Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
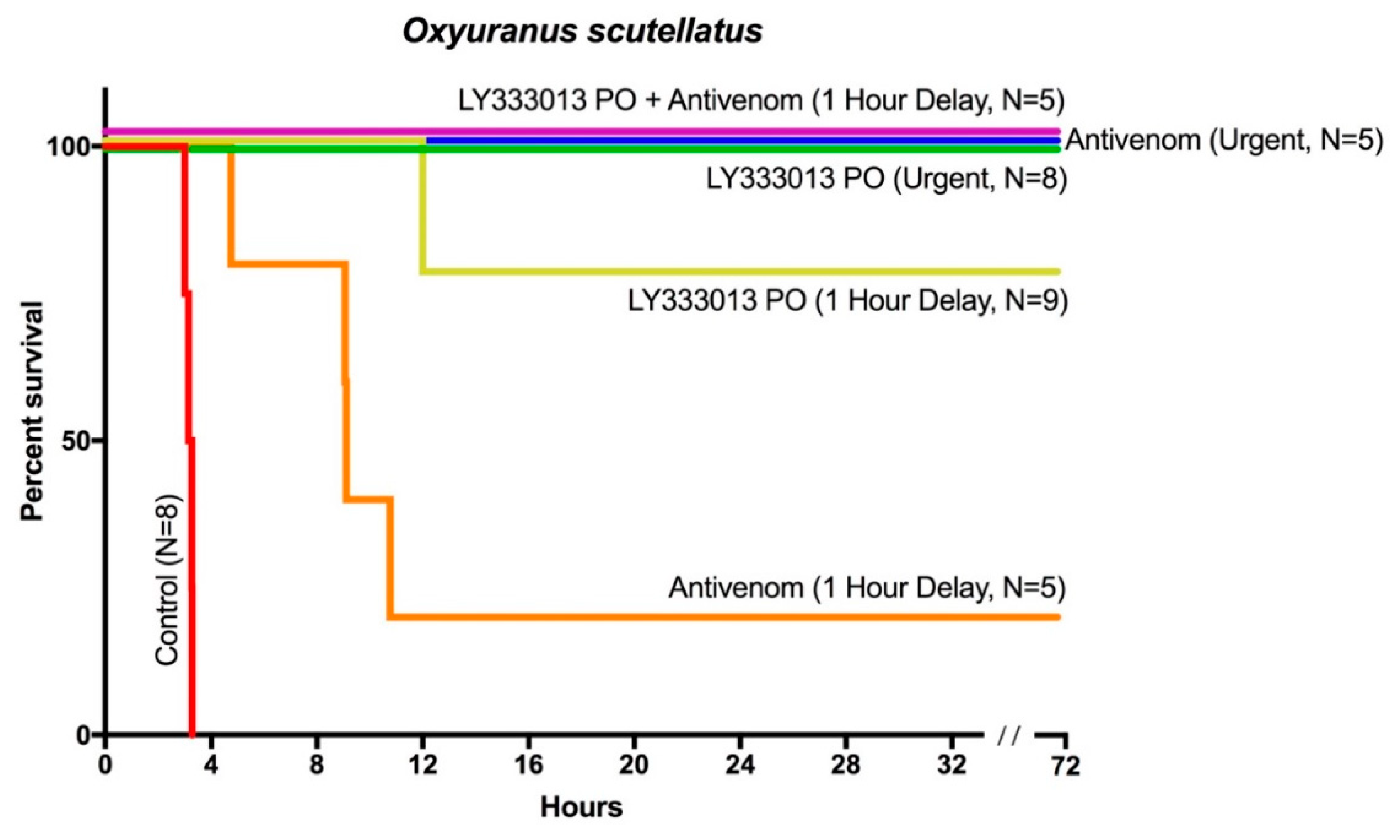
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design to Assess the Efficacy of Drug and Antivenom
4.2. Venom
4.3. sPLA2 Inhibitor and Antivenom
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.M.; Devine, M.; Alcoba, G.; Chappuis, F.; Weiss, D.J.; Ray, S.E.; Ray, N.; Warrell, D.A.; Ruiz de Castañeda, R.; et al. Vulnerability to snakebite envenoming: A global mapping of hotspots. Lancet 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Estrada, R.; Herrera, M.; Gómez, A.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; León, G. Bothrops asper envenoming in cattle: Clinical features and management using equine-derived whole IgG antivenom. Vet. J. 2016, 207, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial Board. Snake-bite envenoming: A priority neglected tropical disease. Lancet 2017, 390, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayrer, J.S. The venomous snakes of India. Eclect. Mag. 1889. Available online: https://archive.org/details/b28710538 (accessed on 3 August 2018).
