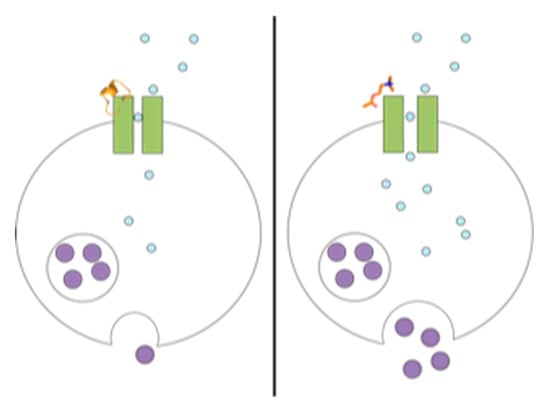
Qualitative Assay to Detect Dopamine Release by Ligand Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
Abstract
1. Introduction
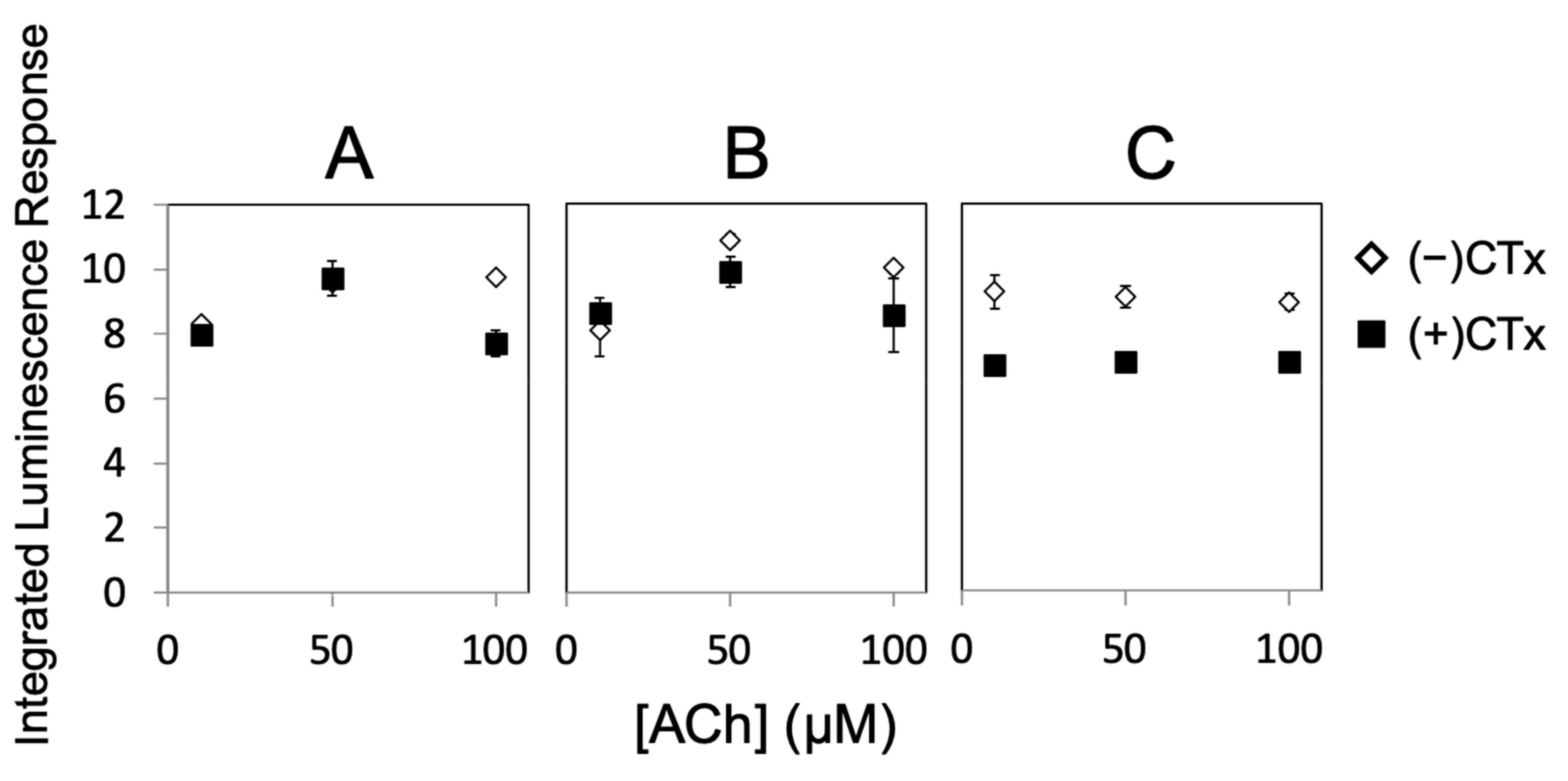
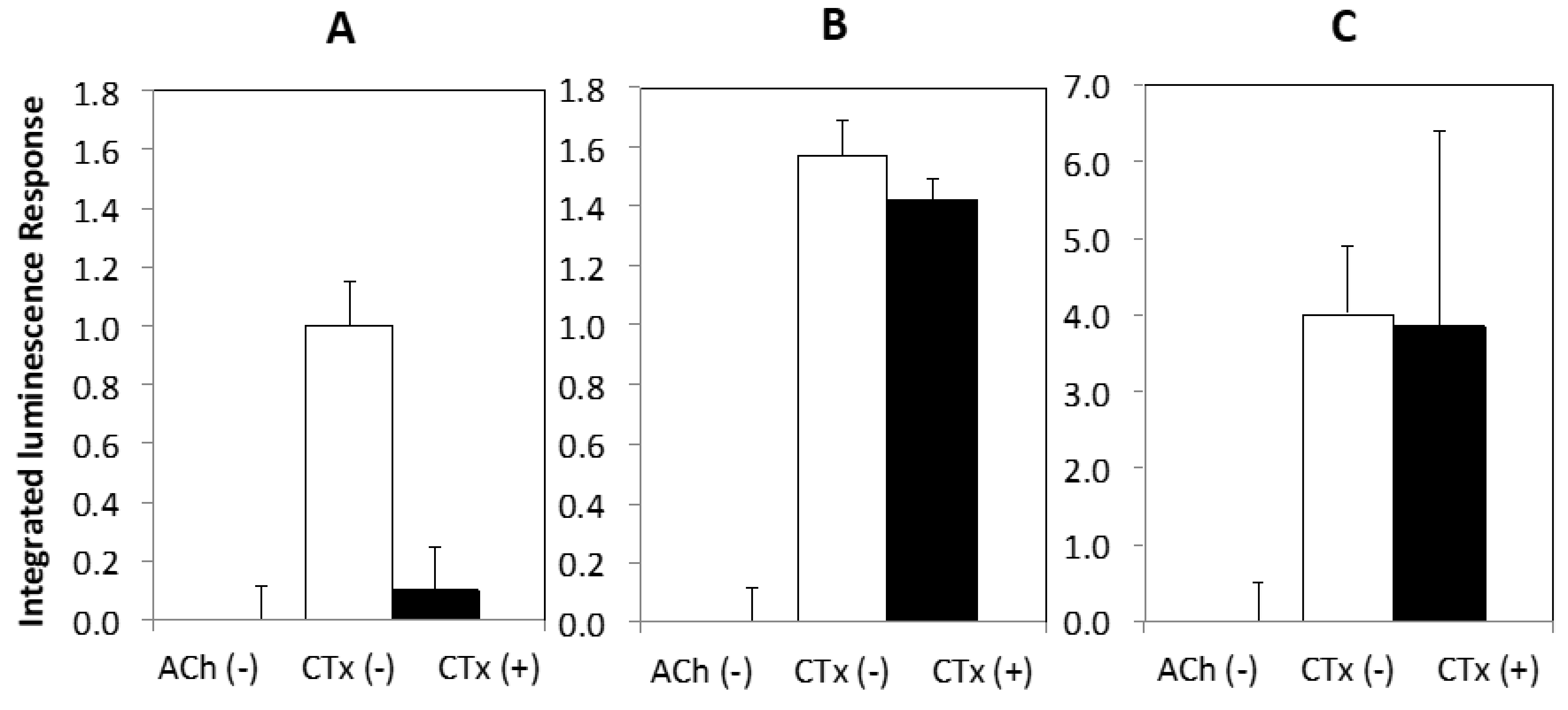
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quik, M.; Wonnacott, S. Alpha 6 beta 2* and alpha 4 beta 2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as drug targets for Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 938–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordia, T.; Grady, S.R.; McIntosh, J.M.; Quik, M. Nigrostriatal damage preferentially decreases a subpopulation of alpha 6 beta 2* nAChRs in mouse, monkey, and Parkinson’s disease striatum. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 72, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, G.; Vijayaraghavan, S. Nicotinic receptors: Role in addiction and other disorders of the brain. Subst. Abus. Res. Treat. 2008, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.W.; Geyer, M.A. Evaluating the role of the alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, S.; Maskos, U. Role of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease pathology and treatment. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, D.; Terry, A.V. The wonderland of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 151, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, A.V.; Callahan, P.M. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligands, cognitive function, and preclinical approaches to drug discovery. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2019, 21, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, N.S. A review of experimental techniques used for the heterologous expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.B.; Ensign, B.