Nitzschia. Toxicon 1997, 35, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Fuchino, H.; Satake, M.; Agatsuma, Y.; Sekita, S. In vitro screening of leishmanicidal activity of Myanmar timber extracts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mastoparan | INLKALAALAKKIL-NH2 | EMP-AF | INLLKIAKGIIKSL-NH2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMP-EF | FDVMGIIKKIASAL-NH2 | EMP-OD | GRILSFIKGLAEHL-NH2 |
| EMP-ER | FDIMGLIKKVAGAL-NH2 | OdVP3 | KDLHTVVSAILQAL-NH2 |
| EMP-EM1 | LKLMGIVKKVLGAL-NH2 | EpVP2a | FDLLGLVKKVASAL-NH2 |
| EMP-EM2 | LKLLGIVKKVLGAI-NH2 | EpVP2b | FDLLGLVKSVVSAL-NH2 |
| Fr. No. | Retention Time (min) | [M + H]+ m/z |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0–1.5 | 90.054, 106.049, 112.086, 116.070, 118.085, 120.065, 147.076, 147.112, 148.060, 156.076, 175.118, 184.072, 487.358 |
| 2 | 1.5–2.0 | 132.101, 150.057, 182.080, 268.102, 269.087, 284.097, 317.239, 336.157, 339.237, 348.068, 361.206, 374.324, 418.314, 664.113 |
| 3 | 2.0–3.0 | 166.085, 428.035 |
| 4 | 3.0–4.0 | 302.206, 320.162, 359.227, 756.532 |
| 5 | 4.0–5.0 | 346.232, 372.258, 473.306, 999.663, 1080.504, 2064.020 |
| 6 | 5.0–6.0 | 599.421, 955.662, 1029.681, 1316.626 |
| 7 | 6.0–7.0 | 471.326, 543.383, 939.669, 1011.722 |
| 8 | 7.0–8.0 | 589.331, 883.631, 901.584, 969.639, 2257.190, 2413.290, 3225.613, 4898.1853 |
| 9 | 8.0–9.0 | 582.256, 931.577, 996.686, 1050.594, 1109.697, 1125.691, 1241.615, 1510.765 |
| 10 | 9.0–10.0 | 564.299, 1046.653, 1973.176, 2039.289 |
| 11 | 10.0–10.4 | 940.575, 1074.226, 1449.976, 2607.505 |
| 12 | 10.4–11.4 | 918.559, 1350.095, 1368.902, 1497.980 |
| 13 | 11.4–12.0 | 815.497, 1222.854, 1481.986, 1539.990 |
| 14 | 12.0–12.5 | 1464.032 |
| 15 | 12.5–13.0 | 2113.272, 2095.261 |
| 16 | 13.0–14.0 | 1518.894, 2078.259 |
| 17 | 14.0–14.5 | 1353.871, 1345.833, 1505.866, 3564.943 |
| 18 | 14.5–15.2 | 1500.941, 1502.903, 1558.943, 1701.020, 1703.984 |
| Retention Time (min) | [M + H]+ m/z |
|---|---|
| 1.10 | 112.086 (histamine), 147.112 (lysine), 156.076 (histidine) |
| 1.24 | 175.118 (arginine) |
| 1.31 | 90.054 (alanine), 106.049 (serine), 116.070 (proline), 118.085 (valine), 120.065 (threonine), 147.076 (glutamine), 148.060 (glutamic acid) |
| 1.53 | 348.068 (AMP) |
| 1.60 | 150.057 (methionine), 664.112 (NAD) |
| 1.68 | 154.085 (dopamine) |
| 1.75 | 132.101 (leucine/isoleucine), 138.090 (tyramine), 268.102 (adenosine) |
| 1.83 | 182.080 (tyrosine) |
| 1.98 | 269.087 (inosine), 284.097 (guanosine) |
| 2.21 | 428.035 (ADP) |
| 2.44 | 166.085 (phenylalanine) |
| 2.67 | 122.096 (phenethylamine) |
| 4.30 | 205.096 (tryptophan) |
| Fr. No. | [M + H]+ | Sequence | Fr. No. | [M + H]+ | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 361.206 | VVSG | 10 | 564.299 | FDLLG |
| 1046.653 | FDLLGLLKK | ||||
| 4 | 302.206 | LLG | 12 | 918.559 | FDLGLLK |
