Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC–MS/MS Platform
Abstract
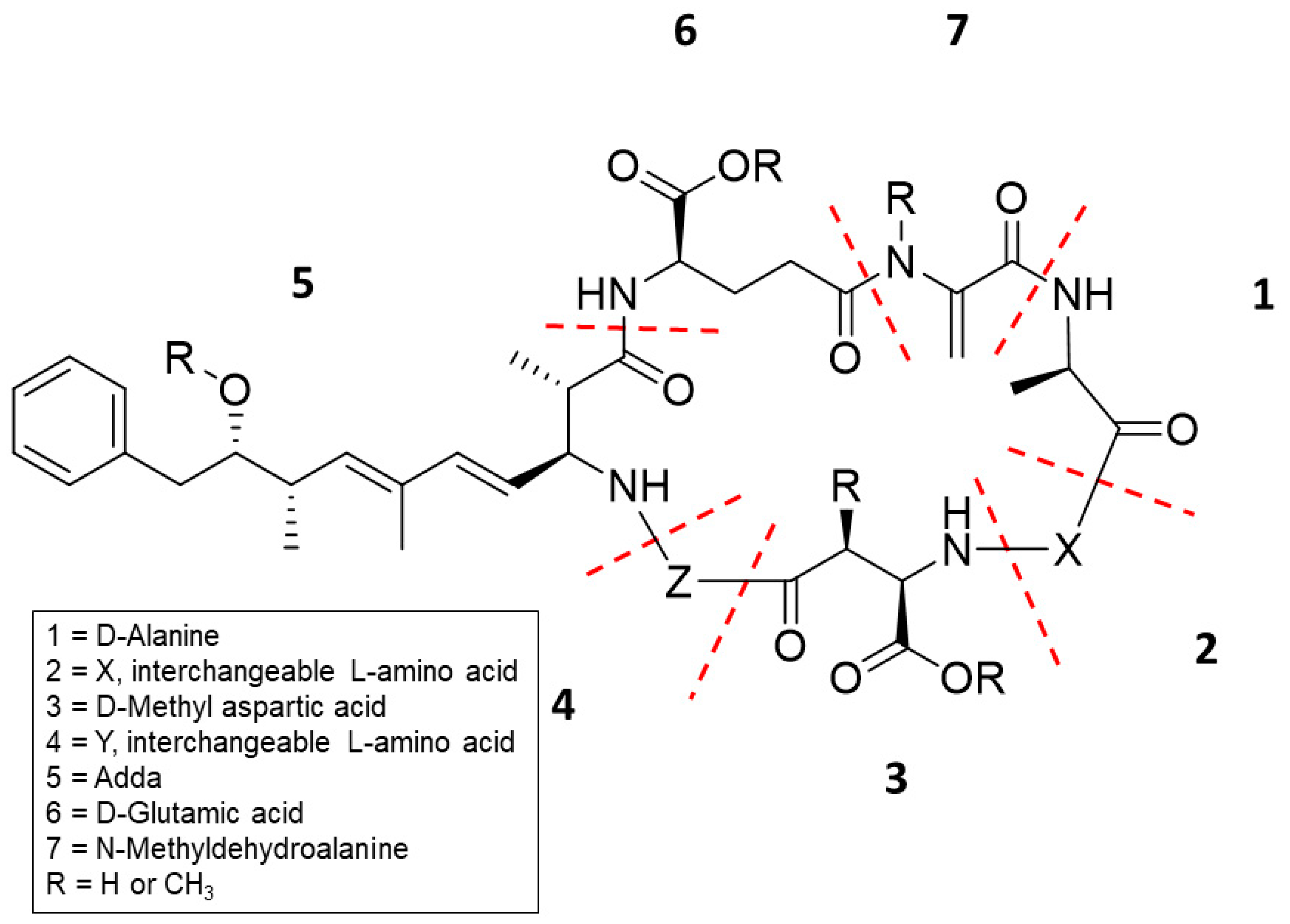
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LC–MS/MS and Adda-ELISA Quantitation
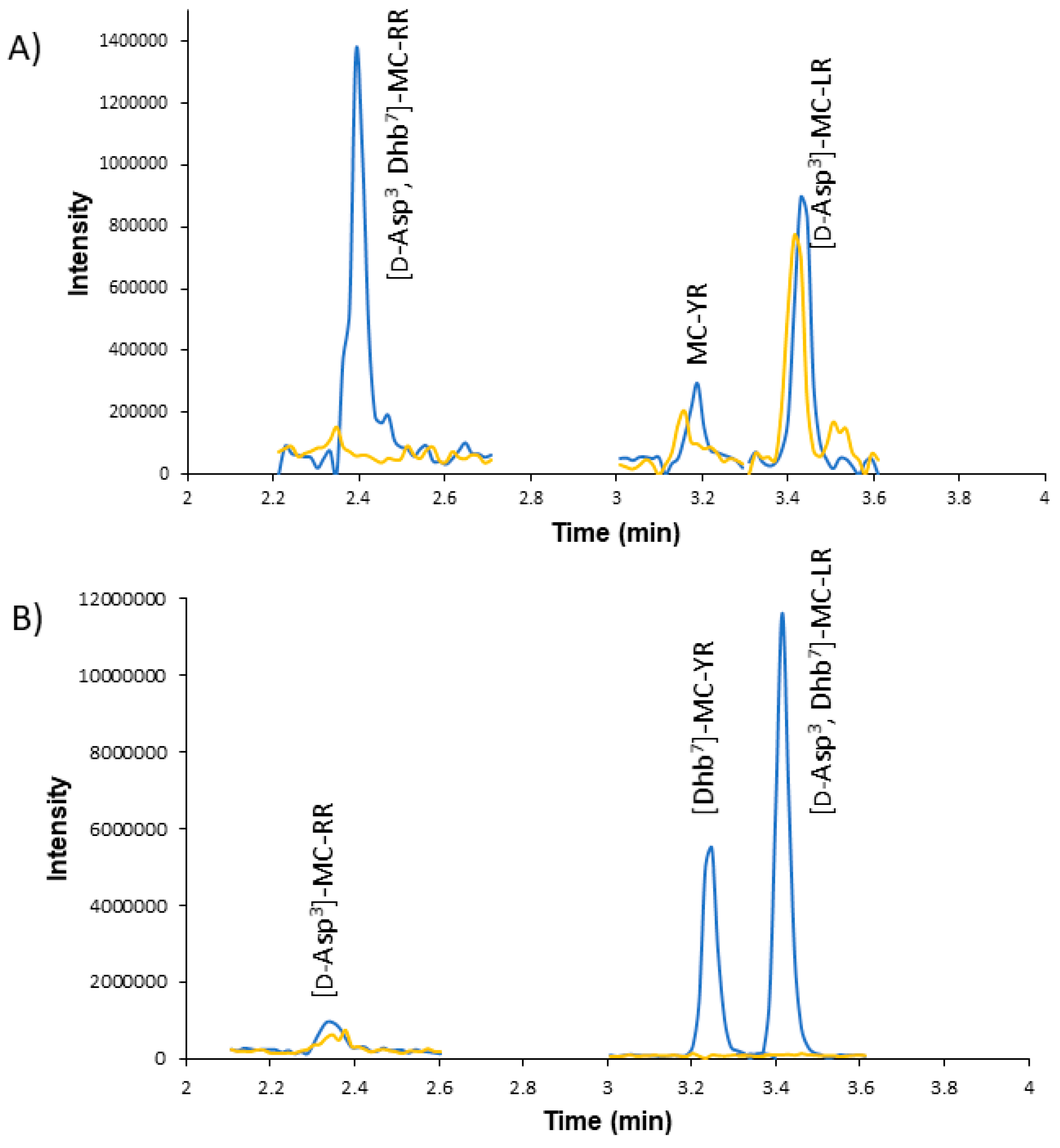
2.2. Using HRMS to Verify MC Isomers
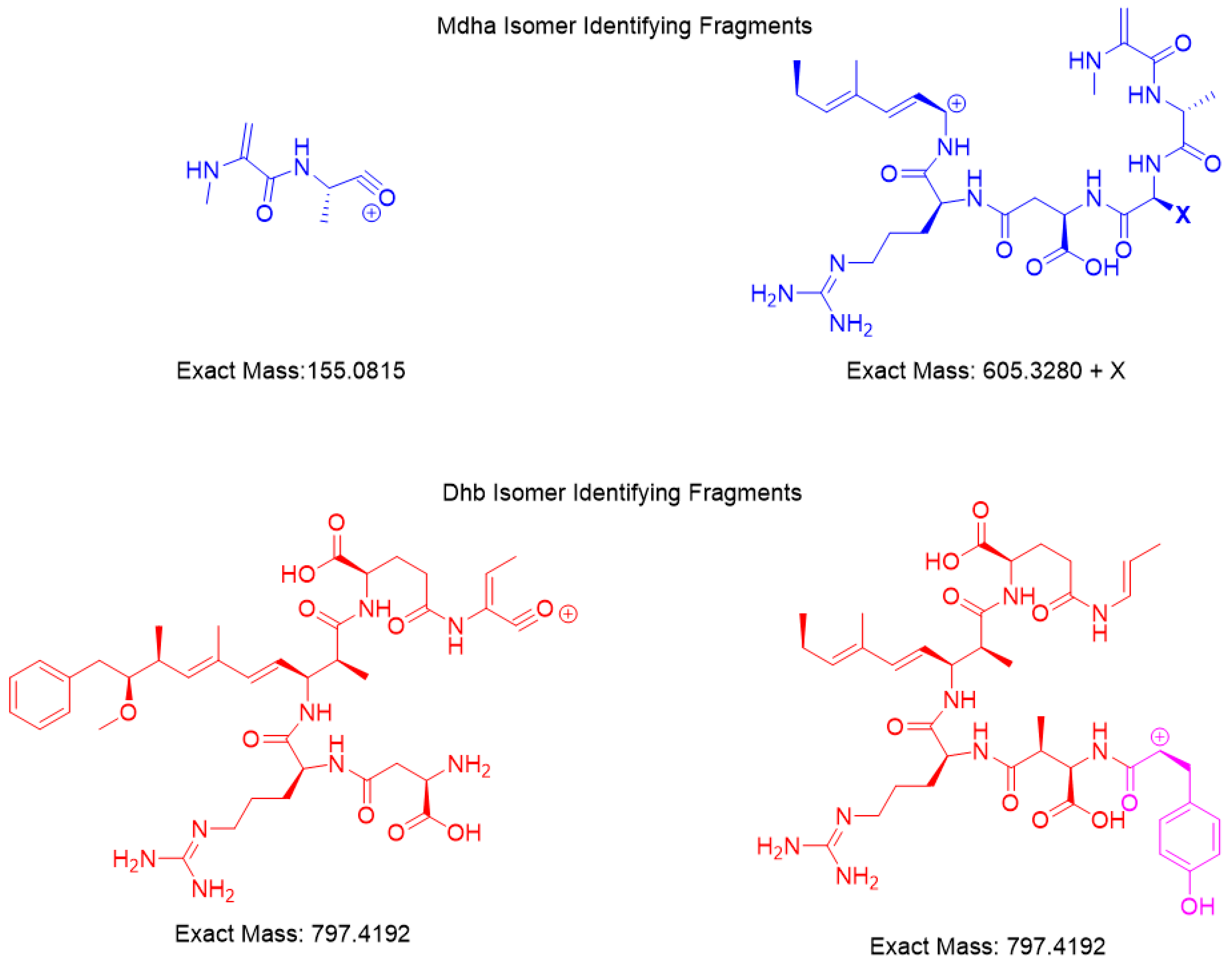
2.3. Chemical Derivatization and HRMS Fragmentation to Identify Untargeted MCs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Reagents
5.2. Sample Collection
5.3. ELISA
5.4. Online Concentration Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
5.5. High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
5.6. Solid-Phase Extraction
5.7. Fractionation of SPE Concentrated Samples by HPLC-PDA
5.8. Chemical Derivatization of MCs
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lad, A.; Su, R.C.; Breidenbach, J.D.; Stemmer, P.M.; Carruthers, N.J.; Sanchez, N.K.; Khalaf, F.K.; Zhang, S.; Kleinhenz, A.L.; Dube, P. Chronic Low Dose Oral Exposure to Microcystin-LR Exacerbates Hepatic Injury in a Murine Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Toxins 2019, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherine, A.; Bernard, C.; Spoof, L.; Bruno, M. Chapter 11: Microcystins and Nodularins; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2017; pp. 109–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, M.; Foss, A.J.; Miles, C.O.; Ozen, M.; Demir, N.; Balci, M.; Beach, D.G. Comprehensive multi-technique approach reveals the high diversity of microcystins in field collections and an associated isolate of Microcystis aeruginosa from a Turkish lake. Toxicon 2019, 167, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Wu, S.; Wahome, P.G.; Bertin, M.J.; Pedone, A.C.; Beauchesne, K.R.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Carter, G.T. Microcystins Containing Doubly Homologated Tyrosine Residues from a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom: Structures and Cytotoxicity. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citriglia, M.E.; Agrawal, S.E.