Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spider Venom Gland Reveals Venom Diversity and Species Consanguinity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
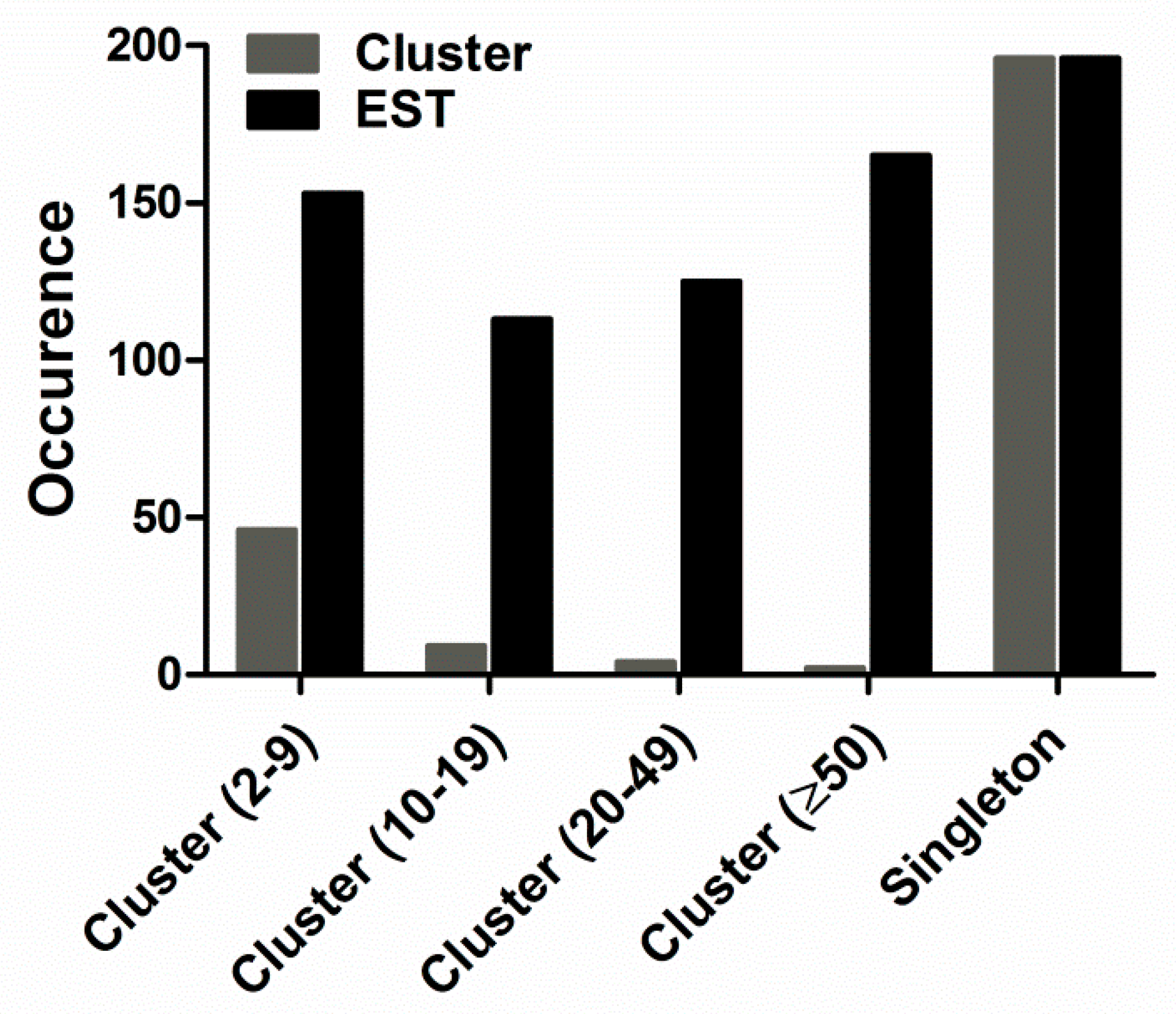
2.1. cDNA Library and EST Analysis
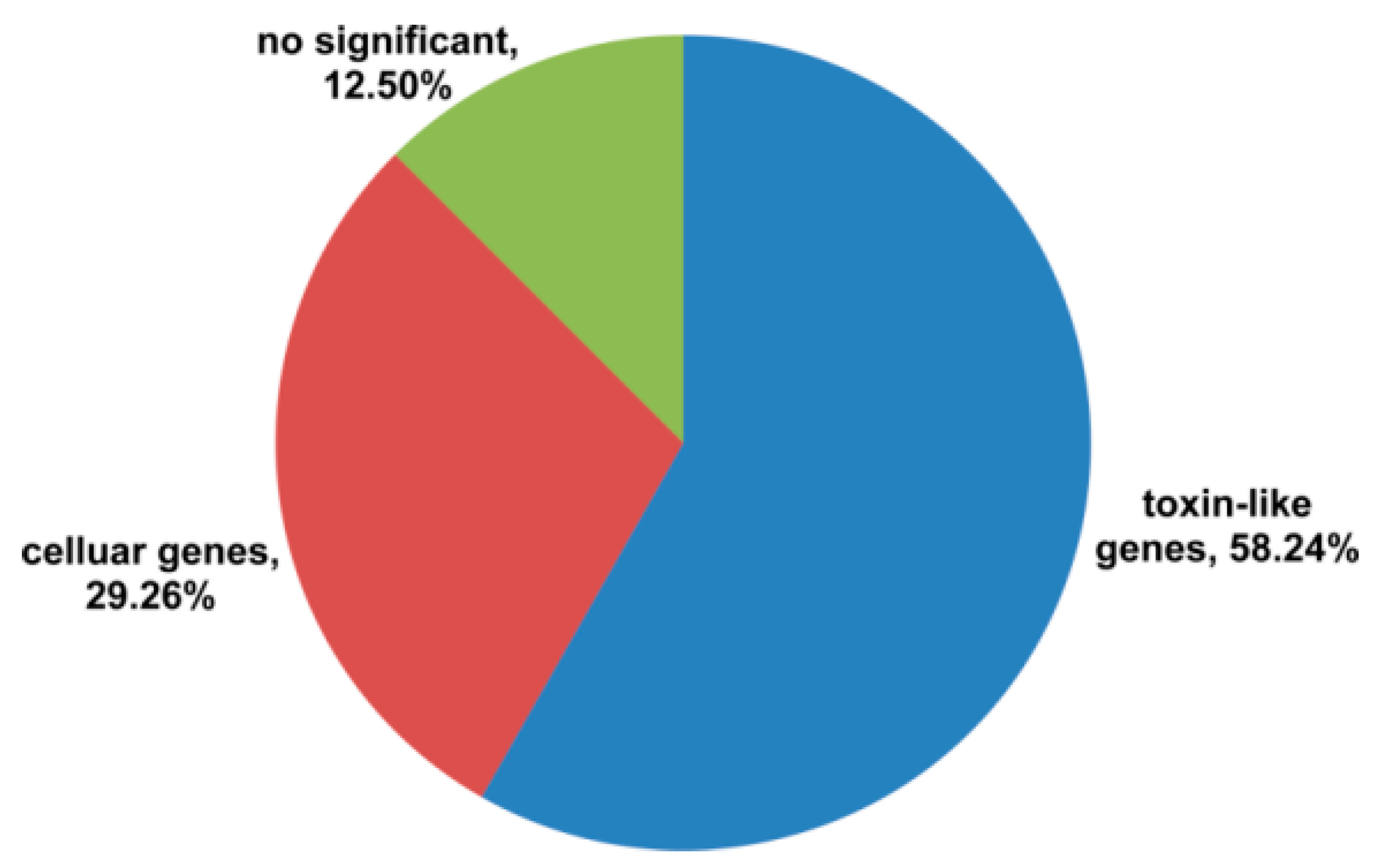
2.2. Classification of Toxin-Like Precursors
2.2.1. Superfamily A
2.2.2. Superfamily B
2.2.3. Superfamily C
2.2.4. Superfamily D
2.2.5. Superfamily E
2.2.6. Superfamily F
2.2.7. Superfamily G
2.2.8. Superfamily H
2.2.9. Superfamily I
2.2.10. Superfamily J
2.2.11. Superfamily K
2.2.12. Superfamily L
2.2.13. Superfamily M
2.2.14. Superfamily N
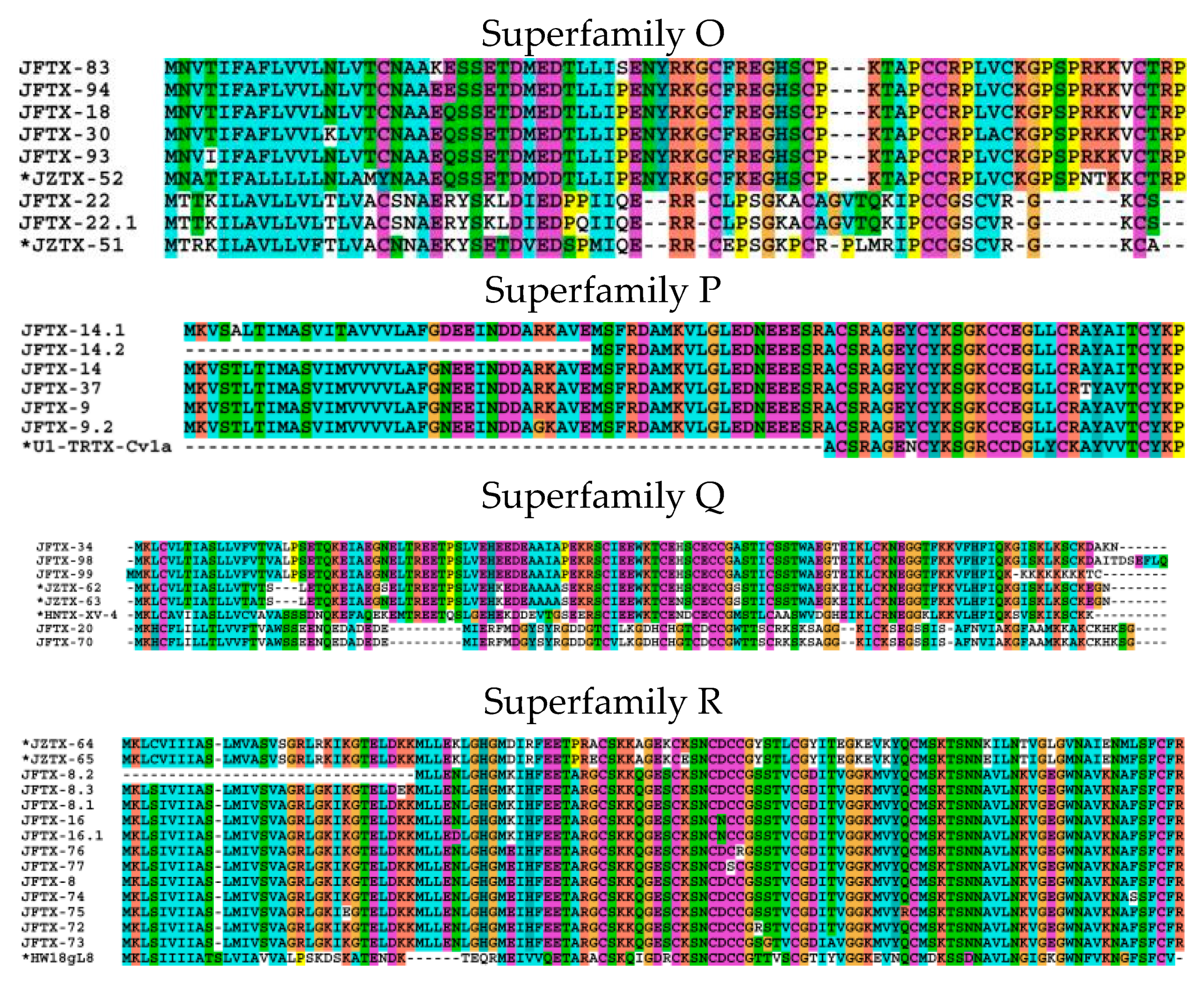
2.2.15. Superfamily O
2.2.16. Superfamily P
2.2.17. Superfamily Q
2.2.18. Superfamily R
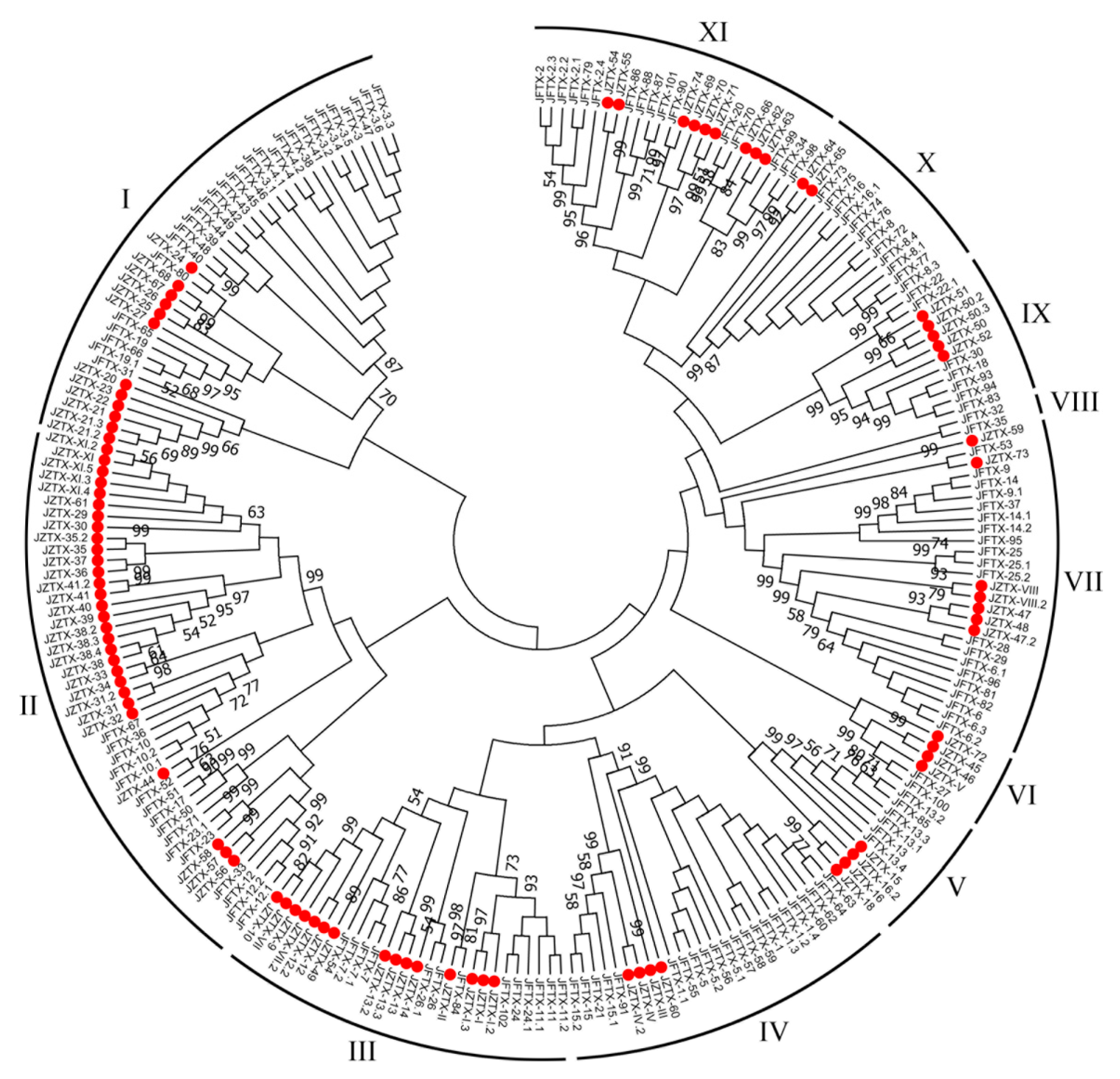
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Putative Toxins from Spiders S. jiafu and C. jingzhao
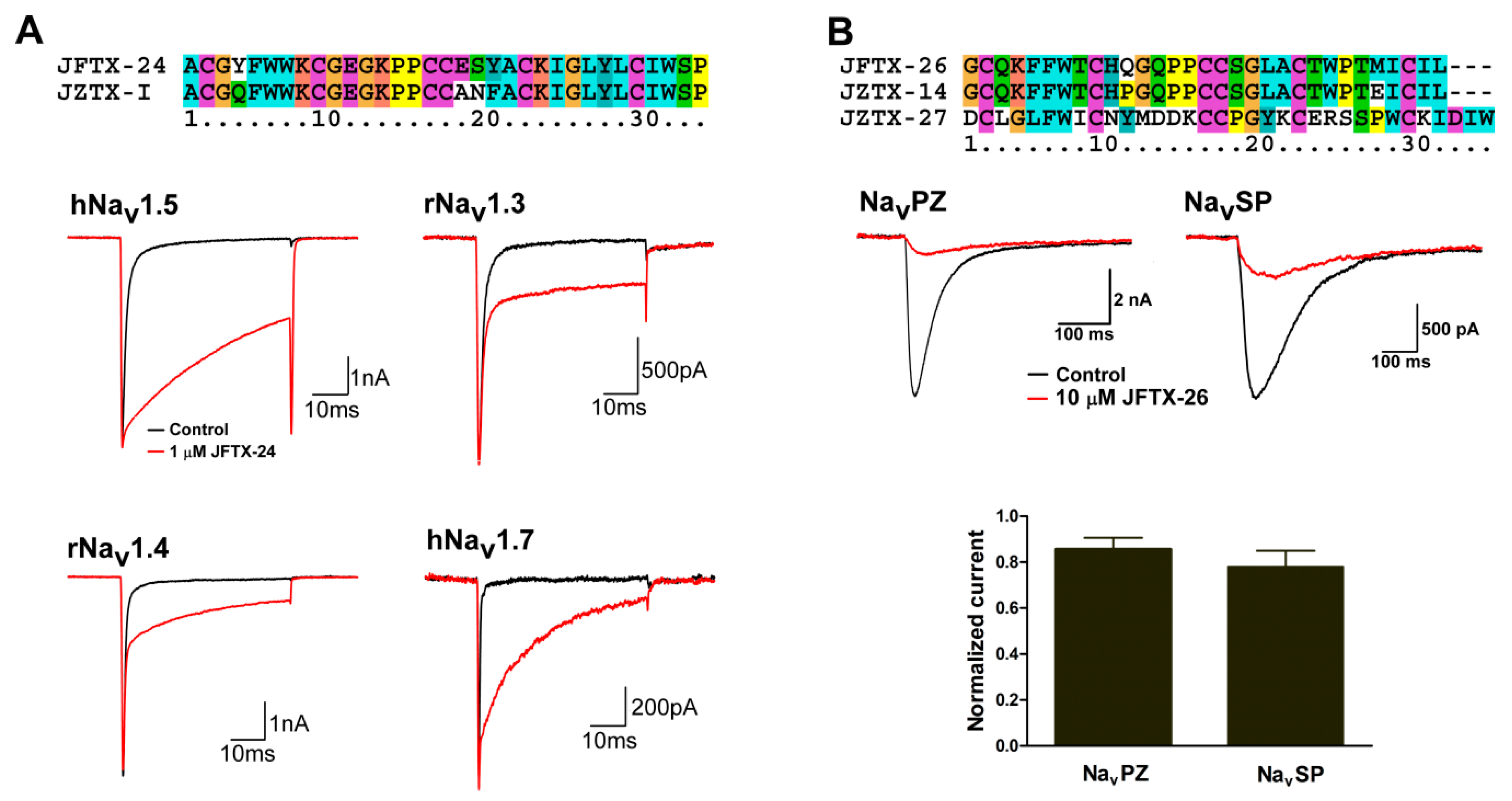
2.4. Pharmacological Activity Analysis of Peptide Toxins from S. jiafu
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. cDNA Library Construction
4.2. DNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.4. Electrophysiology
4.5. Study Approval
4.6. Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hormiga, G.; Griswold, C.E. Systematics, phylogeny, and evolution of orb-weaving spiders. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Smith, J.J.; Herzig, V.; Pineda, S.S.; Dziemborowicz, S.; Er, S.Y.; Durek, T.; Gilchrist, J.; Alewood, P.F.; Nicholson, G.M.; et al. Isolation of two insecticidal toxins from venom of the Australian theraphosid spider Coremiocnemis tropix. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2016, 123, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F.; Hardy, M.C. Spider-venom peptides: Structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F.; Gentz, M.C.