Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin—Evidence from Human Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clinical Evidence
3. Neurophysiological Evidence
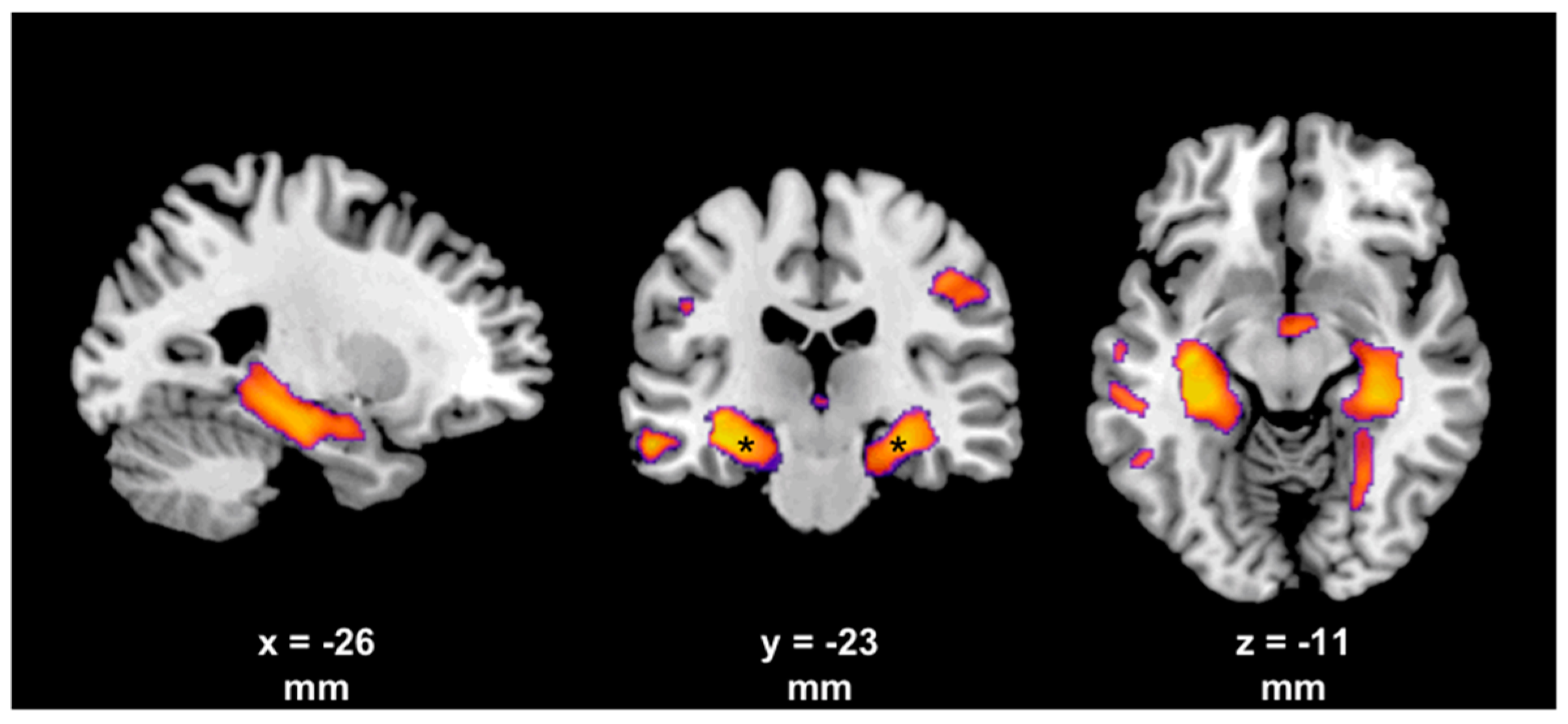
4. Evidence from Neuroimaging
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, P.; Naumann, M. (Eds.) Handbook of Botulinum Toxin Treatment, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Malden, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Currà, A.; Berardelli, A. Do the unintended actions of botulinum toxin at distant sites have clinical implications? Neurology 2009, 72, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montecucco, C.; Schiavo, G. Mechanism of action of tetanus and botulinum neurotoxins. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, E.; Erdmann, G. Pharmacokinetic and histoautoradiographic evidence for the intraaxonal movement of toxin in the pathogenesis of tetanus. Toxicon 1978, 16, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, H.; Erdmann, G.; Wellhöner, H.H. 125I-labelled botulinum A neurotoxin: Pharmacokinetics in cats after intramuscular injection. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1976, 292, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, H.; Wellhöner, H.H. The action of botulinum A neurotoxin on the inhibition by antidromic stimulation of the lumbar monosynaptic reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1977, 298, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, F.; Rossi, C.; Gianfranceschi, L.; Rossetto, O.; Caleo, M. Long-distance retrograde effects of botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3689–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomba-Warczak, E.; Vevea, J.D.; Brittain, J.M.; Figueroa-Bernier, A.; Tepp, W.H.; Johnson, E.A.; Yeh, F.L.; Chapman, E.R. Interneuronal Transfer and Distal Action of Tetanus Toxin and Botulinum Neurotoxins A and D in Central Neurons. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1974–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, N.; Shin, M.-C.; Wakita, M.; Torii, Y.; Harakawa, T.; Ginnaga, A.; Kato, K.; Kaji, R.; Kozaki, S. Transsynaptic inhibition of spinal transmission by A2 botulinum toxin. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, B.I. Botulinum toxin physiology in focal hand and cranial dystonia. Toxins 2012, 4, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.G.; Hallett, M.; Geller, B.D.; Hochberg, F. Treatment of focal dystonias of the hand with botulinum toxin injections. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1989, 52, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamjian, J.A.; Walker, F.O. Serial neurophysiological studies of intramuscular botulinum-A toxin in humans. Muscle Nerve 1994, 17, 1385–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchio, R.; Caleo, M. More than at the neuromuscular synapse: Actions of botulinum neurotoxin A in the central nervous system. Neuroscientist 2015, 21, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.J. Botulinum toxin in muscle spasticity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, A.; Berardelli, A.; Mercuri, B.; Manfredi, M. Physiological effects produced by botulinum toxin treatment of upper limb dystonia. Changes in reciprocal inhibition between forearm muscles. Brain 1995, 118 Pt 3, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. Mechanism of action of botulinum neurotoxin: Unexpected consequences. Toxicon 2018, 147, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner-Stokes, L.; Ashford, S. Serial injection of botulinum toxin for muscle imbalance due to regional spasticity in the upper limb. Disabil. Rehabil. 2007, 29, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquenazi, A.; Mayer, N.; Garreta, R. Influence of botulinum toxin type A treatment of elbow flexor spasticity on hemiparetic gait. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 87, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdal, J.; Ostergaard, L.; Fuglsang-Frederiksen, A.; Werdelin, L.; Dalager, T.; Sjö, O.; Regeur, L. Long-term botulinum toxin treatment of cervical dystonia—EMG changes in injected and noninjected muscles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girlanda, P.; Quartarone, A.; Sinicropi, S.; Nicolosi, C.; Messina, C. Unilateral injection of botulinum toxin in blepharospasm: Single fiber electromyography and blink reflex study. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, D.J.; Brin, M.F.; Warner, C.L.; Fahn, S.; Lovelace, R.E. Distant effects of local injection of botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 1987, 10, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miscio, G.; Del Conte, C.; Pianca, D.; Colombo, R.; Panizza, M.; Schieppati, M.; Pisano, F. Botulinum toxin in post-stroke patients: Stiffness modifications and clinical implications. J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinti, M.; Costantino, F.; Bayle, N.; Simpson, D.M.; Weisz, D.J.; Gracies, J.-M. Spastic cocontraction in hemiparesis: Effects of botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 2012, 46, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cioncoloni, D.; Taddei, S.; Bielli, S.; Annunziata, P.; Mazzocchio, R. Meaningful improvement in walking performance after Botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT-A) in chronic spastic patients. NeuroRehabilitation 2014, 34, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Relja, M.; Miletić, V. When movement disorders hurt: Addressing pain in hyperkinetic disorders. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 44, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, P.D.; Adler, C.H.; Stacy, M.; Comella, C.; Jankovic, J.; Manack Adams, A.; Schwartz, M.; Brin, M.F. Cervical dystonia and pain: Characteristics and treatment patterns from CD PROBE (Cervical Dystonia Patient Registry for Observation of OnabotulinumtoxinA Efficacy). J. Neurol. 2014, 261, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, C.H.F.; Cattai, L.; Teive, H.A.G. Pain Relief in Cervical Dystonia with Botulinum Toxin Treatment. Toxins 2015, 7, 2321–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, D.; Gentner, R.; Zeller, D.; Nagel, A.; Reinsberger, C.; Rumpf, J.-J.; Classen, J. Focal hand dystonia: Lack of evidence for abnormality of motor representation at rest. Neurology 2012, 78, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, R.; Hutchinson, M. Molding the sensory cortex: Spatial acuity improves after botulinum toxin treatment for cervical dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trompetto, C.; Currà, A.; Buccolieri, A.; Suppa, A.; Abbruzzese, G.; Berardelli, A. Botulinum toxin changes intrafusal feedback in dystonia: A study with the tonic vibration reflex. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfarth, K.; Schubert, M.; Rothe, B.; Elek, J.; Dengler, R. Remote F-wave changes after local botulinum toxin application. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand-Pauvert, V.; Aymard, C.; Giboin, L.-S.; Dominici, F.; Rossi, A.; Mazzocchio, R. Beyond muscular effects: Depression of spinal recurrent inhibition after botulinum neurotoxin A. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, A.; Fabbrini, G.; Belvisi, D.; Marsili, L.; Di Stasio, F.; Berardelli, A. Electrical activation of the orbicularis oculi muscle does not increase the effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A in patients with blepharospasm. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls-Sole, J.; Tolosa, E.S.; Ribera, G. Neurophysiological observations on the effects of botulinum toxin treatment in patients with dystonic blepharospasm. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1991, 54, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ce, P. Central effects of botulinum toxin: Study of brainstem auditory evoked potentials. Eur. J. Neurol. 2000, 7, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielamowicz, S.; Ludlow, C.L. Effects of botulinum toxin on pathophysiology in spasmodic dysphonia. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2000, 109, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.B.; Evinger, C. Long-term potentiation of the human blink reflex. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartarone, A.; Sant’Angelo, A.; Battaglia, F.; Bagnato, S.; Rizzo, V.; Morgante, F.; Rothwell, J.C.; Siebner, H.R.; Girlanda, P. Enhanced long-term potentiation-like plasticity of the trigeminal blink reflex circuit in blepharospasm. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuner, K.E.; Knutzen, A.; Al-Ali, A.; Hallett, M.; Deuschl, G.; Bergmann, T.O.; Siebner, H.R. Associative stimulation of the supraorbital nerve fails to induce timing-specific plasticity in the human blink reflex. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frascarelli, F.; Di Rosa, G.; Bisozzi, E.; Castelli, E.; Santilli, V. Neurophysiological changes induced by the botulinum toxin type A injection in children with cerebral palsy. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. EJPN 2011, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Park, C.I.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, Y.R. The effect of spasticity on cortical somatosensory-evoked potentials: Changes of cortical somatosensory-evoked potentials after botulinum toxin type A injection. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1592–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contarino, M.F.; Kruisdijk, J.J.M.; Koster, L.; de Visser, B.W.O.; Speelman, J.D.; Koelman, J.H.T.M. Sensory integration in writer’s cramp: Comparison with controls and evaluation of botulinum toxin effect. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2195–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanovský, P.; Streitová, H.; Dufek, J.; Znojil, V.; Daniel, P.; Rektor, I. Change in lateralization of the P22/N30 cortical component of median nerve somatosensory evoked potentials in patients with cervical dystonia after successful treatment with botulinum toxin A. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilio, F.; Currà, A.; Lorenzano, C.; Modugno, N.; Manfredi, M.; Berardelli, A. Effects of botulinum toxin type A on intracortical inhibition in patients with dystonia. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, N.; de Oliva Fonte-Boa, P.M.; Tomaz, C.A.B.; Brasil-Neto, J.P. Lack of effect of botulinum toxin on cortical excitability in patients with cranial dystonia. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2005, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroojerdi, B.; Cohen, L.G.; Hallett, M. Effects of botulinum toxin on motor system excitability in patients with writer’s cramp. Neurology 2003, 61, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumann, M.; Reiners, K. Long-latency reflexes of hand muscles in idiopathic focal dystonia and their modification by botulinum toxin. Brain 1997, 120 Pt 3, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomar, F.J.; Mir, P. Neurophysiological changes after intramuscular injection of botulinum toxin. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, K.; Kunesch, E.; Cohen, L.G.; Benecke, R.; Classen, J. Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain 2000, 123 Pt 3, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, D.; Schramm, A.; Stefan, K.; Wolters, A.; Reiners, K.; Naumann, M.; Classen, J. The two sides of associative plasticity in writer’s cramp. Brain 2006, 129, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weise, D.; Schramm, A.; Beck, M.; Reiners, K.; Classen, J. Loss of topographic specificity of LTD-like plasticity is a trait marker in focal dystonia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojovic, M.; Caronni, A.; Bologna, M.; Rothwell, J.C.; Bhatia, K.P.; Edwards, M.J. Botulinum toxin injections reduce associative plasticity in patients with primary dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, M.L.; Thickbroom, G.W.; Wilson, S.A.; Sacco, P.; Shipman, J.M.; Stell, R.; Mastaglia, F.L. The corticomotor representation of upper limb muscles in writer’s cramp and changes following botulinum toxin injection. Brain 1998, 121 Pt 5, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, M.L.; Mastaglia, F.L.; Walters, S.E.; Archer, S.-A.R.; Thickbroom, G.W. Primary writing tremor: Motor cortex reorganisation and disinhibition. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2005, 12, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thickbroom, G.W.; Byrnes, M.L.; Stell, R.; Mastaglia, F.L. Reversible reorganisation of the motor cortical representation of the hand in cervical dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceballos-Baumann, A.O.; Sheean, G.; Passingham, R.E.; Marsden, C.D.; Brooks, D.J. Botulinum toxin does not reverse the cortical dysfunction associated with writer’s cramp. A PET study. Brain 1997, 120 Pt 4, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.O.; Thomassen, M.; Schulz, G.M.; Hosey, L.A.; Varga, M.; Ludlow, C.L.; Braun, A.R. Alterations in CNS activity induced by botulinum toxin treatment in spasmodic dysphonia: An H215O PET study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. JSLHR 2006, 49, 1127–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Kiyosawa, M.; Wakakura, M.; Ishii, K.; Ishiwata, K.; Mochizuki, M. Glucose hypermetabolism in the thalamus of patients with hemifacial spasm. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, U.; Jonsson, T.; Bergfeldt, L.; Julin, P. Cortical activation changes and improved motor function in stroke patients after focal spasticity therapy—An interventional study applying repeated fMRI. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manganotti, P.; Acler, M.; Formaggio, E.; Avesani, M.; Milanese, F.; Baraldo, A.; Storti, S.F.; Gasparini, A.; Cerini, R.; Mucelli, R.P.; et al. Changes in cerebral activity after decreased upper-limb hypertonus: An EMG-fMRI study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 28, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veverka, T.; Hluštík, P.; Hok, P.; Otruba, P.; Zapletalová, J.; Tüdös, Z.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P. Sensorimotor modulation by botulinum toxin A in post-stroke arm spasticity: Passive hand movement. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 362, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-L.; Weber, D.J.; Munin, M.C. Changes in Cerebellar Activation After Onabotulinumtoxin A Injections for Spasticity After Chronic Stroke: A Pilot Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomášová, Z.; Hluštík, P.; Král, M.; Otruba, P.; Herzig, R.; Krobot, A.; Kaňovský, P. Cortical activation changes in patients suffering from post-stroke arm spasticity and treated with botulinum toxin a. J. Neuroimaging 2013, 23, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senkárová, Z.; Hlustík, P.; Otruba, P.; Herzig, R.; Kanovský, P. Modulation of cortical activity in patients suffering from upper arm spasticity following stroke and treated with botulinum toxin A: An fMRI study. J. Neuroimaging 2010, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrlý, M.; Hluštík, P.; Hok, P.; Otruba, P.; Tüdös, Z.; Kaňovský, P. Changes in sensorimotor network activation after botulinum toxin type A injections in patients with cervical dystonia: A functional MRI study. Exp. Brain Res. 2018, 236, 2627–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresel, C.; Bayer, F.; Castrop, F.; Rimpau, C.; Zimmer, C.; Haslinger, B. Botulinum toxin modulates basal ganglia but not deficient somatosensory activation in orofacial dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresel, C.; Haslinger, B.; Castrop, F.; Wohlschlaeger, A.M.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O. Silent event-related fMRI reveals deficient motor and enhanced somatosensory activation in orofacial dystonia. Brain 2006, 129, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opavský, R.; Hluštík, P.; Otruba, P.; Kaňovský, P. Sensorimotor network in cervical dystonia and the effect of botulinum toxin treatment: A functional MRI study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 306, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opavský, R.; Hluštík, P.; Otruba, P.; Kaňovský, P. Somatosensory cortical activation in cervical dystonia and its modulation with botulinum toxin: An fMRI study. Int. J. Neurosci. 2012, 122, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslinger, B.; Erhard, P.; Dresel, C.; Castrop, F.; Roettinger, M.; Ceballos-Baumann, A.O. “Silent event-related” fMRI reveals reduced sensorimotor activation in laryngeal dystonia. Neurology 2005, 65, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.D.; Raichle, M.E. Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 700–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Kollewe, K.; Samii, A.; Beckmann, C.F.; Dengler, R.; Münte, T.F. Changes in resting-state brain networks in writer’s cramp. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delnooz, C.C.S.; Helmich, R.C.; Toni, I.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.C. Reduced parietal connectivity with a premotor writing area in writer’s cramp. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresel, C.; Li, Y.; Wilzeck, V.; Castrop, F.; Zimmer, C.; Haslinger, B. Multiple changes of functional connectivity between sensorimotor areas in focal hand dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslinger, B.; Noé, J.; Altenmüller, E.; Riedl, V.; Zimmer, C.; Mantel, T.; Dresel, C. Changes in resting-state connectivity in musicians with embouchure dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochim, A.; Li, Y.; Gora-Stahlberg, G.; Mantel, T.; Berndt, M.; Castrop, F.; Dresel, C.; Haslinger, B. Altered functional connectivity in blepharospasm/orofacial dystonia. Brain Behav. 