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Read, R.; Schordock, D.C.; Westrick, J.A.; Birbeck, J.A. Evaluation and Optimization of Microcystin Analytical Methods; WRF 4647; The Water Research Foundation, July 2019; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, W.J.; Garthwaite, I.; Miles, C.O.; Ross, K.M.; Aggen, J.B.; Chamberlin, A.R.; Towers, N.R.; Dietrich, D.R. Congener-independent immunoassay for microcystins and nodularins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4849–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thees, A.; Atari, E.; Birbeck, J.; Westrick, J.A.; Huntley, J.F. Isolation and characterization of lake erie bacteria that degrade the cyanobacterial microcystin toxin MC-LR. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.B.; Lee, A.K.; Yates, R.S.; Liang, S.; Rochelle, P.A. Analysis of Microcystins in Drinking Water by ELISA and LC/MS/MS. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2017, 109, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlag, D.C.; Spies, B.; Szlag, R.G.; Westrick, J.A. Permanganate Oxidation of Microcystin-LA: Kinetics, Quantification, and Implications for Effective Drinking Water Treatment. J. Toxicol. 2019, 2019, 3231473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Stanford, B.D.; Adams, C.; Rosenfeldt, E.J.; Wert, E.C. Varied influence of microcystin structural difference on ELISA cross-reactivity and chlorination efficiency of congener mixtures. Water Res. 2017, 126, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Glukhov, E.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Combined LC-MS/MS and Molecular Networking Approach Reveals New Cyanotoxins from the 2014 Cyanobacterial Bloom in Green Lake, Seattle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14301–14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, P.I.; Vinay Kumar, M.C.; Pan, D.; Swarup, S. A mass spectrometry-based unique fragment approach for the identification of microcystins. Analyst 2015, 140, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namikoshi, M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Sakai, R.; Stotts, R.R.; Dahlem, A.M.; Beasley, V.R.; Carmichael, W.W.; Evans, W.R. Identification of 12 Hepatotoxins from a Homer Lake Bloom of the Cyanobacteria Microcystis-Aeruginosa, Microcystis-Viridis, and Microcystis-Wesenbergii - 9 New Microcystins. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Sandvik, M.; Nonga, H.E.; Rundberget, T.; Wilkins, A.L.; Rise, F.; Ballot, A. Thiol Derivatization for LC-MS Identification of Microcystins in Complex Matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8937–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouhaddada, R.; Nelieu, S.; Nasri, H.; Delarue, G.; Bouaicha, N. High