Abstract
Cytolytic pore-forming toxins including alpha hemolysin (Hla) and bicomponent leukotoxins play an important role in the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus. These toxins kill the polymorphonuclear phagocytes (PMNs), disrupt epithelial and endothelial barriers, and lyse erythrocytes to provide iron for bacterial growth. The expression of these toxins is regulated by the two-component sensing systems Sae and Agr. Here, we report that a point mutation (L18P) in SaeS, the histidine kinase sensor of the Sae system, renders the S. aureus Newman hemolytic activity fully independent of Hla and drastically increases the PMN lytic activity. Furthermore, this Hla-independent activity, unlike Hla itself, can lyse human erythrocytes. The Hla-independent activity towards human erythrocytes was also evident in USA300, however, under strict agr control. Gene knockout studies revealed that this Hla-independent Sae-regulated activity was entirely dependent on gamma hemolysin A subunit (HlgA). In contrast, hemolytic activity of Newman towards human erythrocytes from HlgAB resistant donors was completely dependent on agr. The culture supernatant from Newman S. aureus could be neutralized by antisera against two vaccine candidates based on LukS and LukF subunits of Panton-Valentine leukocidin but not by an anti-Hla neutralizing antibody. These findings display the complex involvement of Sae and Agr systems in regulating the virulence of S. aureus and have important implications for vaccine and immunotherapeutics development for S. aureus disease in humans.
Key Contribution:
Staphylococcus aureus causes several human disorders including invasive and life-threatening bacteremia, pneumonia, osteomyelitis and surgical site infections. The problem is exacerbated with the growing prevalence of methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Currently, MRSA is responsible for over 12,000 deaths per year in the US. S. aureus has a large arsenal of toxins that disable the host immune system, kill red blood cells to extract iron for bacterial growth, and cause tissue destruction and inflammation. We have identified an important role of a leukotoxin component HlgA in the Newman strain to kill human red blood cells independent of agr but dependent on a point mutation (L18P) in SaeS. The findings are significant because neutralizing this toxin can deprive the bacteria of iron, a critical nutrient that the bacteria absolutely need for their growth.
1. Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is an opportunistic human pathogen that can cause a variety of acute and chronic infections [1,2,3,4,5]. Because of its high adaptability and genomic plasticity, S. aureus has been able to acquire resistance to commonly prescribed antibiotics [6,7,8], and has already emerged as a multi drug resistant “superbug”. In addition to the antibiotic treatments, therapeutic options including active immunization and passive immunotherapy have been applied, but neither of these methods has been successful. Vaccine approaches that target surface antigens of S. aureus, not only failed in clinical trials, but also appear to exacerbate the fatal sequelae of the disease [9]. This concern has been further reinforced in animal studies using cell-associated antigens [10,11]. Toxin-based vaccines may represent an effective alternative.
In S. aureus, complex networks of transcriptional regulators, two-component systems (TCSs) [12,13] and quorum sensing systems [14,15] tightly regulate numerous virulence factors including surface proteins and toxins. Three groups of pore-forming cytotoxins appear to be critical for S. aureus pathogenesis. The first group, called alpha toxin, or alpha hemolysin (Hla), is a single component toxin that binds to a specific cell receptor, a zinc-dependent metalloprotease called ADAM10, and forms transmembrane pores [16,17]. The second group is bicomponent pore-forming toxins (BCPFTs) that require two components (S and F), as well as specific receptors to oligomerize and form functional pores in key immune cells including polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) [18,19,20]. The third group of toxins is small amphiphilic peptides called phenol soluble modulins (PSM) [19,21] that directly insert into the host cell membrane to form pores [21]. The PMN-lytic activity of S. aureus serves the purpose of immune evasion while the hemolytic activity provides the bacteria with a source of the critical nutrient-iron.
The expression of these toxins is regulated by the S. aureus exoprotein expression (Sae) locus, a well-characterized TCS that acts as an activator of toxin production [22] along with other regulators like agr [15]. Several studies showed that sae is essential for bacterial virulence in animal models [23,24,25]. For example, the sae locus regulates the hla expression in a rabbit infective endocarditis model in the absence of both agr and sarA [26]. The sae locus consists of four open reading frames (ORFs): P, Q, R, and S [27,28]. The TCS consists of SaeRS [23,29], with SaeS being a transmembrane histidine kinase and SaeR, a response regulator [23]. Initially, SaePQ transcripts have been predicted to play a role as autoinducers in activation of the saeRS locus [27,28]; in more recent studies, the SaePQ protein complex has been shown to activate SaeS phosphatase activity [30].
SaeS senses the environmental signals through unknown ligands. The extracellular (EC) loop of SaeS plays a critical role in S. aureus virulence. It is the overall conformation, not the individual amino acid sequence, that is important for the function of SaeS [31,32]. The M31A mutation in this loop leads to a significant reduction in the human neutrophil cytotoxic activity in culture supernatant, whereas mutations in the two aromatic anchor residues, W32A and F33A, disrupt basal signaling of SaeS. Previously, we and other [33] reported a single amino acid mutation in the Newman SaeS protein (L18P) [27] that causes a temporal change in the regulatory network of the Newman strain. One such example is depicted by the accelerated kinetics of surface protein expression in Newman compared to other strains. In addition to the Newman strain, this SaeS-based unique expression pattern has also been reported in ST30 (CC30)-SCCmec IV (USA1100) [34].
In this report, we explored the impact of this mutation (L18P) in the Newman strain. We found that supernatant collected from the Newman strain can lyse rabbit and human red blood cells (RBC) in a Hla-independent manner. We demonstrate that this activity is dependent on gamma hemolysin A subunit (HlgA). HlgA expression is highly elevated in Newman in an Agr-independent but SaeSL18P-dependent manner. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the enhanced cytolytic activity and specific lysis of human RBC vary from donor to donor. HlgA specific lytic activities were more significant in blood from sensitive donors. Lysis of blood from resistant donors was independent of hla and leukotoxins, but dependent on some other proteins activated by agr. In this study, we have established that HlgA is a valid virulence factor and plays a role for the non-canonical pairing of leukotoxins in the pathogenesis of S. aureus strains.
