Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
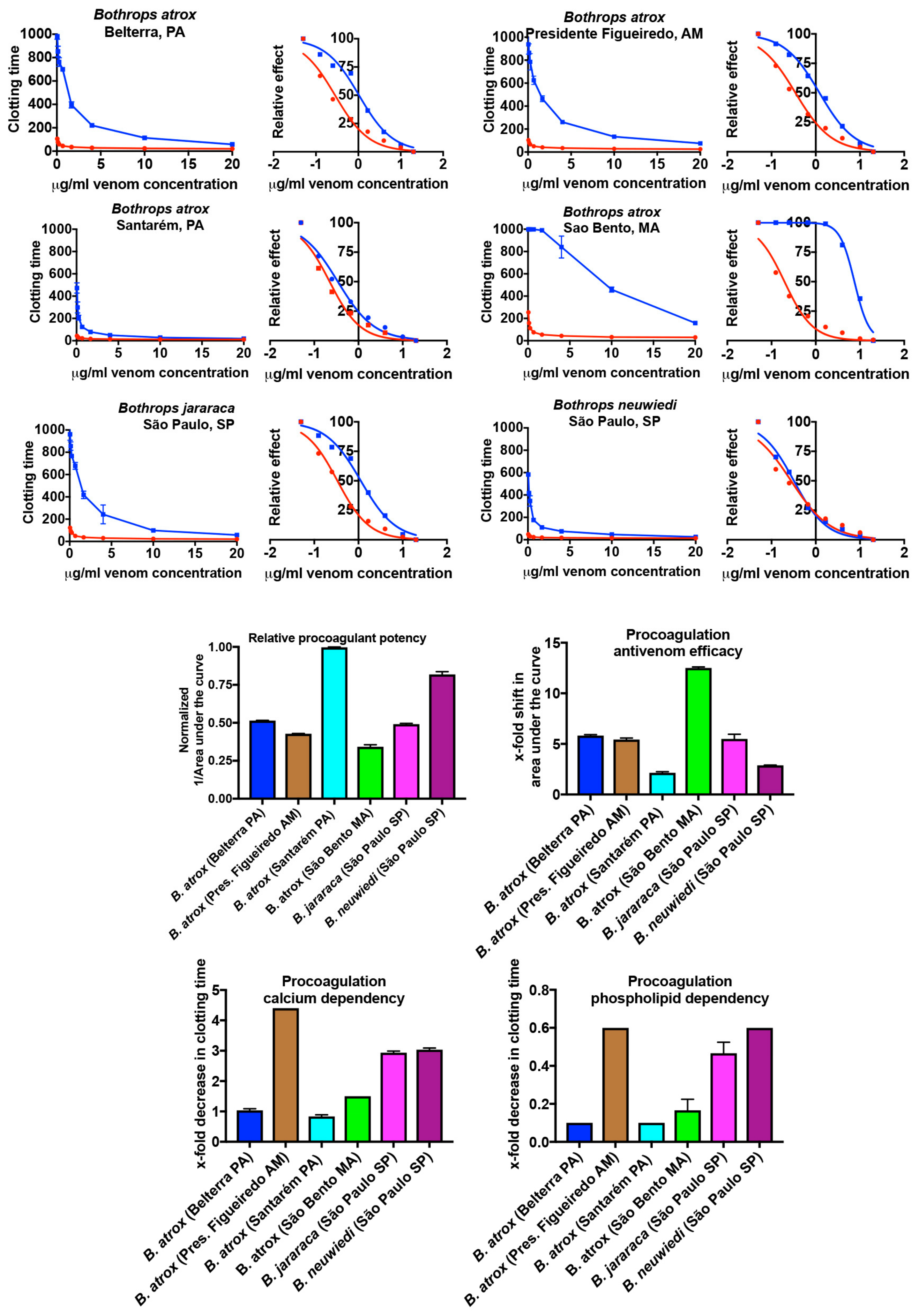
2.1. Coagulation Analyses Using a Stago STA-R Max Coagulation Analysis Robot
2.1.1. Plasma Clotting Activity
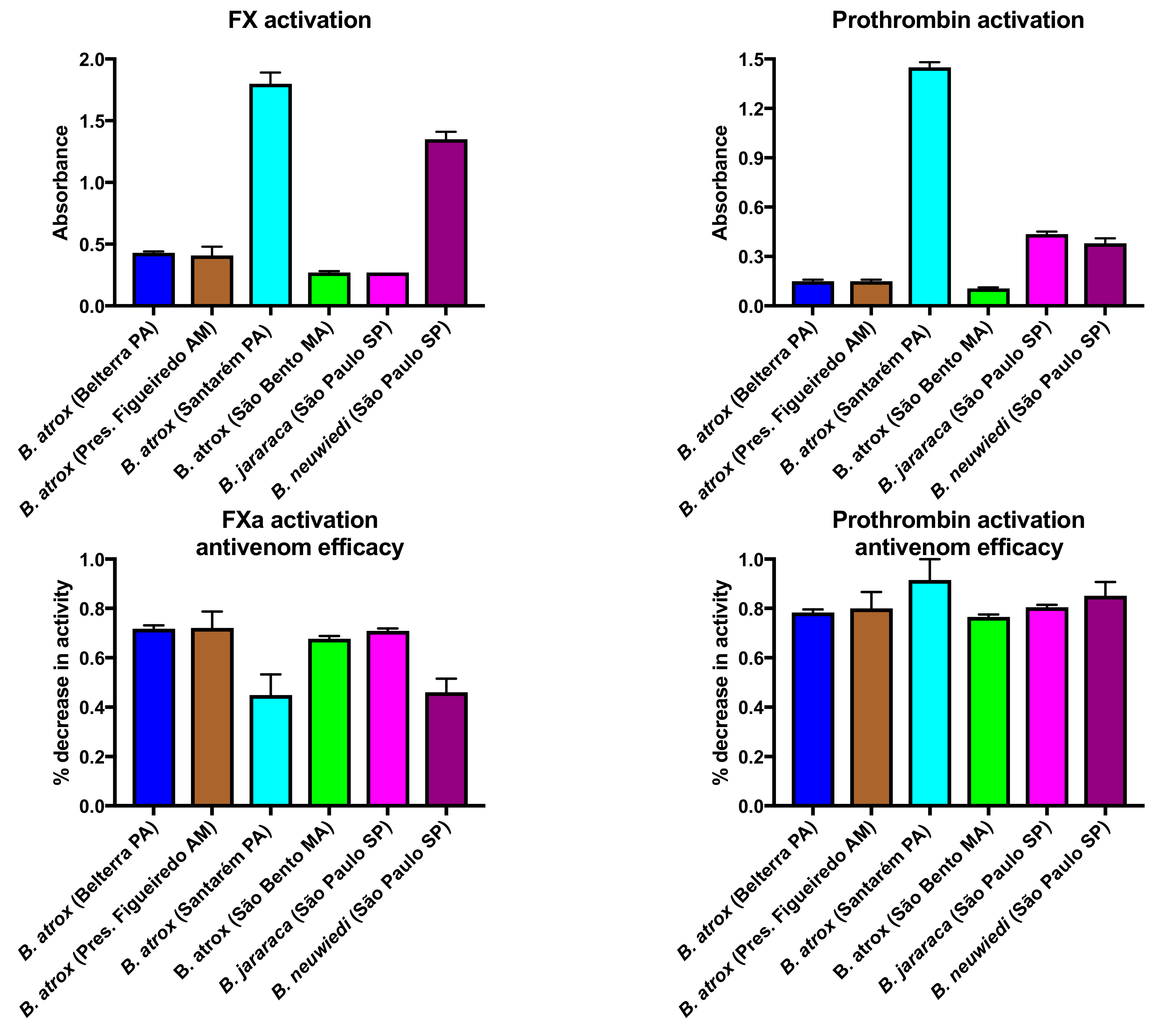
2.1.2. Factor X and Prothrombin Activation Activity
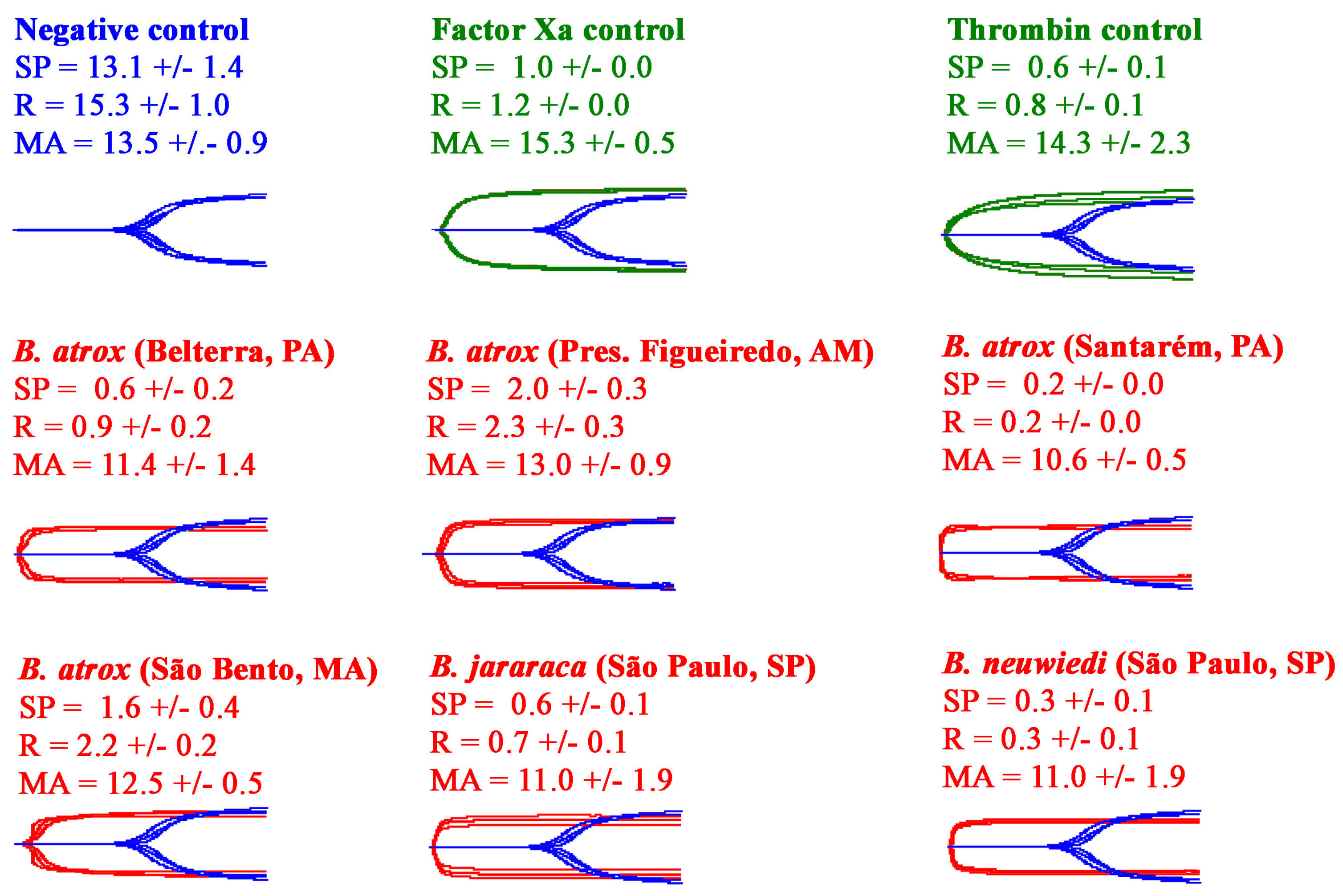
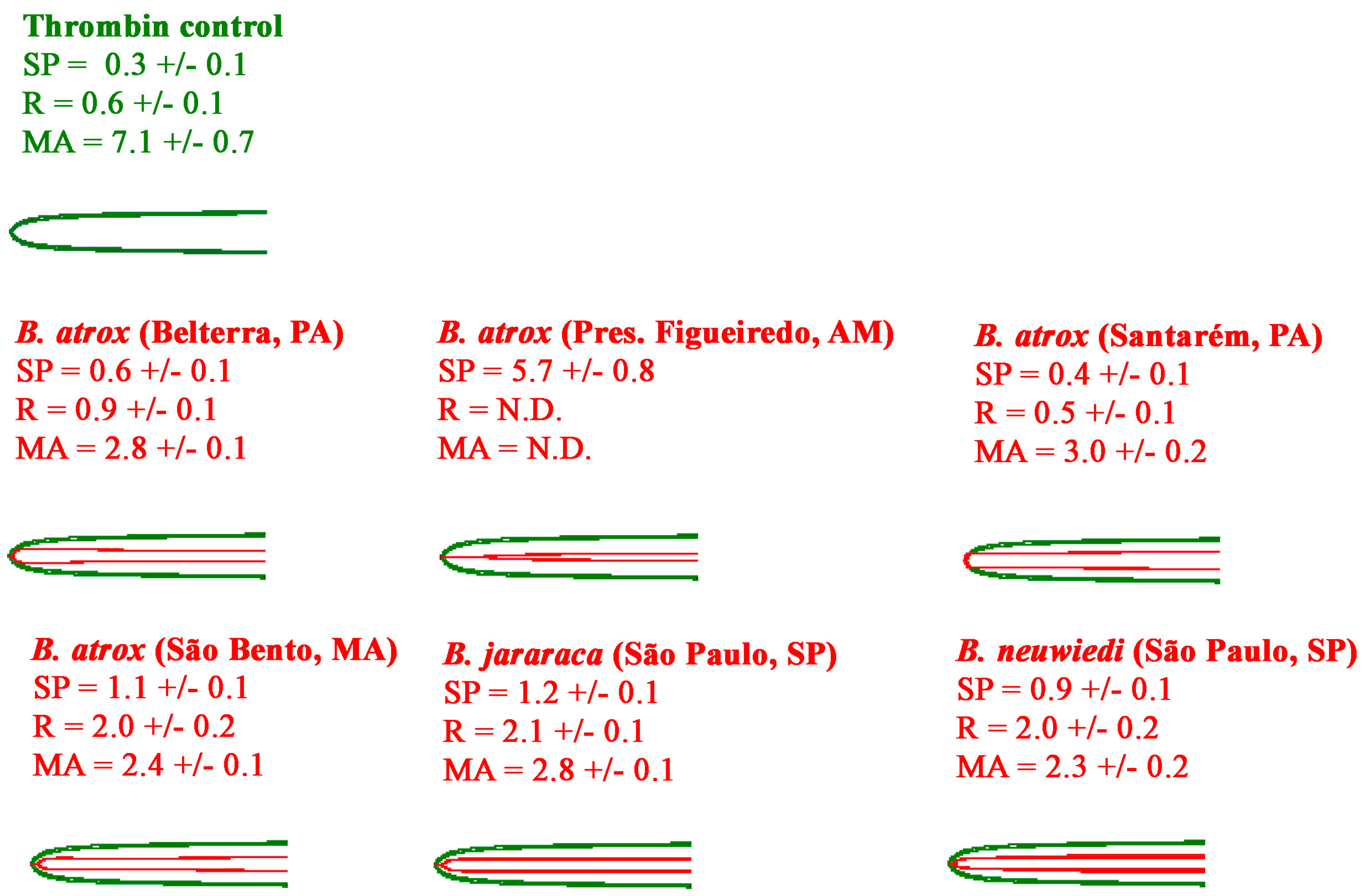
2.2. Thromboelastography Analyses Using Haemonetics TEG5000s
2.2.1. Thromboelastography Tests Using Plasma
2.2.2. Thromboelastography Tests Using Fibrinogen
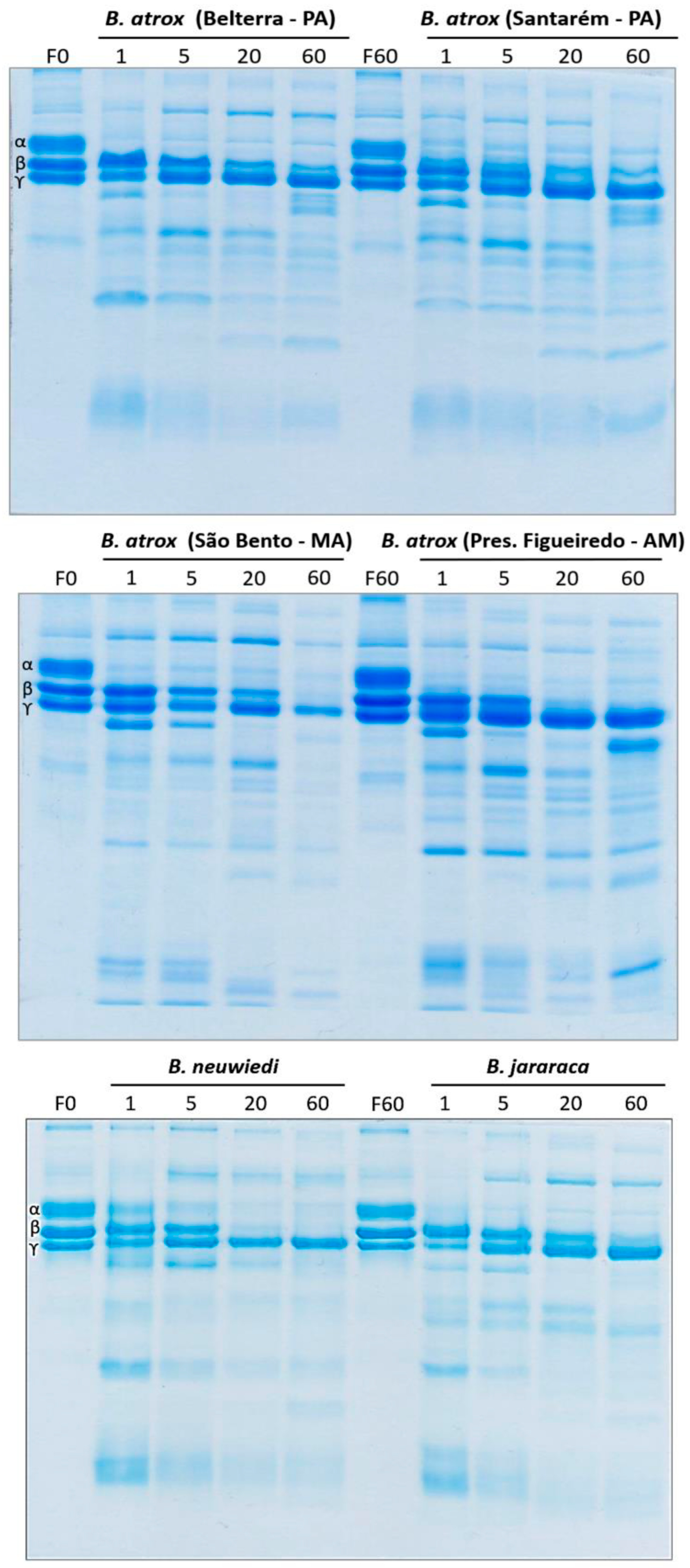
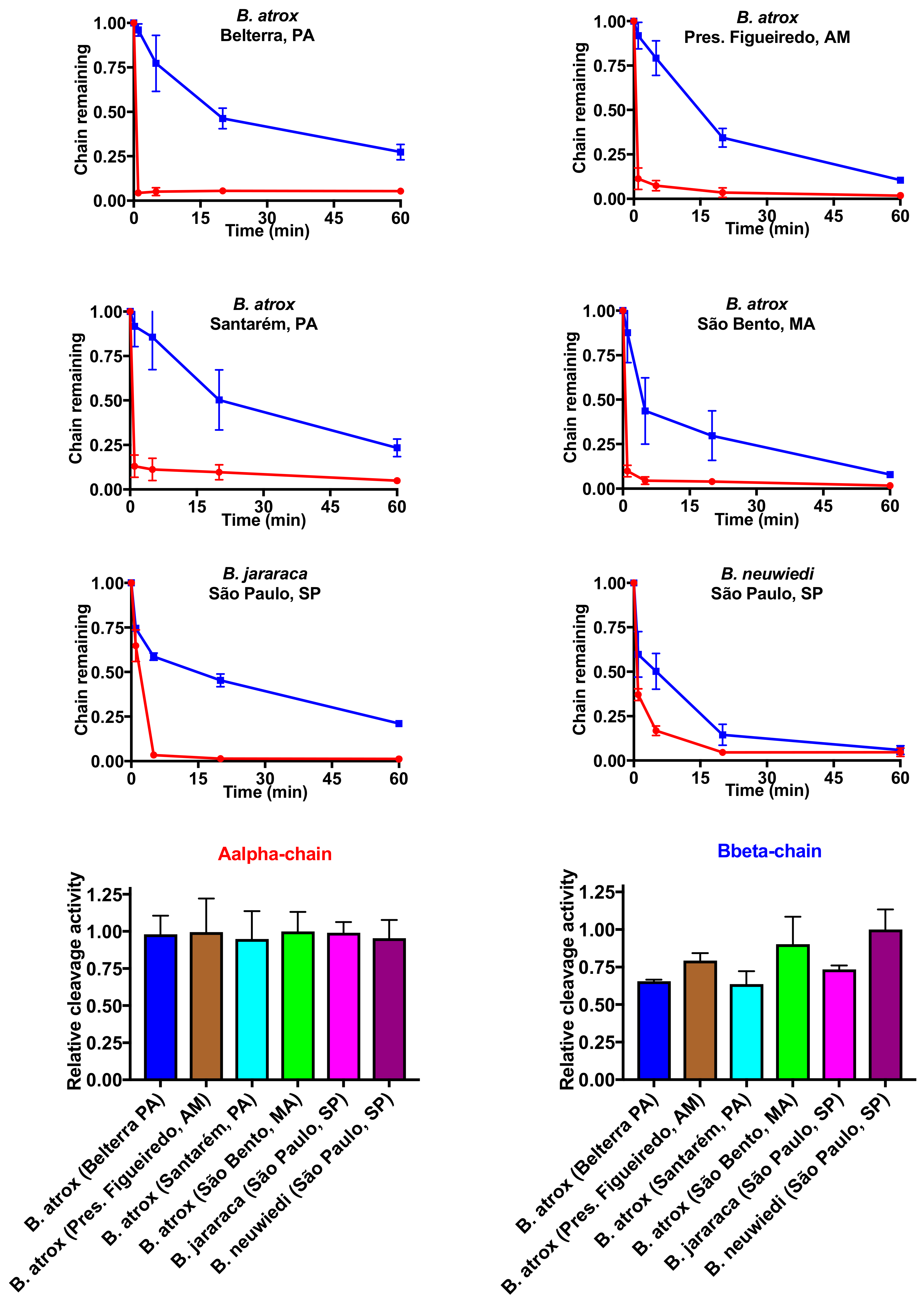
2.3. Fibrinogen Gel Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Venoms
4.2. Antivenom
4.3. Plasmas
4.4. Coagulation Analyses
4.5. Factor X and Prothrombin Activation Activity
4.6. Thromboelastography and Fibrinogenolytic Analyses
4.7. Cleavage of Fibrinogen
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fry, B.G. Snakebite: When the human touch becomes a bad touch. Toxins 2018, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Sunagar, K.; Casewell, N.R.; Kochva, E.; Roelants, K.; Scheib, H.; Wüster, W.; Vidal, N.; Young, B.; Burbrink, F.; et al. The origin and evolution of the Toxicofera reptile venom system. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, M.H.A.; van ‘t Veer, C.; Reitsma, P.H. Molecular Biology and Biochemistry of the Coagulation Factors and Pathways of Hemostasis. In Williams Hematology, 9th ed.; Kaushansky, K., Lichtman, M.A., Prchal, J.T., Levi, M.M., Press, O.W., Burns, L.J., Caligiuri, M., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chester, A.; Crawford, G.P. In vitro coagulant properties of venoms from Australian snakes. Toxicon 1982, 20, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, C.; Arbuckle, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Debono, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dashevsky, D.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Hay, C.; Bush, B.; et al. Catch a tiger snake by its tail: Differential toxicity, co-factor dependence and antivenom efficacy in a procoagulant clade of Australian venomous snakes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2017, 202, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oulion, B.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Lister, C.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Rogalski, A.; Violette, A.; et al. Factor X activating Atractaspis snake venoms and the relative coagulotoxicity neutralising efficacy of African antivenoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirkle, H.; McIntosh, M.; Theodor, I.; Vernon, S. Activation of prothrombin with taipan snake venom. Thromb. Res. 1972, 1, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A.; Soerensen, C.; Op den Brouw, B.; Lister, C.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Gloria, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Casewell, N.R.; Gutierrez, J.M.; et al. Differential procoagulant effects of saw-scaled viper (Serpentes: Viperidae: Echis) snake venoms on human plasma and the narrow taxonomic ranges of antivenom efficacies. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 280, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debono, J.; Dobson, J.; Casewell, N.R.; Romilio, A.; Li, B.; Kurniawan, N.; Mardon, K.; Weisbecker, V.; Nouwens, A.