An Improved Method for the Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 in Human Serum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Detection of Stx1 and Stx2 in Stx-Spiked Human Serum by ELISA
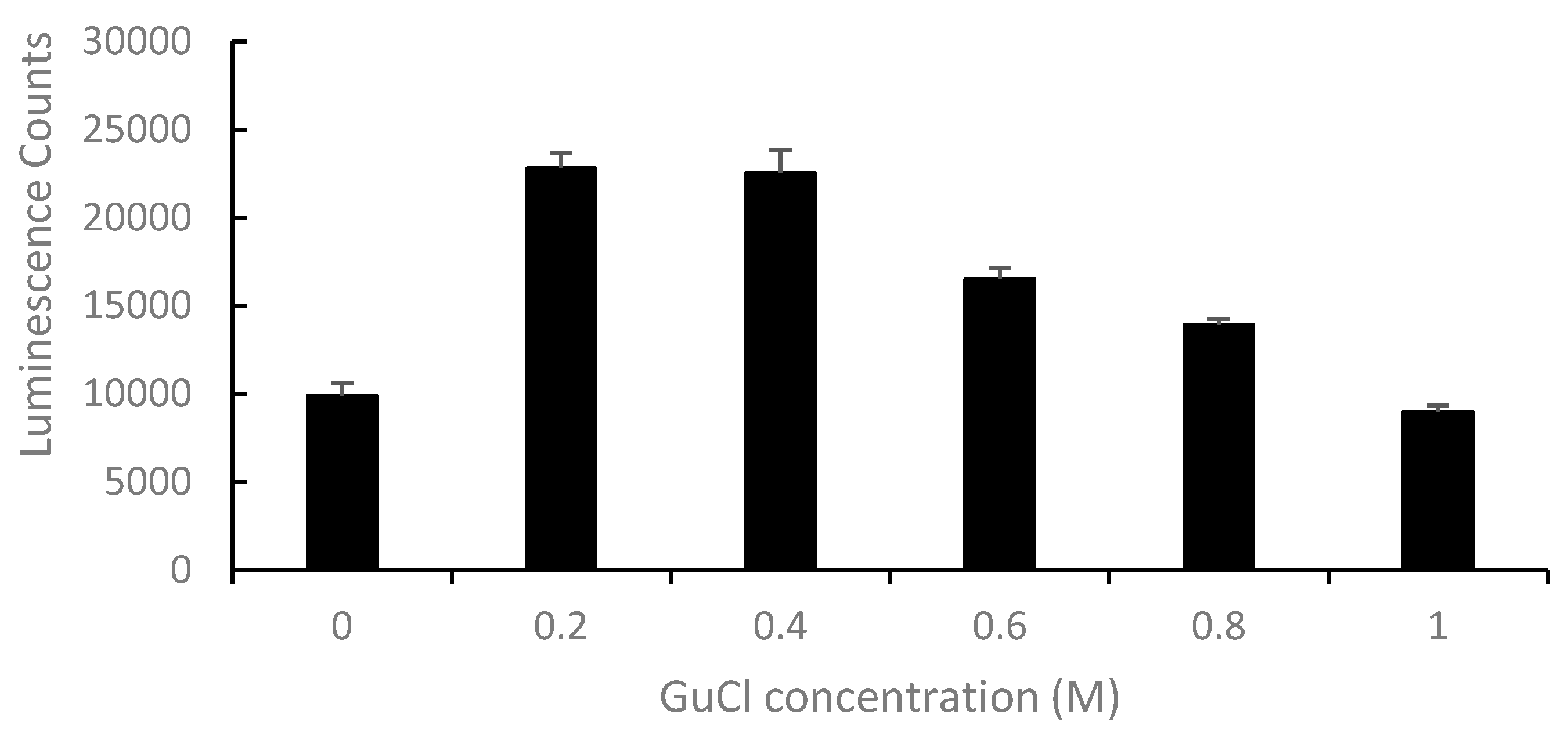
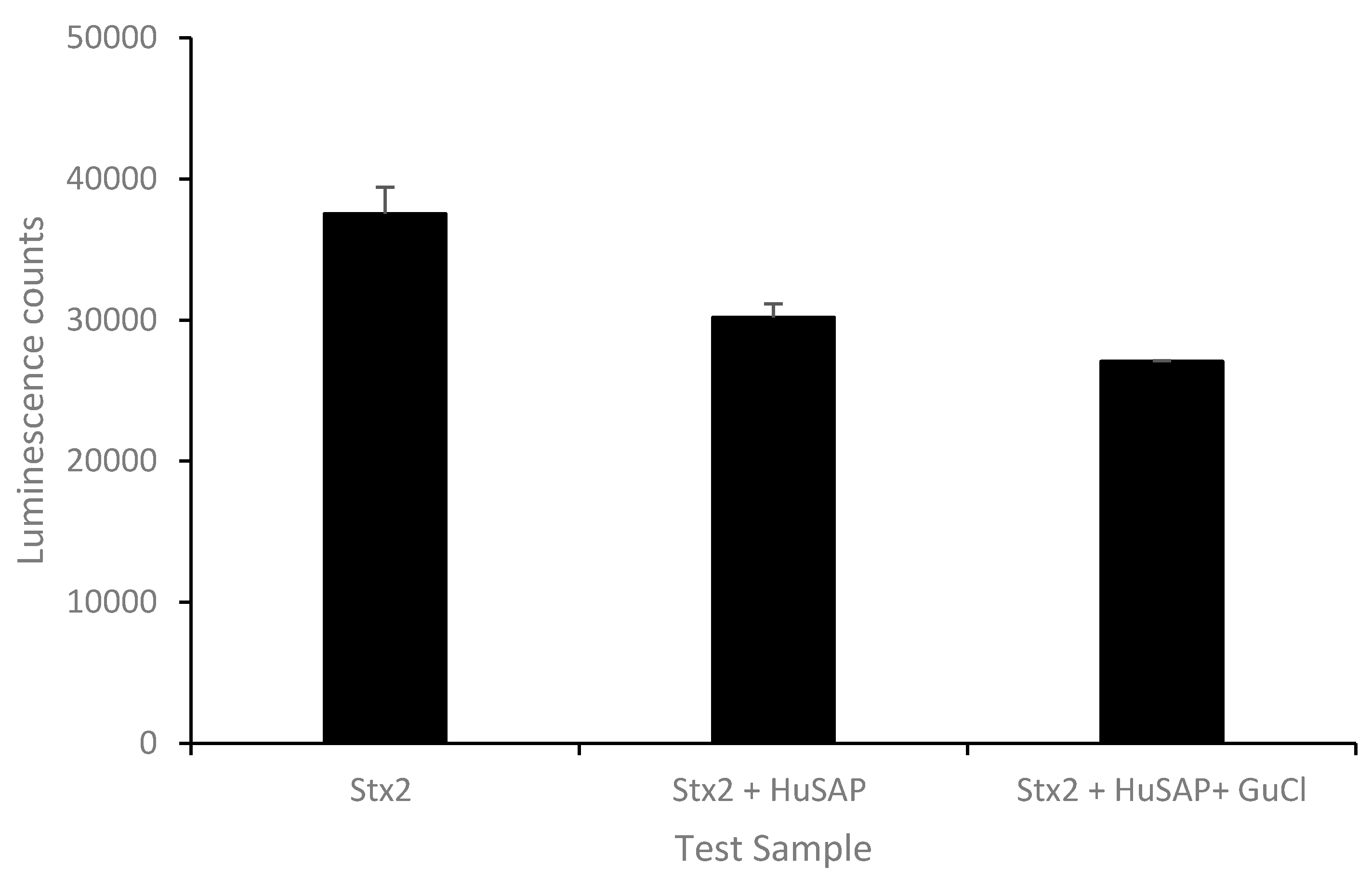
2.2. Effect of GuCl on Detection of Stx2 in Serum
2.3. Detection of Stx in Sera of STEC-Infected Patients
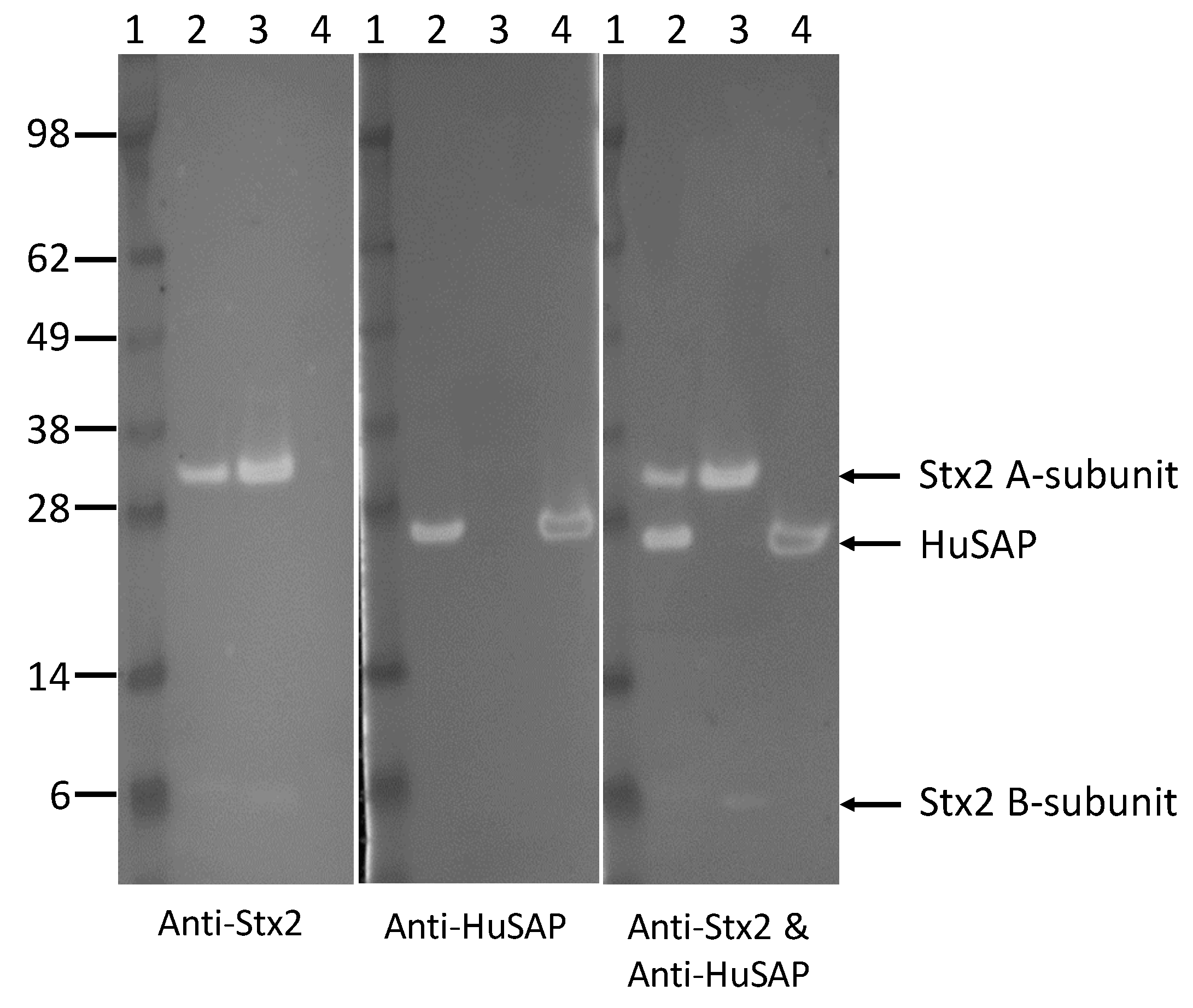
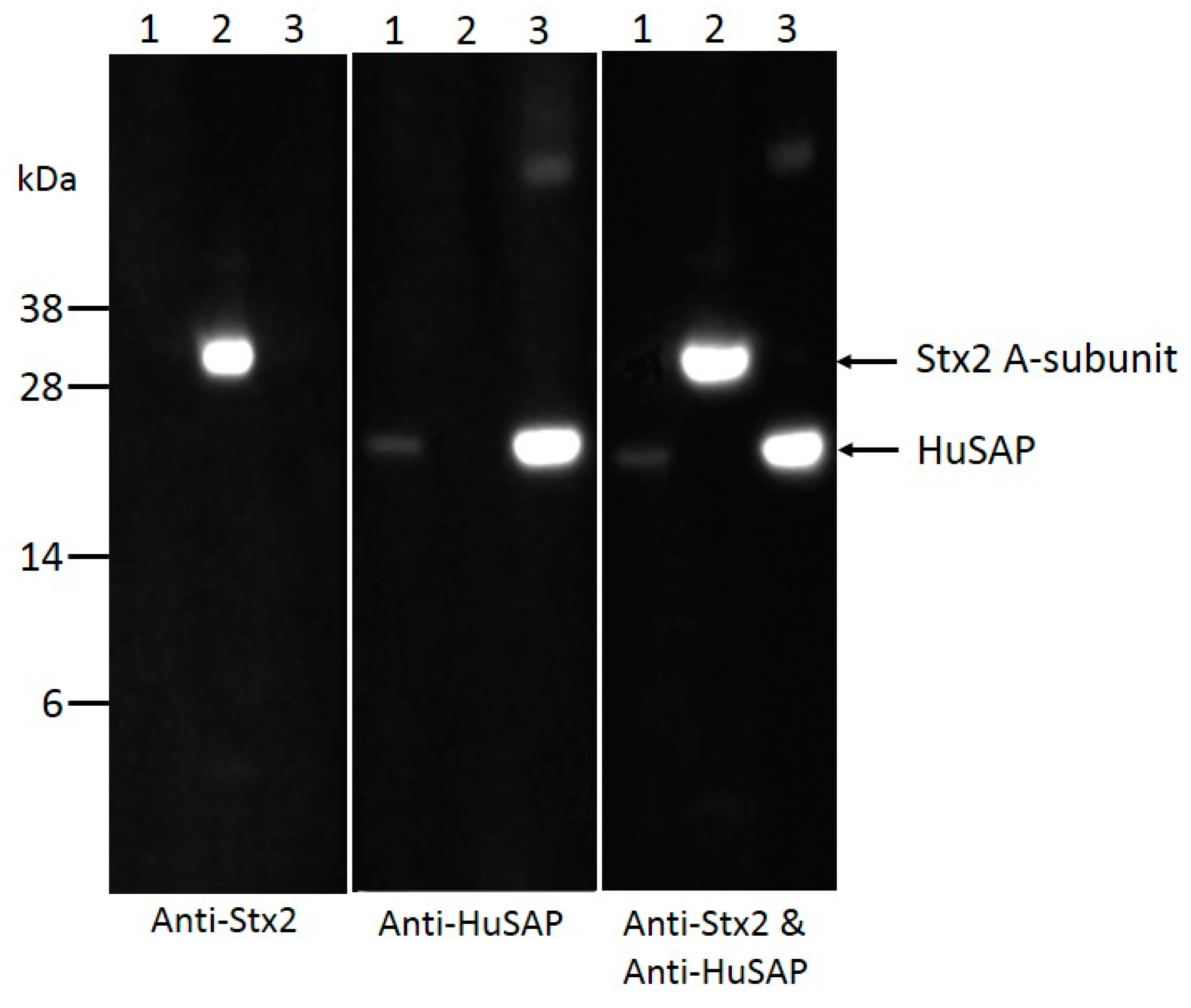
2.4. HuSAP Binds Specifically to the Stx2 in Human Serum Samples.
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Stx and Antibodies Used
4.2. Human Serum Samples
4.3. ELISAs for Detection of Stx1 and Stx2
4.4. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assays
4.5. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Western Blot
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, C.L.; Leibowitz, C.S.; Kurosawa, S.; Stearns-Kurosawa, D.J. Shiga toxins and the pathophysiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome in humans and animals. Toxins 2012, 4, 1261–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisaru, S. Management of hemolytic-uremic syndrome in children. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.S.; Mooney, J.C.; Brandt, J.R.; Staples, A.O.; Jelacic, S.; Boster, D.R.; Watkins, S.L.; Tarr, P.I. Risk factors for the hemolytic uremic syndrome in children infected with Escherichia coli O157:H7: A multivariable analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corogeanu, D.; Willmes, R.; Wolke, M.; Plum, G.; Utermohlen, O.; Kronke, M. Therapeutic concentrations of antibiotics inhibit Shiga toxin release from enterohemorrhagic E. coli O104:H4 from the 2011 german outbreak. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Pierard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.E.; Fujinaga, M.; Cherney, M.M.; Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Twiddy, E.M.; O’Brien, A.D.; James, M.N. Structure of Shiga toxin type 2 (Stx2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27511–27517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Tsurugi, K.; Yutsudo, T.; Takeda, Y.; Ogasawara, T.; Igarashi, K. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingwood, C.A. Verotoxins and their glycolipid receptors. Adv. Lipid Res. 1993, 25, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, A.W.; Bielaszewska, M.; Zhang, W.L.; Pulz, M.; Kuczius, T.; Ammon, A.; Karch, H. Escherichia coli harboring Shiga toxin 2 gene variants: Frequency and association with clinical symptoms. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louise, C.B.; Obrig, T.G. Specific interaction of Escherichia coli O157:H7-derived Shiga-like toxin II with human renal endothelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 