diversity of microcystins in a Microcystis bloom from an Algerian lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Namikoshi, M.; Brittain, S.M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Murphy, T. [D-Leu(1)] microcystin-LR, a new microcystin isoplated from waterbloom in a Canadian prairie lake. Toxicon 2001, 39, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Hilborn, E.D. Microcystin analysis in human sera and liver from human fatalities in Caruaru, Brazil 1996. Toxicon 2006, 48, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Namikoshi, M.; Otsuki, A.; Rinehart, K.L.; Sivonen, K.; Watanabe, M.F. Low-energy collisionally activated decomposition and structural characterization of cyclic heptapeptide microcystins by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Mass. Spectrom. 1999, 34, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Sano, T.; Inoue, H.; Takagi, H. Selective determination of total normal microcystin by colorimetry, LC/UV detection and/or LC/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 450, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.O.; Sandvik, M.; Haande, S.; Nonga, H.; Ballot, A. LC-MS Analysis with Thiol Derivatization to Differentiate [Dhb(7)]- from [Mdha(7)]-Microcystins: Analysis of Cyanobacterial Blooms, Planktothrix Cultures and European Crayfish from Lake Steinsfjorden, Norway. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, J.A.; Tettenhorst, D.R.; de la Cruz, A. Method 544: Determination of Microcystins and Nodularin in Drinking Water by Solid Phase Extraction and Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS); U.S. EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency), National Exposure Research Laboratory: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2015; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Luukkainen, R.; Sivonen, K.; Namikoshi, M.; Fardig, M.; Rinehart, K.L.; Niemela, S.I. Isolation and identification of eight microcystins from thirteen Oscillatoria agardhii strains and structure of a new microcystin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar]