2. Results
The Newman strain is one of the most widely used standard laboratory strain for alpha toxin vaccine studies as well as for research on staphylococcal biology [35,36]. While evaluating a panel of anti-Hla neutralizing antibodies we noted that hemolytic activity of supernatants from the Newman culture cannot be neutralized by our anti-Hla monoclonal antibodies or even by polyclonal anti-Hla IgG, although Newman is known to express Hla [37]. This observation prompted us to examine the nature of Newman hemolytic activity. We first generated hla null mutants of Newman as well as NCTC 8325 as a reference strain. Western blot analysis confirmed comparable expression of Hla in both parental strains and the loss of Hla expression in the mutants (Figure 1A). We used one of our anti-Hla monoclonal neutralizing antibodies, Can6 (CAN24G4-1) [38], to characterize the hemolytic activity in these strains. In the rabbit RBC (RRBC) hemolytic assay, Can6 exhibited potent neutralizing activity towards purified Hla (Figure 1B) (IC50 < 1 nM) as well as the hemolytic activity of NCTC 8325 overnight culture supernatants but not NCTC 8325hla null (Figure 1C). In contrast, in Newman background, there was no difference in hemolytic activities in the wild type versus Hla null strains and Can6 could not neutralize the hemolytic activities (Figure 1D).
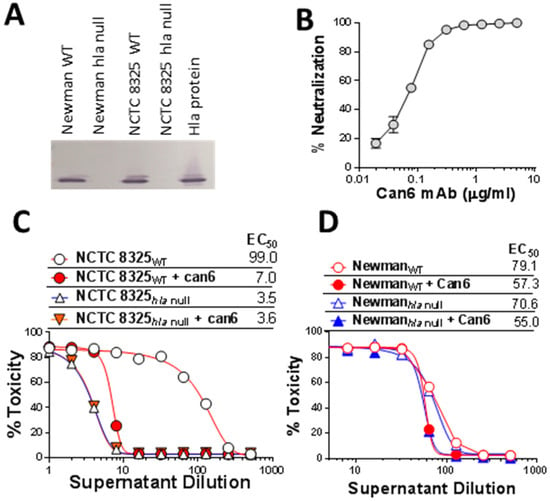
Figure 1.
Expression pattern of Hla in Newman and NCTC8325 S. aureus strains and role of Hla in hemolytic activity. (A) Western blot analysis of supernatant from overnight culture from NCTC 8325 and Newman wild type (WT) and hla null mutants; (B) Neutralization of purified Hla by the monoclonal antibody Can6 in rabbit RBC assay; (C,D) Hemolytic activity of supernatants of WT and hla null mutant of NCTC 8325 (C) and Newman (D) strains in rabbit RBC assay. EC50: 50% toxicity titer.
2.1. Role of SaeS in the Newman Phenotype
We have previously reported that a point mutation in Newman SaeS (L18P) [27] results in early expression of exotoxins. This mutation has also been linked to other regulatory phenotypes [39,40]. We hypothesized that the SaeSL18P mutation can be responsible for the Hla-independent hemolysis phenotype in Newman. To this end, we generated Newman sae mutants that were either complemented in trans with saeS from the Newman strain (NewmanSaeS-P18, resembling wild type Newman) or from the USA300 strain (NewmanSaeS-L18) and analyzed these strains for hemolytic and PMN-lytic activity as well as expression pattern of Hla and various BCPFTs. The hemolytic activity against rabbit RBC was similar in NewmanSaeS-L18 or USA300 compared to NewmanSaeS-P18 (Figure 2A left panel). Moreover, Can6 could only neutralize supernatants from the USA300 and NewmanSaeS-L18 (having USA300 type sae). More dramatic effect of sae mutation became apparent when we tested human RBC lysis. While culture supernatants from USA300 or NewmanSaeS-L18 poorly lysed human RBC, NewmanSaeS-P18 supernatants displayed 10-fold higher hemolysis (Figure 2A right panel). This human RBC hemolytic activity was entirely related to a non-Hla component, since Can6 showed no neutralizing activity for any of the strains, consistent with previous reports that Hla does not lyse human RBC [41,42] also consistent with lack of Hla receptor ADAM10 on human erythrocytes [16,17]. Using a PMN-lysis assay we further demonstrated that the saeS mutation in Newman leads to approximately 3 and 5-fold higher toxicity towards PMN compared to USA300 or Newman carrying L18 SaeS, respectively (Figure 2B). While Newman exhibited higher lytic activity toward PMNs than USA300, reversal of the SaeS to the USA300 type largely abrogated this activity to levels much less than USA300, likely due to expression of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) in USA300 that is not expressed by Newman. Taken together, these data indicate that a single point mutation in the SaeS leads to a largely Hla-independent rabbit RBC hemolytic phenotype and increased lytic activity towards human RBC and PMNs in Newman. Reversion of this mutation makes the Newman hemolytic profile nearly indistinguishable from USA300.
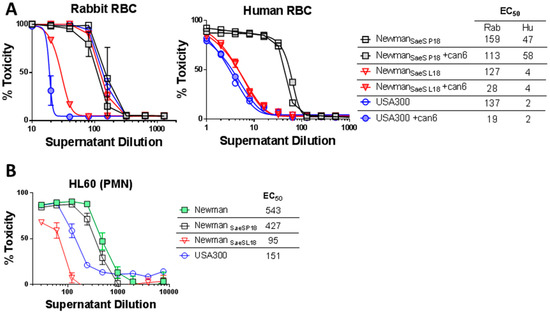
Figure 2.
The impact of L18 mutation in SaeS on hemolytic and PMN lytic activity. (A) Hemolytic assays in rabbit (left panel) and human RBC (right panel) were carried out with dilutions of supernatants from NewmanSaes P18, NewmanSaes L18, and USA300 in presence or absence of 5 µg/mL of Can6; (B) Toxicity of the culture supernatants of Newman, NewmanSaeS P18, NewmanSaeS L18, and USA300 in HL-60 based cytotoxic assays. EC50 values are indicated.
2.2. Critical Role of Newman SaeS Mutation for In Vivo Virulence
Since there was a significant difference in in vitro toxicity between NewmanSaeS-P18 and NewmanSaeS-L18, we sought to examine if this translates into higher virulence in a mouse pneumonia model. Outbred (CD-1) mice were better suited for this study because they are more resistant to S. aureus infection than Balb/C [43]. Four groups of mice (5 mice/group) were challenged with four different doses (1.3 × 108 to 2 ×107 CFU/mouse) of either NewmanSaeS-P18 or NewmanSaeS-L18. All mice challenged with 1.3 × 108/mouse NewmanSaeS-P18 died within the first two days of infection, whereas all mice infected with NewmanSaeS-L18 survived (Figure 3A). Statistical analysis with Log-Rank (Mantel-Cox) test showed that NewmanSaeS-P18 were significantly more pathogenic than NewmanSaeS-L18 (p = 0.0003). In the lower dose group (9 × 107/mouse), 80% of the mice survived in the NewmanSaeS-P18 group whereas 100% mice survived in the NewmanSaeS-L18 group (Figure 3B) and no lethality was observed in the lower doses of either strain. Survival data were consistent with the health score data showing that only NewmanSaeS-P18-challenged mice were sick in all different doses tested, whereas mice in NewmanSaeS-L18 were healthy (Figure 3C).
