Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Antivenom Research
Abstract
1. Introduction
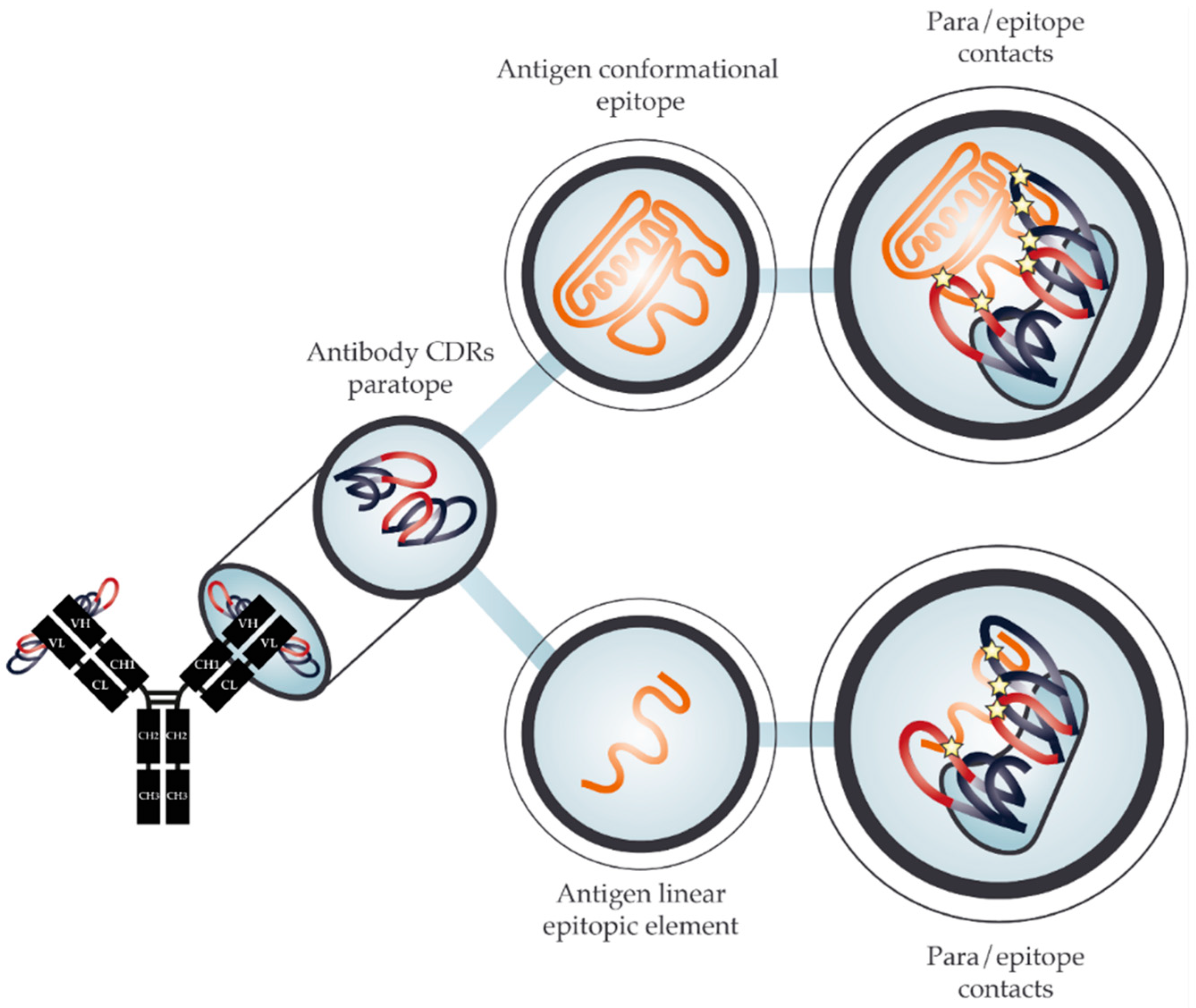
2. The Molecular Basis for Cross-Reactivity
3. Traditional Studies of Cross-Reactivity
3.1. Immunodiffusion
3.2. Immunoblotting
3.3. Whole Venom and Venom Fraction ELISA
3.4. Enzymatic Assays
3.5. In Vivo Experiments
3.6. In Vivo versus In Vitro Determination of Cross-Reactivity
3.7. Surface Plasmon Resonance
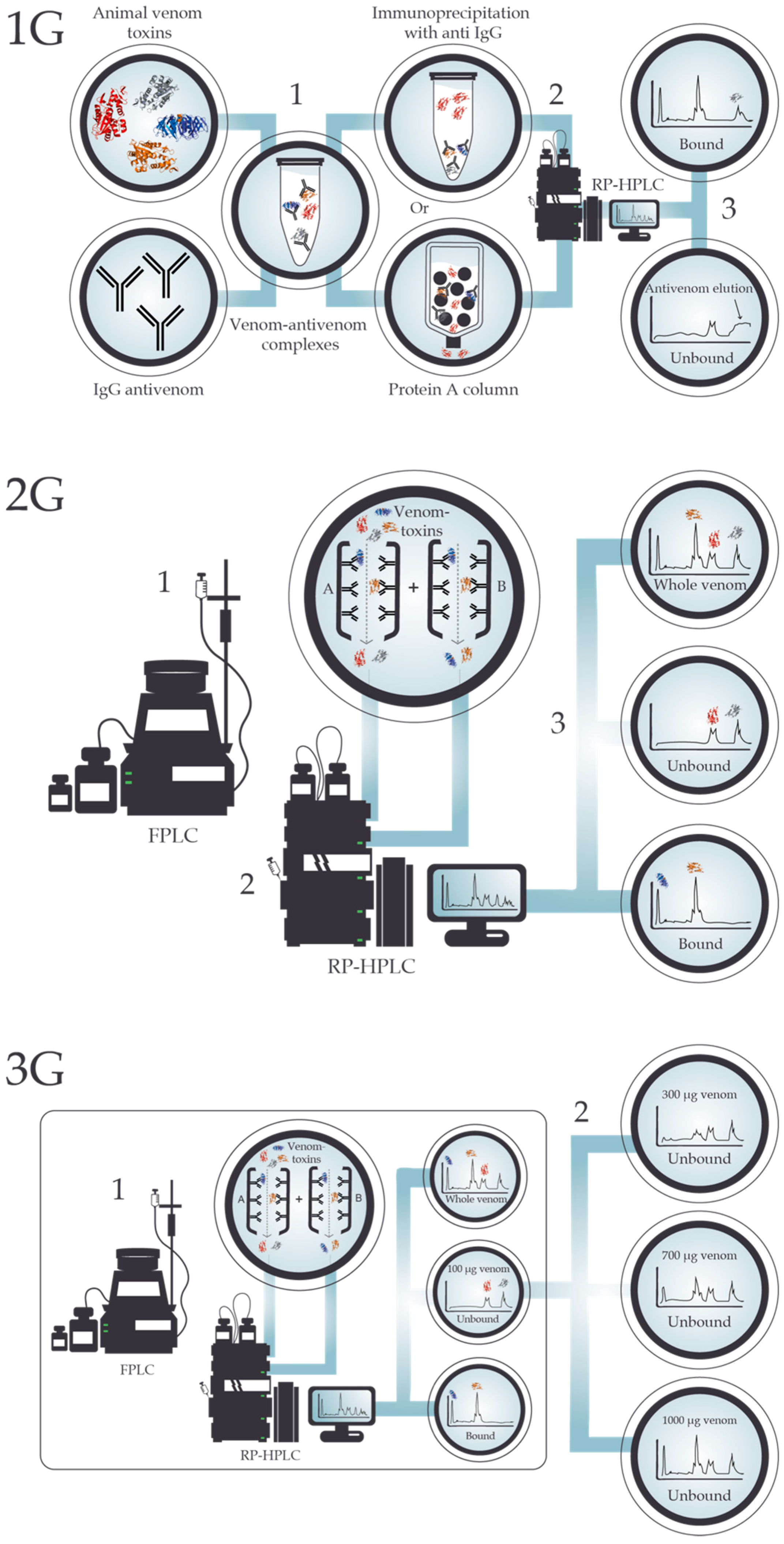
4. Antivenomics
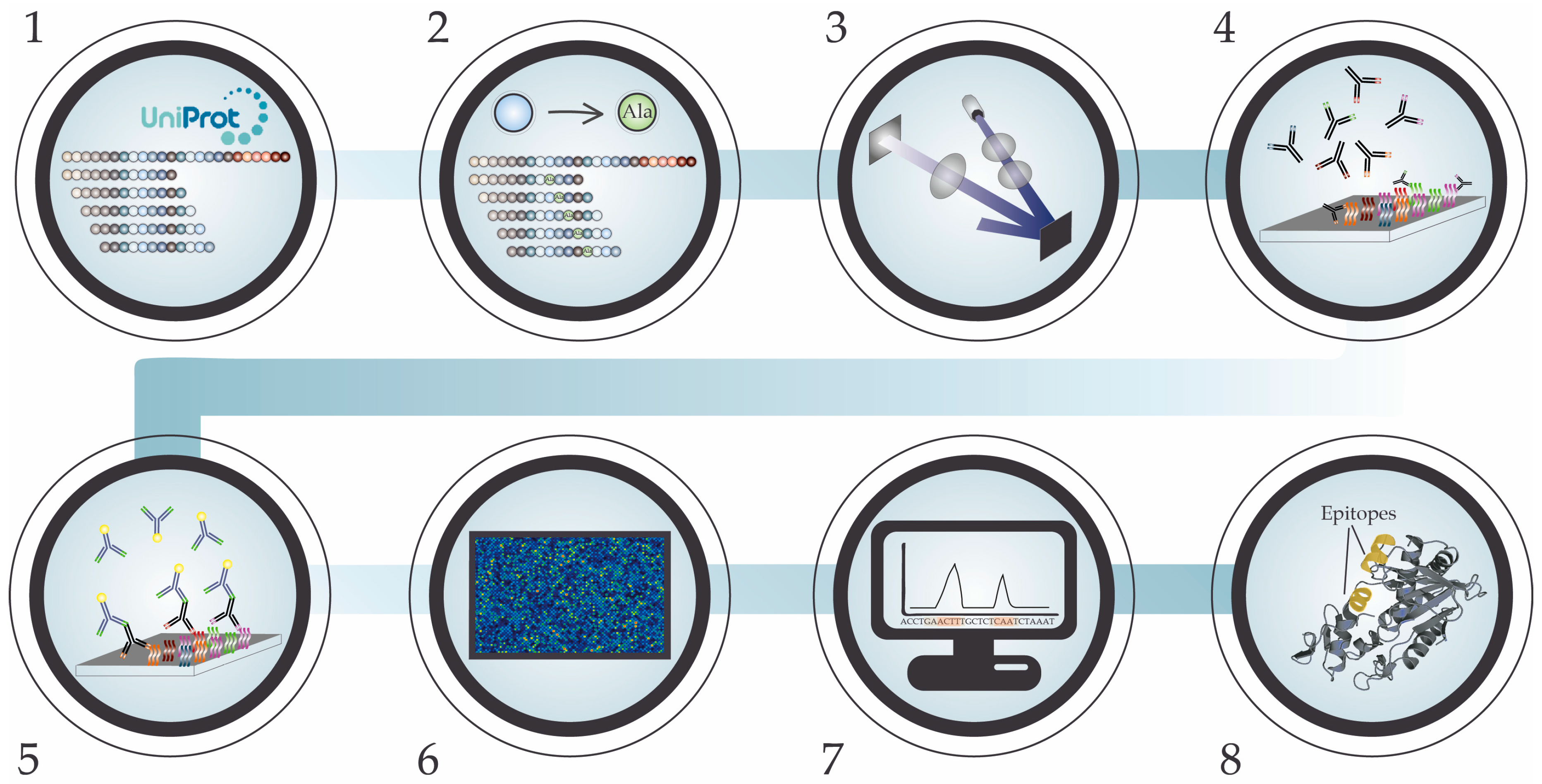
5. High-Density Peptide Microarray
6. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chippaux, J.-P. Snakebite envenomation turns again into a neglected tropical disease! J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Engmark, M.; Milbo, C.; Johannesen, J.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lohse, B. From Fangs to Pharmacology: The Future of Snakebite Envenoming Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 5270–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chippaux, J.P.; Williams, V.; White, J. Snake venom variability: Methods of study, results and interpretation. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltry, J.C.; Wüster, W.; Thorpe, R.S. Diet and snake venom evolution. Nature 1996, 379, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.W.; Stanker, L.H.; Henderson, T.D.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D. Antibody Protection against Botulinum Neurotoxin Intoxication in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 4305–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Knudsen, C.; Johansen, K.H.; Méndez, E.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Jürgensen, J.A.; Øhlenschlæger, M.; Ledsgaard, L.; Esteban, A.M.; et al. Pros and cons of different therapeutic antibody formats for recombinant antivenom development. Toxicon 2018, 146, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kringelum, J.V.; Nielsen, M.; Padkjær, S.B.; Lund, O. Structural analysis of B-cell epitopes in antibody:protein complexes. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 53, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzago, A.; Felici, F.; Tramontano, A.; Pessi, A.; Cortese, R. Mimicking of discontinuous epitopes by phage-displayed peptides, I. Epitope mapping of human H ferritin using a phage library of constrained peptides. Gene 1993, 128, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalenko, M.; Chen, L.; van Roey, M.; Donahue, B.A.; Snyder, R.O.; McArthur, J.G.; Patel, S.D. Epitope mapping of human anti-adeno-associated virus type 2 neutralizing antibodies: Implications for gene therapy and virus structure. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellequer, J.L.; Westhof, E.; Van Regenmortel, M.H. Predicting location of continuous epitopes in proteins from their primary structures. Meth. Enzymol. 1991, 203, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Solano, G.; Pla, D.; Herrera, M.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Sánchez, A.; Sanz, L.; Lomonte, B.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: State-of-the-Art and Challenges Ahead. Toxins 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostolanský, F.; Varecková, E.; Betáková, T.; Mucha, V.; Russ, G.; Wharton, S.A. The strong positive correlation between effective affinity and infectivity neutralization of highly cross-reactive monoclonal antibody IIB4, which recognizes antigenic site B on influenza A virus haemagglutinin. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, J.A.; Maassen, C.B.M.; Leppla, S.H.; Brasky, K.; Patterson, J.L.; Iverson, B.L.; Georgiou, G. Protection against anthrax toxin by recombinant antibody fragments correlates with antigen affinity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.P.; Green, K.; Pinz-Sweeney, S.; Briones, A.T.; Burton, D.R.; Barbas, C.F. CDR walking mutagenesis for the affinity maturation of a potent human anti-HIV-1 antibody into the picomolar range. