The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Eligible Studies and Characteristics
3.2. The Effects of Age and Setting on the Prevalence of VAD and MVAD
3.3. The Prevalence of VAD and MVAD in Chinese Children in 2015 and the Public Health Significance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Murray, C.J. Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fairfield, K.M.; Fletcher, R.H. Vitamins for chronic disease prevention in adults: Scientific review. JAMA 2002, 287, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephensen, C.B. Vitamin A, infection, and immune function. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dary, O.; Mora, J.O. Food fortification to reduce vitamin a deficiency: International vitamin a consultative group recommendations. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2927S–2933S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Allen, L.H.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Caulfield, L.E.; De Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Mathers, C.; Rivera, J.; Maternal and Child Undernutrition Study Group. Maternal and child undernutrition: Global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008, 371, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, M.; Lopez, A.D.; Rodgers, A.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Murray, C.J.; Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating Group. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Global Prevalence of Vitamin a Deficiency in Populations at Risk 1995–2005: Who Global Database on Vitamin a Deficiency; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, L.H.; De Benoist, B.; Dary, O.; Hurrell, R.; World Health Organization. Guidelines on Food Fortification with Micronutrients; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Imdad, A.; Herzer, K.; Mayo-Wilson, E.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin a Supplementation for Preventing Morbidity and Mortality in Children from 6 Months to 5 Years of Age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2010, 12, CD008524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imdad, A.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Sudfeld, C.; Haider, B.A.; Black, R.E.; Bhutta, Z.A. Impact of vitamin a supplementation on infant and childhood mortality. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmathullah, L.; Tielsch, J.M.; Thulasiraj, R.; Katz, J.; Coles, C.; Devi, S.; John, R.; Prakash, K.; Sadanand, A.; Edwin, N. Impact of supplementing newborn infants with vitamin a on early infant mortality: Community based randomised trial in southern india. BMJ 2003, 327, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, C.; Foster, A. Childhood blindness in the context of vision 2020: The right to sight. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gogate, P.; Kalua, K.; Courtright, P. Blindness in childhood in developing countries: Time for a reassessment? PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, G.A.; Bennett, J.E.; Hennocq, Q.; Lu, Y.; De-Regil, L.M.; Rogers, L.; Danaei, G.; Li, G.; White, R.A.; Flaxman, S.R. Trends and mortality effects of vitamin a deficiency in children in 138 low-income and middle-income countries between 1991 and 2013: A pooled analysis of population-based surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e528–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicular, T.; Yue, X.; Gustafsson, B.; Shi, L. The urban–rural income gap and inequality in china. Rev. Income Wealth 2007, 53, 93–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fang, H.; Zhao, Z. Urban–rural disparities of child health and nutritional status in china from 1989 to 2006. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2013, 11, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, I.C. Chinese journals: A guide for epidemiologists. Emerg. Themes Epidemiol. 2008, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wright, J.; Adams, C.E. Five large chinese biomedical bibliographic databases: Accessibility and coverage. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2008, 25, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.F.; Korevaar, D.A.; Wang, J.; Spijker, R.; Bossuyt, P.M. Should we search chinese biomedical databases when performing systematic reviews? Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.M.; Davey, J.; Clarke, M.J.; Thompson, S.G.; Higgins, J.P. Predicting the extent of heterogeneity in meta-analysis, using empirical data from the cochrane database of systematic reviews. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Best, N.G.; Carlin, B.P.; Van Der Linde, A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2002, 64, 583–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, B.A.; Blanck, H.M.; Slutsker, L.; Cookson, S.T.; Larson, M.K.; Duffield, A.; Bhatia, R. Anaemia, iron status and vitamin a deficiency among adolescent refugees in kenya and nepal. Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Department of Population and Employment Statistics of the National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Population and Employment Statistics Yearbook 2016; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Sommer, A.; World Health Organization. Vitamin a Deficiency and Its Consequences: A Field Guide to Detection and Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, S.; Ahmed, A.; Randhawa, M.A.; Atukorala, S.; Arlappa, N.; Ismail, T.; Ali, Z. Prevalence of vitamin a deficiency in south asia: Causes, outcomes, and possible remedies. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotto, I.; Mimouni, M.; Gdalevich, M.; Mimouni, D. Vitamin a supplementation and childhood morbidity from diarrhea and respiratory infections: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. 