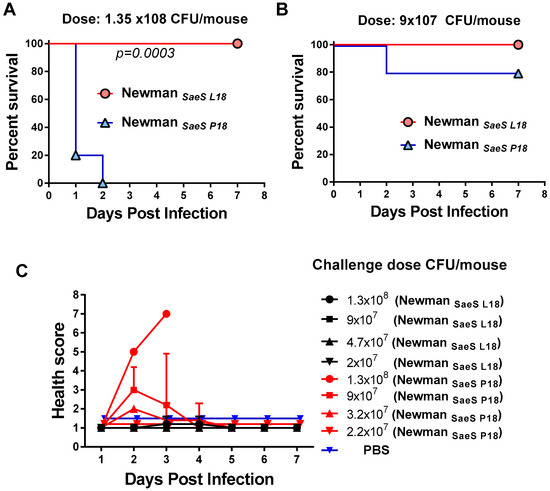
Figure 3.
Pathogenicity of S. aureus NewmanSaes P18 and NewmanSaeS L18 pneumonia infection models. (A) Survival percentages of mice were compared after intranasal (IN) challenge with 1.35 × 108 CFU or (B) 9 × 107 CFU of NewmanSaeS P18 and NewmanSaeS L18; (C) Health scores were compared with four different IN challenge dose in NewmanSaeS P18 with NewmanSaeS L18. Statistical analysis was performed using Log-Rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
2.3. HlgA Plays A Major Role in Newman Virulence
The above data clearly showed that the distinct regulatory networks of NewmanSaeS-P18 and NewmanSaeS-L18 lead to altered virulence in vitro and in vivo. To examine the toxin profile resulting from this single point mutation in the SaeS protein, we first tested the expression of several leukotoxins and Hla in Newman and several other S. aureus strains. As shown in Figure 4A, the Newman strain expressed Hla and all leukotoxins tested except for LukF-PV, with HlgA and LukB expression being particularly high. The high-level expression of HlgA was striking since HlgAB is known to be a potent toxin towards human and murine erythrocyte through binding to Duffy antigen receptor (DARC) [44]. Thus, we examined if the SaeS-P18 mutation leads to altered expression of leukocidins. As shown in Figure 4B, in comparison to wild type and SaeS-P18 reconstructed mutants, HlgA expression was repressed in NewmanSaeS-L18 to levels similar to USA300. Expression of LukB was also reduced in the presence of SaeS-L18. In contrast, expression of Hla, HlgC, and HlgB (Figure 4B) as well as LukA and LukD was independent of L18P mutation in Newman (Figure 4B).
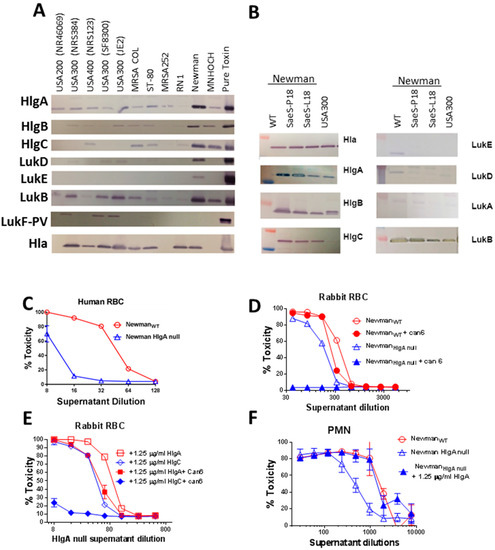
Figure 4.
Expression pattern of Hla and leukotoxins in various S. aureus strains and role of HlgA in Newman phenotype. (A) Leukotoxin subunit expression was analyzed by Western blot in the indicated S. aureus strains. Respective purified toxin subunits (Lane 12) were used as positive control; (B) Western blots analysis of culture supernatants from NewmanSaeS-P18, NewmanSaeS L18, and USA300 with leukotoxin: Specific peptide polyclonal antibodies; (C) Toxicity of the supernatant from Newman wild types (WT) and HlgA null Newman on human RBC; (D) Hemolytic activity of supernatants from WT and HlgA null mutants of Newman in presence or absence of Can6 on rabbit RBC; (E) Supplementation of NewmanHlgA null with HlgA but not HlgC restore the Newman hemolytic phenotype on rabbit RBC; (F) Addition of exogenous HlgA increases PMN lytic activity of NewmanHlgA null supernatants to the level of WT Newman.
To examine if the increased HlgA expression was responsible for the Newman phenotype, we moved the hlgA transposon mutation from the JE2 strain to the Newman strain. The Newman hlgA mutant displayed severely reduced hemolytic activity towards human RBC (Figure 4C). The hemolytic activity of NewmanhlgA null supernatant towards rabbit RBC was reduced by approximately 50% when compared to the wild type strain (hemolysis effective concentration (EC50) as 350 for wild-type and 180 for mutant) (Figure 4D). However, NewmanhlgA null retained significant activity against rabbit RBC (Figure 4D). Interestingly while the hemolytic activity in wild-type Newman was marginally neutralized by Can6, this antibody completely abolished the hemolytic activity of the hlgA null mutant (Figure 4D). These data indicate that in the presence of HlgA overexpression, the HlgA-mediated hemolysis is dominant while, in the absence of HlgA, Newman relies on Hla for hemolysis, suggesting that the elevated expression of HlgA determines the highly virulent phenotype of Newman. To further confirm this hypothesis, we complemented Newman hlgA null mutant culture supernatant with 1.25 μg/mL of purified HlgA or HlgC protein, both S subunits of gamma hemolysin. Supplementing NewmanhlgA null supernatant with HlgC showed no significant effect on its hemolytic activity, while supplementing with HlgA increased the toxicity by two-fold (Figure 4E). A similar effect was observed in HL-60 based PMN assay where hlgA mutant had lower toxicity, and addition of HlgA protein increased its toxicity to WT levels (Figure 4F). We also supplemented this mutant supernatant with other subunits HlgB, LukE, LukD, LukS-PV, and LukF-PV concentration; however, none of these subunits complemented hlgA mutant phenotypes (data not shown).
We next used purified toxins to further examine the potential dominance of HlgAB over Hla in rabbit RBC assay. We first examined if HlgA or HlgB compete with Hla in rabbit RBC assay and observed that HlgA or HlgB alone had no impact on dose dependent lysis of rabbit RBC by Hla (Figure 5A,B) suggesting that there is no competition for receptor binding. However, consistent with the above observations, in the presence of HlgAB functional toxin Hla could only display marginal hemolytic activity as shown by the inability of Can-6 to reduce hemolysis in the presence of Hla + HlgAB (Figure 5C,D).
