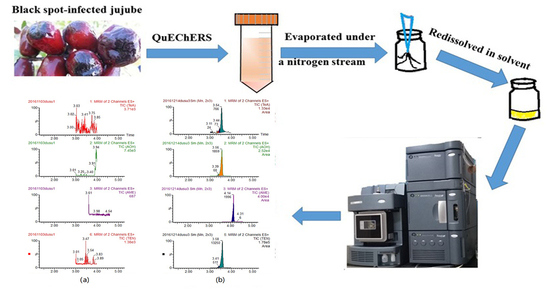
Development and Application of a QuEChERS-Based Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantitate Multi-Component Alternaria Toxins in Jujube
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) Instrumental Detection
2.2. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.3. Optimization of QuEChERS
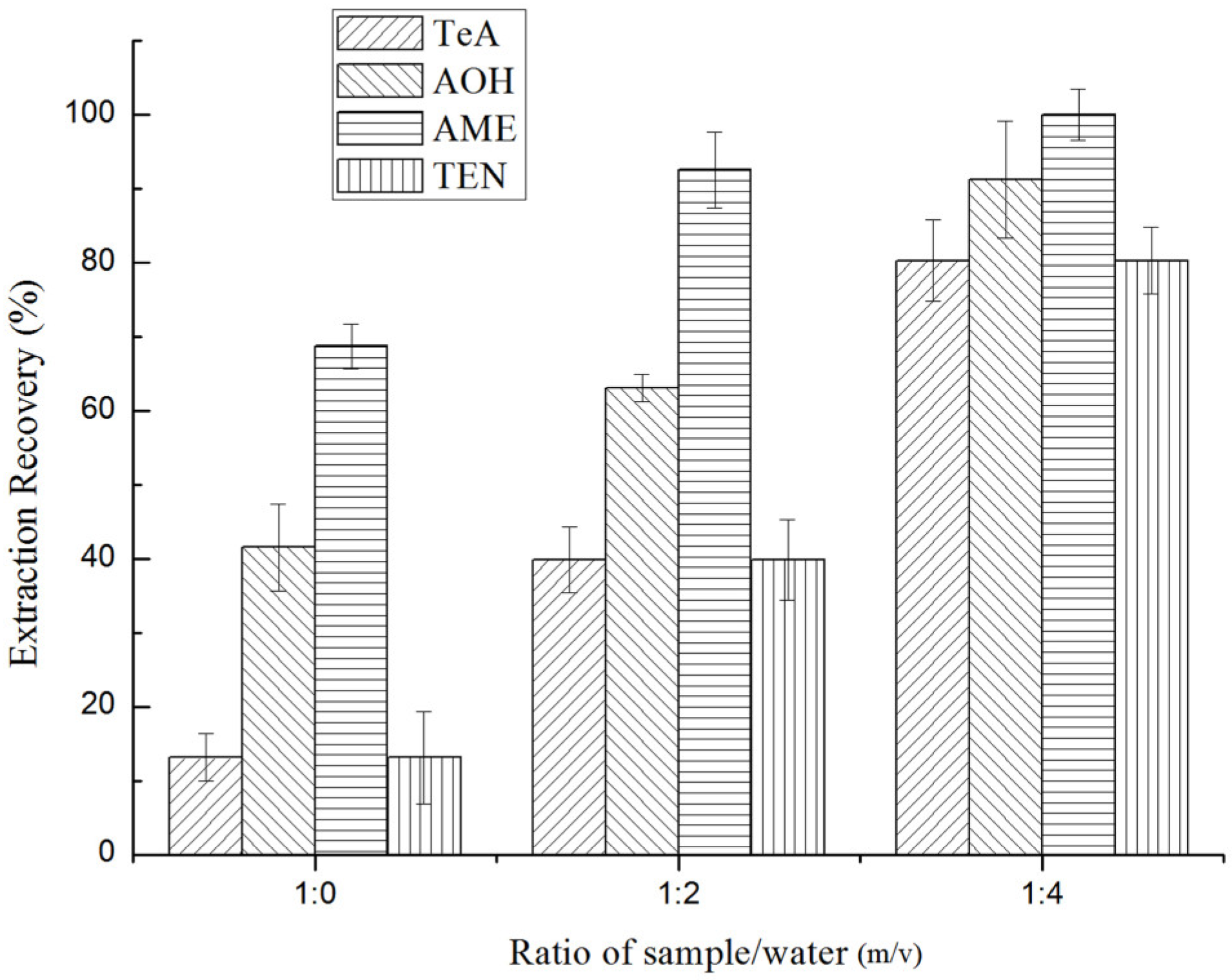
2.3.1. Selection of Raw Sample Treatment Method
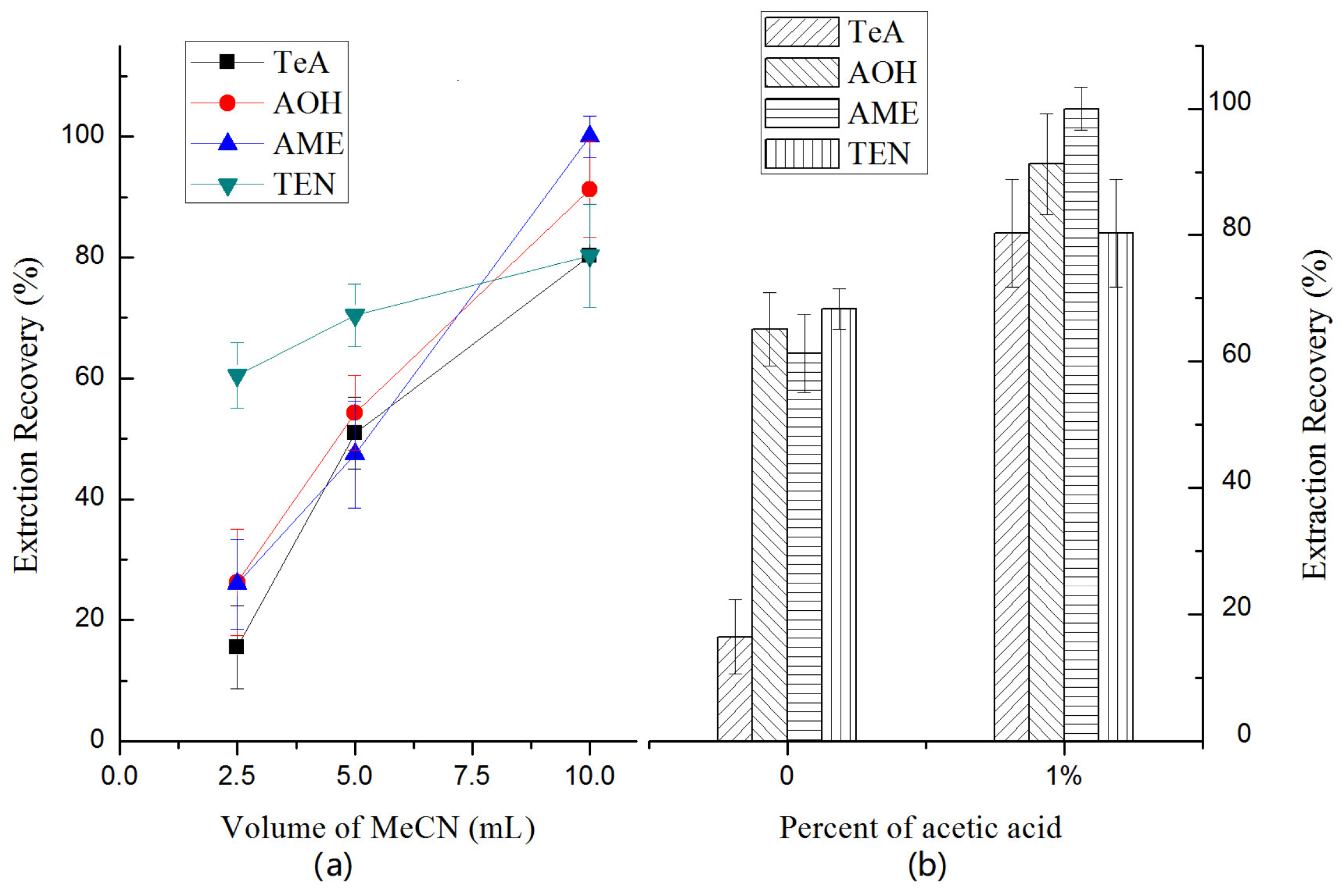
2.3.2. Selection of Extraction Solvent
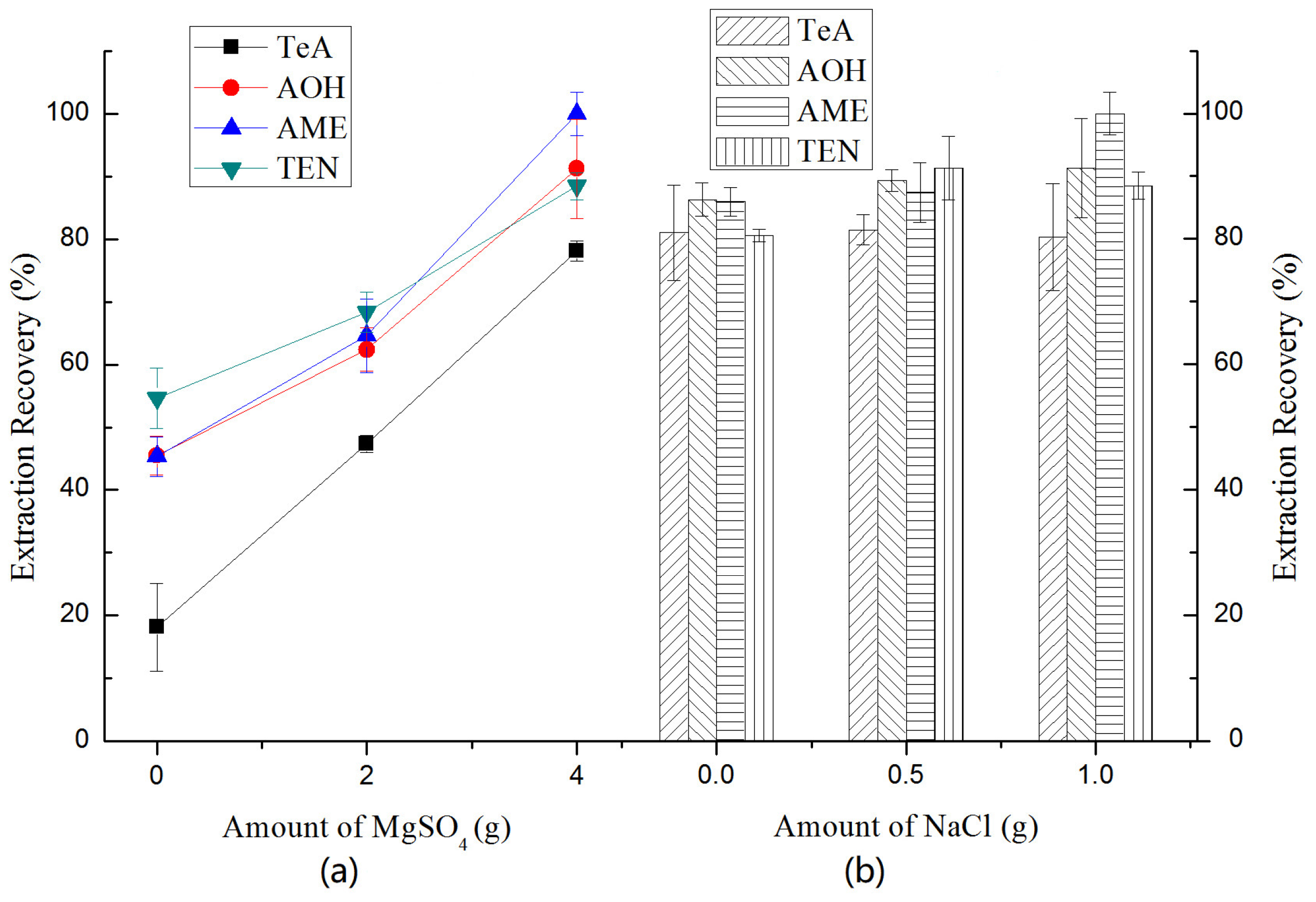
2.3.3. Selection of Salt Addition
2.3.4. Selection of Clean-Up Agent
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Sample Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Instrument
4.3. Samples
4.4. Sample Treatment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EFSA on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM). Scientific Opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of Alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noser, J.; Schneider, P.; Rother, M.; Schmutz, H. Determination of six Alternaria toxins with UPLC-MS/MS and their occurrence in tomatoes and tomato products from the Swiss market. Mycotoxin Res. 2011, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myresiotis, C.K.; Testempasis, S.; Vryzas, Z.; Karaoglanidis, G.S.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Determination of mycotoxins in pomegranate fruits and juices using a QuEChERS-based method. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzo, M.; De Girolamo, A.; Vitti, C.; Visconti, A.; Van den Bulk, R. Liquid chromatographic determination of Alternaria toxins in carrot. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López, P.; Venema, D.; Mol, H.; Spanjer, M.; de Stoppelaar, J.; Pfeiffer, E.; de Nijs, M. Alternaria toxins and conjugates in selected foods in the Netherlands. Food Control 2016, 60, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walravens, J.; Mikula, H.; Rychlik, M.; Asam, S.; Ediage, E.N.; Di Mavungu, J.D.; Van Landschoot, A.; Vanhaecke, L.; De Saeger, S. Development and validation of an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric method for the simultaneous determination of free and conjugated Alternaria toxins in cereal-based foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1372, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Shao, B.; Yang, D.; Li, F. Natural occurrence of four Alternaria mycotoxins in tomato- and citrus-based foods in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwickel, T.; Klaffke, H.; Richards, K.; Rychlik, M. Development of a high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry based analysis for the simultaneous quantification of various Alternaria toxins in wine, vegetable juices and fruit juices. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1455, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Wang, M. Survey of Alternaria toxins and other mycotoxins in dried fruits in China. Toxins 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, P.; Venema, D.; de Rijk, T.; de Kok, A.; Scholten, J.M.; Mol, H.G.J.; de Nijs, M. Occurrence of Alternaria toxins in food products in the Netherlands. Food Control 2016, 60, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntscher, H.; Kütt, M.