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. A rational nomenclature for naming peptide toxins from spiders and other venomous animals. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Peng, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Liang, S. Molecular diversification based on analysis of expressed sequence tags from the venom glands of the Chinese bird spider Ornithoctonus huwena. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 51, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, D.; Tao, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liang, S. Molecular diversification of peptide toxins from the tarantula Haplopelma hainanum (Ornithoctonus hainana) venom based on transcriptomic, peptidomic, and genomic analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 2550–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.; He, Q.Z.; Luo, J.; Zhu, L.; Lu, S.S.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, P.F.; Zeng, X.Z.; Liang, S.P. Structural and functional diversity of peptide toxins from tarantula Haplopelma hainanum (Ornithoctonus hainana) venom revealed by transcriptomic, peptidomic, and patch clamp approaches. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26471–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, L.; Meng, E.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Liang, S. Transcriptome analysis revealed novel possible venom components and cellular processes of the tarantula Chilobrachys jingzhao venom gland. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 52, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Tang, C.; Xiao, Z.; Ying, D.; Liu, Z.; Liang, S. The venom of the spider Selenocosmia jiafu contains various neurotoxins acting on voltage-gated ion channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Toxins 2014, 6, 988–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, J.; Milescu, M.; Salvatierra, J.; Wagner, J.; Klint, J.K.; King, G.F.; Olivera, B.M.; Bosmans, F. From foe to friend: Using animal toxins to investigate ion channel function. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, M.; Daly, M.; King, G.F.; Norton, R.S. Venoms to the rescue. Science 2018, 361, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osteen, J.D.; Herzig, V.; Gilchrist, J.; Emrick, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Castro, J.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Grundy, L.; Rychkov, G.Y.; et al. Selective spider toxins reveal a role for the Nav1.1 channel in mechanical pain. Nature 2016, 534, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, K.L.; Milligan, C.J.; Richardson, R.J.; Jancovski, N.; Grunnet, M.; Jacobson, L.H.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Mobli, M.; Chow, C.Y.; Herzig, V.; et al. Selective NaV1.1 activation rescues Dravet syndrome mice from seizures and premature death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8077–E8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klint, J.K.; Senff, S.; Rupasinghe, D.B.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Nicholson, G.M.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides that target voltage-gated sodium channels: Pharmacological tools and potential therapeutic leads. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2012, 60, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Heijne, G. Patterns of amino acids near signal-sequence cleavage sites. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 133, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.; Malyavka, A.; McCutchen, B.; Lu, A.; Schepers, E.; Herrmann, R.; Grishin, E. A novel strategy for the identification of toxinlike structures in spider venom. Proteins 2005, 59, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.K.; Ligutti, J.; Liu, D.; Zou, A.; Poppe, L.; Li, H.; Andrews, K.L.; Moyer, B.D.; McDonough, S.I.; Favreau, P.; et al. Engineering potent and selective analogues of GpTx-1, a tarantula venom peptide antagonist of the Na(V)1.7 sodium channel. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2299–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Ono, S.; Kubo, T. Molecular Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the cDNAs Encoding Toxin-Like Peptides from the Venom Glands of Tarantula Grammostola rosea. Int. J. Pept. 2012, 2012, 731293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhou, X.; Nguyen, P.T.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; DeCaen, P.G.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z. A novel tarantula toxin stabilizes the deactivated voltage sensor of bacterial sodium channel. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2017, 31, 3167–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Tang, J.; Hu, W.; Xie, J.; Maertens, C.; Tytgat, J.; Liang, S. Jingzhaotoxin-I, a novel spider neurotoxin preferentially inhibiting cardiac sodium channel inactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12069–12076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Wu, Y.; Deng, M.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z.; Liang, S. Molecular determinant for the tarantula toxin Jingzhaotoxin-I slowing the fast inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2016, 111, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Kuang, F.; Sun, Z.; Tao, H.; Cai, T.; Zhong, L.