Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins to Simultaneously Assess the Neutralization Potency of Antivenoms against Neurotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Naja atra Venom
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
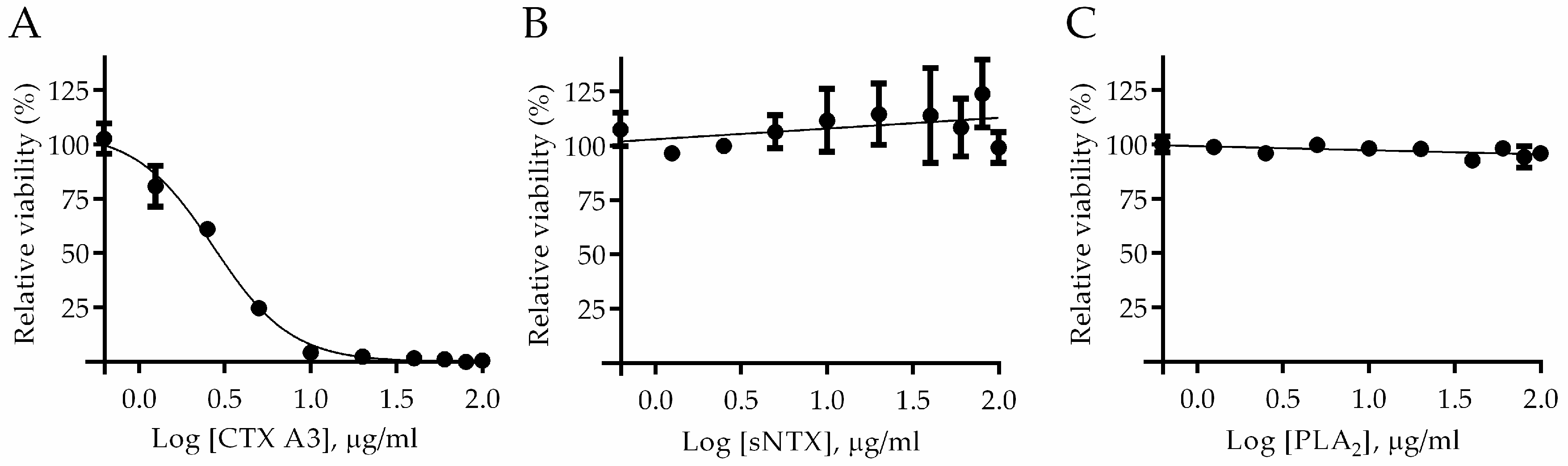
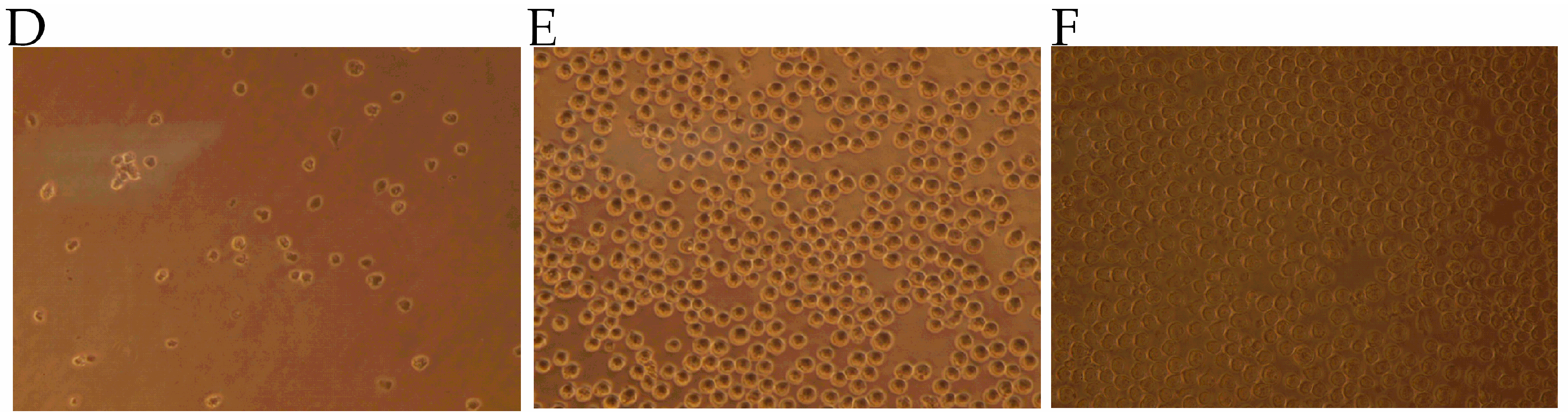
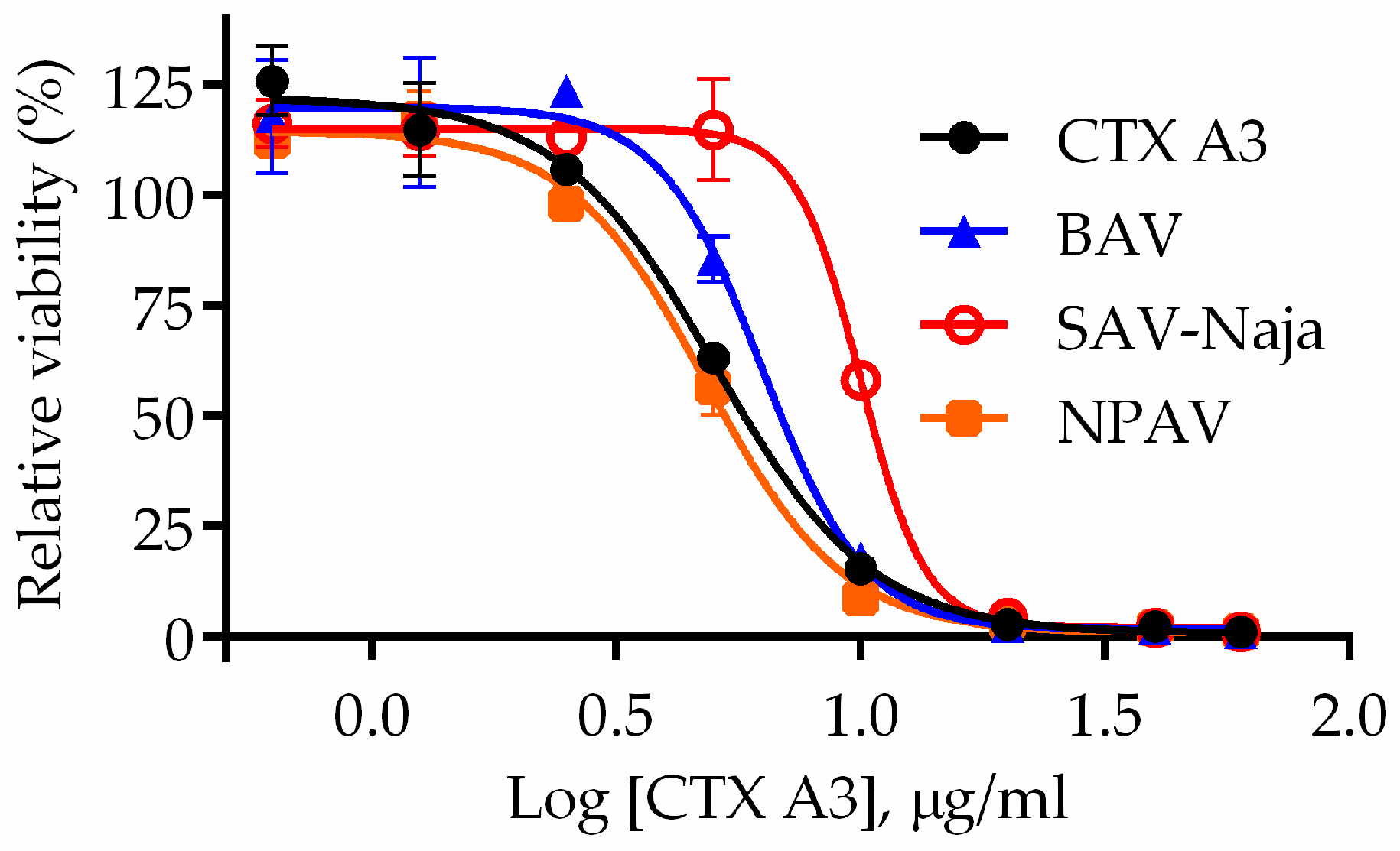
2.1. Determination of Major Toxic Component of N. atra Venom
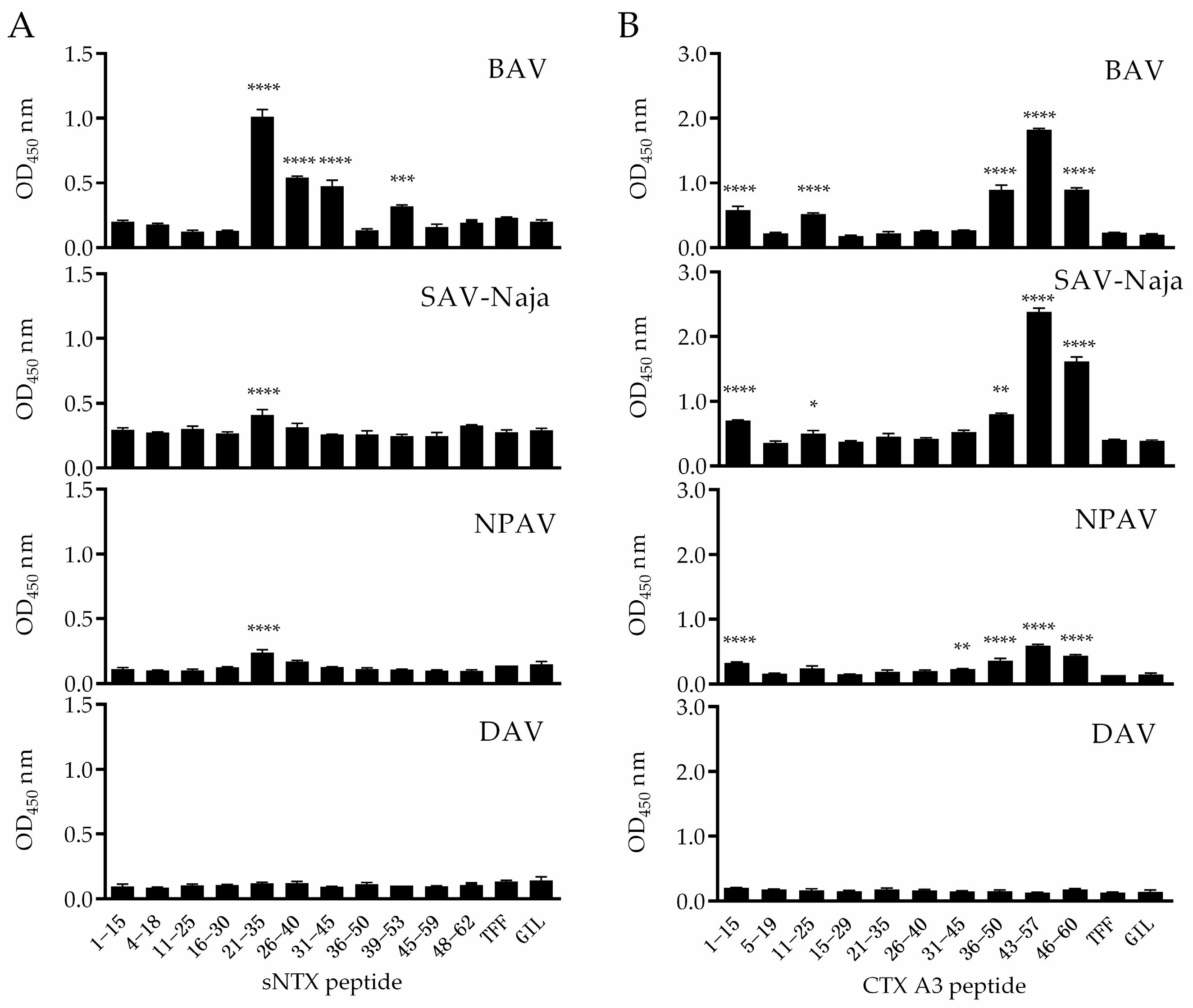
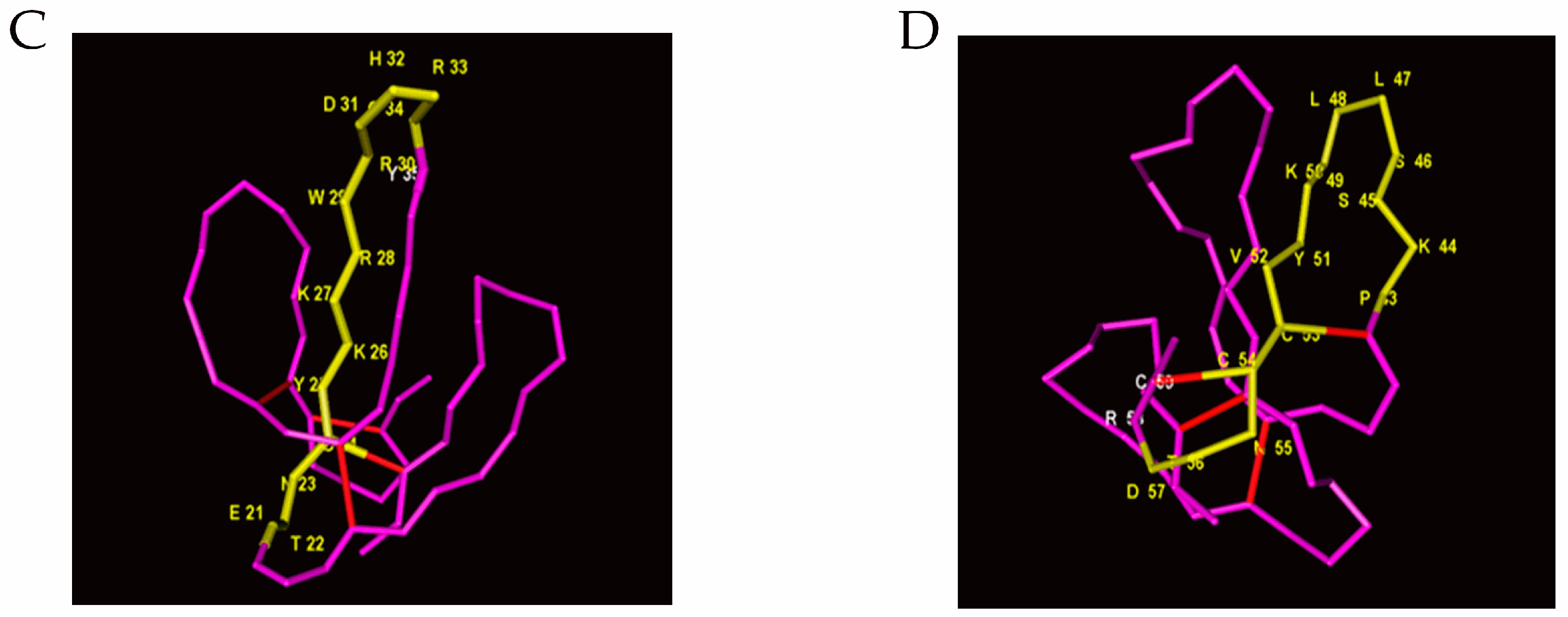
2.2. Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins
2.3. Specificity of Peptide-Specific Antibodies
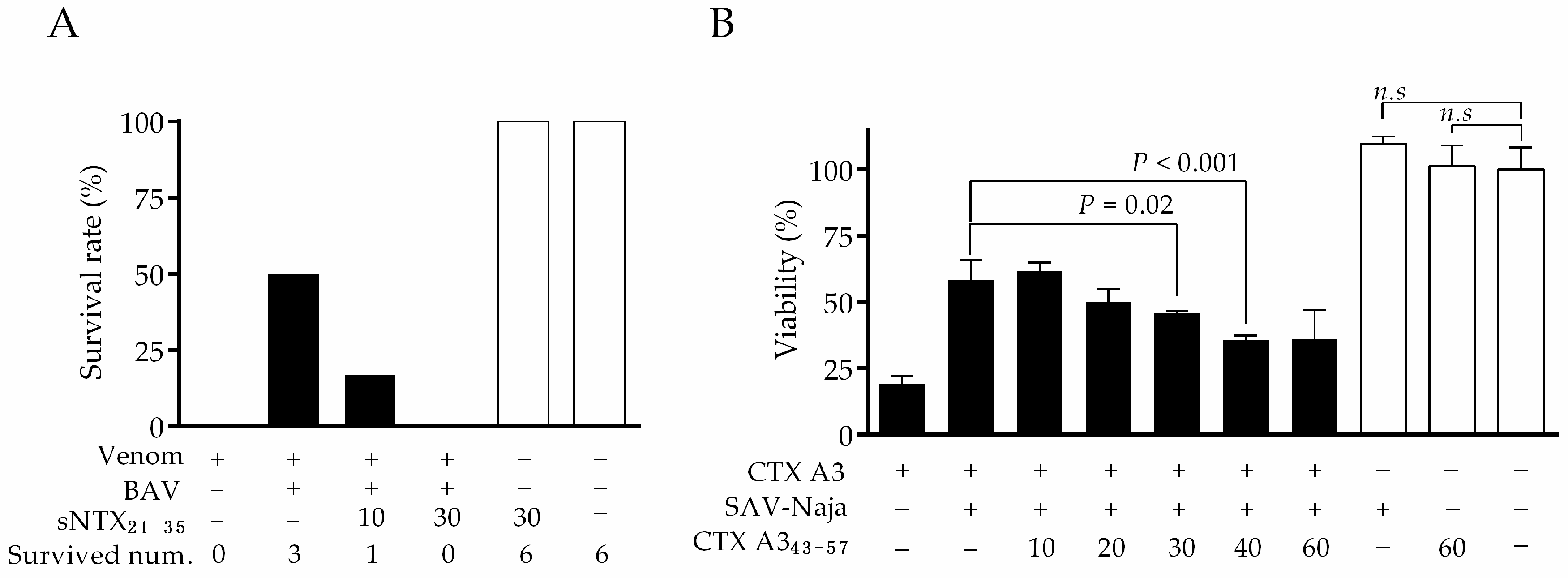
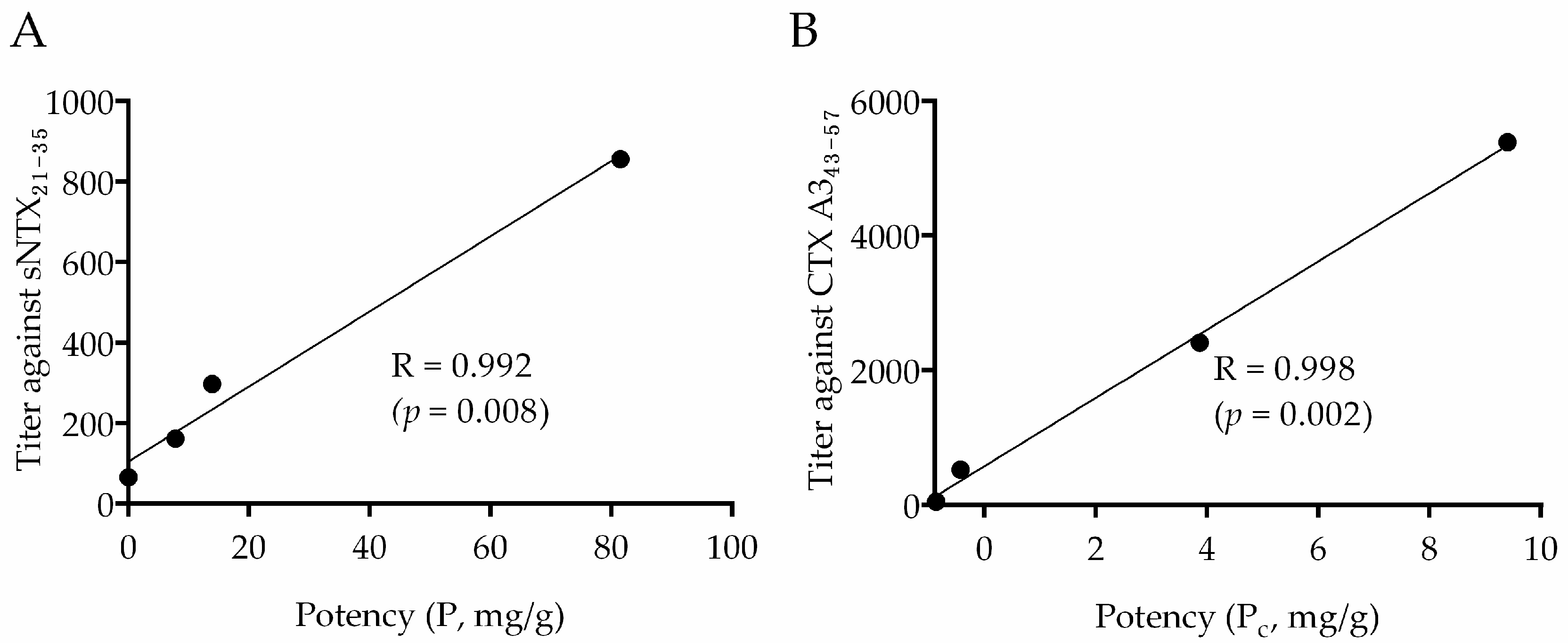
2.4. Correlation between Neutralization Potency and sNTX21–35 Antibody Titer
2.5. Correlation between Cytotoxic Inhibition Potency and CTX A343–57 Antibody Titer
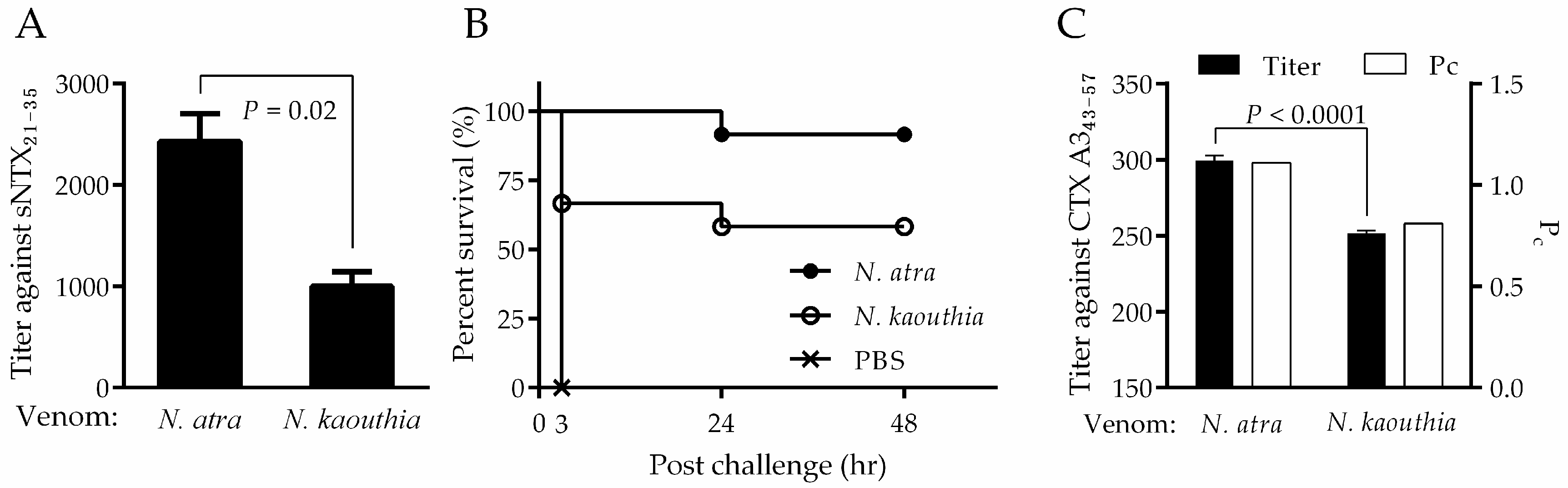
2.6. Assessment of the Neutralizing Capability of Mouse Antiserum by Peptide ELISA
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Preparation of Aantibody-Immobilized Columns
4.3. Immunoaffinity Analysis of Venom Proteins
4.4. Reverse-Phase HPLC Separation of Venom Proteins
4.5. Trypsin Digestion and Protein Identification
4.6. Animal Experiments
4.6.1. Animals
4.6.2. Determination of the Lethality of N. atra Venom and Purified Toxins
4.6.3. In-Vivo Neutralization Assay
4.6.4. Venom Immunization
4.7. Cytotoxicity of Toxins
4.8. In-Vitro Neutralization Assay against Cytotoxicity
4.9. Peptide Synthesis
4.10. Peptide ELISA
4.11. Determination of ELISA Antibody Titer against Immunoreactive Peptides
4.12. sNTX21–35 Peptide Competitive-Binding Block Assay
4.13. CTX A343–57 Peptide-Competitive Binding Block Assay
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, H.Y.; Wang, M.J.; Li, Y.H.; Tang, C.N.; Tsai, M.J. Can surgical need in patients with Naja atra (Taiwan or Chinese cobra) envenomation be predicted in the emergency department? Hong Kong Med. J. 2016, 22, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.L.; Gao, J.F.; Zhang, Y.X.; Shen, S.S.