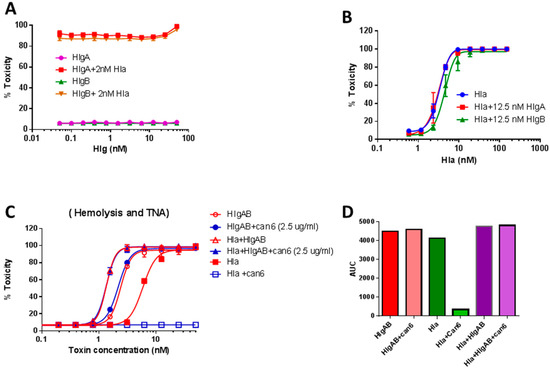
Figure 5.
Dose response of Hla and HlgA + HlgB toxicity in 4% rabbit RBC. (A) Titration curve of HlgA and HlgB in the presence of 2 nM Hla; (B) Titration of Hla in the presence of 12.5 nM HlgA or HlgB; (C) 2.5 μg/mL Can6 can neutralize Hla, whereas when hla is mixed with HlgAB, Can6 cannot neutralize toxicity; (D) Area under the curve (AUC) based on plot (C).
2.4. Agr Independent Lysis of Rabbit RBC in Newman
RNAIII, the regulatory RNA encoded by the agr locus, is known as the major positive regulator of exotoxin production in S. aureus [15] and hlgA is one such gene activated by RNAIII [45]. To evaluate the role of Agr in the unique regulation of toxin production in the Newman strain, we moved an agrC null mutation from the JE2 background into the Newman and USA300 strains. HlgA expression was unaffected in the NewmanagrC null strain, whereas it was abrogated in both agr null and sae null mutants of USA300 (Figure 6A). These data further indicate a profound difference in the regulatory network controlling HlgA expression in Newman and USA300. We also analyzed the expression of Hla and HlgA in hlgA null, agrC null, sae null, WT as well as reconstituted NewmanSaeS-P18 background. Consistent with the above data, the expression of HlgA was not affected in NewmanSaeS-P18 agrC null mutant, whereas Hla expression was entirely dependent on both Agr and Sae, further confirming that the Newman version of SaeS (NewmanSaeS-P18) specifically affects HlgA but not Hla (Figure 6B). The functional hemolytic phenotype of these mutants was consistent with the expression pattern, with the hemolytic activity in the Sae-L18 background (USA300 type) being Agr-dependent and in the Sae-P18 background (Newman type), being Agr-independent as tested in 4% rabbit RBC (Figure 6C).
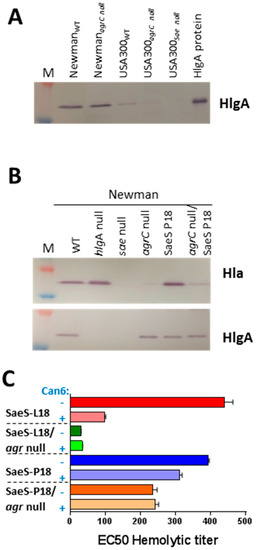
Figure 6.
agr-independent regulation of HlgA subunit in the Newman strain. (A) Western blots were carried out with anti-HlgA polyclonal antibody in culture supernatant from agrC null USA300 and Newman; (B) Western blot analysis of NewmanSaeS L18 and its agrC null mutant with anti-HlgA specific polyclonal antibody along with Hla specific monoclonal antibody; (C) Hemolytic and TNA titers were carried out with NewmanSaeS P18 and its agrC null mutant in the presence and absence of anti-Hla mAb Can6.
2.5. Differential Role of Agr in Lysis of Human Erythrocytes
We have observed low hemolytic activity in agr-defective clinical mutants like MRSA252 (data not shown) towards human RBC. We examined the role of agr in human RBC lysis using USA300 (JE2) and its agr mutant. Human RBC lytic activity was clearly detectable in JE2, and this activity was completely abrogated in the agr null mutant of JE2, indicating that this activity is under full agr control (Figure 7A). In sharp contrast, the Newman supernatant exhibited strong Human RBC lytic activity and this activity was not affected by agr mutation, which is consistent with our findings described above. Spann et al. previously reported that RBC from a portion of the population is resistant to lysis by HlgAB due to a polymorphism in the Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines (DARC) gene [44]. We screened RBCs from multiple individuals and identified several resistant donors. Purified HlgAB lysed sensitive blood with high hemolytic titer (Figure 7B). Interestingly, when the hemolytic activity was tested in RBC from resistant donors, the lytic activity of the both wild type JE2 and Newman exhibited similar levels of lysis, whereas agr null in both backgrounds completely abrogated the lytic activity (Figure 7C) further indicating that the agr-dependent activity can only manifest itself in the absence of HlgAB functionality. As expected, the resistant blood could not be lysed by purified HlgAB (Figure 7D).
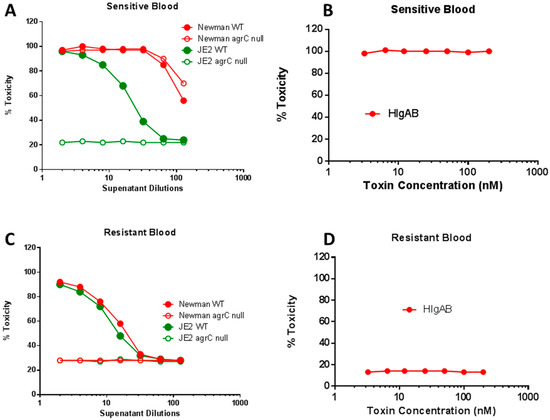
Figure 7.
agr effect in lysis of sensitive and resistant human red blood cells by culture supernatant from Newman and JE2 strain of S. aureus versus purified HlgAB. Blood from sensitive (A,B) and resistant donor (C,D).
2.6. Lysis of Human RBC Requires Free N-Terminus of HlgB
In our previous study, using N-terminally His-tagged HlgA and HlgB, we had observed extremely low toxicity of His-HlgAB towards human RBC, whereas, the non-canonical tag free pair HlgA + LukD was highly hemolytic [42]. The data described above and also reported by Spann et al [44] showing full activity of non-tagged HlgAB suggested that the lack of activity of His-HlgAB was related to the N-terminus of HlgB being occupied, since His-HlgA was fully functional in combination with LukD [42]. Interestingly, while there was little difference between the PMN-lytic activity (Figure 8A) of tagged and tag-free HlgAB, N-terminally tagged HlgAB was completely inactive towards human RBC (Figure 8B) and largely attenuated toward rabbit RBC (Figure 8C). These data indicate that the N terminus of HlgB plays a critical role in lysis of human RBC.