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, C.-P.; Chen, I.-C.; Yu, C.-M.; Peng, H.-P.; Jian, J.-W.; Ma, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Jan, J.-T.; Yang, A.-S. Discovering neutralizing antibodies targeting the stem epitope of H1N1 influenza hemagglutinin with synthetic phage-displayed antibody libraries. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, R.; Alcalay, R.; Mechaly, A.; Lapidoth, G.; Epstein, E.; Kronman, C.; Fleishman, S.J.; Mazor, O. Improved antibody-based ricin neutralization by affinity maturation is correlated with slower off-rate values. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2017, 30, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, A.B.H.; Marissen, W.E.; Kramer, R.A.; Rice, A.B.; Weldon, W.C.; Niezgoda, M.; Hanlon, C.A.; Thijsse, S.; Backus, H.H.J.; de Kruif, J.; et al. Novel human monoclonal antibody combination effectively neutralizing natural rabies virus variants and individual in vitro escape mutants. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9062–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M.; Andersen, M.R.; Laustsen, A.H.; Patel, J.; Sullivan, E.; de Masi, F.; Hansen, C.S.; Kringelum, J.V.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. High-throughput immuno-profiling of mamba (Dendroaspis) venom toxin epitopes using high-density peptide microarrays. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, N.D.; Mayrose, I.; Halperin, D.; Yekutieli, D.; Gershoni, J.M.; Pupko, T. Computational characterization of B-cell epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3477–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.H.; Perlow, R.A.; Roy, S.; Ko, J.; Wu, M.; Huang, J.; Yan, S.; Nicoletta, A.; Vafai, J.; Sun, D.; et al. Analysis of protein sequence/structure similarity relationships. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, M.A.; Schneider, J.J.; Krishnan, B.P.; Lavis, C.; McKendry, A.; Ong, L.K.; Isbister, G.K. Cross-neutralisation of Australian brown and tiger snake venoms with commercial antivenoms: Cross-reactivity or antivenom mixtures? Toxicon 2007, 50, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Schramm, C.A.; Joyce, M.G.; Do Kwon, Y.; Zhou, T.; Sheng, Z.; Zhang, B.; O’Dell, S.; McKee, K.; et al. Maturation and Diversity of the VRC01-Antibody Lineage over 15 Years of Chronic HIV-1 Infection. Cell 2015, 161, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, M.G.; Wheatley, A.K.; Thomas, P.V.; Chuang, G.-Y.; Soto, C.; Bailer, R.T.; Druz, A.; Georgiev, I.S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Kanekiyo, M.; et al. Vaccine-Induced Antibodies that Neutralize Group 1 and Group 2 Influenza A Viruses. Cell 2016, 166, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Laustsen, A.H.; De Masi, F.; Andersen, M.R.; Lund, O. Cross-recognition of a pit viper (Crotalinae) polyspecific antivenom explored through high-density peptide microarray epitope mapping. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M.; Jespersen, M.C.; Lomonte, B.; Lund, O.; Laustsen, A.H. High-density peptide microarray exploration of the antibody response in a rabbit immunized with a neurotoxic venom fraction. Toxicon 2017, 138, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Rasmussen, A.R.; Engmark, M.; Gravlund, P.; Sanders, K.L.; Lohse, B.; Lomonte, B. Danger in the reef: Proteome, toxicity, and neutralization of the venom of the olive sea snake, Aipysurus laevis. Toxicon 2015, 107, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Lohse, B.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Unveiling the nature of black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) venom through venomics and antivenom immunoprofiling: Identification of key toxin targets for antivenom development. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauridsen, L.P.; Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Exploring the venom of the forest cobra snake: Toxicovenomics and antivenom profiling of Naja melanoleuca. J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.; Al-Abdulla, I.; Smith, D.; Coxon, R.; Landon, J. Immunological Cross-Reactivity and Neutralisation of European Viper Venoms with the Monospecific Vipera berus Antivenom ViperaTAb. Toxins 2014, 6, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H. Venom proteome of the yellow-lipped sea krait, Laticauda colubrina from Bali: Insights into subvenomic diversity, venom antigenicity and cross-neutralization by antivenom. J. Proteom. 2017, 166, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, G.D.; Furtado, M.F.D.; Portaro, F.C.V.; Sant’Anna, O.A.; Tambourgi, D.V. Diversity of Micrurus snake species related to their venom toxic effects and the prospective of antivenom neutralization. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, R. The SPOT-synthesis technique. Synthetic peptide arrays on membrane supports—Principles and applications. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 267, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, S.; Petras, D.; Engmark, M.; Süssmuth, R.D.; Whiteley, G.; Albulescu, L.-O.; Kazandjian, T.D.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Rowley, P.; Wüster, W.; et al. The medical threat of mamba envenoming in sub-Saharan Africa revealed by genus-wide analysis of venom composition, toxicity and antivenomics profiling of available antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2018, 172, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Johansen, K.H.; Engmark, M.; Andersen, M.R. Recombinant snakebite antivenoms: A cost-competitive solution to a neglected tropical disease? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinho, A.D.; Morais, I.C.O.; Lima, D.B.; Jorge, A.R.C.; Jorge, R.J.B.; Menezes, R.R.P.P.B.; Mello, C.P.; Pereira, G.J.S.; Silveira, J.A.M.; Toyama, M.H.; et al. Bothropoides pauloensis venom effects on isolated perfused kidney and cultured renal tubular epithelial cells. Toxicon 2015, 108, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauridsen, L.P.; Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Toxicovenomics and antivenom profiling of the Eastern green mamba snake (Dendroaspis angusticeps). J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H. Recombinant Antivenoms, 1st ed.; University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016; ISBN 978-87-93086-61-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gené, J.A.; Gómez, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Cerdas, L. Neutralization of hyaluronidase and indirect hemolytic activities of Costa Rican snake venoms by a polyvalent antivenom. Toxicon 1985, 23, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Xi, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z. Purification and partial characterization of hyaluronidase from five pace snake (Agkistrodon acutus) venom. Toxicon 1982, 20, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Neutralization of the Principal Toxins from the Venoms of Thai Naja kaouthia and Malaysian Hydrophis schistosus: Insights into Toxin-Specific Neutralization by Two Different Antivenoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, P.K.