- Keil, C.; Forchert, A.; Fastner, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Rotard, W.; Chorus, I.; Kratke, R. Toxicity and microcystin content of extracts from a Planktothrix bloom and two laboratory strains. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2133–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fastner, J.; Erhard, M.; Carmichael, W.W.; Sun, F.; Rinehart, K.L.; Ronicke, H.; Chorus, I. Characterization and diversity of microcystins in natural blooms and strains of the genera Microcystis and Planktothrix from German freshwaters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1999, 145, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Mountfort, D.; Selwood, A.I.; Holland, P.T.; Puddick, J.; Cary, S.C. Widespread Distribution and Identification of Eight Novel Microcystins in Antarctic Cyanobacterial Mats. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2008, 74, 7243–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dawson, R.M. The toxicology of microcystins. Toxicon 1998, 36, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeger, S.J.; Schmid, D.; Blom, J.F.; Ernst, B.; Dietrich, D.R. Analytical and functional characterization of microcystins [Asp3]MC-RR and [Asp3,Dhb7]MC-RR: Consequences for risk assessment? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftin, K.A.; Graham, J.L.; Hilborn, E.D.; Lehmann, S.C.; Meyer, M.T.; Dietze, J.E.; Griffith, C.B. Cyanotoxins in inland lakes of the United States: Occurrence and potential recreational health risks in the EPA National Lakes Assessment 2007. Harmful Algae 2016, 56, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaver, J.R.; Tausz, C.E.; Scotese, K.C.; Pollard, A.I.; Mitchell, R.M. Environmental factors influencing the quantitative distribution of microcystin and common potentially toxigenic cyanobacteria in U.S. lakes and reservoirs. Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermeyer, T.H.; Daily, A.; Swiatecka-Hagenbruch, M.; Moscow, J.A. Selectivity and potency of microcystin congeners against OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 expressing cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, X.; Korenkova, E.; Jobst, K.J.; MacPherson, K.A.; Reiner, E.J. A high throughput targeted and non-targeted method for the analysis of microcystins and anatoxin-A using on-line solid phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight high resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4959–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbeck, J.A.; Westrick, J.A.; O’Neill, G.M.; Spies, B.; Szlag, D.C. Comparative Analysis of Microcystin Prevalence in Michigan Lakes by Online Concentration LC/MS/MS and ELISA. Toxins 2019, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, T.; Imamura, S.; Sano, T.; Nakashima, J.