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Guia, A.; Xu, J.Q. Ion-channel assay technologies: Quo vadis? Drug Discov. Today 2001, 6, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accardi, M.V.; Pugsley, M.K.; Forster, R.; Troncy, E.; Huang, H.; Authier, S. The emerging role of in vitro electrophysiological methods in CNS safety pharmacology. J. Pharm. Toxicol. Methods 2016, 81, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Long, T.; Pfalmer, D.L.; Andersen, T.L.; McDougaL, O.M. SPIDR: Small-molecule peptide-influenced drug repurposing. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.D.; Long, T.; Andersen, T.; McDougal, O.M. Genetic Algorithm Managed Peptide Mutant Screening: Optimizing peptide ligands for targeted receptor binding. K. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2016, 56, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.; McDougal, O.M.; Andersen, T. GAMPMS: Genetic algorithm managed peptide mutant screening. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, C.; Cornia, N.; Jacob, R.; Remm, A.; Peavey, T.; Weekes, K.; Mallory, C.; Oxford, J.T.; McDougal, O.M.; Andersen, T.L. DockoMatic 2.0: High throughput inverse virtual screening and homology modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.B.; Andersen, T.; McDougal, O.M. Accessible high-throughput virtual screening molecular docking software for students and educators. PloS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.B.; Bullock, C.W.; Andersen, T.; McDougal, O.M. DockoMatic: Automated peptide analog creation for high throughput virtual screening. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leffler, A.E.; Kuryatov, A.; Zebroski, H.A.; Powell, S.R.; Filipenko, P.; Hussein, A.K.; Gorson, J.; Heizmann, A.; Lyskov, S.; Tsien, R.W.; et al. Discovery of peptide ligands through docking and virtual screening at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor homology models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8100–E8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Ivanov, I.A.; Zhmak, M.N.; Shelukhina, I.V.; Spirova, E.N.; Tabakmakher, V.M.; Zelepuga, E.A.; Efremov, R.G.; et al. High-affinity alpha-conotoxin pnia analogs designed on the basis of the protein surface topography method. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