2003, 142, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.H.; Haskell, M. Estimating the potential for vitamin a toxicity in women and young children. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2907S–2919S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use of and Interpretation of Anthropometry, Report of a Who Expert Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Thurnham, D.I.; McCabe, G.; Northrop-Clewes, C.; Nestel, P. Effects of subclinical infection on plasma retinol concentrations and assessment of prevalence of vitamin a deficiency: Meta-analysis. Lancet 2003, 362, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Wilson, E.; Imdad, A.; Herzer, K.; Yakoob, M.Y.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin a supplements for preventing mortality, illness, and blindness in children aged under 5: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2011, 343, d5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

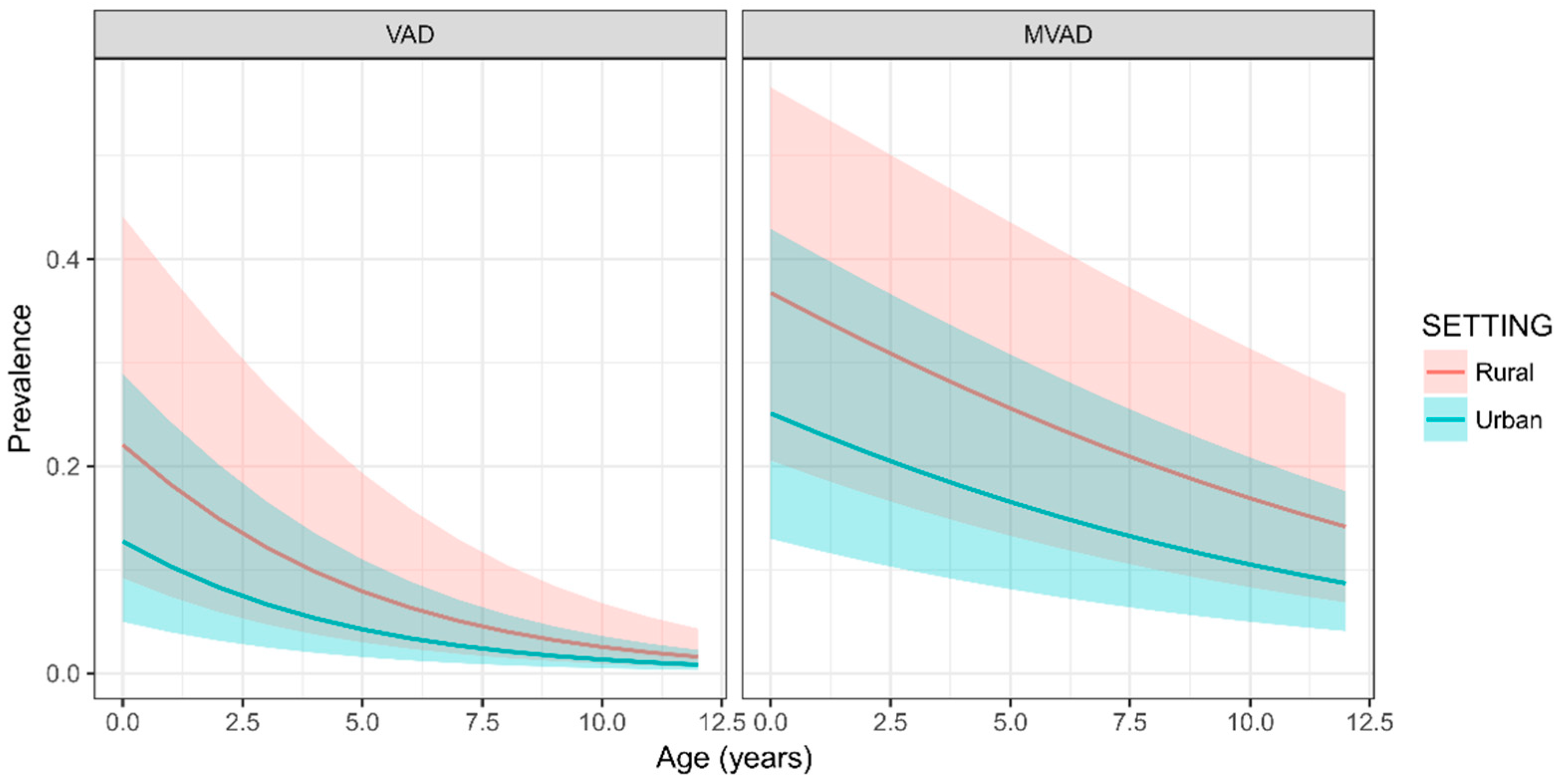
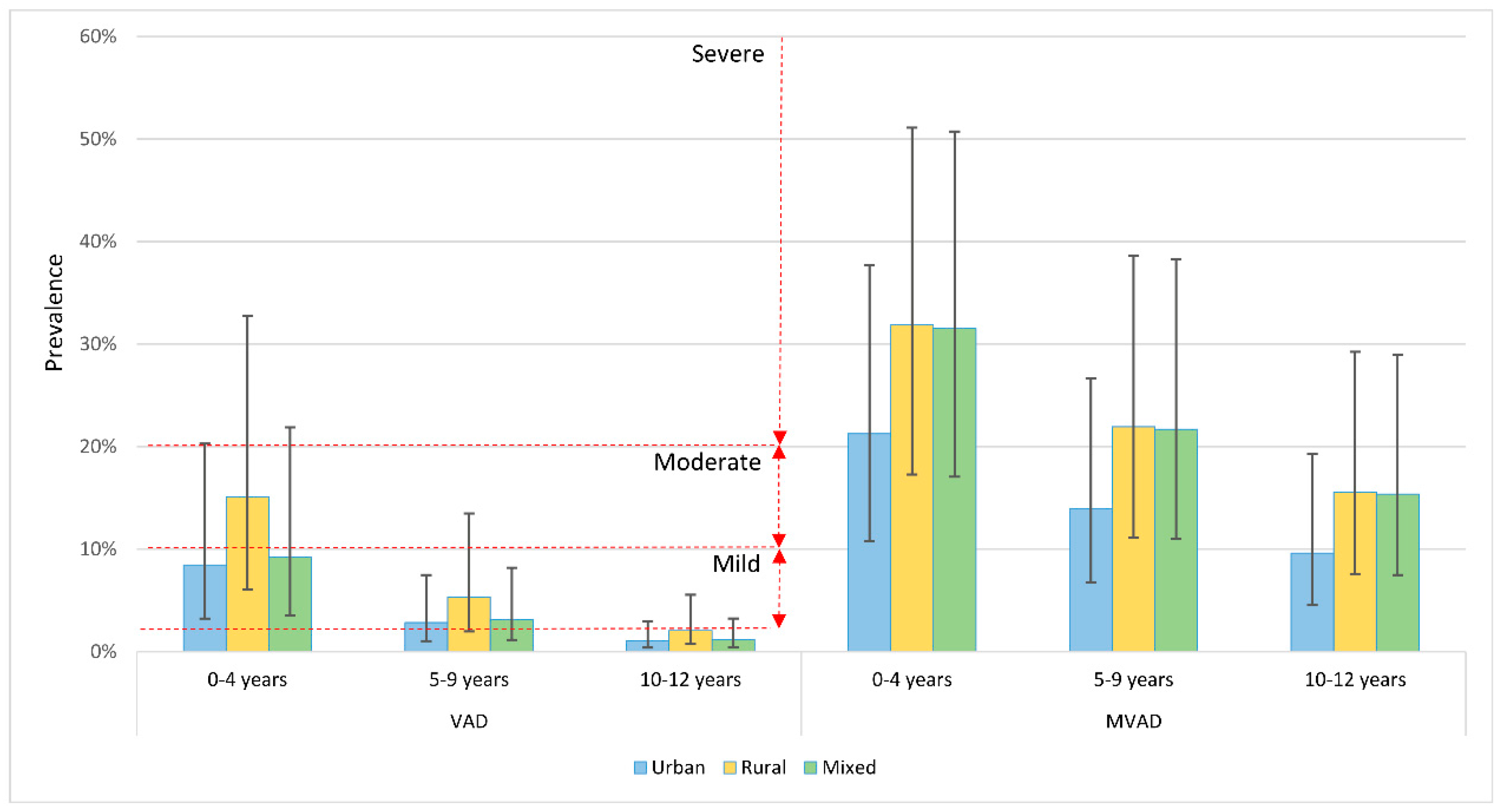
| Age Range | Prevalence of VAD (%, 95% CrI) | Prevalence of MVAD (%, 95% CrI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Rural | Mixed | Urban | Rural | Mixed | |
| 0–4 years | 8.45 | 15.10 | 9.23 | 21.28 | 31.86 | 31.53 |
| (3.22–20.29) | (6.05–32.75) | (3.54–21.88) | (10.77–37.69) | (17.28–51.11) | (17.06–50.73) | |
| 5–9 years | 2.83 | 5.33 | 3.11 | 13.98 | 21.94 | 21.68 |
| (1.03–7.49) | (1.98–13.48) | (1.14–8.18) | (6.76–26.68) | (11.15–38.61) | (11.00–38.25) | |
| 10–12 years | 1.08 | 2.06 | 1.18 | 9.62 | 15.56 | 15.36 |
| (0.39–2.94) | (0.75–5.55) | (0.43–3.23) | (4.53–19.27) | (7.59–29.25) | (7.48–28.94) | |
| Overall (0–12 years) | 4.99 | 8.11 | 5.16 | 16.36 | 24.07 | 24.29 |
| (1.88–12.30) | (3.17–18.62) | (1.95–12.64) | (8.10–30.10) | (12.55–40.99) | (12.69–41.27) | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, P.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Chang, X.; Wang, M.; An, L. The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121285
Song P, Wang J, Wei W, Chang X, Wang M, An L. The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2017; 9(12):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121285
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Peige, Jiawen Wang, Wei Wei, Xinlei Chang, Manli Wang, and Lin An. 2017. "The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 9, no. 12: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121285
APA StyleSong, P., Wang, J., Wei, W., Chang, X., Wang, M., & An, L. (2017). The Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency in Chinese Children: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 9(12), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9121285