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yoshimoto, M.; Yasumoto, T. The effect of structural variation in 21 microcystins on their inhibition of PP2A and the effect of replacing cys269 with glycine. Toxicon 2009, 54, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, K.; Sano, T. A photodetoxification mechanism of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR by ultraviolet irradiation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1998, 11, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, K.; Ogawa, K.; Kimura, Y.; Murata, H.; Suzuki, M.; Thorn, P.M.; Evans, W.R.; Carmichael, W.W. Microcystins from Anabaena-Flos-Aquae Nrc-525-17. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1991, 4, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, J.F.; Robinson, J.A.; Juttner, F. High grazer toxicity of [D-Asp(3) (E)-Dhb(7)]microcystin-RR of Planktothrix rubescens as compared to different microcystins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.F.; Baumann, H.I.; Codd, G.A.; Juttner, F. Sensitivity and adaptation of aquatic organisms to oscillapeptin J and [D-Asp(3),(E)-Dhb(7)]microcystin-RR. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2006, 167, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, C.; Penuela, G.A. Detected cyanotoxins by UHPLC MS/MS technique in tropical reservoirs of northeastern Colombia. Toxicon 2019, 167, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, P.B.; Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Duy, S.V.; Prévost, M.; Sauvé, S. On-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of cyanotoxins in algal blooms. Toxicon 2015, 108, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, A.J.; Aubel, M.T. Using the MMPB technique to confirm microcystin concentrations in water measured by ELISA and HPLC (UV, MS, MS/MS). Toxicon 2015, 104, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Boyer, G.L. Standardization of microcystin extraction from fish tissues: A novel internal standard as a surrogate for polar and non-polar variants. Toxicon 2009, 53, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Analyte | Standard Ion Ratio (%) | Sample Ion Ratio (%) | Standard Retention Time (min) | Sample Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [d-Asp3]-MC-RR | 12 | 14 | 2.56 | 2.50 |
