Differences in Dietary Preferences, Personality and Mental Health in Australian Adults with and without Food Addiction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Dietary Behaviour
3.2.1. Food Addiction
3.2.2. Associations with Weight
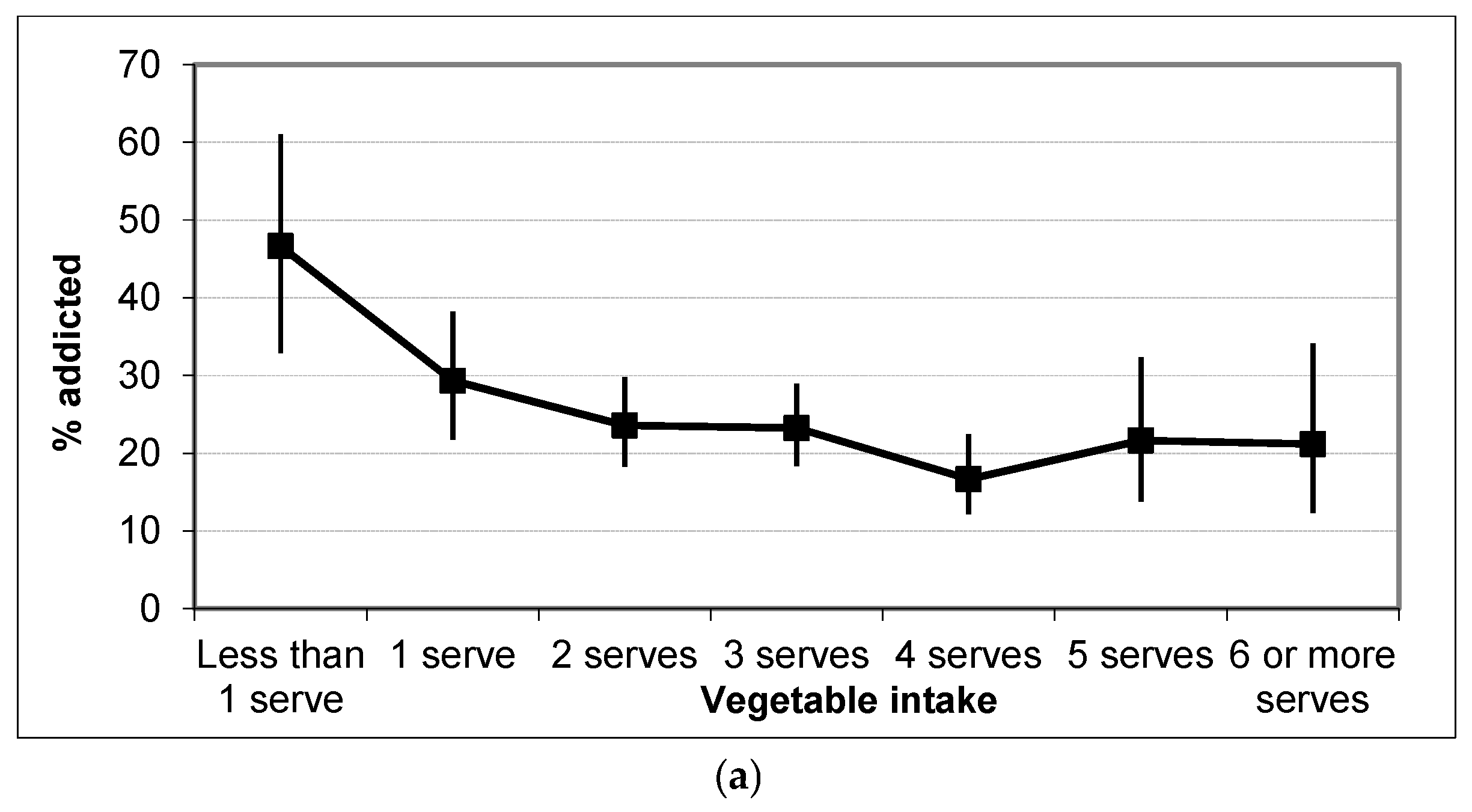
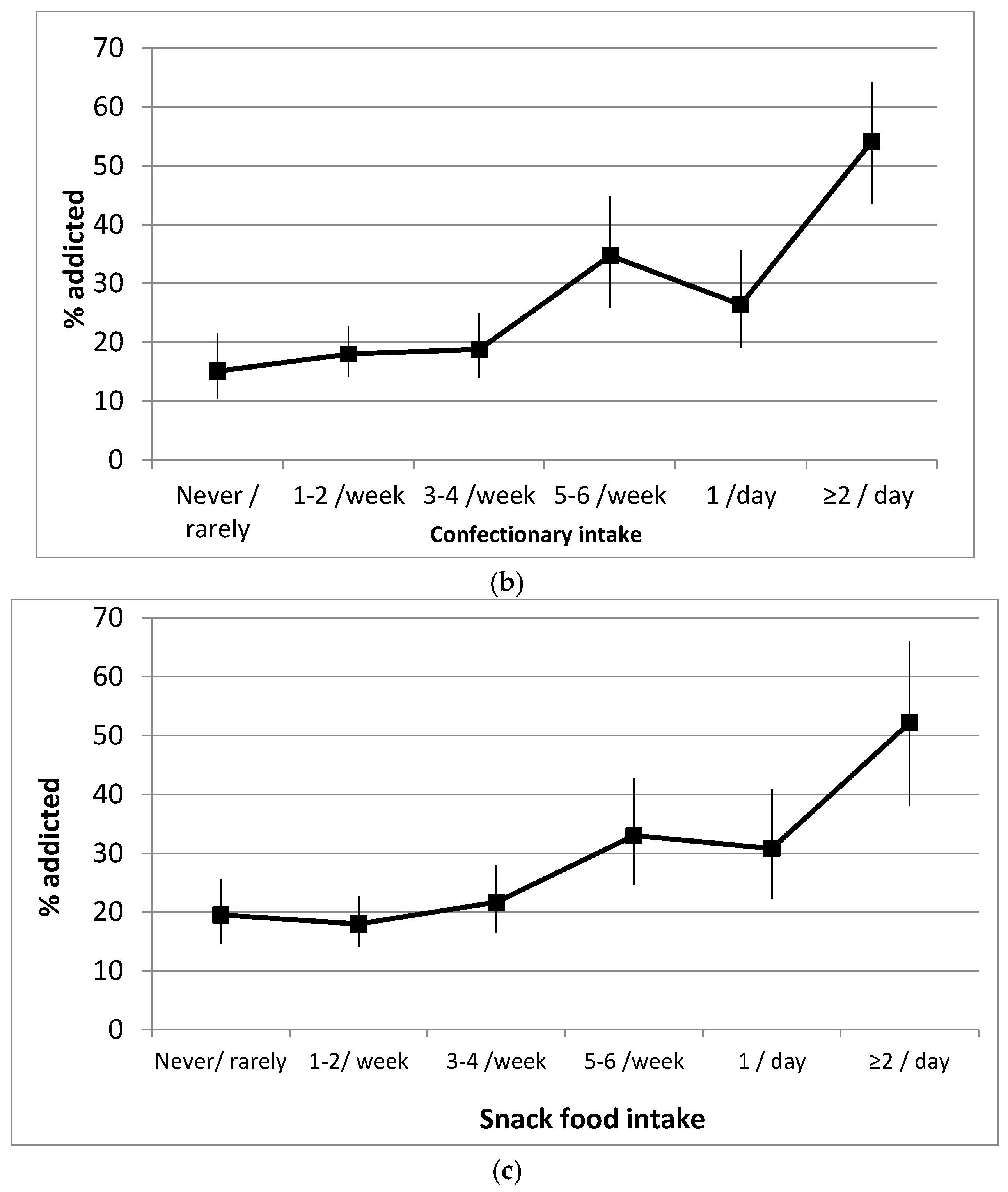
3.2.3. Associations with Diet
3.2.4. Associations with Personality and Mental Health
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meule, A. Focus: Addiction: Back by Popular Demand: A Narrative Review on the History of Food Addiction Research. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairnsa, G.; Angusa, K.; Hastingsa, G.; Caraherb, M. Systematic reviews of the evidence on the nature, extent and effects of food marketing to children. A retrospective summary. Appetite 2013, 62, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (Ed.) Australian Health Survey: Nutrition First Results—Foods and Nutrients, 2011–2012; Australian Bureau of Statistics: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Gearhardt, A.; Yokum, S.; Orr, P.; Stice, E.; Corbin, W.; Brownell, K. Neural correlates of food addiction. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.; Loxton, N.J.; Levitan, R.D.; Kaplan, A.S.; Carter, J.C.; Kennedy, J.L. ‘Food Addiction’ and its Association with a Dopaminergic Multilocus Genetic Profile. Physiol. Behav. 2013, 118, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.M.; Stojek, M.K.; MacKillop, J. Interrelationships among impulsive personality traits, food addiction, and body mass index. Appetite 2014, 73, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Kübler, A. Food cravings in food addiction: The distinct role of positive reinforcement. Eat. Behav. 2012, 13, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Gearhardt, A. Five years of the Yale Food Addiction Scale: Taking stock and moving forward. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2014, 1, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursey, K.M.; Stanwell, P.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Collins, C.E.; Burrows, T.L. The Prevalence of Food Addiction as Assessed by the Yale Food Addiction Scale: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4552–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pursey, K.M.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Burrows, T.L. The relationship between “food addiction” and visceral adiposity in young females. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 157, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.; Corbin, W.; Brownwell, K.D. Preliminary validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale. Appetite 2009, 52, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.; Roberto, C.; Seamans, M.; Corbin, W.; Brownell, K. Preliminary validation of the Yale Food Addiction Scale for children. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, S.; Rodriguez, S.; Carmin Fernandez, M.; Tamez, J.; Cepedo-Bernito, A. Clinical Validation of the Trait and State Versions of the Food Craving Questionnaire. Assessment 2008, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.; Whisenhunt, B.; Williamson, D.; Greenway, F.; Netemeyer, R. Development and validation of the food-craving inventory. Obes Res. 2002, 10, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.; Bergers, G.; Defares, P. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for assessment of restrained, emotional, and external eating behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, P.; Wadden, D.; Amini, P.; Gulliver, W.; Randell, E.; Cahill, F.; Vasdev, S.; Goodridge, A.; Carter, J.C.; Zhai, G.; et al. Food Addiction: Its Prevalence and Significant Association with Obesity in the General Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, E.; Avena, N.; Gearhardt, A. Which Foods May Be Addictive? The Roles of Processing, Fat Content, and Glycemic Load. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pursey, K.; Stanwell, P.; Collins, C.; Burrows, T. Foods and dietary profiles associated with ‘food addiction’ in young adults. Addict. Behav. Rep. 2015, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromann, C.B.; Nielsen, C.T. A case of cola dependency in a woman with recurrent depression. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Stein, R.I.; Eagon, J.C.; Klein, S. Bariatric surgery-induced weight loss causes remission of food addiction in extreme obesity. Obesity 2014, 22, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hides, L.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Daglish, M.; Cotton, S.; Connor, J.P.; Barendregt, J.J.; Young, R.M.; Sanders, D.; White, A.; Mergard, L. The Quik Fix study: A randomised controlled trial of brief interventions for young people with alcohol related injuries and illnesses accessing emergency department and crisis support care. BMC Emerg. Med. 2014, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.; Burgess, E.S.; Clark, M.; Zvolensky, M.J.; Brown, R.A. Anxiety sensitivity, self-reported motives for alcohol and nicotine use, and level of consumption. J. Anxiety Disord. 