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.M.; Ji, X. Proteomic characterization and comparison of venoms from two elapid snakes (Bungarus multicinctus and Naja atra) from China. J. Proteome 2016, 138, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Chaou, C.H.; Tseng, C.Y. An investigation of snakebite antivenom usage in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2016, 115, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Offset Publication. Progress in the Characterization of Venoms and Standardization of Antivenoms; WHO Offset Publication: Geneva, Switzerland, 1981; Volume 58, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Theakston, R.D.; Warrell, D.A. Antivenoms: A list of hyperimmune sera currently available for the treatment of envenoming by bites and stings. Toxicon 1991, 29, 1419–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theakston, R.D.; Reid, H.A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in assessing antivenom potency. Toxicon 1979, 17, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsiwongse, J.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Development of an ELISA to assess the potency of horse therapeutic antivenom against Thai cobra venom. J. Immunol. Methods 1991, 136, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Pla, D.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M. Omics meets biology: Application to the design and preclinical assessment of antivenoms. Toxins 2014, 6, 3388–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Escolano, J.; Fernandez, J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and antivenomics of the arboreal neotropical pitvipers Bothriechis lateralis and Bothriechis schlegelii. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J.; Pla, D. Immunological profile of antivenoms: Preclinical analysis of the efficacy of a polyspecific antivenom through antivenomics and neutralization assays. J. Proteome 2014, 105, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, M.; Paiva, O.K.; Pagotto, A.H.; Segura, A.; Serrano, S.M.