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Coagulating colubrids: Evolutionary, pathophysiological and biodiscovery implications of venom variations between boomslang (Dispholidus typus) and twig snake (Thelotornis mossambicanus). Toxins 2017, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; Boyer, L.V.; Redford, D.T.; Ford, P. Thrombelastographic characterization of the thrombin-like activity of Crotalus simus and Bothrops asper venoms. Blood Coagul. Fibrinol. 2017, 28, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, V.G.; Frank, N.; Matika, R.W. Carbon monoxide inhibits hemotoxic activity of Elapidae venoms: Potential role of heme. BioMetals 2017, 31, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Woods, D.; Alley, S.; O′Leary, M.A.; Seldon, M.; Lincz, L.F. Endogenous thrombin potential as a novel method for the characterization of procoagulant snake venoms and the efficacy of antivenom. Toxicon 2010, 56, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O′Leary, M.A.; Isbister, G.K. A turbidimetric assay for the measurement of clotting times of procoagulant venoms in plasma. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2010, 61, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Still, K.; Nandlal, R.; Slagboom, J.; Somsen, G.; Casewell, N.; Kool, J. Multipurpose HTS coagulation analysis: Assay development and assessment of coagulopathic snake venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.; Segura, A.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Estrada, R.; Cerdas, M.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; Winkel, K.D.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of caprylic acid-fractionated IgG antivenom for the treatment of Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) envenoming in Papua New Guinea. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, V.; White, J.; Mirtschin, P.J. Comparative study on the procoagulant from the venom of Australian brown snakes (Elapidae; Pseudonaja spp.). Toxicon 1994, 32, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resiere, D.; Arias, A.S.; Villalta, M.; Rucavado, A.; Brouste, Y.; Cabie, A.; Neviere, R.; Cesaire, R.; Kallel, H.; Megarbane, B.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of the neutralizing ability of a monospecific antivenom for the treatment of envenomings by Bothrops lanceolatus in Martinique. Toxicon 2018, 148, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, S.; Slagboom, J.; Alomran, N.; Pla, D.; Alhamdi, Y.; King, S.I.; Bolton, F.M.S.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Vonk, F.J.; Toh, C.-H.; et al. The paraspecific neutralisation of snake venom induced coagulopathy by antivenoms. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Comstock (Cornell University Press): Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake bites in Central and South America: Epidemiology, clinical features and clinical management. In The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 709–761. [Google Scholar]