2003, 17, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woicik, P.A.; Stewart, S.H.; Pihl, R.O.; Conrod, P.J. The Substance Use Risk Profile Scale: A scale measuring traits linked to reinforcement-specific substance use profiles. Addict. Behav. 2009, 34, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.; Corbin, W.; Brownwell, K.D. Development of the Yale Food Addiction Scale Version 2.0. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2016, 30, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, V.; Webb, K.; Rangan, A. Recommendations for Short Questions to Assess Food Consumption in Children for the NSW Health Surveys; NSW Centre for Public Health Nutrition: Sydney, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, J.; Crawford, J. The short-form version of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21): Construct validity and normative data in a large non-clinical sample. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 44, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchison, D.; Hay, P.; Slewa-Younan, S.; Mond, J. Time trends in the population prevalence of eating disorder behaviours and their relationship to quality of life. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magid, V.; MacLean, M.; Coldera, C. Differentiating between sensation seeking and impulsivity through their mediated relations with alcohol use and problems. Addict. Behav. 2007, 32, 2046–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhardt, A.; White, M.; Masheb, R.; Grilo, C. An examination of food addiction in a racially diverse sample of obese patients with binge eating disorder in primary care setting. Compr. Psychiatry 2013, 54, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heatherton, T.F.; Baumeister, R.F. Binge eating as escape from self-awareness. Psychol. Bull. 1991, 110, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mond, J.M. Eating Disorders, ‘mental health literacy’: An introduction. J. Ment. Health 2014, 23, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | 18–34 Years | 35–54 Years | 55+ Years | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| n | n | n | n | n | n | ||||