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Jensen, S.D.; Leon, G.; Williams, D.J.; et al. Antivenomic characterization of two antivenoms against the venom of the taipan, Oxyuranus scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Paiva, O.K.; Sanz, L.; Beutler, M.; Wright, C.E.; Calvete, J.J.; Williams, D.J.; Gutierrez, J.M. Preclinical efficacy of Australian antivenoms against the venom of the small-eyed snake, Micropechis ikaheka, from Papua New Guinea: An antivenomics and neutralization study. J. Proteome 2014, 110, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sintiprungrat, K.; Chaisuriya, P.; Watcharatanyatip, K.; Ratanabanangkoon, K. Immunoaffinity chromatography in antivenomics studies: Various parameters that can affect the results. Toxicon 2016, 119, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, W.S.; Cambuy, M.O.; Costa, J.O.; Velarde, D.T.; Chavez-Olortegui, C. Neutralizing potency of horse antibothropic antivenom. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro methods. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R. The SPOT-synthesis technique. Synthetic peptide arrays on membrane supports—Principles and applications. J. Immunol. Methods 2002, 267, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Napoleao-Pego, P.; Teixeira-Pinto, L.A.; Santos, J.D.; De-Simone, T.S.; Melgarejo, A.R.; Aguiar, A.S.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P. Linear B-cell epitopes in BthTX-1, BthTX-II and BthA-1, phospholipase A(2)’s from Bothrops jararacussu snake venom, recognized by therapeutically neutralizing commercial horse antivenom. Toxicon 2013, 72, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B. Identification of linear B-cell epitopes on myotoxin II, a Lys49 phospholipase A(2) homologue from Bothrops asper snake venom. Toxicon 2012, 60, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, K.L.; Duarte, C.