- Warrell, D.A. Snake bite. Lancet 2010, 375, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Chappuis, F.; Jha, N.; Bovier, P.A.; PLoutan, L.; Koirala, S. Impact of snake bites and determinants of fatal outcomes in Southeastern Nepal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.A.; Hargreaves, A.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Faragher, B.; Lalloo, D.G. Snake Envenoming: A Disease of Poverty. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) Appears to Be a Potent, Broad-Spectrum, Inhibitor of Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 and a Possible Pre-Referral Treatment for Envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, N.A.; Pereira, B.M.; do Nascimento, M.C.; Parente, J.P.; Mors, W.B. Pharmacological screening of plants recommended by folk medicine as snake venom antidotes; IV. Protection against jararaca venom by isolated constituents. Planta Med. 1994, 60, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panfoli, I.; Calzia, D.; Ravera, S.; Morelli, A. Inhibition of hemorrhagic snake venom components: Old and new approaches. Toxins 2010, 2, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.S.; Rucavado, A.; Gutierrez, J.-M. Peptidomimetic hydroxamate metalloproteinase inhibitors abrogate local and systemic toxicity induced by Echis ocellatus (saw-scaled) snake venom. Toxicon 2017, 132, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H. Snakebites: Costing recombinant antivenoms. Nature 2016, 538, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiyapuri, S.; Vaiyapuri, R.; Ashokan, R.; Ramasamy, K.; Nattamaisundar, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Chandran, V.; Gajjeraman, P.; Baksh, M.F.; Gibbins, J.M.; et al. Snakebite and Its Socio-Economic Impact on the Rural Population of Tamil Nadu, India. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, A.G.; Brown, N.I. The snakebite problem and antivenom crisis from a health-economic perspective. Toxicon 2018, 150, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzel, B.J.; Samuel, S.P.; Bulfone, T.C.; Raj, C.S.; Lewin, M.; Kahn, J.G. Snakebite: An Exploratory Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Adjunct Treatment Strategies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J. Proteomic tools against the neglected pathology of snake bite envenoming. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2011, 8, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.B.; Grubb, B.D.; Maltin, C.A.; Dixon, R. The neurotoxicity of the venom phospholipases A(2), notexin and taipoxin. Exp. Neurol. 2000, 161, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Ownby, C.L. Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: Insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 2003, 42, 915–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, D.W.; Bach, N.J.; Dillard, R.D.; Draheim, S.E.; Carlson, D.G.; Fox, N.; Roehm, N.W.; Armstrong, C.T.; Chang, C.H.; Hartley, L.W.; et al. Pharmacology of LY315920/S-5920, [[3-(aminooxoacetyl)-2-ethyl-1-(phenylmethyl)-1H-indol-4-yl]oxy] acetate, a potent and selective secretory phospholipase A2 inhibitor: A new class of anti-inflammatory drugs, SPI. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clemetson, K.J.; Lu, Q.; Clemetson, J.M. Snake venom proteins affecting platelets and their applications to anti-thrombotic research. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, H.; Xiong, S.; Huang, C. Exploration of the Inhibitory Potential of Varespladib for Snakebite Envenomation. Molecules 2018, 23, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adis, R.; Profile, D. Varespladib. Am. J. Cardiovasc Drugs 2011, 11, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Fohlman, J.; Eaker, D.; Karlsoon, E.; Thesleff, S. Taipoxin, an extremely potent presynaptic neurotoxin from the venom of the Australian snake taipan (Oxyuranus s. scutellatus). Isolation, characterization, quaternary structure and pharmacological properties. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 68, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalloo, D.G.; Trevett, A.J.; Korinhona, A.; Nwokolo, N.; Laurenson, I.F.; Paul, M.; Black, J.; Naraqi, S.; Mavo, B.; Saweri, A.; et al. Snake bites by the Papuan taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus canni): Paralysis, hemostatic and electrocardiographic abnormalities, and effects of antivenom. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 52, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevett, A.J.; Lalloo, D.G.; Nwokolo, N.C.; Naraqi, S.; Kevau, I.H.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Warrell, D.A. The efficacy of antivenom in the treatment of bites by the Papuan taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus canni). Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1995, 89, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasarnpun, S.; Walsh, J.; Awad, S.S.; Harris, J.B. Envenoming bites by kraits: The biological basis of treatment-resistant neuromuscular paralysis. Brain 2005, 128, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Fernández, J.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Segura, Á.; León, G.; Angulo, Y.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of the venom of the taipan snake, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia: Role of neurotoxic and procoagulant effects in venom toxicity. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.; Gutiérrez, J. Priority Actions and Progress to Substantially and Sustainably Reduce the Mortality, Morbidity and Socioeconomic Burden of Tropical Snakebite. Toxins 2016, 8, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; de Cássia de O Collaço, R.; Villalta, M.; Segura, Á.; Vargas, M.; Wright, C.E.; Paiva, O.K.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; León, G.; et al. Neutralization of the neuromuscular inhibition of venom and taipoxin from the taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) by F(ab)2 and whole IgG antivenoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 241, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lewin, M.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Samuel, S.P.; Herrera, M.; Bryan-Quirós, W.; Lomonte, B.; Bickler, P.E.; Bulfone, T.C.; Williams, D.J. Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100380
Lewin MR, Gutiérrez JM, Samuel SP, Herrera M, Bryan-Quirós W, Lomonte B, Bickler PE, Bulfone TC, Williams DJ. Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom. Toxins. 2018; 10(10):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100380
Chicago/Turabian StyleLewin, Matthew R., José María Gutiérrez, Stephen P. Samuel, María Herrera, Wendy Bryan-Quirós, Bruno Lomonte, Philip E. Bickler, Tommaso C. Bulfone, and David J. Williams. 2018. "Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom" Toxins 10, no. 10: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100380
APA StyleLewin, M. R., Gutiérrez, J. M., Samuel, S. P., Herrera, M., Bryan-Quirós, W., Lomonte, B., Bickler, P. E., Bulfone, T. C., & Williams, D. J. (2018). Delayed Oral LY333013 Rescues Mice from Highly Neurotoxic, Lethal Doses of Papuan Taipan (Oxyuranus scutellatus) Venom. Toxins, 10(10), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10100380