-L.; Skrinjar, P.; Mikula, H.; Podlech, J.; Fröhlich, J.; Marko, D.; Warth, B. Tracking emerging mycotoxins in food: Development of an LC-MS/MS method for free and modified Alternaria toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4481–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, C.; Oueslati, S.; Mañes, J. Evaluation of Alternaria mycotoxins in strawberries: Quantification and storage condition. Food Addit. Contam. 2016, 33, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana Di Mavungu, J.; Monbaliu, S.; Scippo, M.-L.; Maghuin-Rogister, G.; Schneider, Y.-J.; Larondelle, Y.; Callebaut, A.; Robbens, J.; Van Peteghem, C.; De Saeger, S. LC-MS/MS multi-analyte method for mycotoxin determination in food supplements. Food Addit. Contam. 2009, 26, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asam, S.; Konitzer, K.; Schieberle, P.; Rychlik, M. Stable isotope dilution assays of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5152–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prelle, A.; Spadaro, D.; Garibaldi, A.; Gullino, M.L. A new method for detection of five Alternaria toxins in food matrices based on LC–APCI-MS. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, T.; Gomez-Cordoves, C.; Scott, P.M. Determination of alternariol and alternariol methyl ether in apple juice using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 731, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, J.; Kong, X.; Yue, A.; Wu, S. Simultaneous determination of four Alternaria toxins in apple juice concentrate by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2010, 28, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.; Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, W. Determination of Alternaria mycotoxins in wine and juice using ionic liquid modified countercurrent chromatography as a pretreatment method followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1436, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font, G.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Moltó, J.C.; Berrada, H. Monitoring Alternaria mycotoxins and pesticide residues in tomato by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to gas chromatography—Tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lehotay, S. AOAC official method 2007.01, pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2007, 90, 485–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foods of Plant Origin—Determination of Pesticide Residues Using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS Following Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and Clean-Up by Dispersive SPE-QuEChERS-Method. Available online: http://www.chromnet.net/Taiwan/QuEChERS_Dispersive_SPE/QuEChERS_%E6%AD%90%E7%9B%9F%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95_EN156622008_E.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2012).