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Machado de Avila, R.A.; Schneider, F.S.; Oliveira, D.; Freitas, C.F.; Kalapothakis, E.; Ho, P.L.; Chavez-Olortegui, C. Identification and characterization of B-cell epitopes of 3FTx and PLA2 toxins from Micrurus corallinus snake venom. Toxicon 2015, 93, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, F.S.; de Almeida Lima, S.; Reis de Avila, G.; Castro, K.L.; Guerra-Duarte, C.; Sanchez, E.F.; Nguyen, C.; Granier, C.; Molina, F.; Chavez-Olortegui, C. Identification of protective B-cell epitopes of Atroxlysin-I: A metalloproteinase from Bothrops atrox snake venom. Vaccine 2016, 34, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M.; Jespersen, M.C.; Lomonte, B.; Lund, O.; Laustsen, A.H. High-density peptide microarray exploration of the antibody response in a rabbit immunized with a neurotoxic venom fraction. Toxicon 2017, 138, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engmark, M.; Andersen, M.R.; Laustsen, A.H.; Patel, J.; Sullivan, E.; de Masi, F.; Hansen, C.S.; Kringelum, J.V.; Lomonte, B.; Gutierrez, J.M.; et al. High-throughput immuno-profiling of mamba (Dendroaspis) venom toxin epitopes using high-density peptide microarrays. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, N.D.; Pereira, S.S.; da Silva, M.P.; Morais, M.S.; Kayano, A.M.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Luiz, M.B.; Zanchi, F.B.; Fuly, A.L.; Huacca, M.E.; et al. Inhibition of the Myotoxicity Induced by Bothrops jararacussu Venom and Isolated Phospholipases A2 by Specific Camelid Single-Domain Antibody Fragments. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.W.; Liu, B.S.; Chien, K.Y.; Chiang, L.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Sung, W.C.; Wu, W.G. Cobra venom proteome and glycome determined from individual snakes of Naja atra reveal medically important dynamic range and systematic geographic variation. J. Proteome 2015, 128, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagides, N.; Jackson, T.N.; Ikonomopoulou, M.P.; Arbuckle, K.; Pretzler, R.; Yang, D.C.; Ali, S.A.; Koludarov, I.; Dobson, J.; Sanker, B.; et al. How the cobra got its flesh-eating venom: Cytotoxicity as a defensive innovation and its co-evolution with hooding, aposematic marking, and spitting. Toxins 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laustsen, A.H.; Lohse, B.; Lomonte, B.; Engmark, M.; Gutierrez, J.M. Selecting