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, S. Jingzhaotoxin-IX, a novel gating modifier of both sodium and potassium channels from Chinese tarantula Chilobrachys jingzhao. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Diao, J.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Lin, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, S. JZTX-IV, a unique acidic sodium channel toxin isolated from the spider Chilobrachys jingzhao. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2008, 52, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, C.Y.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Undheim, E.A.; King, G.F.; Rash, L.D. Three Peptide Modulators of the Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel 1.7, an Important Analgesic Target, from the Venom of an Australian Tarantula. Toxins 2015, 7, 2494–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swartz, K.J.; MacKinnon, R. An inhibitor of the Kv2.1 potassium channel isolated from the venom of a Chilean tarantula. Neuron 1995, 15, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Chen, J.; Tao, H.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Lu, M.; Su, H.; Chi, Y.; Cai, T.; Zhao, L.; et al. Molecular basis of the tarantula toxin jingzhaotoxin-III (beta-TRTX-Cj1alpha) interacting with voltage sensors in sodium channel subtype Nav1.5. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2011, 25, 3177–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Chen, J.J.; Xiao, Y.C.; Wu, Y.Y.; Su, H.B.; Li, D.; Wang, H.Y.; Deng, M.C.; Wang, M.C.; Liu, Z.H.; et al. Analysis of the interaction of tarantula toxin Jingzhaotoxin-III (beta-TRTX-Cj1alpha) with the voltage sensor of Kv2.1 uncovers the molecular basis for cross-activities on Kv2.1 and Nav1.5 channels. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7439–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.S.; Hardy, M.C.; Wood, D.; Bailey, T.; King, G.F. SVM-based prediction of propeptide cleavage sites in spider toxins identifies toxin innovation in an Australian tarantula. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, G.; Bernard, C.; Clement, H.; Villegas, E.; Bosmans, F.; Tytgat, J.; Possani, L.D.; Darbon, H.; Alagon, A. Insecticidal peptides from the theraposid spider Brachypelma albiceps: An NMR-based model of Ba2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cai, T.; Zhu, Q.; Deng, M.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structure and function of hainantoxin-III, a selective antagonist of neuronal tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels isolated from the Chinese bird spider Ornithoctonus hainana. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20392–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, M.C.; Daly, N.L.; Mobli, M.; Morales, R.A.; King, G.F. Isolation of an orally active insecticidal toxin from the venom of an Australian tarantula. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, R.A.; Sasaki, T.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Sato, K.; Kini, R.M.; Bay, B.H. Purification, structure determination and synthesis of covalitoxin-II, a short insect-specific neurotoxic peptide from the venom of the Coremiocnemis validus (Singapore tarantula). FEBS Lett. 2000, 474, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S. An overview of peptide toxins from the venom of the Chinese bird spider Selenocosmia huwena Wang [=Ornithoctonus huwena (Wang)]. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2004, 43, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z. A Comparative Analysis of the Venom Gland Transcriptomes of the Fishing Spiders Dolomedes mizhoanus and Dolomedes sulfurous. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D41–D47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, T.; Ota, T.; Kawai, Y.; Ishii, S.; Saito, K.; Yamamoto, J.; Wakamatsu, A.; Ozawa, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Sugano, S.; et al. Database and analysis system for cDNA clones obtained from full-length enriched cDNA libraries. Silico Biol. 2002, 2, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, J.D.; Nielsen, H.; von Heijne, G.; Brunak, S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 340, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spider Venom Gland Reveals Venom Diversity and Species Consanguinity. Toxins 2019, 11, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020068
Hu Z, Chen B, Xiao Z, Zhou X, Liu Z. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spider Venom Gland Reveals Venom Diversity and Species Consanguinity. Toxins. 2019; 11(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhaotun, Bo Chen, Zhen Xiao, Xi Zhou, and Zhonghua Liu. 2019. "Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spider Venom Gland Reveals Venom Diversity and Species Consanguinity" Toxins 11, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020068
APA StyleHu, Z., Chen, B., Xiao, Z., Zhou, X., & Liu, Z. (2019). Transcriptomic Analysis of the Spider Venom Gland Reveals Venom Diversity and Species Consanguinity. Toxins, 11(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020068