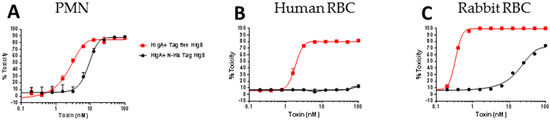
Figure 8.
Cytotoxicity of N-His tag HlgB versus tag free HlgB. (A) Polymorphonuclear phagocyte (PMN) lytic activity; (B) Hemolytic activity towards 2% human RBC; (C) Hemolytic activity towards 4% rabbit RBC.
2.7. Antibodies Elicited by PVL-Based Vaccines Neutralize Human RBC Hemolytic Activity
We have previously reported two mutants of PVL subunits, LukSmut9 (LukST28F/K97A/S209A) and LukFmut1 (LukFK102A), as promising vaccine candidates with cross-neutralizing activity against other BCPFTs [42,46]. In light of our new findings, we further tested polyclonal antibodies against LukSmut9, LukFmut1, or Hla in supernatants of NewmanWT. As shown in Figure 9, antibodies against LukS and LukF but not anti-Hla were able to effectively neutralize the hemolytic activity. A combination of antibodies against both subtypes provided the highest level of neutralization. The effectiveness of antibodies against both subunits further indicates that the responsible toxin for the Hla-independent human RBC lysis contains both S and F subunits and further justifies the use of both subunit toxoids in a multivalent vaccine.
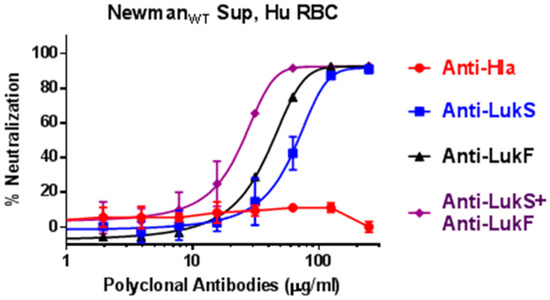
Figure 9.
Neutralization of human RBC hemolytic activity in overnight culture supernatants of NewmanWT using antibodies against hla versus Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL) subunits.
3. Discussion
The virulence of S. aureus, particularly the recently emerging community-acquired MRSA (CA-MRSA) clones, is largely related to its ability to produce a variety of hemolysins and leukotoxins [47,48]. S. aureus controls the expression of many of these secreted toxins using the TCS environmental sensing systems agr and sae. Alpha hemolysin (Hla), a toxin regulated by both agr and sae [26], is known as the primary mediator of red blood cell lysis providing a rich source of iron for bacterial growth [49]. Bicomponent leukotoxins including PVL, HlgAB, HlgCB, LukED, and LukAB (also known as LukGH) are primarily known for their lytic activity towards the polymorphonuclear phagocytes (PMNs) [50], while HlgAB and LukED also possess hemolytic activity [44]. Here, we demonstrate that the Sae-regulated HlgA production conveys remarkably high virulence to S. aureus and provide evidence that this increased virulence is correlated with in-vivo and in-vitro studies.
The S. aureus sae locus encodes the environmental sensor histidine kinase SaeS and the response regulator SaeR that constitute the two-component system as well as two additional proteins SaeP and Q [28]. The N-terminus of SaeS consists of two transmembrane (TM) domains flanking a 9-residue extracellular loop. A recent study showed that kinase activity of SaeS is determined by the extracellular loop, as mutating this linker leads to elevated kinase activity even in the absence of any extracellular signals [32]. It is believed that the TM domains and the extracellular loop control the kinase activity of SaeS via conformational changes [32]. Previously we reported that a single point mutation within the first TM domain of SaeS (L18P) in the S. aureus strain Newman protein results in expression of multiple exoproteins in the earlier log phase compared to other WT strains [27]. The L18P mutation introduces a kink in the middle of the TM1 alpha helix, likely inducing conformational changes in the SaeS histidine kinase leading to its augmented activity. This is consistent with previous reports of a constitutively active status of sae TCS in Newman [33,51]. Here, we report that this mutation creates a regulatory switch rendering most of the cytolytic activity as well as in vivo pathogenesis of the Newman strain dependent on HlgA.
Our analysis of the L18P mutation further revealed a dominant Hla-independent hemolytic activity in S. aureus Newman. We noted that despite the high level of Hla expression, more than 90% of the hemolytic activity in the Newman supernatant remained non-neutralized by an anti-Hla neutralizing antibody. Consistent with this, Newmanhla null retained nearly all of its hemolytic activity towards rabbit RBC, while the hla deletion largely abrogated this activity in NCTC 8325. This Hla-independent hemolytic phenotype was entirely reversed by mutating the proline at position 18 in Newman SaeS back to leucine. In contrast to Newman, the hemolytic activity of USA300 (NRS384) carrying L18 SaeS towards rabbit RBC was entirely Hla-dependent. The L18P mutation also dramatically increased the PMN-lytic activity of Newman as compared to USA300. We further demonstrate that this phenotype is responsible for increased in vivo virulence in a mouse model of S. aureus pneumonia. At doses as high as 1.3 × 108 CFU, replacing the Newman SaeS with that of USA300 completely abrogated virulence both in terms of lethality and weight loss underscoring the critical role of this single mutation. These findings provide a molecular explanation for the previously reported highly virulent nature of S. aureus Newman [35,36,52,53,54].
The Hla-independent hemolytic phenotype of Newman was entirely due to upregulation of HlgA. Deleting the hlgA gene reverted this phenotype to a fully Hla-dependent hemolysis indicating that HlgA dominated the hemolytic activity when co-expressed with Hla. Furthermore, supplementing the NewmanhlgA null supernatant with purified HlgA restored the Hla-independent phenotype. This Sae-dependent HlgA expression in Newman was fully independent of agr, while HlgA expression in USA300 required both Sae and Agr. These data are consistent with the constitutive activity of Sae in Newman being independent of agr [51]. An interesting aspect of our findings is the interplay between Hla and HlgAB and Agr versus Sae dependent activities. Our findings show that in Newman while both toxins are present the Sae-dependent HlgAB activity is dominant. This was corroborated by in vitro experiments using purified toxins (Figure 5). While neither HlgA or HlgB subunits alone had any impact on Hla-mediated lysis of rabbit RBCs, in presence of HlgAB, the lysis was entirely dependent on HlgAB. We further show that, in blood from human donors that are sensitive to HlgAB, lysis of RBCs by Newman is fully independent of agr, while the same activity in USA300 is completely abrogated by mutating agr. In contrast, when blood from HlgAB resistant donors was used, both Newman and USA300 activities were entirely dependent on agr. Since Hla cannot lyse human RBC, the nature of this agr-dependent human RBC lytic activity as well as the basis of this dominance remains to be determined.