key toxins for focused development of elapid snake antivenoms and inhibitors guided by a Toxicity Score. Toxicon 2015, 104, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calvete, J.J.; Lomonte, B. A bright future for integrative venomics. Toxicon 2015, 107, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirtschin, P.J.; Dunstan, N.; Hough, B.; Hamilton, E.; Klein, S.; Lucas, J.; Millar, D.; Madaras, F.; Nias, T. Venom yields from Australian and some other species of snakes. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.H.; Wong, K.Y.; Tan, C.H. Venomics of Naja sputatrix, the Javan spitting cobra: A short neurotoxin-driven venom needing improved antivenom neutralization. J. Proteome 2017, 157, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.G. Cobra cardiotoxin and phospholipase A2 as GAG-binding toxins: On the path from structure to cardiotoxicity and inflammation. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1998, 8, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Guan, H.H.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, W.N.; Tjong, S.C.; Chen, C.J.; Wu, W.G. Structural basis of citrate-dependent and heparan sulfate-mediated cell surface retention of cobra cardiotoxin A3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9567–9577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.J.; Leung, Y.M.; Huang, S.J.; Kwan, C.Y. Dual effects of extracellular Ca2+ on cardiotoxin-induced cytotoxicity and cytosolic Ca2+ changes in cultured single cells of rabbit aortic endothelium. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1330, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhar, F.; Huang, W.N.; Liu, J.H.; Chien, K.Y.; Wu, W.G.; Hsiao, C.D. Structural basis of membrane-induced cardiotoxin A3 oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21980–21988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padlan, E.A.; Silverton, E.W.; Sheriff, S.; Cohen, G.H.; Smith-Gill, S.J.; Davies, D.R. Structure of an antibody-antigen complex: Crystal structure of the HyHEL-10 