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Sim, S.M.; Tan, N.H. Immunological cross-reactivity and neutralization of the principal toxins of Naja sumatrana and related cobra venoms by a Thai polyvalent antivenom (Neuro Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). Acta Trop. 2015, 149, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.H.; Tan, K.Y.; Lim, S.E.; Tan, N.H. Venomics of the beaked sea snake, Hydrophis schistosus: A minimalist toxin arsenal and its cross-neutralization by heterologous antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2015, 126, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.W. On the electrical resonance of metal particles light waves—Second communication. Philos. Mag. 1902, 4, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couture, M.; Zhao, S.S.; Masson, J.F. Modern surface plasmon resonance for bioanalytics and biophysics. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 11190–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, M.; Knezevic, I.; Kang, H.N.; Thorpe, R. Immunogenicity assessment of biotherapeutic products: An overview of assays and their utility. Biologicals 2015, 43, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cretich, M.; Damin, F.; Pirri, G.; Chiari, M. Protein and peptide arrays: Recent trends and new directions. Biomol. Eng. 2006, 23, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Paiva, O.K.; Pagotto, A.H.; Segura, A.; Serrano, S.M.T.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Jensen, S.D.; León, G.; Williams, D.J.; et al. Antivenomic characterization of two antivenoms against the venom of the taipan, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, N.D.R.; Pereira, S.S.; da Silva, M.P.; Morais, M.S.S.; Kayano, A.M.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Luiz, M.B.; Zanchi, F.B.; Fuly, A.L.; Huacca, M.E.F.; et al. Inhibition of the Myotoxicity Induced by Bothrops jararacussu Venom and Isolated Phospholipases A2 by Specific Camelid Single-Domain Antibody Fragments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Gupta, C.; Nair, D.T.; Salunke, D.M. MP-4 Contributes to Snake Venom Neutralization by Mucuna Pruriens Seeds through an Indirect Antibody-Mediated Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11373–11384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, G.D.; Salbo, R.; Jørgensen, T.J.D.; Bloch, C.; Erba, E.B.; Robinson, C.V.; Tanjoni, I.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Roepstorff, P.; Domont, G.B.; et al. The Interaction of the Antitoxin DM43 with a Snake Venom Metalloproteinase Analyzed by Mass Spectrometry and Surface Plasmon Resonance. Toxicon 2012, 60, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz, M.B.; Pereira, S.S.; Prado, N.D.R.; Gonçalves, N.R.; Kayano, A.M.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Zanchi, F.B.; Fuly, A.L.; Fernandes, C.F.; et al. Camelid Single-Domain Antibodies (VHHs) against Crotoxin: A Basis for Developing Modular Building Blocks for the Enhancement of Treatment or Diagnosis of Crotalic Envenoming. Toxins 2018, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, N.; Steinicke, F.; Lindigkeit, R.; Ernst, L.; Beuerle, T. Determination of cross-reactivity of poly- and monoclonal antibodies for synthetic cannabinoids by direct SPR and ELISA. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 280, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.N.; Konwar, B.; Kaur, S.; Doley, R.; Mondal, B. Study on Snake Venom Protein-Antibody Interaction by Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy. Photonic Sens. 2018, 8, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, A.H. Guiding recombinant antivenom development by omics technologies. New Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Rodríguez, Y.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Pla, D. Toxin-resolved antivenomics-guided assessment of the immunorecognition landscape of antivenoms. Toxicon 2018, 148, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Escolano, J.; Fernández, J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of the arboreal neotropical pitvipers Bothriechis lateralis and Bothriechis schlegelii. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Solano, G.; Pla, D.; Herrera, M.; Segura, Á.; Villalta, M.; Vargas, M.; Sanz, L.; Lomonte, B.; Calvete, J.J.; et al. Assessing the preclinical efficacy of antivenoms: From the lethality neutralization assay to antivenomics. Toxicon 2013, 69, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Wüster, W.; Ratanabanangkoon, K.; Paiva, O.; Brown, N.I.; Casewell, N.R.; Harrison, R.A.; Rowley, P.D.; et al. Ending the drought: New strategies for improving the flow of affordable, effective antivenoms in Asia and Africa. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1735–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldrati, V.; Arrell, M.; Violette, A.; Perret, F.; Sprüngli, X.; Wolfender, J.-L.; Stöcklin, R. Advances in venomics. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 3530–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antúnez, J.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Sanz, L.; Pérez, A.; Calvete, J.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Antivenomics of Atropoides mexicanus and Atropoides picadoi snake venoms: Relationship to the neutralization of toxic and enzymatic activities. J. Venom Res. 2010, 1, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boldrini-França, J.; Corrêa-Netto, C.; Silva, M.M.; Rodrigues, R.S.; De La Torre, P.; Sanz, L.; Soares, A.M.; Zingali, R.B.; Nogueira, R.A.; Rodrigues, V.M.; et al. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Crotalus durissus subspecies from Brazil: Assessment of geographic variation and its implication on snakebite management. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1758–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Borges, A.; Segura, A.; Escolano, J.; Sanz, L.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Diez, N.; De Sousa, L.; Kiriakos, D.; Faks, J.G.; et al. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops colombiensis, a medically important pitviper of the Bothrops atrox-asper complex endemic to Venezuela: Contributing to its taxonomy and snakebite management. J. Proteom. 2009, 72, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Pérez, A.; Borges, A.; Vargas, A.M.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Moura-Da-Silva, A.M.; Chalkidis, H.M.; Furtado, M.F.; et al. Snake population venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox: Paedomorphism along its transamazonian dispersal and implications of geographic venom variability on snakebite management. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Escolano, J.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Rucavado, A.; Warrell, D.A.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the Lesser Antillean pit vipers Bothrops caribbaeus and Bothrops lanceolatus: Correlation with toxicological activities and immunoreactivity of a heterologous antivenom. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4396–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, V.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; De La Torre, P.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Bothrops atrox venoms from Colombia and the Amazon regions of Brazil, Perú and Ecuador suggest the occurrence of geographic variation of venom phenotype by a trend towards paedomorphism. J. Proteom. 2009, 73, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Second generation snake antivenomics: Comparing immunoaffinity and immunodepletion protocols. Toxicon 2012, 60, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, L.; Makran, B.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Oukkache, N.; Lkhider, M.; Harrison, R.A.; Ghalim, N.; Calvete, J.J. Venomics and antivenomics profiles of North African Cerastes cerastes and C. vipera populations reveals a potentially important therapeutic weakness. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Molina-Sánchez, P.; Zorita, V.; Madrigal, M.