Within the infected hosts, bacteria are under enormous stress because they constantly encounter antimicrobial peptides and reactive oxygen species produced by immune cells as well as an environment low in key nutrients such as iron. Iron is an essential nutrient for all living organisms, and bacterial pathogens have evolved a variety of mechanisms to scavenge iron from the high-affinity iron-binding proteins and transport them into the cells. S. aureus is strictly dependent on acquiring iron in the host for its survival and persistence within abscesses [55,56,57,58,59]. In vertebrates, 99% of the iron is located intracellularly [60] and mostly stored in erythrocytes in complex with hemoglobin. Since the intracellular pool of iron is not available to bacterial pathogens, many bacteria including S. aureus produce hemolytic toxins to lyse the erythrocyte and release iron for their growth. Electron microscopy studies have demonstrated the abundance of erythrocytes within S. aureus abscess providing an immediate source of iron for bacterial growth. S. aureus may have gained the sae mutation to acquire growth advantage by more effectively lysing human RBCs.
Currently toxoid based vaccines for S. aureus are receiving renewed attention. Our findings of the importance of HlgAB suggest that an effective toxoid vaccine must be also able to neutralize this toxin. HlgA and HlgB have a high degree of sequence identity with LukS-PV and LukF-PV, respectively [18,19,20]. Our findings show that polyclonal antibodies against two toxoids of LukS-PV and LukF-PV can block the hemolysis of human erythrocytes by supernatants of Newman WT S. aureus while anti-Hla antibody had no effect. This finding has important implications for treatment and vaccination against S. aureus, as vaccines and immunotherapy neutralizing HlgA alone could be developed that severely hamper the ability of S. aureus to access iron during infection in humans.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Growth Media and Bacterial Strains
General method applied for bacterial culture was described in previous literature [27,61]. S. aureus strains were grown in brain heart infusion broth/agar (BHI) media at 37 °C overnight. Transduction and selection of transductants were carried out by standard transduction techniques with phage 80α [27]. Most of the bacterial mutants used in this paper were obtained from the NARSA (now BEI) repository. Strains used in this study are listed in the following table (Table 1).

Table 1.
Bacterial strains used.
4.2. Western Blot Analysis
Unique peptide specific rabbit polyclonal antibodies were generated targeting unique sequences of HlgABC, LukED, LukAB and LukF (from GenScript) to specifically detect these proteins. SDS-PAGE and Western blots were carried out using iBlot 2 Dry Blotting System (from ThermoFisher Scientific) as per manufacturer’s instructions.
Hemolytic and toxin neutralization assays: Hemolytic assays were performed based on our previously published report [42], with RBC from Rabbit that were purchased from Colorado Serum company, Co. (Denver, Colorado, USA) and human blood that was purchased from BIoreclamation IVT Inc. (Baltimore, MD, USA). For Rabbit RBC assays, blood was used within 10 days of the date of blood drawn because the hemolytic titer from older blood samples falls out of specification. Human blood was used within 1 month. Whole blood from both human and rabbit were washed twice with PBS and re-suspended in PBS to obtain 8% (wt/vol.) for rabbit RBC and 4% (wt/vol.) for human RBC. 100 µL of blood was mixed with 100 µL of diluted culture supernatant in 96-well ELISA plates resulting in 4% and 2% of final RBC for rabbit and human, respectively. Plates were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min and centrifuged for 5 min at 3.5 K RPM in Sorvall. 100 μL of supernatants were transferred to NUNC ELISA plates, without disturbing the pellet. OD 416 nm was read, and 4-PL plots were generated with diluted supernatant by using Softmax (Molecular devices). EC50 values (hemolytic titers) were calculated and defined as supernatant dilution at which 50% of hemolysis occurs.
Toxin neutralization assays were carried out using an anti-alpha toxin monoclonal antibody called Can6 and rabbit anti-Hla, anti-LukS and anti-LukF polyclonals (GenScript). Can6 (CAN24G4-1) is a well characterized reagent for its Hla neutralizing titer [38]. In neutralization assays, diluted culture supernatants were incubated at room temperature with antibodies for 10 min, allowing antibodies to neutralize toxins in the supernatants, followed by incubation at 37 °C.
PMN lysis assays: PMN cytotoxicity was determined in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) induced HL-60 cells (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). The HL-60 cells were cultured for seven days in RPMI media supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1.5% DMSO for optimal induction. Cell induction was confirmed by the expression of CD11b on induced versus non-induced cells using flow cytometry analysis. The cells were then harvested and washed with RPMI media containing 2% FBS. Overnight bacterial culture supernatants were normalized based on culture OD 600 nm. Supernatants were filtered through sterile 0.2 µm filter. Sterility of the supernatants were confirmed by culturing 20 μL of the filtered supernatants on BHI agar plate. Serially two-fold diluted culture supernatants were then mixed with HL-60 derived neutrophils at a final density of 5 × 105 cells/well, then incubated for 3 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Cells and BHI broth alone controls were also included, and all samples were run as quadruplicates. Upon cell-supernatant incubation, this mixture was further incubated with 100 μg/mL of XTT with 1% electron coupling solution (Cell signaling) for 16 h and the cell viability was measured by colorimetric measurement at OD 470 nm (background subtracted at OD 690 nm).
In vivo experiments: In vivo experiments were performed for SaeS complemented Newman strains (NewmanSaeS P18 or NewmanSaeS L18) using CD-1 mice from Charles River that were 10–12 weeks old during the studies. Animals were housed under pathogen-free conditions and fed laboratory chow and water ad libitum. Animal studies were conducted per approved protocol by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUC) at Nobel Life Sciences (Gaithersburg, MD, USA).
Challenge dose preparation and back-titer: Bacteria were streaked from glycerol stocks on BHI agar media for single colonies. From BHI plates, isolated colonies were inoculated into 50 mL Falcon tubes containing 7 mL of BHI broth. Tubes were incubated in a shaking incubator at 230 rpm at 37 °C for 16 h. Cells were harvested and washed two times with sterile PBS. The pellets were then re-suspended in required volume of PBS to make the target challenge dose. From each challenge dose, suspension aliquots were back-titered to calculate the actual challenge dose and converted to CFU/mL.