1995, 172, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigotti, M.; Tazzari, P.L.; Ravanelli, E.; Carnicelli, D.; Rocchi, L.; Arfilli, V.; Scavia, G.; Minelli, F.; Ricci, F.; Pagliaro, P.; et al. Clinical relevance of Shiga toxin concentrations in the blood of patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, E.L.; Contrini, M.M.; Glatstein, E.; Ayala, S.G.; Santoro, R.; Ezcurra, G.; Teplitz, E.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sato, H.; Sakai, K.; et al. An epidemiologic surveillance of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli infection in argentinean children: Risk factors and serum Shiga-like toxin 2 values. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2012, 31, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitzan, M.; Klemt, M.; Steffens, R.; Muller-Wiefel, D.E. Differences in verotoxin neutralizing activity of therapeutic immunoglobulins and sera from healthy controls. Infection 1993, 21, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprioli, A.; Luzzi, I.; Seganti, L.; Marchetti, M.; Karmali, M.; Clarke, I.; Boyd, B. Frequent and Nature of Verocytotoxin 2 (VT2) Neutralizing Activity (NA) in Human and Animal Sera; Elsvier Science Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, T.; Tani, S.; Matsumoto Yi, Y.; Takeda, T. Serum amyloid P component is the Shiga toxin 2-neutralizing factor in human blood. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 41576–41579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.J.; Erickson-Beltran, M.L.; Skinner, C.B.; Patfield, S.A.; He, X. Mass spectrometry-based method of detecting and distinguishing type 1 and type 2 Shiga-like toxins in human serum. Toxins 2015, 7, 5236–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, J.; Yennawar, H.P.; Banerjee, S.; Luo, J.; Farber, G.K. The effect of denaturants on protein structure. Protein Sci. 1997, 6, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfilli, V.; Carnicelli, D.; Ardissino, G.; Torresani, E.; Scavia, G.; Brigotti, M. A rapid and sensitive method to measure the functional activity of Shiga toxins in human serum. Toxins 2015, 7, 4564–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Tani, S.; Motoki, M.; Matsumoto, Y. Role of Shiga toxin 2 (Stx2)-binding protein, human serum amyloid p component (HuSAP), in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections: Assumption from in vitro and in vivo study using HuSAP and anti-Stx2 humanized monoclonal antibody TMA-15. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, A.L.; Arvidsson, I.; Johansson, K.E.; Chromek, M.; Rebetz, J.; Loos, S.; Kristoffersson, A.C.; Bekassy, Z.D.; Morgelin, M.; Karpman, D. A novel mechanism of bacterial toxin transfer within host blood cell-derived microvesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villysson, A.; Tontanahal, A.; Karpman, D. Microvesicle involvement in Shiga toxin-associated infection. Toxins 2017, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigotti, M.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzi, A.E.; Tazzari, P.L.; Ricci, F.; Conte, R.; Carnicelli, D.; Procaccino, M.A.; Minelli, F.; Ferretti, A.V.; et al. Shiga toxins present in the gut and in the polymorphonuclear leukocytes circulating in the blood of children with hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, W.L.; Hohenester, E.; Pepys, M.B. Human serum amyloid P component is a single uncomplexed pentamer in whole serum. Mol. Med. 2000, 6, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skinner, C.; McMahon, S.; Rasooly, R.; Carter, J.M.; He, X. Purification and characterization of Shiga toxin 2f, an immunologically unrelated subtype of shiga toxin 2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, C.; Patfield, S.; Stanker, L.H.; Fratamico, P.; He, X. New high-affinity monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 1 facilitate the detection of hybrid Stx1/Stx2 in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; McMahon, S.; Skinner, C.; Merrill, P.; Scotcher, M.C.; Stanker, L.H. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Shiga toxin 2 and their application for toxin detection in milk. J. Immunol. Methods 2013, 389, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Patfield, S.; Hnasko, R.; Rasooly, R.; Mandrell, R.E. A polyclonal antibody based immunoassay detects seven subtypes of Shiga toxin 2 produced by Escherichia coli in human and environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprioli, A.; Scavia, G.; Morabito, S. Public health microbiology of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 263–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
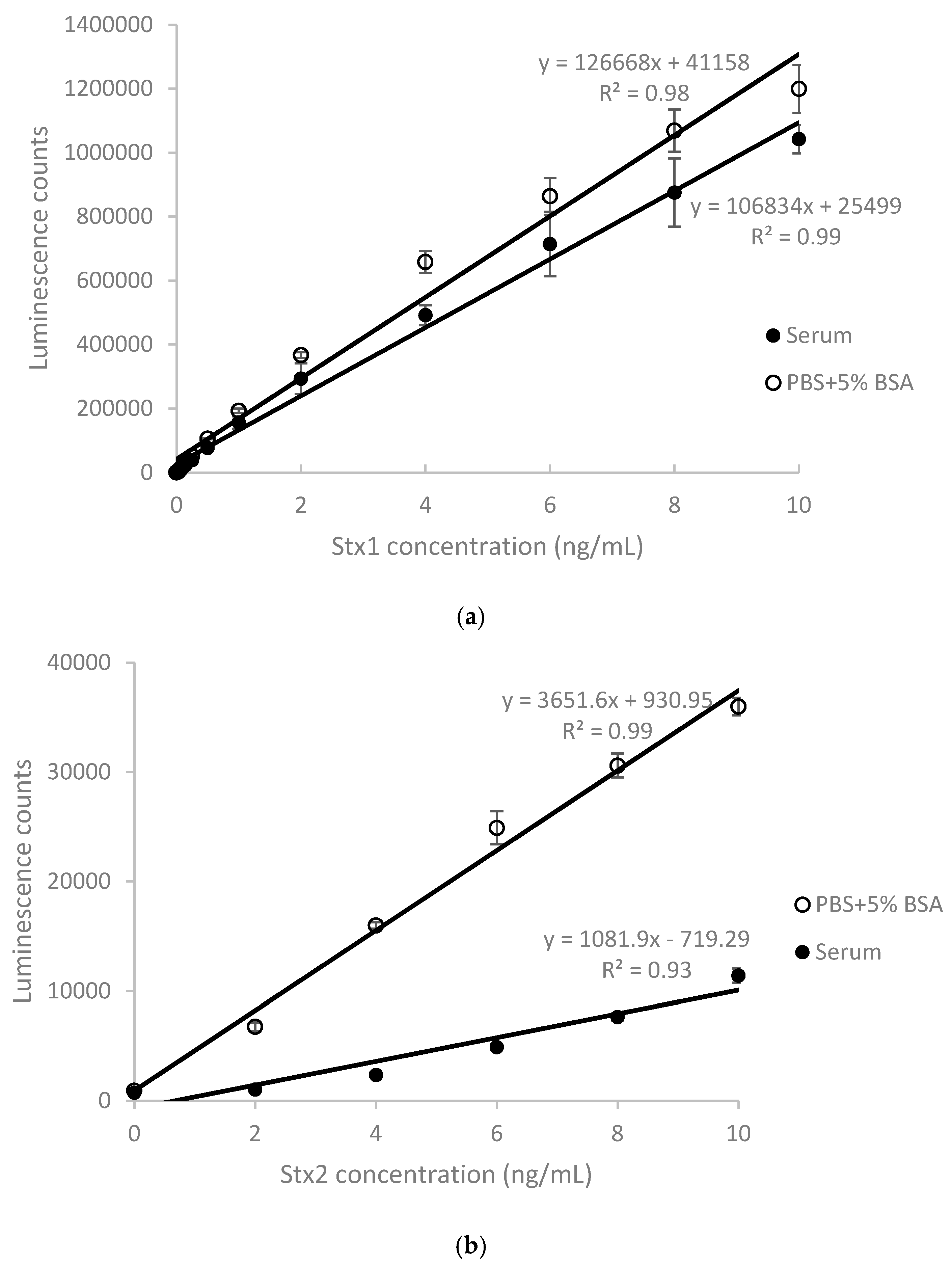
| Stx Added (ng/mL) | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stx1 recovery (%) ± SD | 79.8 ± 11.1 | 74.6 ± 0.8 | 82.5 ± 6.2 | 81.7 ± 4.9 | 86.9 ± 1.7 | 81.1 ± 4.9 |
| Stx2 recovery (%) ± SD | 4.8 ± 0.8 | 10.7 ± 0.8 | 17.4 ± 1.4 | 23.3 ± 0.6 | 30.4 ± 0.2 | 17.3 ± 0.7 |
| Stx2 Added (ng/mL) | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) ± SD | 41.23 ± 5.31 | 58.21 ± 1.04 | 66.90 ± 5.21 | 75.72 ± 4.66 | 68.71 ± 3.53 | 62.15 ± 3.95 |
| Pt. | Age (y) | Sex | Clinical Symptoms | E. coli Serotype a | Detection of stx Genes in Feces | Stx2 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.3 | F | Diarrhea | nd b | stx2+ by PCR-based rev dot blot, RT-PCR | 2.99 ± 0.20 |
| 2 | 0.2 | M | Bloody diarrhea | O157 | stx2+ by PCR-based rev dot blot | 0.40 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | 0.8 | M | diarrhea, proteinuria | O157 | stx2+ by PCR-based rev dot blot | 4.89 ± 0.77 |
| 4 | 5.6 | M | diarrhea, proteinuria | O127 | stx2+ by PCR-based rev dot blot, RT-PCR | 3.50 ± 0.75 |
| 5 | 6.3 | M | Proteinuria | O127 | stx2+ by RT-PCR | 3.57 ± 0.04 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Ardissino, G.; Patfield, S.; Cheng, L.W.; Silva, C.J.; Brigotti, M. An Improved Method for the Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 in Human Serum. Toxins 2018, 10, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020059
He X, Ardissino G, Patfield S, Cheng LW, Silva CJ, Brigotti M. An Improved Method for the Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 in Human Serum. Toxins. 2018; 10(2):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020059
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaohua, Gianluigi Ardissino, Stephanie Patfield, Luisa W. Cheng, Christopher J. Silva, and Maurizio Brigotti. 2018. "An Improved Method for the Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 in Human Serum" Toxins 10, no. 2: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020059
APA StyleHe, X., Ardissino, G., Patfield, S., Cheng, L. W., Silva, C. J., & Brigotti, M. (2018). An Improved Method for the Sensitive Detection of Shiga Toxin 2 in Human Serum. Toxins, 10(2), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10020059