Fab-lysozyme complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5938–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruchart-Gaillard, C.; Gilquin, B.; Antil-Delbeke, S.; Le Novere, N.; Tamiya, T.; Corringer, P.J.; Changeux, J.P.; Menez, A.; Servent, D. Experimentally based model of a complex between a snake toxin and the alpha 7 nicotinic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3216–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Menez, A.; Kessler, P. How do short neurotoxins bind to a muscular-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptor? J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25741–25747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunagar, K.; Jackson, T.N.; Undheim, E.A.; Ali, S.A.; Antunes, A.; Fry, B.G. Three-Fingered RAVERs: Rapid accumulation of variations in exposed residues of snake venom toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 2172–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Geer, L.Y.; Chappey, C.; Kans, J.A.; Bryant, S.H. Cn3D: Sequence and structure views for Entrez. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, K.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Hseu, Y.C.; Vyas, A.A.; Rule, G.S.; Wu, W. Two distinct types of cardiotoxin as revealed by the structure and activity relationship of their interaction with zwitterionic phospholipid dispersions. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14473–14483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jayaraman, G.; Kumar, T.K.; Tsai, C.C.; Srisailam, S.; Chou, S.H.; Ho, C.L.; Yu, C. Elucidation of the solution structure of cardiotoxin analogue V from the Taiwan cobra (Naja naja atra)—Identification of structural features important for the lethal action of snake venom cardiotoxins. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.C.; Loh, K.S.; Lin, S.T.; Chien, T.L.; Chiang, J.R.; Hsieh, W.C.; Miao, B.L.; Su, C.F.; Yang, W.J. Consensus sequence L/PKSSLL mimics crucial epitope on Loop III of Taiwan cobra cardiotoxin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, P.K.; Sim, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Sumana, K.; Sitprija, V.; Tan, N.H. Cross neutralization of Afro-Asian cobra and Asian krait venoms by a Thai polyvalent snake antivenom (Neuro Polyvalent Snake Antivenom). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.Y.; Tan, C.H.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H. Venomics, lethality and neutralization of Naja kaouthia (monocled cobra) venoms from three different geographical regions of Southeast Asia. J. Proteome 2015, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lee, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Venom gland transcriptomes of two elapid snakes (Bungarus multicinctus and Naja atra) and evolution of toxin genes. BMC Genom. 2011, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmi, L.; Makran, B.; Pla, D.; Sanz, L.; Oukkache, N.; Lkhider, M.; Harrison, R.A.; Ghalim, N.; Calvete, J.J. Venomics and antivenomics profiles of North African Cerastes cerastes and C. vipera populations reveals a potentially important therapeutic weakness. J. Proteome 2012, 75, 2442–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalta, M.; Pla, D.; Yang, S.L.; Sanz, L.; Segura, A.; Vargas, M.; Chen, P.Y.; Herrera, M.; Estrada, R.; Cheng, Y.F.; et al. Snake venomics and antivenomics of Protobothrops mucrosquamatus and Viridovipera stejnegeri from Taiwan: Keys to understand the variable immune response in horses. J. Proteome 2012, 75, 5628–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.A.; Russo, R.C.; Thurston, R.V. Trimmed Spearman-Karber Method for Estimating Median Lethal Concentrations in Toxicity Bioassays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1977, 11, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, V.; Ifran, S.; Berasain, P.; Massaldi, H. Antivenoms: Potency or median effective dose, which to use? J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 2010, 16, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein | Percentage of Retained Protein b (%) | LD50 (μg/g) | IC50 (μg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antivenomic | |||||