Lethal Pneumonia model: For the pneumonia model, isoflurane was used to anesthetize mice, followed by intranasal (IN) inoculation of a target dose of S. aureus Newman (NewmanSaeS P18 or NewmanSaeS L18) in 50 μL PBS. Animals were monitored for 7 days post challenge for morbidity (weight, and health score) and mortality two times daily until termination of study. Animal studies were conducted per approved protocol by IACUC at Nobel Life Sciences (Gaithersburg, MD, USA).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.P.A. and M.J.A; Data generation, T.K., N.G., R.M. and A.V.; Formal analysis, A.V., T.K., N.G., R.M., I.M. and R.P.A.; Methodology, R.P.A, A.V. and I.M.; Project administration, M.J.A.; Supervision, S.K., T.B., M.J.A. and R.P.A.; Writing–original draft, M.J.A and R.P.A.; Writing–review & editing, M.J.A. and R.P.A.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIAID) (R01AI111205) to MJA and NIAIDs: AI 106162, and AI098232 to RPA.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledged grants support from National Institute of Infectious Diseases (NIAID) (R01AI111205) to MJA and NIAIDs: AI 106162, and AI098232 to RPA. The authors would like to thank Richard Proctor for reading and providing valuable suggestions to this manuscript. Authors would also like to thank Sergey Shulenin, for polyclonal antibody purification; Frederick W. Holtsberg and Thomas Kort, for protein purification and QCs; and Julia Biggins for assistance with animal studies.
Conflicts of Interest
MJA and RPA have stocks or stock options in Integrated Biotherapeutics, Inc.
References
- Shinefield, H.R.; Ruff, N.L. Staphylococcal infections: A historical perspective. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheagren, J.N. Staphylococcal infections of the skin and skin structures. Cutis 1985, 36, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McGahee, W.; Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcal infections in the intensive care unit. Semin. Respir. Infect. 2000, 15, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.; Stevens, N.T.; Humphreys, H.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Current and future approaches to the prevention and treatment of staphylococcal medical device-related infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcal infections: Mechanisms of biofilm maturation and detachment as critical determinants of pathogenicity. Annu. Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combating MRSA: The drug-resistant “superbug”. Bacteria that don’t succumb to the usual antibiotics give everyone the jitters. But there’s a lot we can do to keep the upper hand. Harv. Womens Health Watch 2008, 15, 4–5.
- Washer, P.; Joffe, H. The “hospital superbug”: Social representations of MRSA. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 63, 2141–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, M.; Barton, M.; Conly, J.; Nicolle, L.; Barry, C.; Ford-Jones, E.L. Community-associated MRSA: Superbug at our doorstep. CMAJ 2007, 176, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeely, T.B.; Shah, N.A.; Fridman, A.; Joshi, A.; Hartzel, J.S.; Keshari, R.S.; Lupu, F.; DiNubile, M.J. Mortality among recipients of the Merck V710 Staphylococcus aureus vaccine after postoperative S. aureus infections: An analysis of possible contributing host factors. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2014, 10, 3513–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karauzum, H.; Haudenschild, C.C.; Moore, I.N.; Mahmoudieh, M.; Barber, D.L.; Datta, S.K. Lethal CD4 T Cell Responses Induced by Vaccination Against Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaulding, A.R.; Salgado-Pabon, W.; Merriman, J.A.; Stach, C.S.; Ji, Y.; Gillman, A.N.; Peterson, M.L.; Schlievert, P.M. Vaccination against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada-Matsuo, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Komatsuzawa, H. Role of two-component systems in the resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to antibacterial agents. Virulence 2011, 2, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Quadri, L.E.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M. Quorum sensing by peptide pheromones and two-component signal-transduction systems in Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 24, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, R.P.; Geisinger, E. Quorum sensing in staphylococci. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 541–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, R.P. Autoinduction and signal transduction in the regulation of staphylococcal virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1429–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, G.A.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. Role of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 in Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin-mediated cellular injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13473–13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakdi, S.; Tranum-Jensen, J. Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 55, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aman, M.J.; Adhikari, R.P. Staphylococcal bicomponent pore-forming toxins: Targets for prophylaxis and immunotherapy. Toxins 2014, 6, 950–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenesch, F.; Lina, G.; Henry, T. Staphylococcus aureus hemolysins, bi-component leukocidins, and cytolytic peptides: A redundant arsenal of membrane-damaging virulence factors? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Robles, T.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus Pore-Forming Toxins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 409, 121–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Braughton, K.R.; Kretschmer, D.; Bach, T.H.; Queck, S.Y.; Li, M.; Kennedy, A.D.; Dorward, D.W.; Klebanoff, S.J.; Peschel, A.; et al. Identification of novel cytolytic peptides as key virulence determinants for community-associated MRSA. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, A.T.; Raspanti, C.G.; Calzolari, A.; Nagel, R. Characterization of a Tn551-mutant of Staphylococcus aureus defective in the production of several exoproteins. Can. J. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, A.T.; Calzolari, A.; Cataldi, A.A.; Bogni, C.; Nagel, R. The sae locus of Staphylococcus aureus encodes a two-component regulatory system. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 177, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampone, H.; Martinez, G.L.; Giraudo, A.T.; Calzolari, A.; Nagel, R. In vivo expression of exoprotein synthesis with a Sae mutant of Staphylococcus aureus. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1996, 60, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Yu, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Landwehr, C.; Holmes, D.; Ji, Y. Inactivation of a two-component signal transduction system, SaeRS, eliminates adherence and attenuates virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 4655–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Willard, J.; Yeaman, M.R.; Cheung, A.L.; Bayer, A.S. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin gene (hla) expression by agr, sarA, and sae in vitro and in experimental infective endocarditis. J. Infect. Dis. 2006, 194, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, R.P.; Novick, R.P. Regulatory organization of the staphylococcal sae locus. Microbiology 2008, 154, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novick, R.P.; Jiang, D. The staphylococcal saeRS system coordinates environmental signals with agr quorum sensing. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, A.T.; Cheung, A.L.; Nagel, R. The sae locus of Staphylococcus aureus controls exoprotein synthesis at the transcriptional level. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 168, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.W.; Cho, H.; Jones, M.B.; Shatzkes, K.; Sun, F.