| Gender | 88 (16%) | 462 (84%) | n = 550 | 107 (22%) | 382 (78%) | n = 489 | 43 (24%) | 139 (76%) | n = 182 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.7 ± 5.57 | 25.2 ± 6.49 | 25.4 ± 6.4 | 29.2 ± 5.82 | 29.5 ± 13.6 | 24.5 ± 12.4 | 30.08 ± 7.7 | 29.4 ± 7.1 | 29.6 ± 7.2 |
| Healthy weight (%) | 44.8 | 63.5 | 60.4 | 21.9 | 38.0 | 34.4 | 26.8 | 30.6 | 27.5 |
| Overweight (%) | 34.5 | 19.2 | 21.6 | 41.9 | 26.0 | 29.5 | 29.3 | 30.6 | 30.3 |
| Obese (%) | 20.7 | 17.4 | 17.9 | 36.2 | 36.1 | 36.1 | 43.9 | 41.8 | 42.3 |
| SES (ISRAD) 1 | 6.2 ± 2.9 | 6.2 ± 2.8 | 5.9 ± 2.6 | ||||||
| Food addiction 2 (% Addicted) | 12.2 | 23.7 | 21.4 | 12.6 | 24.9 | 22.3 | 16.7 | 26.6 | 24.1 |
| - Mild | 0 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| - Moderate | 2.7 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| - Severe | 9.5 | 19.7 | 18.1 | 10.3 | 19.9 | 17.8 | 16.7 | 25.8 | 23.5 |
| Total FA symptoms (Range 0–12) | 3.5 ± 2.39 | 4.06 ± 2.93 | 4.0 ± 2.9 | 3.21 ± 2.36 | 4.14 ± 2.83 | 3.9 ± 2.8 | 3.64 ± 2.5 | 4.36 ± 2.86 | 4.2 ± 2.8 |
| Variables | Not Food Addicted n = 659 | Food Addicted n = 202 | p Value | Mild n = 7 | Moderate n = 24 | Severe n = 171 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food Addiction Symptoms | 2.83 ± 1.8 | 7.72 ± 2.11 | <0.001 | 2.71 ± 0.49 | 4.56 ± 0.51 | 8.35 ± 1.57 | <0.001 |
| DASS depression (total domain score) | 6.9 ± 6.8 | 15.7 ± 10.4 | <0.001 | 17.4 ± 10.1 | 10.2 ± 8.1 | 16.5 ± 10.5 | <0.001 |
| - Mild (%) | 10.5 | 9.4 | <0.001 | 14.3 | 20.8 | 7.6 | <0.001 |
| - Moderate (%) | 9.9 | 27.7 | 28.6 | 25 | 28.1 | ||
| - Severe (%) | 2.0 | 12.2 | 14.0 | 0 | 14 | ||
| - Extremely severe (%) | 2.1 | 16.8 | 14.3 | 4.2 | 18.7 | ||
| DASS anxiety (total domain score) | 4.3 ± 4.5 | 9.8 ± 7.4 | <0.001 | 7.7 ± 6.5 | 5.6 ± 4.9 | 10.8 ± 7.5 | <0.001 |
| - Mild (%) | 12.1 | 14.9 | <0.001 | 14.3 | 29.2 | 12.9 | <0.001 |
| - Moderate (%) | 5.9 | 15.8 | 28.6 | 4.2 | 17 | ||
| - Severe (%) | 1.5 | 10.9 | 14.3 | 0 | 12.8 | ||
| - Extremely severe (%) | 1.4 | 12.9 | 0 | 4.2 | 14.6 | ||
| DASS Stress (total domain score) | 9.7 ± 7.1 | 17.3 ± 8.8 | <0.001 | 15.4 ± 9.6 | 13.6 ± 8.1 | 17.9 ± 8.8 | <0.001 |
| - Mild (%) | 9.7 | 14.4 | <0.001 | 14.3 | 20.8 | 13.5 | <0.001 |
| - Moderate (%) | 7.9 | 17.8 | 0 | 12.5 | 19.3 | ||
| - Severe (%) | 2.7 | 19.8 | 28.6 | 4.2 | 21.6 | ||
| - Extremely severe (%) | 0.3 | 3.0 | 0 | 4.2 | 2.9 | ||
| SURPS | |||||||
| Hopelessness | 18.62 ± 3.1 | 15.37 ± 3.7 | <0.001 | 14.29 ± 4.27 | 17.25 ± 3.4 | 15.14 ± 3.66 | <0.001 |
| Anxiety sensitivity | 11.86 ± 2.69 | 13.37 ± 2.86 | <0.001 | 11.86 ± 3.02 | 12.67 ± 3.13 | 13.53 ± 2.79 | <0.001 |
