Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antiplatelet Peptide from Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification of Antiplatelet Aggregation Peptides from D. acutus Venom
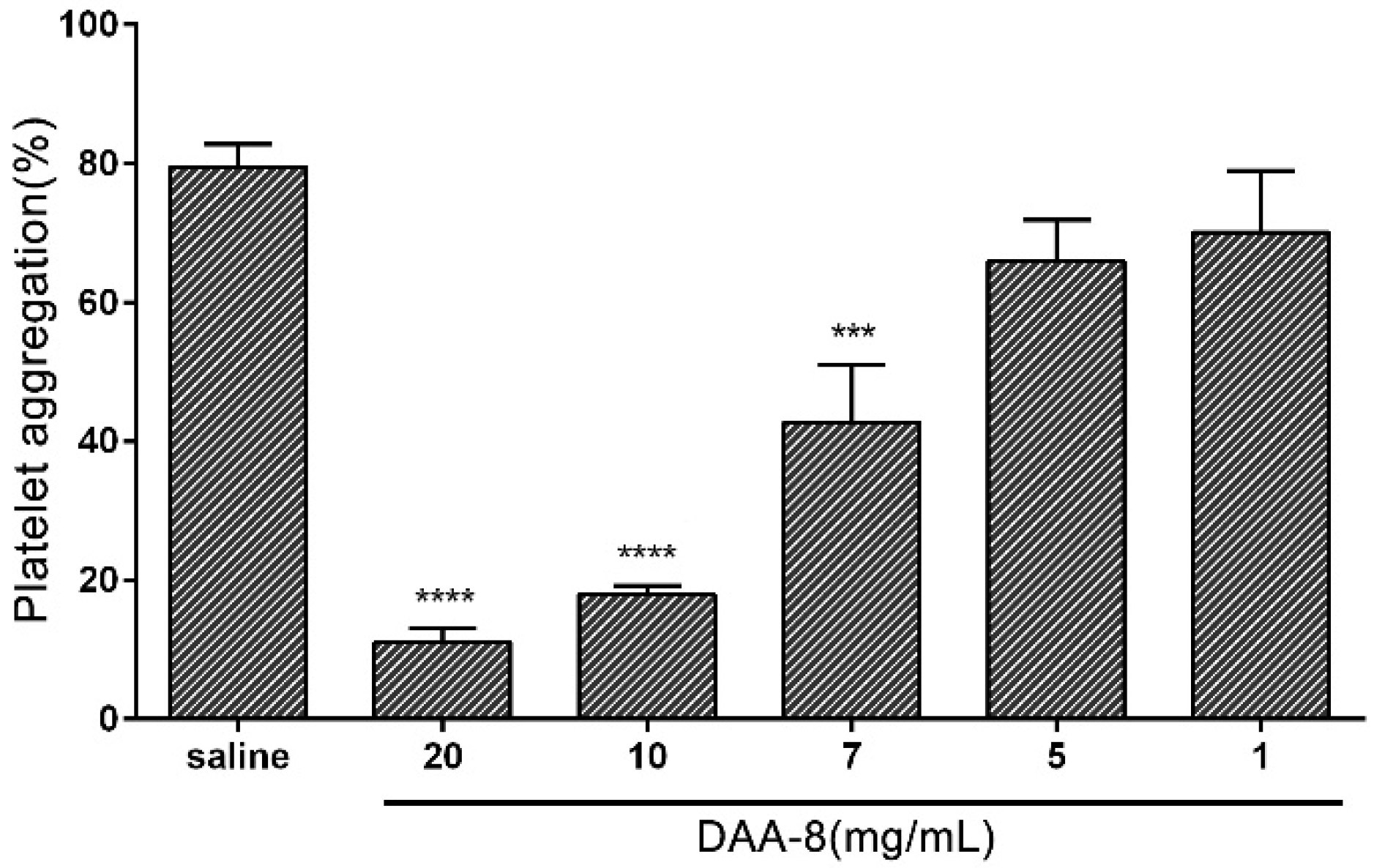
2.2. DAA-8 Inhibited Platelet Aggregation in Vitro
2.3. DAA-8 Inhibited Arterio-Venous Shunt Thrombosis in Rat
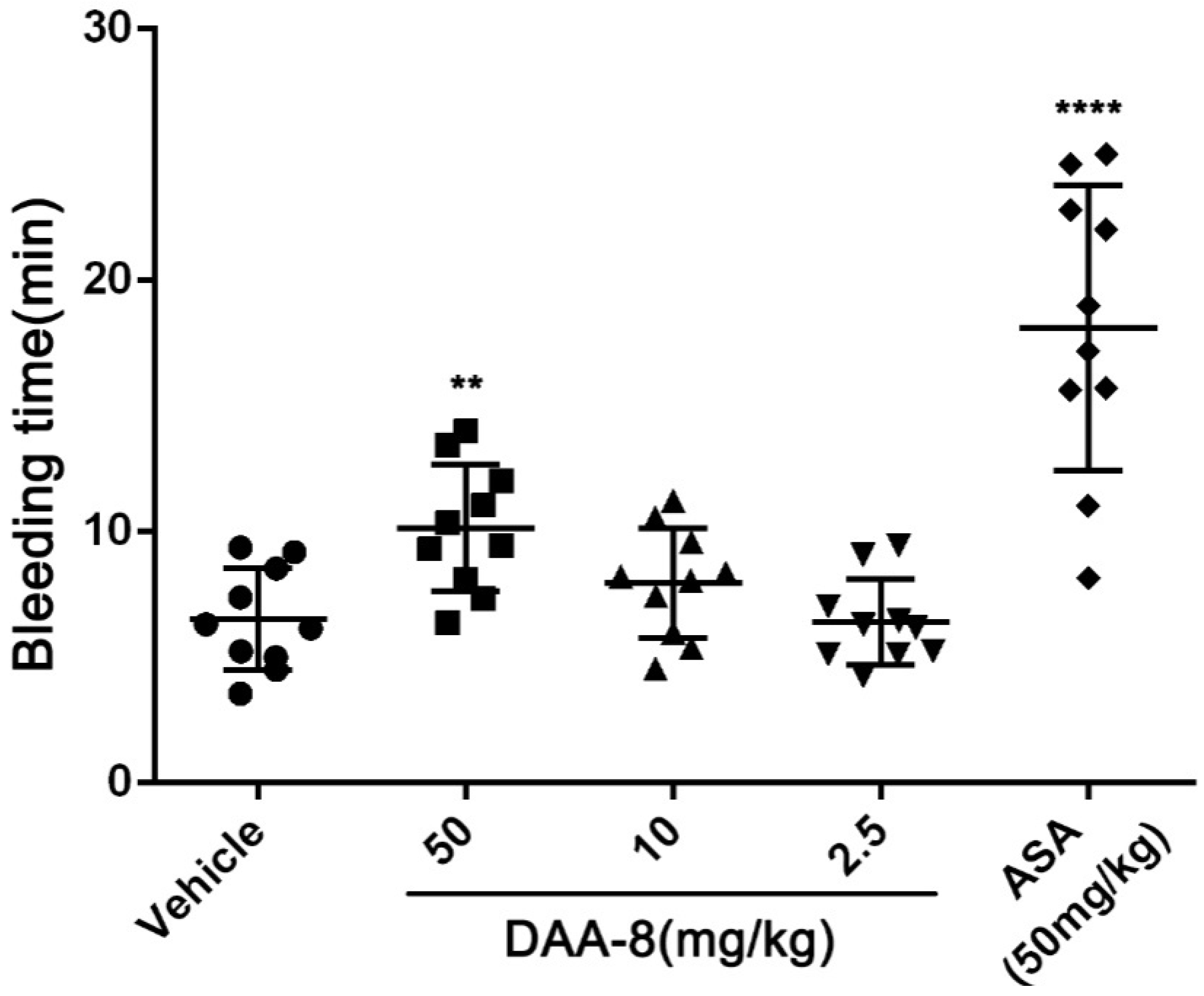
2.4. DAA-8 Exhibited Low Bleeding Risk in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials and Reagents
5.2. Animals and Human Samples
5.3. Purification of DAA-8
5.4. Platelet Preparation
5.5. Platelet Aggregation Assay
5.6. Arterio-Venous Shunt Model in Rats
5.7. Bleeding Time Assay
5.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goto, S.; Tomita, A. Antithrombotic therapy for prevention of various thrombotic diseases. Drug Dev. Res. 2013, 74, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenburgh, J.C.; Gross, P.L.; Weitz, J.I. Emerging anticoagulant strategies. Blood 2017, 129, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.P. The growing complexity of platelet aggregation. Blood 2007, 109, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegner, D.; Nieswandt, B. Platelet receptor signaling in thrombus formation. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 89, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Arthur, J.F.; Gardiner, E.E.; Andrews, R.K.; Zeng, L.; Xu, K. Regulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation by reactive oxygen species. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.Z.; He, A.D.; Wang, D.C.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, Y.J.; Liu, G.; Liang, M.L.; Da, X.W.; Yao, G.Q.; Xie, W.; et al. Antiplatelet activity of loureirin A by attenuating Akt phosphorylation: In vitro studies. Eur. J. Pharm. 2015, 746, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkin, Y.N. Animal venom studies: Current benefits and future developments. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenta, J.; Stach, Z.; Michalek, P. Envenoming by crotalid snake chinese moccasin agkistrodonacutus bite—A case report. Prague Med. Rep. 2015, 116, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.B.; Yu, Q.S.; Huang, G.W.; Tokeshi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kinjoh, K.; Kosugi, T. Hemostatic disturbances observed in patients with snakebite in south China. Toxicon 2000, 38, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajevic, T.; Leonardi, A.; Krizaj, I. Hemostatically active proteins