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Q.; Peterson, S.N.; He, C.; Bae, T. The auxiliary protein complex SaePQ activates the phosphatase activity of sensor kinase SaeS in the SaeRS two-component system of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 86, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flack, C.E.; Zurek, O.W.; Meishery, D.D.; Pallister, K.B.; Malone, C.L.; Horswill, A.R.; Voyich, J.M. Differential regulation of staphylococcal virulence by the sensor kinase SaeS in response to neutrophil-derived stimuli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E2037–E2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cho, H.; Yeo, W.S.; Bae, T. The extracytoplasmic linker peptide of the sensor protein SaeS tunes the kinase activity required for staphylococcal virulence in response to host signals. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainiero, M.; Goerke, C.; Geiger, T.; Gonser, C.; Herbert, S.; Wolz, C. Differential target gene activation by the Staphylococcus aureus two-component system saeRS. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramundo, M.S.; Beltrame, C.O.; Botelho, A.M.; Coelho, L.R.; Silva-Carvalho, M.C.; Ferreira-Carvalho, B.T.; Nicolas, M.F.; Guedes, I.A.; Dardenne, L.E.; O’Gara, J.; et al. A unique SaeS allele overrides cell-density dependent expression of saeR and lukSF-PV in the ST30-SCCmecIV lineage of CA-MRSA. Int J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 306, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Schneewind, O. Vaccine protection against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.D.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Gardner, D.J.; Long, D.; Whitney, A.R.; Braughton, K.R.; Schneewind, O.; DeLeo, F.R. Targeting of alpha-hemolysin by active or passive immunization decreases severity of USA300 skin infection in a mouse model. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajcs, J.J.; Austin, M.S.; Sloop, G.D.; Moreau, J.M.; Hume, E.B.; Thompson, H.W.; McAleese, F.M.; Foster, T.J.; O’Callaghan, R.J. Corneal pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus strain Newman. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Berry, J.; Saward, L.; Cassan, R.; Han, X.; Aman, M.J.; Adhikari, R.P.; Karauzum, H. Staphlococcus Aureus Alpha-Hemolysin Antibodies. U.S. Patent WO/2013/013323, 31 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, S.; Ziebandt, A.K.; Ohlsen, K.; Schafer, T.; Hecker, M.; Albrecht, D.; Novick, R.; Gotz, F. Repair of global regulators in Staphylococcus aureus 8325 and comparative analysis with other clinical isolates. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 2877–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, D.; Lam, T.T.; Geiger, T.; Mainiero, M.; Engelmann, S.; Hussain, M.; Bosserhoff, A.; Frosch, M.; Bischoff, M.; Wolz, C.; et al. A point mutation in the sensor histidine kinase SaeS of Staphylococcus aureus strain Newman alters the response to biocide exposure. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 7306–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, A.; Pohl, M.; Bhakdi, S. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. Dual mechanism of binding to target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17195–17200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, R.P.; Kort, T.; Shulenin, S.; Kanipakala, T.; Ganjbaksh, N.; Roghmann, M.C.; Holtsberg, F.W.; Aman, M.J. Correction: Antibodies to S. aureus LukS-PV Attenuated Subunit Vaccine Neutralize a Broad Spectrum of Canonical and Non-Canonical Bicomponent Leukotoxin Pairs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; Rohde, M.; Oehmcke, S.; Miller, L.S.; Cheung, A.L.; Herwald, H.; Foster, S.; Medina, E. Immunological mechanisms underlying the genetic predisposition to severe Staphylococcus aureus infection in the mouse model. Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 173, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaan, A.N.; Reyes-Robles, T.; Badiou, C.; Cochet, S.; Boguslawski, K.M.; Yoong, P.; Day, C.J.; de Haas, C.J.; van Kessel, K.P.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Targets the Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines (DARC) to Lyse Erythrocytes. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronner, S.; Stoessel, P.; Gravet, A.; Monteil, H.; Prevost, G. Variable expressions of Staphylococcus aureus bicomponent leucotoxins semiquantified by competitive reverse transcription-PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3931–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karauzum, H.; Adhikari, R.P.; Sarwar, J.; Devi, V.S.; Abaandou, L.; Haudenschild, C.; Mahmoudieh, M.; Boroun, A.R.; Vu, H.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Structurally designed attenuated subunit vaccines for S. aureus LukS-PV and LukF-PV confer protection in a mouse bacteremia model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labandeira-Rey, M.; Couzon, F.; Boisset, S.; Brown, E.L.; Bes, M.; Benito, Y.; Barbu, E.M.; Vazquez, V.; Hook, M.; Etienne, J.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Panton-Valentine leukocidin causes necrotizing pneumonia. Science 2007, 315, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, C.P.; Boyle-Vavra, S.; Adem, P.V.; Lee, J.C.; Husain, A.N.; Clasen, J.; Daum, R.S. Comparison of virulence in community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pulsotypes USA300 and USA400 in a rat model of pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, J.; Kamio, Y. Bacterial two-component and hetero-heptameric pore-forming cytolytic toxins: Structures, pore-forming mechanism, and organization of the genes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 981–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaan, A.N.; van Strijp, J.A.G.; Torres, V.J. Leukocidins: Staphylococcal bi-component pore-forming toxins find their receptors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, T.; Goerke, C.; Mainiero, M.; Kraus, D.; Wolz, C. The virulence regulator Sae of Staphylococcus aureus: Promoter activities and response to phagocytosiFs-related signals. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3419–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.; Baba, T.; Hiramatsu, K.; Schneewind, O. Prophages of Staphylococcus aureus Newman and their contribution to virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Dajcs, J.J.; Thibodeaux, B.A.; Girgis, D.O.; O’Callaghan, R.J. Corneal virulence of Staphylococcus aureus in an experimental model of keratitis. DNA Cell Biol. 2002, 21, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.; DeDent, A.C.; Kim, H.K.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J.; Missiakas, D.M.; Schneewind, O. Abscess formation and alpha-hemolysin induced toxicity in a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus peritoneal infection. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3721–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, N.D.; Skaar, E.P. Molecular mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus iron acquisition. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.G.; Kim, H.K.; Burts, M.L.; Krausz, T.; Schneewind, O.; Missiakas, D.M. Genetic requirements for Staphylococcus aureus abscess formation and persistence in host tissues. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, E.P.; Humayun, M.; Bae, T.; DeBord, K.L.; Schneewind, O. Iron-source preference of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Science 2004, 305, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, V.J.; Stauff, D.L.; Pishchany, G.; Bezbradica, J.S.; Gordy, L.E.; Iturregui, J.; Anderson, K.L.; Dunman, P.M.; Joyce, S.; Skaar, E.P. A Staphylococcus aureus regulatory system that responds to host heme and modulates virulence. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivier, D.; Courcol, R.J. Iron depletion and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 141, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reniere, M.L.; Torres, V.J.; Skaar, E.P. Intracellular metalloporphyrin metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus. Biometals 2007, 20, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, R.P.; Karauzum, H.; Sarwar, J.; Abaandou, L.; Mahmoudieh, M.; Boroun, A.R.; Vu, H.; Nguyen, T.; Devi, V.S.; Shulenin, S.; et al. Novel structurally designed vaccine for S. aureus alpha-hemolysin: Protection against bacteremia and pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).