The C-Terminal Domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba Mosquito-Specific Toxin Serves as a Potential Membrane Anchor
Abstract
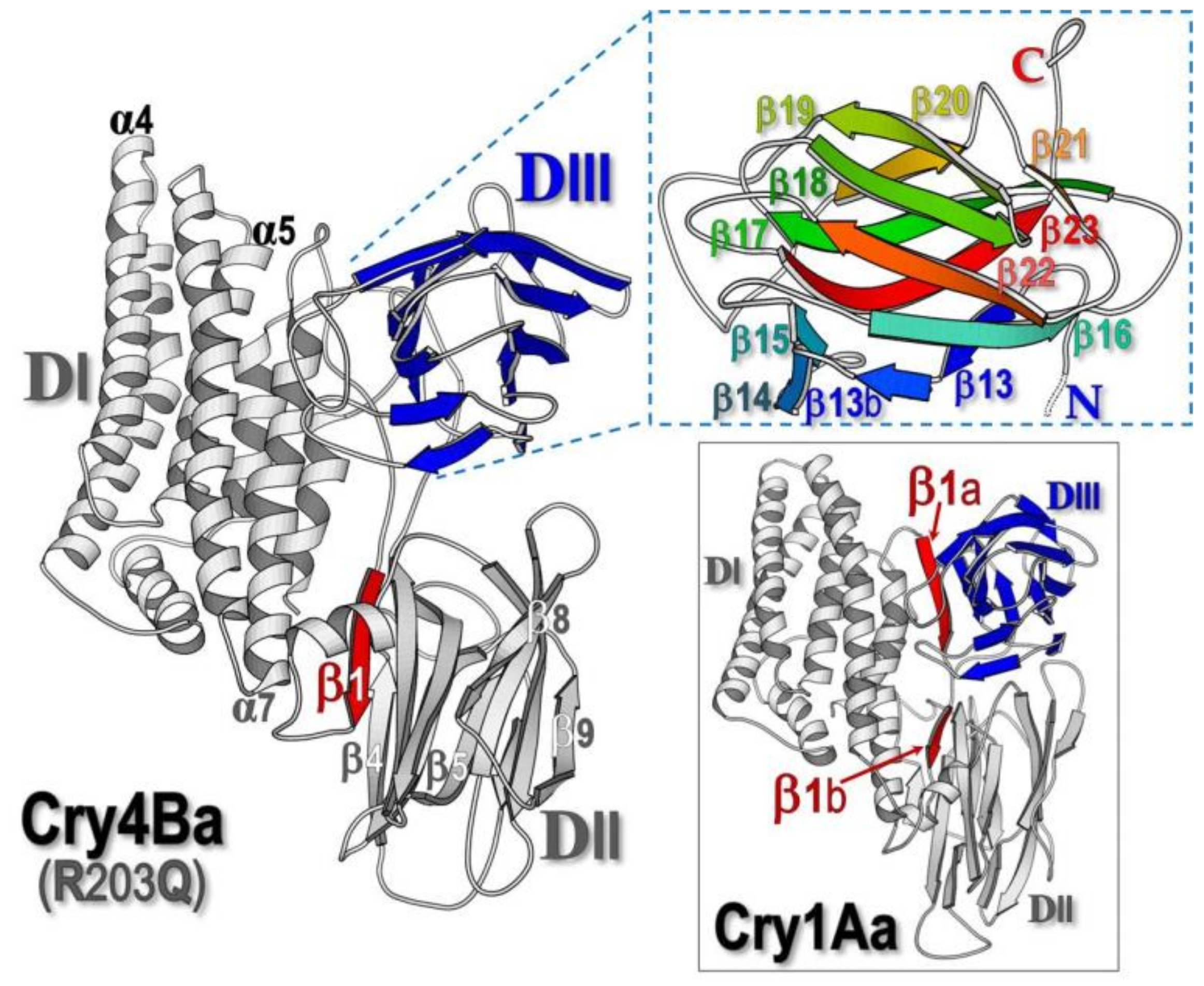
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Feature of the Isolated Cry4Ba-DIII Truncate Revealed by ATR-FTIR
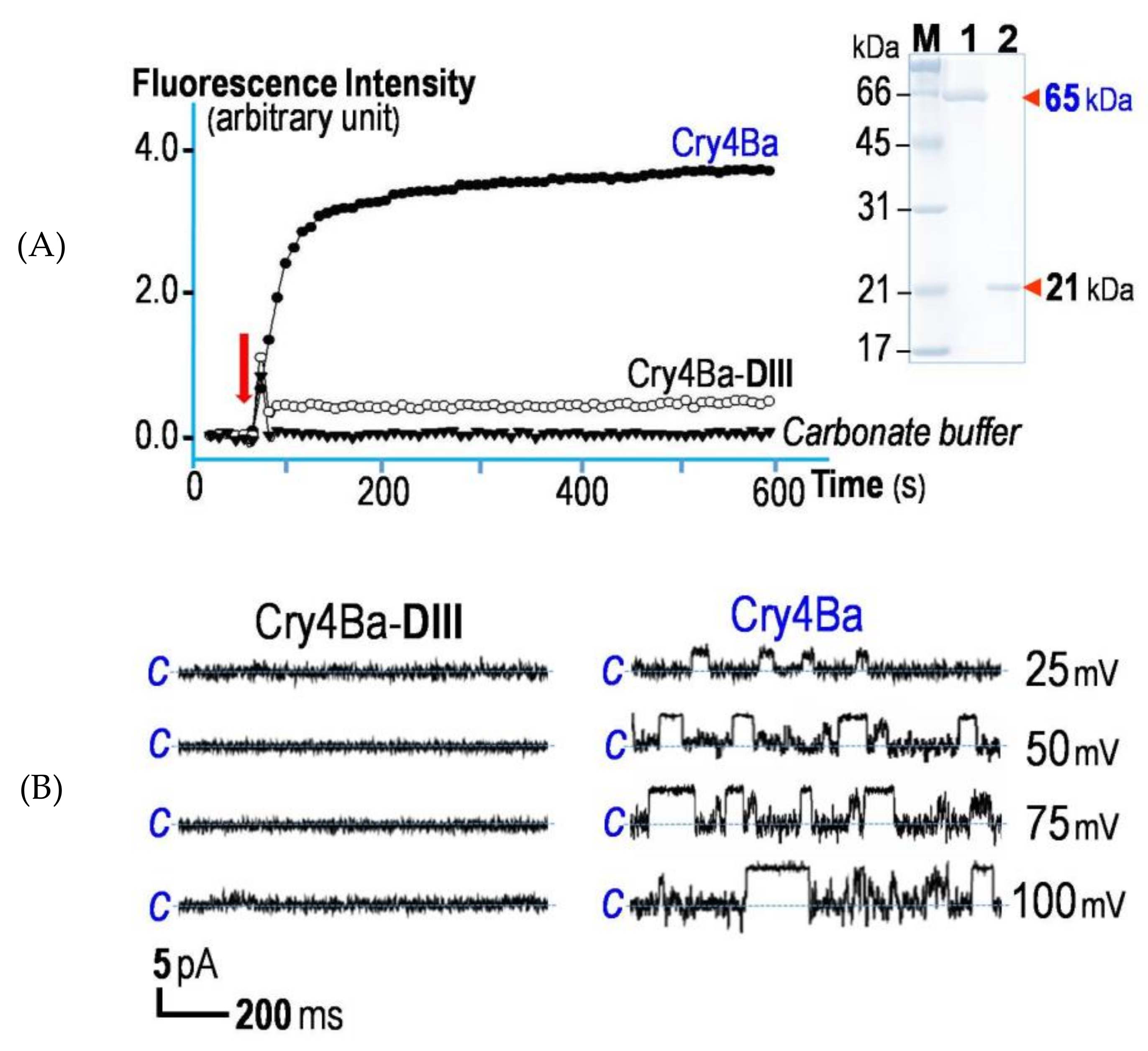
2.2. Membrane-Binding Characteristics of the Isolated Cry4Ba-DIII Truncate
2.3. Cry4Ba-DIII Serves as a Membrane Anchor but not a Membrane-Perturbing or Pore-Forming Moiety
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of the Cry4Ba Active Toxin
3.2. Expression and Purification of the Cry4Ba-DIII Truncate
3.3. Structural Verification of the Cry4Ba-DIII Truncate via ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
3.4. Membrane-Binding Assays of the Cry4Ba Proteins via SPR Spectroscopy
3.5. Proteinase K Protection Assays of the Cry4Ba Proteins
3.6. Membrane Perturbation Assays of the Cry4Ba Proteins
3.7. Single-Channel Analysis of the Cry4Ba Proteins via Planar Lipid Bilayers (PLBs)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATR-FTIR | attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared |
| Cry | crystal |
| FPLC | fast protein liquid chromatography |
| LUVs | large unilamellar vesicles |
| OG | n-octyl-β-d-glucopyranoside |
| PLBs | planar lipid bilayers |
| SPR | surface plasmon resonance |
References
- Schnepf, E.; Crickmore, N.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Feitelson, J.; Zeigler, D.R.; Dean, D.H. Bacillus thuringiensis and its pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, N.; Ludwig, M. Investigations on possible resistance in Aedes vexans field populations after a 10-year application of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1993, 9, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Federici, B.A.; Park, H.W.; Bideshi, D.K. Overview of the basic biology of Bacillus thuringiensis with emphasis on genetic engineering of bacterial larvicides for mosquito control. Open Toxinol. J. 2010, 3, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dov, E. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and its dipteran-specific toxins subsp. Toxins 2014, 6, 1222–1243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angsuthanasombat, C.; Crickmore, N.; Ellar, D.J. Cytotoxicity of a cloned Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis CryIVB toxin to an Aedes aegypti cell line. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 83, 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Boonserm, P.; Davis, P.; Ellar, D.J.; Li, J. Crystal structure of the mosquito-larvicidal toxin Cry4Ba and its biological implications. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carroll, J.; Ellar, D.J. Crystal structure of insecticidal δ-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 Å resolution. Nature 1991, 353, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochulski, P.; Masson, L.; Borisova, S.; Pusztai-Carey, M.; Schwartz, J.-L.; Brousseau, R.; Cygler, M. Bacillus thuringiensis CrylA(a) insecticidal toxin: Crystal structure and channel formation. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamwiriyasati, N.; Sakdee, S.; Chuankhayan, P.; Katzenmeier, G.; Chen, C.J.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of a full-length active form of the Cry4Ba toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis. Acta Crystallogr. 2010, F66, 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Whalon, M.E.; Wingerd, B.A. Bt: Mode of action and use. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 54, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sramala, I.; Leetachewa, S.; Krittanai, C.; Katzenmeier, G.; Panyim, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Charged residue screening in helix 4 of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4B toxin reveals one critical residue for larvicidal activity. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys. 2001, 5, 219–225. [Google Scholar]