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Alape-Girón, A.; Núñez, V.; Andrés, V.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. Snake venomics of Lachesis muta rhombeata and genus-wide antivenomics assessment of the paraspecific immunoreactivity of two antivenoms evidence the high compositional and immunological conservation across Lachesis. J. Proteom. 2013, 89, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, M.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Barboza, E.; Arroyo-Portilla, C.; Corrêa-Netto, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Alape-Girón, A.; Flores-Díaz, M.; Calvete, J.J. Cross-reactivity, antivenomics, and neutralization of toxic activities of Lachesis venoms by polyspecific and monospecific antivenoms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, L.F.; Nicolau, C.A.; Peixoto, P.S.; Bernardoni, J.L.; Oliveira, S.S.; Portes-Junior, J.A.; Mourão, R.H.V.; Lima-dos-Santos, I.; Sano-Martins, I.S.; Chalkidis, H.M.; et al. Comparison of Phylogeny, Venom Composition and Neutralization by Antivenom in Diverse Species of Bothrops Complex. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, M.; Pla, D.; Yang, S.L.; Sanz, L.; Segura, A.; Vargas, M.; Chen, P.Y.; Herrera, M.; Estrada, R.; Cheng, Y.F.; et al. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Protobothrops mucrosquamatus and Viridovipera stejnegeri from Taiwan: Keys to understand the variable immune response in horses. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5628–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Rodríguez, Y.; Calvete, J.J. Third Generation Antivenomics: Pushing the Limits of the In Vitro Preclinical Assessment of Antivenoms. Toxins 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Arias, A.S.; Rodríguez, Y.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Sánchez, L.V.; Chippaux, J.P.; Pla, D.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Preclinical evaluation of three polyspecific antivenoms against the venom of Echis ocellatus: Neutralization of toxic activities and antivenomics. Toxicon 2016, 119, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Cid, P.; Sanz, L.; Segura, Á.; Villalta, M.; Herrera, M.; León, G.; Harrison, R.; Durfa, N.; Nasidi, A.; et al. Antivenomic Assessment of the Immunological Reactivity of EchiTAb-Plus-ICP, an Antivenom for the Treatment of Snakebite Envenoming in Sub-Saharan Africa. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, C.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Snake Venomics and Antivenomics of Bothrops diporus, a Medically Important Pitviper in Northeastern Argentina. Toxins 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves-Machado, L.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Jorge, R.J.B.; Leitão-De-Araújo, M.; Alves, M.L.M.; Alvares, D.J.; De Miranda, J.; Nowatzki, J.; de Morais-Zani, K.; et al. Combined venomics, venom gland transcriptomics, bioactivities, and antivenomics of two Bothrops jararaca populations from geographic isolated regions within the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest. J. Proteom. 2016, 135, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makran, B.; Fahmi, L.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Oukkache, N.; Lkhider, M.; Ghalim, N.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of Macrovipera mauritanica from Morocco, and assessment of the para-specific immunoreactivity of an experimental monospecific and a commercial antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petras, D.; Sanz, L.; Segura, A.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Solano, D.; Vargas, M.; León, G.; Warrell, D.A.; Theakston, R.D.G.; et al. Snake venomics of African spitting cobras: Toxin composition and assessment of congeneric cross-reactivity of the pan-African EchiTAb-Plus-ICP antivenom by antivenomics and neutralization approaches. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1266–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Bande, B.W.; Welton, R.E.; Paiva, O.K.; Sanz, L.; Segura, Á.; Wright, C.E.; Calvete, J.J.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Williams, D.J. Proteomics and antivenomics of Papuan black snake (Pseudechis papuanus) venom with analysis of its toxicological profile and the preclinical efficacy of Australian antivenoms. J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Calvete, J.J.; Elosua, C.; Paniagua, J. Antivenomics of a European vipera antivenom. Toxicon 2016, 119, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Whiteley, G.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Harrison, R.A.; Casewell, N.R.; Calvete, J.J. What killed Karl Patterson Schmidt? Combined venom gland transcriptomic, venomic and antivenomic analysis of the South African green tree snake (the boomslang), Dispholidus typus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yin, Y.; Shen, S.-S.; Shan, L.-L.; Chen, C.-X.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Gao, J.-F.; Ji, X. Combined venomics, antivenomics and venom gland transcriptome analysis of the monocoled cobra (Naja kaouthia) from China. J. Proteom. 2017, 159, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Immunological profile of antivenoms: Preclinical analysis of the efficacy of a polyspecific antivenom through antivenomics and neutralization assays. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Napoleão-Pego, P.; Teixeira-Pinto, L.A.L.; Santos, J.D.L.; De-Simone, T.S.; Melgarejo, A.R.; Aguiar, A.S.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P. Linear B-cell epitopes in BthTX-1, BthTX-II and BthA-1, phospholipase A2s from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom, recognized by therapeutically neutralizing commercial horse antivenom. Toxicon 2013, 72, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B. Identification of linear B-cell epitopes on myotoxin II, a Lys49 phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 2012, 60, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, K.L.; Duarte, C.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Machado de Avila, R.A.; Schneider, F.S.; Oliveira, D.; Freitas, C.F.; Kalapothakis, E.; Ho, P.L.; Chávez-Olortegui, C. Identification and characterization of B-cell epitopes of 3FTx and PLA2 toxins from Micrurus corallinus snake venom. Toxicon 2015, 93, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, H.R.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.M.; Novo, J.B.; Castro, K.; Duarte, C.G.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Chavez-Olortegui, C.; Ho, P.L. A Heterologous Multiepitope DNA Prime/Recombinant Protein Boost Immunisation Strategy for the Development of an Antiserum against Micrurus corallinus (Coral Snake) Venom. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, F.S.; de Almeida Lima, S.; Reis de Ávila, G.; Castro, K.L.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Sanchez, E.F.; Nguyen, C.; Granier, C.; Molina, F.; Chávez-Olortegui, C. Identification of protective B-cell epitopes of Atroxlysin-I: A metalloproteinase from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta, C.C.R.; de Freitas Magalhães, B.; Oliveira-Mendes, B.B.R.; do Carmo, A.O.; Duarte, C.G.; Felicori, L.F.; Machado-de-Ávila, R.A.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Kalapothakis, E. Molecular, Immunological, and Biological Characterization of Tityus serrulatus Venom Hyaluronidase: New Insights into Its Role in Envenomation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, W.S.; Velarde, D.T.; Alvarenga, L.M.; Nguyen, C.; Villard, S.; Granier, C.