in snake venoms. Toxicon 2011, 57, 627–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Wang, P.J.; Yu, J.S. Proteomic characterization of six Taiwanese snake venoms: Identification of species-specific proteins and development of a siscapa-mrm assay for cobra venom factors. J. Proteomics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S. Snake venoms and the hemostatic system. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1749–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, R.A.; Warrell, D.A. Action of snake venom components on the hemostatic system. Blood Rev. 1993, 7, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.A.; Niland, S.; Bracht, T.; Mormann, M.; Peter-Katalinic, J.; Pohlentz, G.; Stetefeld, J. The α2β1 integrin-specific antagonist rhodocetin is a cruciform, heterotetrameric molecule. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navdaev, A.; Lochnit, G.; Eble, J.A. The rhodocetinalphabeta subunit targets GPIb and inhibits von willebrand factor induced platelet activation. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Mizuno, H.; Atoda, H.; Morita, T. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray studies of flavocetin-A, a platelet glycoprotein Ib-binding protein from the habu snake venom. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1911–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, F.T.; Eble, J.A. The collagen-binding integrin α2β1 is a novel interaction partner of the Trimeresurus flavoviridis venom protein flavocetin-A. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Wu, W.B.; Huang, T.F. A snake venom metalloproteinase, kistomin, cleaves platelet glycoprotein VI and impairs platelet functions. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2008, 6, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samah, S.; Fatah, C.; Jean-Marc, B.; Safia, K.T.; Fatima, L.D. Purification and characterization of cc-lec, c-type lactose-binding lectin: A platelet aggregation and blood-clotting inhibitor from cerastescerastes venom. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Yoshikawa, T. Basic and translational research on proteinase-activated receptors: Implication of proteinase/proteinase-activated receptor in gastrointestinal inflammation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 108, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Simeon, M.; Simard, C.; Allouche, S.; Plane, A.F.; Ferchaud, V.; Brionne, M.; Rouet, R.; Nowoczyn, M.; Manrique, A.; et al. PAR1 contribution in acute electrophysiological properties of oral anticoagulants in rabbit pulmonary vein sleeve preparations. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2018, 32, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talati, N.; Kamato, D.; Piva, T.J.; Little, P.J.; Osman, N. Thrombin promotes PAI-1 expression and migration in keratinocytes via ERK dependent Smad linker region phosphorylation. Cell. Signal. 2018, 47, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, H.; Ishisaki, A.; Nakajima, K.; Kato, K.; Kozawa, O. A peptide isolated from αB-crystallin, which is a novel and potent inhibitor of platelet aggregation via dual prevention of PAR-1 and GPIb/V/IX. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 1, 2636–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, B.; Pollard, E.; Shen, Y.M. The novel protease-activated receptor 1 antagonist vorapaxar as a treatment for thrombosis in afibrinogenemia. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2018, 44, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, N.C.; Lipinski, M.J.; Lhermusier, T.; Waksman, R. Overview of the 2014 food and drug administration cardiovascular and renal drugs advisory committee meeting about vorapaxar. Circulation 2014, 130, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Shih, C.H.; Huang, T.F. Primary structure and antiplatelet mechanism of a snake venom metalloproteinase, acurhagin, from agkistrodonacutus venom. Biochimie 2005, 87, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zang, J.; Teng, M.; Niu, L. Structural basis of the autolysis of Aahiv suggests a novel target recognizing model for ADAM/reprolysin family proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.X.; Chen, J.S.; Zhou, Y.N.; Qiu, P.X.; Yan, G.M. Purification and biochemical characterization of F IIa, a fibrinolytic enzyme from Agkistrodon acutus venom. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Qiu, P.; Jiang, W.; Cai, X.; Ou, Y.; Su, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, W.; Yan, G. Recombinant fibrinogenase from Agkistrodon acutus venom protects against sepsis via direct degradation of fibrin and TNF-α. Biochem. Pharm. 2008, 76, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.; Li, Q.; Shen, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; He, S.; Wu, Q.; Hu, H.; Mao, X.; et al. Modulation of platelet activation and thrombus formation using a Pan-PI3K inhibitor S14161. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Tang, X.; Yi, W.; Li, Q.; Ren, L.; Liu, X.; Chu, C.; Ozaki, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L. Glaucocalyxin A inhibits platelet activation and thrombus formation preferentially via GPVI signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, F.; De Feo, V.; Caiazzo, E.; De Martino, L.; Cicala, C.; Mascolo, N. Tanshinone IIA, a major component of Salvia milthorriza bunge, inhibits platelet activation via erk-2 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharm. 2014, 155, 1236–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, D.P.; Ahuja, K.D.; Pittaway, J.; Shing, C.; Jacobson, G.A.; Jager, N.; Jurkovic, S.; Narkowicz, C.; Saunders, C.I.; Ball, M.; et al. In vitro antioxidant, antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory activity of Carpobrotusrossii (pigface) extract. J. Ethnopharm. 2011, 134, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Ming, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Su, W.; Kong, Y. A novel direct factor Xa inhibitory peptide with anti-platelet aggregation activity from agkistrodonacutus venom hydrolysates. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperzel, M.; Huetter, J. Evaluation of aprotinin and tranexamic acid in different in vitro and in vivo models of fibrinolysis, coagulation and thrombus formation. J. Thromb. Hemost. 2007, 5, 2113–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugidashi, A.; Asai, F.; Ogama, T.; Inoue, T.; Koike, H. The in vivo pharmacological profile of CS-747, anovel antiplatelet agent with platelet ADP receptor antagonist properties. Br. J. Pharm. 2000, 129, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antiplatelet Peptide from Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080332
Kong Y, Sun Q, Zhao Q, Zhang Y. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antiplatelet Peptide from Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom. Toxins. 2018; 10(8):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080332
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Yi, Qing Sun, Qi Zhao, and Yaqiong Zhang. 2018. "Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antiplatelet Peptide from Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom" Toxins 10, no. 8: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080332
APA StyleKong, Y., Sun, Q., Zhao, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Purification and Characterization of a Novel Antiplatelet Peptide from Deinagkistrodon acutus Venom. Toxins, 10(8), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10080332