- Imtong, C.; Kanchanawarin, C.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Aa insecticidal protein: Functional importance of the intrinsic stability of the unique α4-α5 loop comprising the Pro-rich sequence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiewsiri, K.; Fischer, W.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Lipid-induced conformation of helix 7 from the pore-forming domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin: Implications for toxicity mechanism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 482, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juntadech, T.; Kanintronkul, Y.; Kanchanawarin, C.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Importance of polarity of the α4-α5 loop residue–Asn166 in the pore-forming domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin: Implications for ion permeation and pore opening. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuntitippawan, T.; Boonserm, P.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Targeted mutagenesis of loop residues in the receptor-binding domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin affects larvicidal activity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 242, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikaew, A.; Promptmas, C.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Importance of Thr328 and Thr369 for functional maintenance of two receptor-binding β-hairpins of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin: Implications for synergistic interactions with Cyt2Aa2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 469, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lailak, C.; Khaokhiew, T.; Promptmas, C.; Promdonkoy, B.; Pootanakit, K.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin employs two receptor-binding loops for synergistic interactions with Cyt2Aa2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commu. 2013, 435, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thammasittirong, A.; Dechklar, M.; Leetachewa, S.; Pootanakit, K.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Aedes aegypti membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase expressed in Escherichia coli retains high-affinity binding for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6836–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroonkesorn, A.; Pootanakit, K.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Two specific membrane-bound aminopeptidase N isoforms from Aedes aegypti larvae serve as functional receptors for the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin implicating counterpart specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, M.; Ali, M.B.; Jaoua, S.; Tounsi, S. Amino acids Y229 and F603 are involved in Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac delta-endotoxin stability and toxicity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 329, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, T.; Yoshisue, H.; Ihara, K.; Sakai, H.; Komano, T. Functional analysis of block 5, one of the highly conserved amino acid sequences in the 130-kDa CryIVA protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. FEBS Lett. 1994, 348, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, L.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Mazza, A.; Prefontaine, G.; Potvin, L.; Brousseau, R.; Schwartz, J.L. Mutagenic analysis of a conserved region of domain III in the Cry1Ac toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, D.; Schipper, B.; van der Kleij, H.; de Maagd, R.A.; Stiekema, W. Recombinant Bacillus thuringiensis crystal proteins with new properties: Possibilities for resistance management. Nat. Biotechnol. 