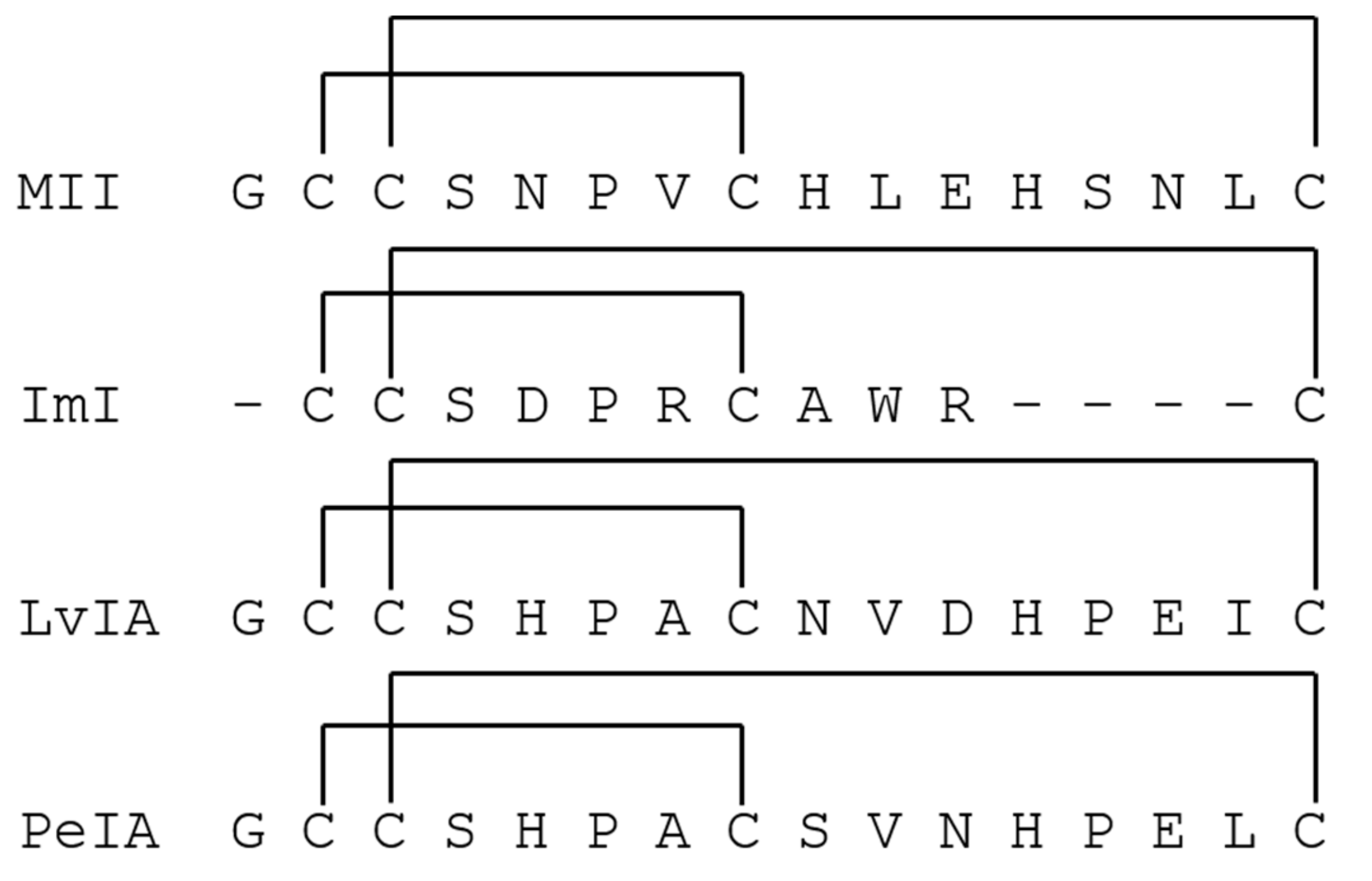
- Luo, S.L.; Zhangsun, D.T.; Schroeder, C.I.; Zhu, X.P.; Hu, Y.Y.; Wu, Y.; Weltzin, M.M.; Eberhard, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; et al. A novel alpha 4/7-conotoxin LvIA from Conus lividus that selectively blocks alpha 3 beta 2 vs. alpha 6/alpha 3 beta 2 beta 3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Faseb J. 2014, 28, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, A.; Blundell, T.L. Comparative protein modeling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 234, 779–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.L.; Kompella, S.N.; Adams, D.J.; Craik, D.J.; Kaas, Q. Determination of the alpha-Conotoxin Vc1.1 Binding Site on the alpha 9 alpha 10 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3557–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koromyslova, A.D.; Chugunov, A.O.; Efremov, R.G. Deciphering fine molecular details of proteins’ structure and function with a protein surface topography (PST) method. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuryatov, A.; Lindstrom, J. Expression of functional human alpha 6 beta 2 beta 3* acetylcholine receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes achieved through subunit chimeras and concatamers. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Drenan, R.M.; Mackey, E.D.W.; McIntosh, J.M.; Lester, H.A. Characterizing functional alpha 6 beta 2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in vitro: Mutant beta 2 subunits improve membrane expression, and fluorescent proteins reveal responsive cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, Y.; Talley, T.T.; Hansen, S.B.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P. Crystal structure of a Cbtx-AChBP complex reveals essential interactions between snake alpha-neurotoxins and nicotinic receptors. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celie, P.H.N.; Klaassen, R.V.; van Rossum-Fikkert, S.E.; van Elk, R.; van Nierop, P.