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; de Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; Premaratna, R.; Savioli, L.; Lalloo, D.G.; de Silva, H.J. The global burden of snakebite: A literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, F.; Málaque, C. Acidente botrópico. In Animais Peçonhentos no Brasil: Biologia, clínica e terapêutica dos acidentes; 2th ed., Cardoso, J., França, F., Wen, F., Málaque, C., Haddad-Junior, V., Eds.; Sarvier: São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2009; pp. 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Baldo, C.; Jamora, C.; Yamanouye, N.; Zorn, T.M.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Mechanisms of vascular damage by hemorrhagic snake venom metalloproteinases: Tissue distribution and in situ hydrolysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Queiroz, M.R.; de Sousa, B.B.; da Cunha Pereira, D.F.; Mamede, C.C.N.; Matias, M.S.; de Morais, N.C.G.; de Oliveira Costa, J.; de Oliveira, F. The role of platelets in hemostasis and the effects of snake venom toxins on platelet function. Toxicon 2017, 133, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Metalloproteases affecting blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and platelet aggregation from snake venoms: Definition and nomenclature of interaction sites. Toxins 2016, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T. Structures and functions of snake venom CLPs (C-type lectin-like proteins) with anticoagulant-, procoagulant-, and platelet-modulating activities. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, T. Structure-function relationships of C-type lectin-related proteins. Pathophysiol. Haemost. Thromb. 2005, 34, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, S.M. The long road of research on snake venom serine proteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Rash, L.D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Isbister, G.K. Defining the role of post-synaptic alpha-neurotoxins in paralysis due to snake envenoming in humans. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardal, P.P.; Souza, S.M.; Monteiro, M.R.; Fan, H.W.; Cardoso, J.L.; Franca, F.O.; Tomy, S.C.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; de Sousa-e-Silva, M.C.; Colombini, M.; et al. Clinical trial of two antivenoms for the treatment of Bothrops and Lachesis bites in the north eastern Amazon region of Brazil. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 98, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga, M.M.; Otero, R.; Nunez, V.; Toro, M.F.; Diaz, A.; Gutierrez, J.M. Ontogenetic variability of Bothrops atrox and Bothrops asper snake venoms from Colombia. Toxicon 2003, 42, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guercio, R.A.; Shevchenko, A.; Shevchenko, A.; Lopez-Lozano, J.L.; Paba, J.; Sousa, M.V.; Ricart, C.A. Ontogenetic variations in the venom proteome of the Amazonian snake Bothrops atrox. Proteome Sci. 2006, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Perez, A.; Borges, A.; Vargas, A.M.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Mourao, R.H.; et al. Snake population venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox: Paedomorphism along its transamazonian dispersal and implications of geographic venom variability on snakebite management. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunez, V.