1994, 12, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Maagd, R.A.; Weemen-Hendriks, M.; Stiekema, W.; Bosch, D. Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin Cry1C domain III can function as a specificity determinant for Spodoptera exigua in different, but not all, Cry1-Cry1C hybrids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.K.; Young, B.A.; Dean, D.H. Domain-III exchanges of Bacilllus thuringiensis CryIA toxins affect binding to different gypsy moth midgut receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 216, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; He, K.; Guo, S. Domain III of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ie toxin plays an important role in binding to peritrophic membrane of Asiancorn borer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136430. [Google Scholar]
- Chayaratanasin, P.; Moonsom, S.; Sakdee, S.; Chaisri, U.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. High level of soluble expression in Escherichia coli and characterisation of the cloned Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba domain III fragment. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 40, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Padron, R.I.; Martinez-Gil, A.F.; Ayra-Pardo, C.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, J.; Prieto-Samsonov, D.L.; de la Riva, G.A. Biochemical characterization of the third domain from Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxins. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1988, 45, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Mozsolits, H.; Wirth, H.-J.; Werkmeister, J.; Aguilar, M.-I. Analysis of antimicrobial peptide interactions with hybrid bilayer membrane systems using surface plasmon resonance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2001, 1512, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidukov, L.; Fish, A.; Mor, A. Analysis of membrane-binding properties of dermaseptin analogues: Relationships between binding and cytotoxicity. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 12866–12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Gutierrez-Aguirre, I.; Barlic, A.; Malovrh, P.; Kristan, K.; Podlesek, Z.; Macek, P.; Turk, D.; Gonzalez-Manas, J.M.; Lakey, J.H.; et al. Two-step membrane binding by Equinatoxin II, a pore-forming toxin from the sea anemone, involves an exposed aromatic cluster and a flexible helix. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41916–41924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shai, Y. Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by α-helical antimicrobial and cell non-selective membrane-lytic peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 1999, 1462, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufareva, I.; Lenoir, M.; Dancea, F.; Sridhar, P.; Raush, E.; Bissig, C.; Gruenber, J.; Abagyan, R.; Overduin, M. Discovery of novel membrane binding structures and functions. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Singh, S.; Ghosh, A.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M.; Bhunia, A. Role of aromatic amino acids in lipopolysaccharide and membrane interactions of antimicrobial peptides for use in plant disease control. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13301–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.S.; Dean, D.H. All domains of Cry1A toxins insert into insect brush border membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26324–26331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntheeranurak, T.; Leetacheewa, S.; Katzenmeier, G.; Krittanai, C.; Panyim, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Expression and biochemical characterization of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4B α1-α5 pore-forming fragment. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 34, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Puntheeranurak, T.; Uawithya, P.; Potvin, L.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Schwartz, J.L. Ion channels formed in planar lipid bilayers by the dipteran-specific Cry4B Bacillus thuringiensis toxin and its α1-α5 fragment. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2004, 21, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwimol, W.; Aroonkesorn, A.; Sakdee, S.; Kanchanawarin, C.; Uchihashi, T.; Ando, T.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Potential prepore trimer formation by the Bacillus thuringiensis mosquito-specific toxin: Molecular insights into a critical prerequisite of membrane-bound momomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20793–20803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D. Quantitation of secondary structure in ATR infrared spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 1999, 77, 2630–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginoya, K.; Thangavel, V.; Pandian, G.N.; Tomimoto, K.; Shitomi, Y.; Azuma, M.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Hori, H. Investigation of physicochemical condition to stabilize phosphatidylcholineliposome enclosing fluorescent calcein and its exploitation for analysis of pore formation with Cry1A toxins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leetachewa, S.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Novel preparation and characterization of the alpha4-loop-alpha5 membrane-perturbing peptide from the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba delta-endotoxin. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 39, 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- Meetum, K.; Imtong, C.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Acylation of the Bordetella pertussis CyaA-hemolysin: Functional implications for efficient membrane insertion and pore formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Proteins | ka(M−1 s−1) a | kd (s−1) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21-kDa DIII truncate | ka1 = 6.9 × 103 | [± 0.8 × 103] | kd1 = 3.5 × 10−2 | [± 0.5 × 10−2] |
| ka2 = 1.5 × 10−2 | [± 0.2 × 10−2] | kd2 = 5.1 × 10−4 | [± 0.9 × 10−4] | |
| 65-kDa full-length toxin | ka1 = 1.9 × 104 | [± 1.1 × 104] | kd1 = 7.6 × 10−2 | [± 2.1 × 10−2] |
| ka2 = 4.7 × 10−3 | [± 0.6 × 10−3] | kd2 = 7.7 × 10−4 | [± 1.5 × 10−4] | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thammasittirong, A.; Imtong, C.; Sriwimol, W.; Sakdee, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C. The C-Terminal Domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba Mosquito-Specific Toxin Serves as a Potential Membrane Anchor. Toxins 2019, 11, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020062
Thammasittirong A, Imtong C, Sriwimol W, Sakdee S, Angsuthanasombat C. The C-Terminal Domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba Mosquito-Specific Toxin Serves as a Potential Membrane Anchor. Toxins. 2019; 11(2):62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020062
Chicago/Turabian StyleThammasittirong, Anon, Chompounoot Imtong, Wilaiwan Sriwimol, Somsri Sakdee, and Chanan Angsuthanasombat. 2019. "The C-Terminal Domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba Mosquito-Specific Toxin Serves as a Potential Membrane Anchor" Toxins 11, no. 2: 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020062
APA StyleThammasittirong, A., Imtong, C., Sriwimol, W., Sakdee, S., & Angsuthanasombat, C. (2019). The C-Terminal Domain of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba Mosquito-Specific Toxin Serves as a Potential Membrane Anchor. Toxins, 11(2), 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11020062