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Crystal structure of acetylcholine-binding protein from Bulinus truncatus reveals the conserved structural scaffold and sites of variation in nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26457–26466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.B.; Sulzenbacher, G.; Huxford, T.; Marchot, P.; Taylor, P.; Bourne, Y. Structures of Aplysia AChBP complexes with nicotinic agonists and antagonists reveal distinctive binding interfaces and conformations. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3635–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombo, D.C.; Mazurov, A.A.; Strachan, J.P.; Bencherif, M. Computational studies of novel carbonyl-containing diazabicyclic ligands interacting with alpha 4 beta 2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) reveal alternative binding modes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5105–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkondon, M.; Albuquerque, E.X. Nicotinic receptor subtypes in rat hippocampal slices are differentially sensitive to desensitization and early in vivo functional up-regulation by nicotine and to block by bupropion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvin, M.C.; Wokosin, D.L.; Banala, S.; Lavis, L.D.; Drenan, R.M. Probing nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function in mouse brain slices via laser flash photolysis of photoactivatable nicotine. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, S.E.; Broderick, H.J.; Drenan, R.M. Local application of drugs to study nicotinic acetylcholine receptor function in mouse brain slices. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temburni, M.K.; Blitzblau, R.C.; Jacob, M.H. Receptor targeting and heterogeneity at interneuronal nicotinic cholinergic synapses in vivo. J. Physiol. Lond. 2000, 525, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimes, A.S.; Horti, A.G.; London, E.D.; Chefer, S.I.; Contoreggi, C.; Ernst, M.; Friello, P.; Koren, A.O.; Kurian, V.; Matochik, J.A.; et al. 2- F-18 F-A85380: PET imaging of brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and whole body distribution in humans. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1331–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malysz, J.; Gronlien, J.H.; Anderson, D.J.; Hakerud, M.; Thorin-Hagene, K.; Ween, H.; Wetterstrand, C.; Briggs, C.A.; Faghih, R.; Bunnelle, W.H.; et al. In vitro pharmacological characterization of a novel allosteric modulator of alpha 7 neuronal acetylcholine receptor, 4-(5-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-methyl-3-propionyl-1h-pyrrol-1-yl)benzenesulfonamide (a-867744), exhibiting unique pharmacological profile. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.W.; Marquart, L.A.; Phillips, P.D.; McDougal, O.M. Mutagenesis of alpha-conotoxins for enhancing activity and selectivity for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Toxins 2019, 11, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.C.; Kirsch, G.E.; Fedorov, N.B.; Wu, C.Y.; Kuryshev, Y.A.; Sewell, A.L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Motter, A.L.; Leggett, C.S.; Orr, M.S. High-throughput patch clamp screening in human alpha 6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Slas Discov. 2017, 22, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, J.; Bowlby, M.; Peri, R.; Vasilyev, D.; Arias, R. High-throughput electrophysiology: An emerging paradigm for ion-channel screening and physiology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.N.; Engle, S.E.; McIntosh, J.M.; Drenan, R.M. Alpha 6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in midbrain dopamine neurons are poised to govern dopamine-mediated behaviors and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 2015, 304, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
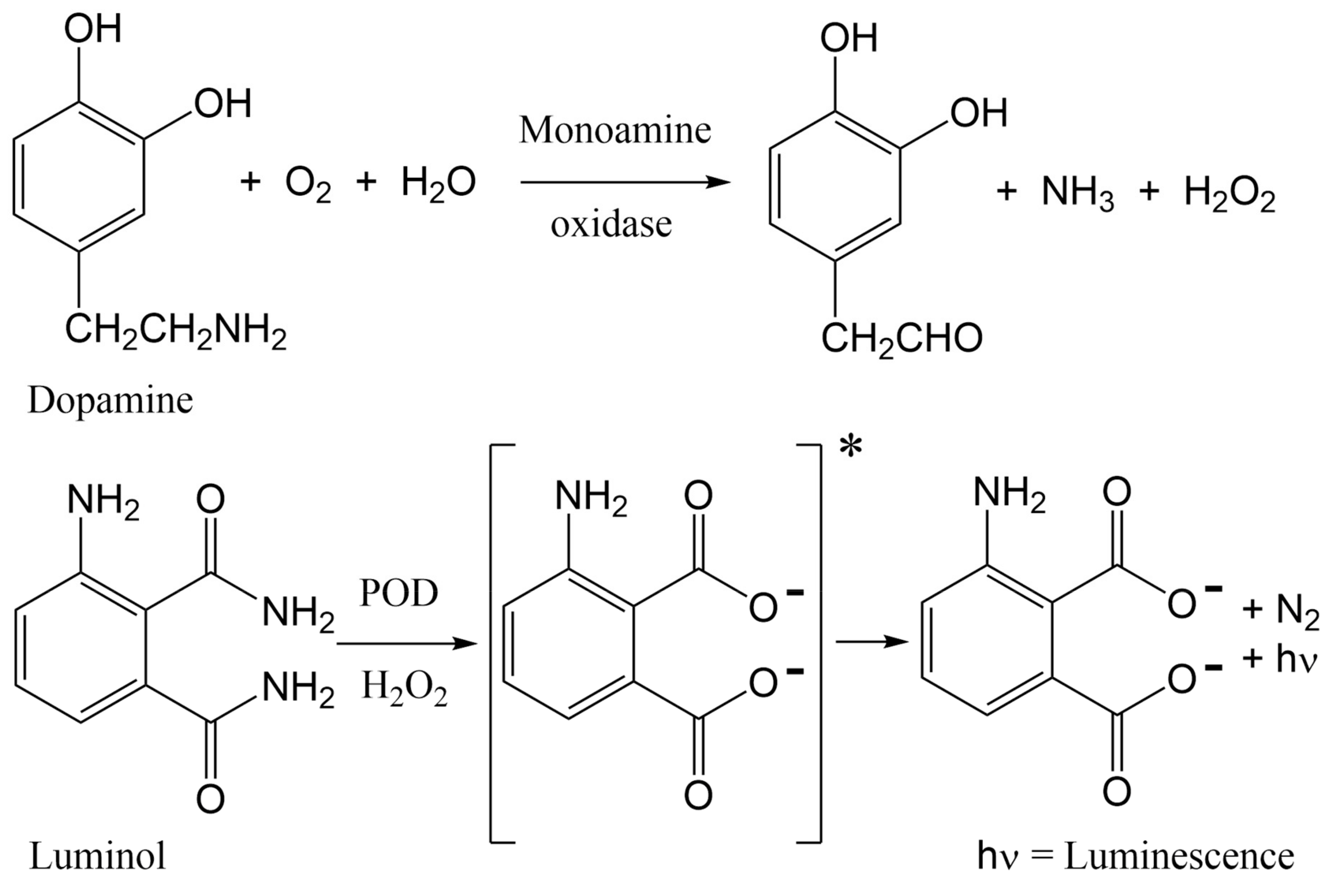