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. Localization of epitopes in the toxins of Tityus serrulatus scorpions and neutralizing potential of therapeutic antivenoms. Toxicon 2005, 46, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, T.M.; Guimarães-Okamoto, P.T.C.; Machado-de-Avila, R.A.; Oliveira, D.; Melo, M.M.; Lobato, Z.I.; Kalapothakis, E.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C. General characterization of Tityus fasciolatus scorpion venom. Molecular identification of toxins and localization of linear B-cell epitopes. Toxicon 2015, 99, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramada, J.S.; Becker-Finco, A.; Minozzo, J.C.; Felicori, L.F.; Machado de Avila, R.A.; Molina, F.; Nguyen, C.; de Moura, J.; Chávez-Olórtegui, C.; Alvarenga, L.M. Synthetic peptides for in vitro evaluation of the neutralizing potency of Loxosceles antivenoms. Toxicon 2013, 73, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geysen, H.M.; Meloen, R.H.; Barteling, S.J. Use of peptide synthesis to probe viral antigens for epitopes to a resolution of a single amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3998–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Pellois, J.P.; Na, Y.; Kim, Y.; Gulari, E.; Zhou, X. High density peptide microarrays. In situ synthesis and applications. Mol. Divers. 2004, 8, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetz, O. Protein microarrays for antibody profiling: Specificity and affinity determination on a chip. Proteomics 2005, 5, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buus, S.; Rockberg, J.; Forsstrom, B.; Nilsson, P.; Uhlen, M.; Schafer-Nielsen, C. High-resolution Mapping of Linear Antibody Epitopes Using Ultrahigh-density Peptide Microarrays. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Gasson, S.; Green, R.D.; Yue, Y.; Nelson, C.; Blattner, F.; Sussman, M.R.; Cerrina, F. Maskless fabrication of light-directed oligonucleotide microarrays using a digital micromirror array. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, W.M.; Damschroder, M.M.; Lowe, D.C. Current approaches to fine mapping of antigen–antibody interactions. Immunology 2014, 142, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershoni, J.M.; Roitburd-Berman, A.; Siman-Tov, D.D.; Tarnovitski Freund, N.; Weiss, Y. Epitope mapping: The first step in developing epitope-based vaccines. Biodrugs 2007, 21, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M. Epitope-Mapping of Snake Toxins and Perspectives for Antivenom Development. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Laustsen, A.H. Toxin-centric development approach for next-generation antivenoms. Toxicon 2018, 150, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ledsgaard, L.; Jenkins, T.P.; Davidsen, K.; Krause, K.E.; Martos-Esteban, A.; Engmark, M.; Rørdam Andersen, M.; Lund, O.; Laustsen, A.H. Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Antivenom Research. Toxins 2018, 10, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100393
Ledsgaard L, Jenkins TP, Davidsen K, Krause KE, Martos-Esteban A, Engmark M, Rørdam Andersen M, Lund O, Laustsen AH. Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Antivenom Research. Toxins. 2018; 10(10):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100393
Chicago/Turabian StyleLedsgaard, Line, Timothy P. Jenkins, Kristian Davidsen, Kamille Elvstrøm Krause, Andrea Martos-Esteban, Mikael Engmark, Mikael Rørdam Andersen, Ole Lund, and Andreas Hougaard Laustsen. 2018. "Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Antivenom Research" Toxins 10, no. 10: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100393
APA StyleLedsgaard, L., Jenkins, T. P., Davidsen, K., Krause, K. E., Martos-Esteban, A., Engmark, M., Rørdam Andersen, M., Lund, O., & Laustsen, A. H. (2018). Antibody Cross-Reactivity in Antivenom Research. Toxins, 10(10), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100393