| BAV | SAV-Naja | NPAV | |||
| sNTX | 100.0 | 32.5 | 21.8 | 0.23 (0.17–0.31) | N.D. d |
| CTXs a | 19.9 | 50.2 | 9.6 | 2.12 (1.82–2.49) | 6.82 (5.99–7.76) |
| PLA2 | 17.6 | 74.2 | 100.0 | >50 c | N.D. |
| Antivenom | 5 × LD50 N. atra Venom | CTX A3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED50 (mg) a | ER50 (mg/g) b | P (mg/g) c | Pc (mg/g) d | |
| BAV | 0.66 | 101.82 (86.97–119.17) | 81.5 | 3.87 * |
| SAV-Naja | 3.86 | 17.41 (14.87–20.38) | 13.9 | 9.40 § |
| NPAV | 6.93 | 9.70 (8.28–11.35) | 7.8 | NE |
| DAV | NE e | NE | NE | NE |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.-S.; Wu, W.-G.; Lin, M.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Jiang, B.-R.; Wu, S.-C.; Leng, C.-H.; Sung, W.-C. Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins to Simultaneously Assess the Neutralization Potency of Antivenoms against Neurotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Naja atra Venom. Toxins 2018, 10, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010010
Liu B-S, Wu W-G, Lin M-H, Li C-H, Jiang B-R, Wu S-C, Leng C-H, Sung W-C. Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins to Simultaneously Assess the Neutralization Potency of Antivenoms against Neurotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Naja atra Venom. Toxins. 2018; 10(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bing-Sin, Wen-Guey Wu, Min-Han Lin, Chi-Han Li, Bo-Rong Jiang, Suh-Chin Wu, Chih-Hsiang Leng, and Wang-Chou Sung. 2018. "Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins to Simultaneously Assess the Neutralization Potency of Antivenoms against Neurotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Naja atra Venom" Toxins 10, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010010
APA StyleLiu, B.-S., Wu, W.-G., Lin, M.-H., Li, C.-H., Jiang, B.-R., Wu, S.-C., Leng, C.-H., & Sung, W.-C. (2018). Identification of Immunoreactive Peptides of Toxins to Simultaneously Assess the Neutralization Potency of Antivenoms against Neurotoxicity and Cytotoxicity of Naja atra Venom. Toxins, 10(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010010