| Impulsivity | 9.85 ± 2.42 | 10.95 ± 2.65 | <0.001 | 11 ± 4.32 | 10.79 ± 2.64 | 10.98 ± 2.58 | <0.001 |
| Sensation Seeking | 12.21 ± 3.29 | 10.91 ± 3.32 | <0.001 | 11.86 ± 1.95 | 12.96 ± 3.41 | 10.58 ± 3.25 | <0.001 |
| Variable | B (S.E) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety sensitivity a | 0.155 (0.041) | 1.59 ( 1.25–2.03) * | <0.001 |
| Vegetable consumption | −0.205 (0.068) | 0.81 (0.71–0.93) | 0.003 |
| Soft drink consumption | 0.307 (0.121) | 1.36 (1.07–1.32) | 0.011 |
| Females | −1.294 (0.341) | 3.65 (1.86–7.11) | 0.000 |
| Depression Nil b | - | ||
| Depression Mild | 0.440 (0.356) | 1.55 (0.77–3.12) | 0.217 |
| Depression Moderate | 1.885 (0.263) | 6.58 (3.93–11.04) | 0.000 |
| Depression Severe | 2.581 (0.416) | 13.2 (5.84–29.83) | 0.000 |
| Depression Extremely severe | 2.747 (0.402) | 15.59 (7.1–34.3) | 0.000 |
| Confectionaries Never or rarely | - | - | - |
| Confectionaries 1–2 per week | 0.402 (0.371) | 1.49 (0.72–3.09) | 0.279 |
| Confectionaries 3–4 per week | 0.170 (0.404) | 1.18 (0.54–2.61) | 0.673 |
| Confectionaries 5–6 per week | 0.914(0.432) | 2.4 (1.1–5.8) | 0.034 |
| Confectionaries 1 per day | 0.891(0.419) | 2.43 (1.1–5.5) | 0.033 |
| Confectionaries ≥2 per day | 1.963(0.417) | 7.1 (3.1–16.1) | 0.000 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Burrows, T.; Hides, L.; Brown, R.; Dayas, C.V.; Kay-Lambkin, F. Differences in Dietary Preferences, Personality and Mental Health in Australian Adults with and without Food Addiction. Nutrients 2017, 9, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030285
Burrows T, Hides L, Brown R, Dayas CV, Kay-Lambkin F. Differences in Dietary Preferences, Personality and Mental Health in Australian Adults with and without Food Addiction. Nutrients. 2017; 9(3):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030285
Chicago/Turabian StyleBurrows, Tracy, Leanne Hides, Robyn Brown, Christopher V Dayas, and Frances Kay-Lambkin. 2017. "Differences in Dietary Preferences, Personality and Mental Health in Australian Adults with and without Food Addiction" Nutrients 9, no. 3: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030285
APA StyleBurrows, T., Hides, L., Brown, R., Dayas, C. V., & Kay-Lambkin, F. (2017). Differences in Dietary Preferences, Personality and Mental Health in Australian Adults with and without Food Addiction. Nutrients, 9(3), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030285