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; De La Torre, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox venoms from Colombia and the Amazon regions of Brazil, Peru and Ecuador suggest the occurrence of geographic variation of venom phenotype by a trend towards paedomorphism. J. Proteom. 2009, 73, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, A.M.; Rodriguez-Acosta, A.; Giron, M.E.; Aguilar, I.; Guerrero, B. A comparative analysis of the clotting and fibrinolytic activities of the snake venom (Bothrops atrox) from different geographical areas in Venezuela. Thromb. Res. 2007, 120, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amazonas, D.R.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Nicolau, C.A.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Mourao, R.H.V.; Grazziotin, F.G.; Rokyta, D.R.; Gibbs, H.L.; Valente, R.H.; et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying intraspecific variation in snake venom. J. Proteom. 2018, 181, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, H.L.; Sovic, M.; Amazonas, D.; Chalkidis, H.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Moura-Da-Silva, A.M. Recent lineage diversification in a venomous snake through dispersal across the River Amazon. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 123, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, L.F.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Nicolau, C.A.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Amazonas, D.R.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Mourao, R.H.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Valente, R.H.; et al. Functional proteomic analyses of Bothrops atrox venom reveals phenotypes associated with habitat variation in the Amazon. J. Proteom. 2017, 159, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, M.F.; Maruyama, M.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Antonio, L.C. Comparative study of nine Bothrops snake venoms from adult female snakes and their offspring. Toxicon 1991, 29, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bénard-Valle, M.; Neri-Castro, E.E.; Fry, B.G.; Boyer, L.; Cochran, C.; Alam, M.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Paniagua, D.; Olvera-Rodríguez, F.; Koludarov, I.; et al. Antivenom research and development. In Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology and Biodiscovery; Fry, B.G., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Scheib, H.; Gren, E.C.; Cochran, C.; Person, C.E.; Koludarov, I.; Kelln, W.; Hayes, W.K.; King, G.F.; et al. Intraspecific venom variation in the medically significant Southern Pacific Rattlesnake (Crotalus oreganus helleri): Biodiscovery, clinical and evolutionary implications. J. Proteom. 2014, 99, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, H.; Bon, C. Blood coagulation induced by the venom of Bothrops atrox. 2. Identification, purification, and properties of two factor X activators. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, H.; Bon, C. Blood coagulation induced by the venom of Bothrops atrox. 1. Identification, purification, and properties of a prothrombin activator. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, H.; Dumarey, C.; Bon, C. Blood coagulation induced by Bothrops atrox venom: Identification and properties of a factor X activator. Biochimie 1983, 65, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, M.L.; Sano-Martins, I.S. Different clotting mechanisms of Bothrops jararaca snake venom on human and rabbit plasmas. Toxicon 1993, 31, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, M.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Tomy, S.C.; Antonio, L.C.; Sugiki, M.; Mihara, H. Prothrombin and factor X activating properties of Bothrops erythromelas venom. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1992, 86, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.B.; Schattner, M.; Ramos, C.R.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Guarnieri, M.C.; Lazzari, M.A.; Sampaio, C.A.; Pozner, R.G.; Ventura, J.S.; Ho, P.L.; et al. A prothrombin activator from Bothrops erythromelas (jararaca-da-seca) snake venom: Characterization and molecular cloning. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senis, Y.A.; Kim, P.Y.; Fuller, G.L.; Garcia, A.; Prabhakar, S.; Wilkinson, M.C.; Brittan, H.; Zitzmann, N.; Wait, R.; Warrell, D.A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of cotiaractivase, a novel low molecular weight prothrombin activator from the venom of Bothrops cotiara. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardoni, J.L.; Sousa, L.F.; Wermelinger, L.S.; Lopes, A.S.; Prezoto, B.C.; Serrano, S.M.; Zingali, R.B.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Functional variability of snake venom metalloproteinases: Adaptive advantages in targeting different prey and implications for human envenomation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahas, L.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Barros, M.A. Thrombin-like and factor X-activator components of Bothrops snake venoms. Thromb. Haemost. 1979, 41, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, L.F.; Nicolau, C.A.; Peixoto, P.S.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Oliveira, S.S.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Mourao, R.H.; Lima-dos-Santos, I.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; Chalkidis, H.M.; et al. Comparison of phylogeny, venom composition and neutralization by antivenom in diverse species of Bothrops complex. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loria, G.D.; Rucavado, A.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.; Fox, J.W.; Alape, A.; Gutierrez, J.M. Characterization of ′basparin A,′ a prothrombin-activating metalloproteinase, from the venom of the snake Bothrops asper that inhibits platelet aggregation and induces defibrination and thrombosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 418, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, J.C.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Neves-Ferreira, A.G.; Fritzen, M.; Oliva, M.L.; Ho, P.L.; Perales, J.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. Insularinase A, a prothrombin activator from Bothrops insularis venom, is a metalloprotease derived from a gene encoding protease and disintegrin domains. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Pinto, A.F.; Guimaraes, J.A. Purification and functional characterization of bothrojaractivase, a prothrombin-activating metalloproteinase isolated from Bothrops jararaca snake venom. Toxicon 2008, 51, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, E.S.; Garcia, T.C.; Menezes, M.C.; Tashima, A.K.; Zelanis, A.; Serrano, S.M. Cotiarinase is a novel prothrombin activator from the venom of Bothrops cotiara. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1655–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niewiarowski, S.; Kirby, E.P.; Brudzynski, T.M.; Stocker, K. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 2. Interaction with platelets and plasma-clotting factors. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3570–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niewiarowski, S.; Kirby, E.P.; Stocker, K. Throbocytin-a novel platelet activating enzyme from Bothrops atrox venom. Thromb. Res. 1977, 10, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.P.; Niewiarowski, S.; Stocker, K.; Kettner, C.; Shaw, E.; Brudzynski, T.M. Thrombocytin, a serine protease from Bothrops atrox venom. 1. Purification and characterization of the enzyme. Biochemistry 1979, 18, 3564–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K. Snakebite doesn′t cause disseminated intravascular coagulation: Coagulopathy and thrombotic microangiopathy in snake envenoming. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swenson, S.; Markland, F.S., Jr. Snake venom fibrin(ogen)olytic enzymes. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1021–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markland, F.S. Snake venoms and the hemostatic system. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1749–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A. The cell-based model of coagulation. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care (San Antonio) 2009, 19, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, D.; Sekiya, F.; Morita, T. Prothrombin and factor X activator activities in the venoms of Viperidae snakes. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1997, 35, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wuster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and snake venom evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.C.; Deuis, J.R.; Dashevsky, D.; Dobson, J.; Jackson, T.N.; Brust, A.; Xie, B.; Koludarov, I.; Debono, J.; Hendrikx, I.; et al. The snake with the scorpion′s sting: Novel three-Finger toxin sodium channel activators from the venom of the long-glanded blue coral snake (Calliophis bivirgatus). Toxins 2016, 8, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Scheib, H.; van der Weerd, L.; Young, B.; McNaughtan, J.; Ramjan, S.F.; Vidal, N.; Poelmann, R.E.; Norman, J.A. Evolution of an arsenal: Structural and functional diversification of the venom system in the advanced snakes (Caenophidia). Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 215–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.; Koludarov, I.; Ali, S.A.; Dobson, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dashevsky, D.; Op den Brouw, B.; Masci, P.P.; Nouwens, A.; Josh, P.; et al. Rapid Radiations and the race to redundancy: An investigation of the evolution of Australian elapid snake venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, T.N.