- González-Curbelo, M.Á.; Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; González-Sálamo, J.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Evolution and applications of the QuEChERS method. TRAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berardis, S.; De Paola, E.L.; Montevecchi, G.; Garbini, D.; Masino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Melucci, D. Determination of four Alternaria alternata mycotoxins by QuEChERS approach coupled with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in tomato-based and fruit-based products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walravens, J.; Mikula, H.; Rychlik, M.; Asam, S.; Devos, T.; Njumbe Ediage, E.; Diana Di Mavungu, J.; Jacxsens, L.; Van Landschoot, A.; Vanhaecke, L.; et al. Validated UPLC-MS/MS methods to quantitate free and conjugated Alternaria toxins in commercially available tomato products and fruit and vegetable juices in Belgium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5101–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, J.J.; Cai, Z.X.; Huang, B.F.; Jin, M.C.; Ren, Y.P. Simultaneous determination of five Alternaria toxins in cereals using QuEChERS-based methodology. J Chromatogr. B 2017, 1068–1069, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Jiao, B. Rapid determination of five Alternaria mycotoxins in citrus by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, J.; Dzuman, Z.; Vaclavikova, M.; Zachariasova, M.; Soler, C.; Hajslove, J. Analysis of mycotoxins in barley using ultra high liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry: Comparison of efficiency and efficacy of different extraction procedures. Talanta 2012, 99, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beccari, G.; Caproni, L.; Tini, F.; Uhlig, S.; Covarelli, L. Presence of Fusarium species and other toxigenic fungi in malting barley and multi-mycotoxin analysis by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4390–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo, M.S.; Barros, G.G.; Chulze, S.N.; Ramirez, M.L. Natural occurrence of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in soya beans. Mycotoxin Res. 2012, 28, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuman, Z.; Zachariasova, M.; Lacina, O.; Veprikova, Z.; Slavikova, P.; Hajslova, J. A rugged high-throughput analytical approach for the determination and quantification of multiple mycotoxins in complex feed matrices. Talanta 2014, 121, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Xue, X.; Pan, C. Multiresidue analysis of 16 pesticides in jujube using gas chromatography and mass spectrometry with multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a sorbent. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3362–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njumbe Ediage, E.; Van Poucke, C.; De Saeger, S. A multi-analyte LC–MS/MS method for the analysis of 23 mycotoxins in different sorghum varieties: The forgotten sample matrix. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, C.; Chamari, K.; Oueslati, S.; Mañes, J. Rapid quantification method of three Alternaria mycotoxins in strawberries. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 9, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogendrarajah, P.; Van Poucke, C.; De Meulenaer, B.; De Saeger, S. Development and validation of a QuEChERS based liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of multiple mycotoxins in spices. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1297, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenich, A.G.; Romero-González, R.; Gómez-Pérez, M.L.; Vidal, J.L.M. Multi-mycotoxin analysis in eggs using a QuEChERS-based extraction procedure and ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Coruna 2011, 1218, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asam, S.; Rychlik, M. Recent developments in stable isotope dilution assays in mycotoxin analysis with special regard to Alternaria toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7563–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, I.; Ortu, G.; Gilardi, G.; Gullino, M.L.; Garibaldi, A. Mycotoxin production in liquid culture and on plants infected with Alternaria spp. isolated from rocket and cabbage. Toxins 2015, 7, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquera, S.; Patriarca, A.; Fernández Pinto, V. Influence of environmental parameters on mycotoxin production by Alternaria arborescens. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 219, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analyte | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Molecular Ion | Cone Voltage (V) | Production (m/z) | Collision Energy (eV) | Retention Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tenuazonic acid (TeA) | 198.92 | [M + H] + | 35 | 124.8 1 152.9 | 15 14 | 3.54 |