| 320.162 | LMG | 1350.095 | KLLGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 | ||
| 359.227 | VLQ | 1368.902 | KLMGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 | ||
| 756.532 | LVKKVLG | 1497.980 | LKLmGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 | ||
| 5 | 346.232 372.258 473.306 | LLT LGAL-NH2 VVSGL-NH2 | 13 | 815.497 1222.852 1481.986 1539.990 | PVGFLGLL LLGLSLVLLGLLL-NH2 LKLMGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 LKLMGLVKKVLGALG |
| 6 | 599.421 | KVLGAL-NH2 | 14 | 1464.032 | LKLGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 |
| 955.662 | LLKKVVGSL-NH2 | ||||
| 1029.681 | LKKMGLVKK | ||||
| 7 | 471.326 | VLGAL-NH2 | 16 | 1518.894 | FDLGmLVKKVLAGL-NH2 |
| 543.383 | LKLLG | ||||
| 939.669 | LVKQKVLL-NH2 | ||||
| 1011.722 | LKLLGLVKK | ||||
| 8 | 589.331 | PVGFLG | 17 | 1353.871 1355.833 | DLLGLLKKVVSGL-NH2 DLGMLVKKVLAGL-NH2 |
| 883.631 | LKLLGLVK | ||||
| 901.584 | LKLMGLVK | ||||
| 969.639 | LNLLKLAKG | ||||
| 9 | 582.256 | FDLGM | 18 | 1500.941 1502.903 1558.943 | FDLLGLLKKVVSGL-NH2 FDLGMLVKKVLAGL-NH2 FDLLGLLKKVVSGLG |
| 931.577 | TLKVGSLLT | ||||
| 1109.697 | VLNVLNVLL-NH2 | ||||
| 1125.691 | VLNTQNVLL-NH2 | ||||
| 1241.615 | LKLMGLVKKVL |
| RT | [M + H]+ | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| EMP-EM1 | ||
| 7.16 | 901.584 | LKLMGLVK |
| 6.02 | 1029.681 | LKLMGLVKK |
| 8.81 | 1241.615 | LKLMGLVKKVL |
| 1.88 | 336.157 | LmG |
| 3.09 | 320.162 | LMG |
| 3.32 | 756.532 | LVKKVLG |
| 4.94 | 372.259 | LGAL-NH2 |
| 6.55 | 471.326 | VLGAL-NH2 |
| 5.12 | 599.420 | KVLGAL-NH2 |
| 10.65 | 1368.906 | KLMGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 |
| 10.64 | 1497.980 | LKLmGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 |
| 11.72 | 1481.987 | LKLMGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 (EMP-EM1) |
| 11.59 | 1539.995 | LKLMGLVKKVLGALG |
| EMP-EM2 | ||
| 6.80 | 543.883 | LKLLG |
| 7.64 | 883.631 | LKLLGLVK |
| 6.47 | 1011.722 | LKLLGLVKK |
| 3.63 | 302.206 | LLG |
| 10.84 | 1350.095 | KLLGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 |
| 12.12 | 1464.032 | LKLLGLVKKVLGAL-NH2 (EMP-EM2) |
| EMP-EM3 | ||
| 9.25 | 564.299 | FDLLG |
| 10.77 | 918.559 | FDLLGLLK |
| 9.54 | 1046.653 | FDLLGLLKK |
| 1.73 | 361.206 | VVSG |
| 4.73 | 473.305 | VVSGL-NH2 |
| 5.35 | 955.662 | LLKKVVSGL-NH2 |
| 14.42 | 1353.871 | DLLGLLKKVVSGL-NH2 |
| 14.76 | 1500.940 | FDLLGLLKKVVSGL-NH2 (EMP-EM3) |
| 14.57 | 1558.951 | FDLLGLLKKVVSGLG |
| EMP-EM4 | ||
| 8.83 | 582.256 | FDLGM |
| 14.43 | 1355.833 | DLGMLVKKVVSGL-NH2 |
| 13.50 | 1518.895 | FDLGmLVKKVVSGL-NH2 |
| 14.89 | 1502.902 | FDLGMLVKKVVSGL-NH2 (EMP-EM4) |
| RT | [M + H]+ | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 8.58 | 931.575 | TLKVGSLLT |
| 8.51 | 1125.691 | VLNTQLNVLL-NH2 |
| 8.67 | 1109.697 | VLNVNLNVLL-NH2 |