2018, 8, e00894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delnooz, C.C.S.; Pasman, J.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.C. Task-free functional MRI in cervical dystonia reveals multi-network changes that partially normalize with botulinum toxin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delnooz, C.C.S.; Pasman, J.W.; Beckmann, C.F.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.C. Altered striatal and pallidal connectivity in cervical dystonia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blood, A.J.; Tuch, D.S.; Makris, N.; Makhlouf, M.L.; Sudarsky, L.R.; Sharma, N. White matter abnormalities in dystonia normalize after botulinum toxin treatment. Neuroreport 2006, 17, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, C.; Pantano, P.; Calistri, V.; Totaro, P.; Fabbrini, G.; Berardelli, A. Diffusion tensor imaging in primary cervical dystonia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 1591–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, K.; Mueller, J.; Schocke, M.; Brenneis, C.; Rinnerthaler, M.; Seppi, K.; Trieb, T.; Wenning, G.K.; Hallett, M.; Poewe, W. Voxel based morphometry reveals specific gray matter changes in primary dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganski, B.; Thun-Hohenstein, C.; Bogdahn, U.; Winkler, J.; May, A. “Motor circuit” gray matter changes in idiopathic cervical dystonia. Neurology 2003, 61, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bono, F.; Salvino, D.; Cerasa, A.; Vescio, B.; Nigro, S.; Quattrone, A. Electrophysiological and structural MRI correlates of dystonic head rotation in drug-naïve patients with torticollis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, M.; Yaldizli, O.; de Greiff, A.; Lachenmayer, M.L.; Buhl, A.R.; Tumczak, F.; Gizewski, E.R.; Diener, H.-C.; Maschke, M. Morphometric changes of sensorimotor structures in focal dystonia. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh, J.L.; Kuster, J.K.; Levenstein, J.M.; Makris, N.; Multhaupt-Buell, T.J.; Sudarsky, L.R.; Breiter, H.C.; Sharma, N.; Blood, A.J. Thalamic Volume Is Reduced in Cervical and Laryngeal Dystonias. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinin, C.C.; Piovesana, L.G.; Santos, M.C.A.; Guimarães, R.P.; de Campos, B.M.; Rezende, T.J.R.; Campos, L.S.; Torres, F.R.; Amato-Filho, A.C.; França, M.C.; et al. Diffuse decreased gray matter in patients with idiopathic craniocervical dystonia: A voxel-based morphometry study. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, P.; Totaro, P.; Fabbrini, G.; Raz, E.; Contessa, G.M.; Tona, F.; Colosimo, C.; Berardelli, A. A transverse and longitudinal MR imaging voxel-based morphometry study in patients with primary cervical dystonia. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weise, C.M.; Awissus, C.; Baum, P.; Classen, J.; Villringer, A.; Ragert, P.; Weise, D. Strukturelle Hirnveränderungen bei Patienten mit zervikaler Dystonie—Abhängigkeit von der Behandlung mit Botulinumneurotoxin. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the German Neurological Society (DGN), Berlin, Germany, 25–28 September 2018. FV 699. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandru, H.; Muthuraman, M.; Chirumamilla, V.C.; Koirala, N.; Paktas, B.; Deuschl, G.; Zeuner, K.E.; Groppa, S. Grey Matter Microstructural Integrity Alterations in Blepharospasm Are Partially Reversed by Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delnooz, C.C.S.; Pasman, J.W.; van de Warrenburg, B.P.C. Dynamic cortical gray matter volume changes after botulinum toxin in cervical dystonia. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 73, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weise, D.; Weise, C.M.; Naumann, M. Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin—Evidence from Human Studies. Toxins 2019, 11, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010021
Weise D, Weise CM, Naumann M. Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin—Evidence from Human Studies. Toxins. 2019; 11(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeise, David, Christopher M. Weise, and Markus Naumann. 2019. "Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin—Evidence from Human Studies" Toxins 11, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010021
APA StyleWeise, D., Weise, C. M., & Naumann, M. (2019). Central Effects of Botulinum Neurotoxin—Evidence from Human Studies. Toxins, 11(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11010021