| Alternariol (AOH) | 258.9 | [M + H] + | 34 | 184.9 213.0 | 25 27 | 3.52 |
| Alternariol monomethyl ether (AME) | 272.9 | [M + H] + | 35 | 257.9 226.8 | 26 27 | 4.12 |
| Tentoxin (TEN) | 415.0 | [M + H] + | 36 | 199.0 170.9 | 14 20 | 3.54 |
| Analyte | TeA | AOH | AME | TEN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear range (μg mL−1) | 0.01–1 | 0.01–1 | 0.01–1 | 0.01–1 |
| Calibration curves in pure solvent | ||||
| Equation of the curve | y = 9229.1x − 323.72 | y = 19,285x + 863.15 | y = 23,975x + 983 | y = 221,548x + 2969.8 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.9996 | 0.9893 | 0.9855 | 0.9922 |
| Calibration curves in a blank jujube sample | ||||
| Equation of the curve | y = 2489.1x − 54.376 | y = 12,613x − 471.32 | y = 15,189x − 371 | y = 73,096x + 495.47 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2) | 0.9897 | 0.9997 | 0.9866 | 0.9980 |
| Slope ratio | 0.2697 | 0.6540 | 0.6335 | 0.3299 |
| Limit of Detection (LOD) (μg kg−1) | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.20 |
| Limit of Quantitation (LOQ) (μg kg−1) | 0.47 | 0.87 | 0.72 | 0.66 |
| Intra-day precision (RSD%1, n = 3) 2 | 0.1 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| Inter-day precision (RSD%, n = 3) 2 | 2.4 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 1.9 |
| Average recovery ± RSD% (n = 3) for red jujube | ||||
| Concentration (μg kg−1) | ||||
| 160 | 91.0 ± 1.4 | 91.3 ± 0.9 | 109.6 ± 0.4 | 89.3 ± 3.6 |
| 80 | 87.1 ± 4.4 | 86.0 ± 2.9 | 93.0 ± 4.8 | 86.5 ± 3.3 |
| 40 | 83.5 ± 6.5 | 84.8 ± 4.2 | 88.6 ± 2.4 | 85.2 ± 2.7 |
| No. | Sample | Location | TeA | AOH | AME | TEN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-1 | Uninfected jujube | Pishan County, Hotan Prefecture | 1.0933 (0.62) 1 | <LOQ 2 | <LOQ | 0.0104 (3.05) |
| S-2 | Infected jujube | 8.2735 (3.62) | 0.0228 (0.69) | 0.0692 (1.85) | 0.0074 (3.42) | |
| S-3 | Uninfected jujube | The 8th Company, the10th Regiment, Alar City | 0.1817 (0.33) | <LOQ | nd 3 | 0.0078 (3.21) |
| S-4 | Infected jujube | 3.3141 (2.58) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0064 (4.63) | |
| S-5 | Uninfected jujube | The 5th Company, the 224th Regiment, Hotan Prefecture | 0.2944 (4.39) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0029 (3.78) |
| S-6 | Infected jujube | 0.8390 (0.55) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0095 (3.41) | |
| S-7 | Uninfected jujube | The 20th Company, the 50th Regiment, Alar City | <LOQ | nd | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| S-8 | Infected jujube | 0.1879 (1.04) | nd | nd | <LOQ | |
| S-9 | Uninfected jujube | The 5th Company, the 14th Regiment, Alar City | 0.1506 (5.04) | 0.0012 (8.33) | 0.0046 (2.38) | 0.0247 (0.55) |
| S-10 | Infected jujube | 0.8506 (1.62) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0058 (1.72) | |
| S-11 | Uninfected jujube | The 12th Company, the 224th Regiment, Hotan Prefecture | 0.0964 (8.66) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0086 (1.64) |
| S-12 | Infected jujube | 0.1373 (0.11) | 0.0015 (6.67) | 0.0011 (9.09) | 0.0072 (1.55) | |
| S-13 | Uninfected jujube | The 8th Company, the 224th Regiment, Hotan Prefecture | 0.4179 (0.42) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0053 (2.63) |
| S-14 | Infected jujube | 5.3881 (5.49) | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.0070 (1.43) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Fan, Y.; He, W.; Hu, D.; Wu, A.; Wu, W. Development and Application of a QuEChERS-Based Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantitate Multi-Component Alternaria Toxins in Jujube. Toxins 2018, 10, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100382
Wang C, Fan Y, He W, Hu D, Wu A, Wu W. Development and Application of a QuEChERS-Based Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantitate Multi-Component Alternaria Toxins in Jujube. Toxins. 2018; 10(10):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100382
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Cheng, Yingying Fan, Weizhong He, Dongqiang Hu, Aibo Wu, and Wenliang Wu. 2018. "Development and Application of a QuEChERS-Based Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantitate Multi-Component Alternaria Toxins in Jujube" Toxins 10, no. 10: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100382
APA StyleWang, C., Fan, Y., He, W., Hu, D., Wu, A., & Wu, W. (2018). Development and Application of a QuEChERS-Based Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method to Quantitate Multi-Component Alternaria Toxins in Jujube. Toxins, 10(10), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100382