| MC-YR | 68 | 28 | 3.34 | 3.40 |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-LR | 63 | 26 | 3.60 | 3.59 |
| MC-LY | 75 | 84 | 4.64 | 4.64 |
| Standard Analyte | Calculated Mass (m/z) | Found Mass (m/z) | Charge | Δ ppm |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-RR | 512.7824 | 512.7816 | 2 | −1.5 |
| MC-YR | 523.2713 | 523.2715 | 2 | 0.4 |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-LR | 491.2738 | 491.2738 | 2 | 0 |
| Sample Analyte | Calculated Mass (m/z) | Found Mass (m/z) | Charge | Δ ppm |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-RR | 512.7824 | 512.7825 | 2 | 0.2 |
| MC-YR | 523.2713 | 523.2717 | 2 | 0.8 |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-LR | 491.2738 | 491.2740 | 2 | 0.4 |
| Analyte | Quantifier Ion (m/z) | Qualifier Ion (m/z) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [d-Asp3]-MC-RR | 135.07 | 498.91 | 2.56 |
| MC-RR | 135.07 | 212.97 | 2.65 |
| Nodularin | 135.00 | 389.16 | 3.04 |
| MC-YR | 135.00 | 213.03 | 3.34 |
| MC-HtyR | 135.05 | 1031.46 | 3.44 |
| MC-LR | 135.07 | 155.08 | 3.56 |
| [d-Asp3]-MC-LR | 135.01 | 213.07 | 3.60 |
| MC-HilR | 135.00 | 155.08 | 3.82 |
| MC-WR | 135.03 | 626.25 | 3.93 |
| MC-LA | 776.41 | 372.16 | 4.44 |
| MC-LY | 868.42 | 494.18 | 4.64 |
| MC-LW | 517.18 | 446.17 | 5.35 |
| MC-LF | 852.41 | 478.17 | 5.49 |
| C2D5 MC-LR | 135.09 | 163.08 | 4.64 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Birbeck, J.A.; Peraino, N.J.; O’Neill, G.M.; Coady, J.; Westrick, J.A. Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC–MS/MS Platform. Toxins 2019, 11, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110653
Birbeck JA, Peraino NJ, O’Neill GM, Coady J, Westrick JA. Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC–MS/MS Platform. Toxins. 2019; 11(11):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110653
Chicago/Turabian StyleBirbeck, Johnna A., Nicholas J. Peraino, Grace M. O’Neill, Julia Coady, and Judy A. Westrick. 2019. "Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC–MS/MS Platform" Toxins 11, no. 11: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110653
APA StyleBirbeck, J. A., Peraino, N. J., O’Neill, G. M., Coady, J., & Westrick, J. A. (2019). Dhb Microcystins Discovered in USA Using an Online Concentration LC–MS/MS Platform. Toxins, 11(11), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11110653