| 7.91 | 589.331 | PVGFLG |
| 11.89 | 815.498 | PVGFLGLL |
| 11.59 | 1222.851 | LLGLSLVLGLLL-NH2 |
| Peptides | N | Q | C-term | <H> | µ | fH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFE | SDS | PC | ||||||
| EMP-EM1 | 14 | +4 | amide | 0.104 | 0.258 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.11 |
| EMP-EM2 | 14 | +4 | amide | 0.138 | 0.278 | 0.37 | 0.41 | <0.03 |
| EMP-AF1 | 14 | +4 | amide | 0.051 | 0.342 | 0.55 | 0.72 | 0.16 |
| EMP-ER2 | 14 | +2 | amide | 0.131 | 0.251 | 0.53 | 0.59 | nd |
| EMP-EF2 | 14 | +2 | amide | 0.115 | 0.279 | 0.41 | 0.44 | nd |
| Microorganism | MIC (µM) * | |
|---|---|---|
| EM1 | EM2 | |
| Gram-positive | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 | 34 | 17 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 7 | 3 |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus (CS) | 3 | 3 |
| Staphylococcus epidermis (CS) | 34 | 34 |
| Bacillus subtilis CCT 2471 | 68 | 68 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis (WT) | NA** | NA |
| Gram-negative | ||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 7 | 3 |
| Escherichia coli CCT 1371 | 17 | 34 |
| Escherichia cloacae ATCC 23355 | 17 | 34 |
| Proteus mirabilis (CS) | NA | NA |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 15442 | NA | 34 |
| Yeast | ||
| Candida albicans (UMP) | NA | NA |
| Peptide | IC50 (μM) * |
|---|---|
| EMP-EM1 | 36 |
| EMP-EM2 | 36 |
| EMP-ER | 20 ** |
| EMP-EF | 40 ** |
| EMP-AF | 35 ** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konno, K.; Kazuma, K.; Rangel, M.; Stolarz-de-Oliveira, J.; Fontana, R.; Kawano, M.; Fuchino, H.; Hide, I.; Yasuhara, T.; Nakata, Y. New Mastoparan Peptides in the Venom of the Solitary Eumenine Wasp Eumenes micado. Toxins 2019, 11, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030155
Konno K, Kazuma K, Rangel M, Stolarz-de-Oliveira J, Fontana R, Kawano M, Fuchino H, Hide I, Yasuhara T, Nakata Y. New Mastoparan Peptides in the Venom of the Solitary Eumenine Wasp Eumenes micado. Toxins. 2019; 11(3):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030155
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonno, Katsuhiro, Kohei Kazuma, Marisa Rangel, Joacir Stolarz-de-Oliveira, Renato Fontana, Marii Kawano, Hiroyuki Fuchino, Izumi Hide, Tadashi Yasuhara, and Yoshihiro Nakata. 2019. "New Mastoparan Peptides in the Venom of the Solitary Eumenine Wasp Eumenes micado" Toxins 11, no. 3: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030155
APA StyleKonno, K., Kazuma, K., Rangel, M., Stolarz-de-Oliveira, J., Fontana, R., Kawano, M., Fuchino, H., Hide, I., Yasuhara, T., & Nakata, Y. (2019). New Mastoparan Peptides in the Venom of the Solitary Eumenine Wasp Eumenes micado. Toxins, 11(3), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030155