- Shinohara, H.; Wang, F.F.; Hossain, S.M.Z. A convenient, high-throughput method for enzyme-luminescence detection of dopamine released from PC12 cells. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.A.; Shinohara, H.; Shimizu, Y. Enzyme-luminescence method: Tool for evaluation of neuronal differentiation based on real-time monitoring of dopamine release response from PC12 cells. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.M.; Davila-Garcia, M.I.; Ascarrunz, V.S.; Xiao, Y.X.; Kellar, K.J. Differential regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in PC12 cells by nicotine and nerve growth factor (Reprinted from Soc Neurosci Abstr, vol 26, pg 373, 2000). Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabbani, N.; Nordman, J.C.; Corgiat, B.A.; Veltri, D.P.; Shehu, A.; Seymour, V.A.; Adams, D.J. Are nicotinic acetylcholine receptors coupled to G proteins? Bioessays 2013, 35, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordman, J.C.; Kabbani, N. An interaction between 7 nicotinic receptors and a G-protein pathway complex regulates neurite growth in neural cells. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5502–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, D.; Ciruela, F.; Patkar, K.; Borycz, J.; Solinas, M.; Lluis, C.; Franco, R.; Wise, R.A.; Goldberg, S.R.; Hope, B.T.; et al. Heteromeric nicotinic acetylcholine-dopamine autoreceptor complexes modulate striatal dopamine release. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Nordman, J.C.; Bridges, S.P.; Lin, M.K.; Kabbani, N. Identification and Characterization of a G Protein-binding Cluster in α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 20060–20070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, A.A.; Resende, R.R.; Martins, A.H.; Trujillo, C.A.; Eterovic, V.A.; Ulrich, H. Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Expression and Activity During Neuronal Differentiation of PC12 Pheochromocytoma Cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2010, 41, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.P.; Gdovin, M.J.; Liu, C.L.; Gardner, P.D.; Maue, R.A. Nerve Growth-Factor Increases Nicotinic ACh Receptor Gene-Expression and Current-Density in Wild-Type and Protein-Kinase A-Deficient PC12 Cells. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, K.; Teng, Y.F.; Pan, Y.P.; Dani, J.A.; Lindstrom, J.; Gras, E.A.G.; McIntosh, J.M.; De Biasi, M. UBXD4, a UBX-Containing Protein, Regulates the Cell Surface Number and Stability of alpha 3-Containing Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 6883–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, G.E.; Yoshikami, D.J.; Gray, W.R.; Luo, S.Q.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. A new alpha-conotoxin which targets alpha 3 beta 2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7522–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Azam, L.; Staheli, S.; Dowell, C.; Lindstrom, J.M.; Kuryatov, A.; Garrett, J.E.; Marks, M.J.; Whiteaker, P. Analogs of alpha-conotoxin MII are selective for alpha 6-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, S.C.; McIntosh, J.M.; Cartier, G.E.; Maddox, F.N.; Luetje, C.W. Determinants of specificity for alpha-conotoxin MII on alpha 3 beta 2 neuronal nicotinic receptors. Mol. Pharm. 1997, 51, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.S.; Martinez, J.; Elgoyhen, A.B.; Heinemann, S.F.; McIntosh, J.M. Alpha-conotoxin Im(I) exhibits subtype-specific nicotinic acetylcholine-receptor blockade-preferential inhibition of homomeric alpha-7 and alpha-9 receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hone, A.J.; Scadden, M.; Gajewiak, J.; Christensen, S.; Lindstrom, J.; McIntosh, J.M. Alpha-conotoxin PeIA S9H,V10A,E14N potently and selectively blocks alpha 6 beta 2 beta 3 versus alpha 6 beta 4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.W.; Mandelzys, A.; Deneris, E.S.; Cooper, E.; Heinemann, S. The expression of nicotinic acetylcholine-receptors by PC12 cells treated with NGF. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 4611–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohrman, D.P.; Reiter, C.K. Chronic ethanol reduces nicotine-induced dopamine release in PC12 cells. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, H.; Govind, A.P.; Mastro, R.; Hoda, J.C.; Bertrand, D.; Vallejo, Y.; Green, W.N. Up-regulation of nicotinic receptors by nicotine varies with receptor subtype. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 6022–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.T.; Harkness, P.C.; Baker, E.R.; Millar, N.S. Up-regulation of cell-surface alpha 4 beta 2 neuronal nicotinic receptors by lower temperature and expression of chimeric subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 27145–27152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, R.J. Effects of chronic nicotinic ligand exposure on functional-activity of nicotinic acetylcholine-receptors expressed by cells of the PC12 rat pheochromocytoma or the Te671/Rd human clonal line. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, R.H.S.; Ewing, A.G. The PC12 cell as model for neurosecretion. Acta Physiol. 2008, 192, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
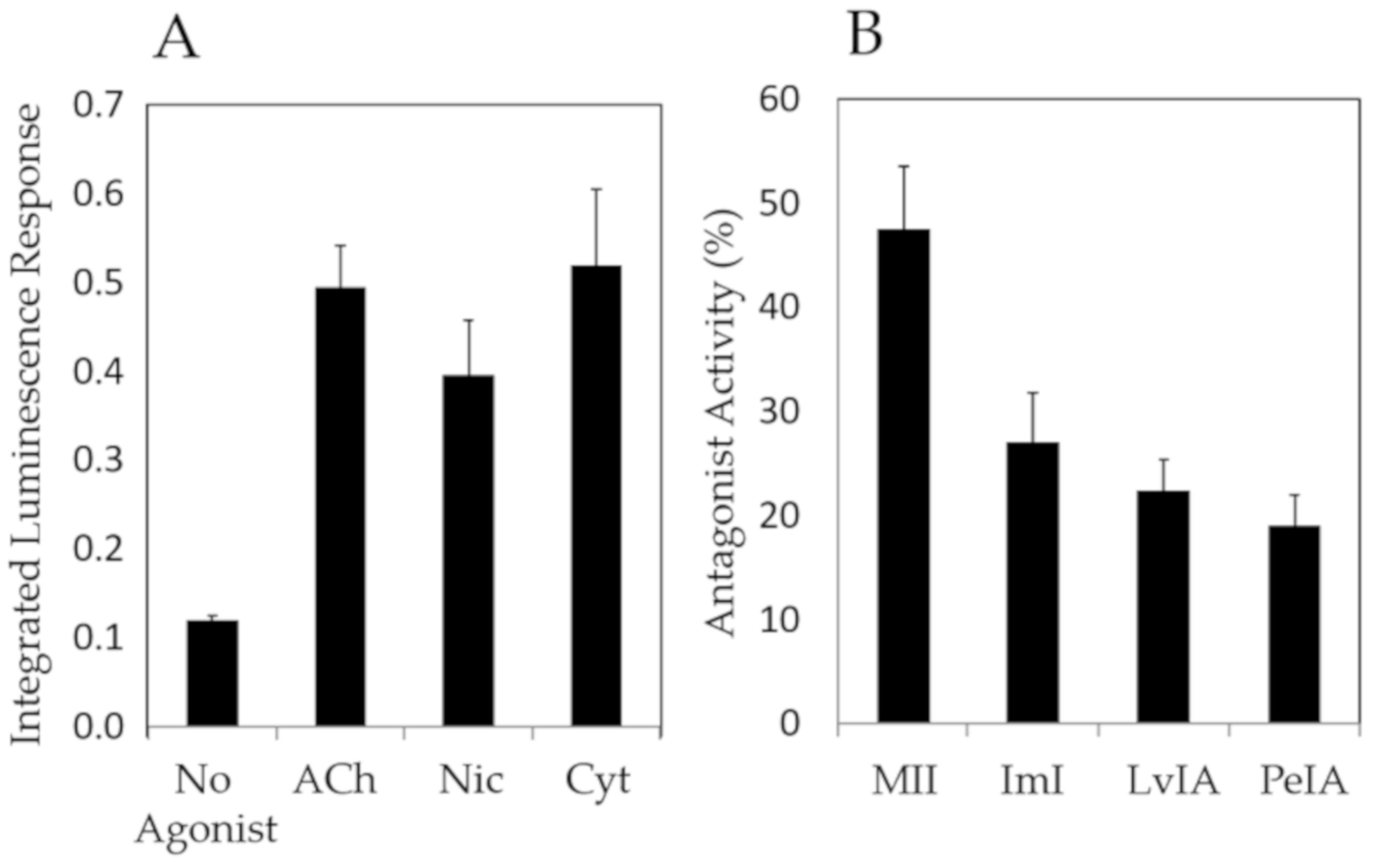
| Agonist | EC50 | Emax |
|---|---|---|
| Acetylcholine | 118 ± 23 | 307 ± 24 |
| Nicotine | 33 ± 1.5 | 232 ± 23 |
| Cytisine | 42 ± 8.6 | 256 ± 21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marquart, L.A.; Turner, M.W.; McDougal, O.M. Qualitative Assay to Detect Dopamine Release by Ligand Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2019, 11, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120682
Marquart LA, Turner MW, McDougal OM. Qualitative Assay to Detect Dopamine Release by Ligand Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):682. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarquart, Leanna A., Matthew W. Turner, and Owen M. McDougal. 2019. "Qualitative Assay to Detect Dopamine Release by Ligand Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors" Toxins 11, no. 12: 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120682
APA StyleMarquart, L. A., Turner, M. W., & McDougal, O. M. (2019). Qualitative Assay to Detect Dopamine Release by Ligand Action on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins, 11(12), 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120682