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Koludarov, I.; Chan, A.H.; Sanders, K.; Ali, S.A.; Hendrikx, I.; Dunstan, N.; Fry, B.G. Venom down under: Dynamic evolution of Australian elapid snake toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 2621–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G. From genome to ′venome′: Molecular origin and evolution of the snake venom proteome inferred from phylogenetic analysis of toxin sequences and related body proteins. Genome Res. 2015, 15, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolittle, R.F. Step-by-step evolution of vertebrate blood coagulation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2009, 74, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Kristensen, A.T.; Jarvis, E.D.; Gilbert, M.T.; da Fonseca, R.R. A refined model of the genomic basis for phenotypic variation in vertebrate hemostasis. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentoni, J.; Polini, N.N.; Casanave, E.B. Comparative vertebrate fibrinolysis. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 19, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, R.F.; Feng, D.F. Reconstructing the evolution of vertebrate blood coagulation from a consideration of the amino acid sequences of clotting proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1987, 52, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponczek, M.B.; Gailani, D.; Doolittle, R.F. Evolution of the contact phase of vertebrate blood coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maduwage, K.P.; Scorgie, F.E.; Lincz, L.F.; O′Leary, M.A.; Isbister, G.K. Procoagulant snake venoms have differential effects in animal plasmas: Implications for antivenom testing in animal models. Thromb. Res. 2016, 137, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyborne, W.H.; Mackessy, S.P. Identification and characterization of a taxon-specific three-finger toxin from the venom of the Green Vinesnake (Oxybelis fulgidus; family Colubridae). Biochimie 2013, 95, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modahl, C.M.; Mrinalini; Frietze, S.; Mackessy, S.P. Adaptive evolution of distinct prey-specific toxin genes in rear-fanged snake venom. Proc. Biol. Sci./R. Soc. 2018, 285, 20181003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, J.; Mackessy, S.P.; Fry, B.G.; Bhatia, M.; Mourier, G.; Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Servent, D.; Menez, R.; Stura, E.; Menez, A.; et al. Denmotoxin, a three-finger toxin from the colubrid snake Boiga dendrophila (Mangrove Catsnake) with bird-specific activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29030–29041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, J.; Mackessy, S.P.; Sixberry, N.M.; Stura, E.A.; Le Du, M.H.; Menez, R.; Foo, C.S.; Menez, A.; Nirthanan, S.; Kini, R.M. Irditoxin, a novel covalently linked heterodimeric three-finger toxin with high taxon-specific neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. In vitro neurotoxic effects of Pseudechis spp. venoms: A comparison of avian and murine skeletal muscle preparations. Toxicon 2013, 63, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Isbister, G.K.; O′Donnell, P.; Williamson, N.A.; Hodgson, W.C. Species differences in the neuromuscular activity of post-synaptic neurotoxins from two Australian black snakes (Pseudechis porphyriacus and Pseudechis colletti). Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 219, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanhajariya, S.; Duffull, S.B.; Isbister, G.K. Pharmacokinetics of snake venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, H.L.; Mackessy, S.P. Functional basis of a molecular adaptation: Prey-specific toxic effects of venom from Sistrurus rattlesnakes. Toxicon 2009, 53, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriani, V.; Debono, J.; Goldenberg, J.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Arbuckle, K.; Dobson, J.; Koludarov, I.; Li, B.; Hay, C.; Dunstan, N.; et al. Correlation between ontogenetic dietary shifts and venom variation in Australian brown snakes (Pseudonaja). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2017, 197, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, F.C.P.; Dobson, J.; Zdenek, C.N.; den Brouw, B.O.; Hamilton, B.; Debono, J.; Masci, P.; Frank, N.; Ge, L.; Kwok, H.F.; et al. Does size matter? Venom proteomic and functional comparison between night adder species (Viperidae: Causus) with short and long venom glands. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 211, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, J.; Yang, D.C.; Op den Brouw, B.; Cochran, C.; Huynh, T.; Kurrupu, S.; Sanchez, E.E.; Massey, D.J.; Baumann, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; et al. Rattling the border wall: Pathophysiological implications of functional and proteomic venom variation between Mexican and US subspecies of the desert rattlesnake Crotalus scutulatus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2017, 205, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koludarov, I.; Jackson, T.N.; Brouw, B.O.D.; Dobson, J.; Dashevsky, D.; Arbuckle, K.; Clemente, C.J.; Stockdale, E.J.; Cochran, C.; Debono, J.; et al. Enter the dragon: The dynamic and multifunctional evolution of Anguimorpha lizard venoms. Toxins 2017, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, L.F.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Gillett, A.; Del-Rei, T.H.M.; Chalkidis, H.D.M.; Sant’Anna, S.; Teixeira-da-Rocha, M.M.; et al. Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation. Toxins 2018, 10, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100411
Sousa LF, Zdenek CN, Dobson JS, Op den Brouw B, Coimbra FCP, Gillett A, Del-Rei THM, Chalkidis HDM, Sant’Anna S, Teixeira-da-Rocha MM, et al. Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation. Toxins. 2018; 10(10):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100411
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Leijiane F., Christina N. Zdenek, James S. Dobson, Bianca Op den Brouw, Francisco C. P. Coimbra, Amber Gillett, Tiago H. M. Del-Rei, Hipócrates De M. Chalkidis, Sávio Sant’Anna, Marisa M. Teixeira-da-Rocha, and et al. 2018. "Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation" Toxins 10, no. 10: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100411
APA StyleSousa, L. F., Zdenek, C. N., Dobson, J. S., Op den Brouw, B., Coimbra, F. C. P., Gillett, A., Del-Rei, T. H. M., Chalkidis, H. D. M., Sant’Anna, S., Teixeira-da-Rocha, M. M., Grego, K., Travaglia Cardoso, S. R., Moura da Silva, A. M., & Fry, B. G. (2018). Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation. Toxins, 10(10), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100411






