Abstract
Human thioredoxin (TRX) is a 12-kDa protein with redox-active dithiol in the active site -Cys-Gly-Pro-Cys-, which is induced by biological stress due to oxidative damage, metabolic dysfunction, chemicals, infection/inflammation, irradiation, or hypoxia/ischemia-reperfusion. Our research has demonstrated that exogenous TRX is effective in a wide variety of inflammatory diseases, including viral pneumonia, acute lung injury, gastric injury, and dermatitis, as well as in the prevention and amelioration of food allergies. Preclinical and clinical studies using recombinant TRX (rhTRX) are now underway. We have also identified substances that induce the expression of TRX in the body, in vegetables and other plant ingredients. Skincare products are being developed that take advantage of the anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action of TRX. Furthermore, we are currently engaged in the highly efficient production of pure rhTRX in several plants, such as lettuce, grain and rice.
1. Introduction
Thioredoxin (TRX) is a small protein with a catalytically active dithiol site (Cys-Gly-Pro-Cys) found in a variety of life forms on earth, including bacteria, plants, and animals [1,2,3]. The active site contains two cysteines (dithiol) undergoing reversible redox change between an oxidized disulfides (-S-S-) and a reduced dithiol (-SH, -SH). TRX in the reduced state catalyzes the cleavage of disulfide bonds in the target proteins, and it becomes oxidized after completion of the reaction. Oxidized TRX is restored to the reduced form by the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent thioredoxin reductase. TRX quenches reactive oxygen species by coupling with TRX-dependent peroxidases, or peroxiredoxins [4].
Subsequent studies have shown that TRX is involved in various redox-dependent cellular processes, such as gene expression, signal transduction, cell growth and apoptosis. Various kinds of TRX targets and interacting molecules have been reported. TRX exerts a variety of regulatory actions maintaining the cellular, as well as extracellular, redox homeostasis (Figure 1).
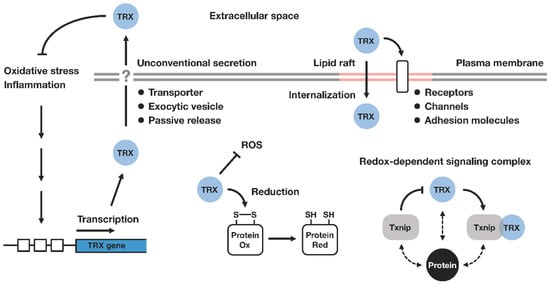
Figure 1.
Thioredoxin-mediated redox regulation. Thioredoxin (TRX) is transcriptionally upregulated in response to environmental or pathological factors associated with oxidative stress. TRX catalyzes the cleavage of protein disulfide bonds, thereby contributing to the maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis. TRX is secreted into the extracellular compartment via ER/Golgi-independent mechanisms (unconventional or nonclassical secretion), where it exhibits its protective effects against inflammation. Extracellular TRX is associated with membrane lipid rafts, where it can control the redox state of cell surface molecules, and influence the downstream signaling pathway. The internalization of extracellular TRX is also mediated through lipid rafts. Intracellularly, TRX interacts with a number of signaling molecules in a redox-dependent fashion. Txnip (also known as TBP-2 or VDUP1) has been identified as a negative regulator of TRX and the binding of Txnip inhibits the reducing activity of TRX. TRX and Txnip form a redox-sensitive signaling complex termed ‘redoxisome’, which may play a central role in the regulation of diverse biological processes ranging from metabolic and immunological pathways to inflammatory response and tumorigenesis. Ox, oxidized; Red, reduced; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TRX, thioredoxin; Txnip, thioredoxin interacting protein.
2. Background of TRX Research Associated with Human Diseases
In the early 1960s, TRX was reported as a ribonucleotide-reducing co-enzyme by the Karolinska Institute [5]. In addition, Immunoglobulin E (IgE) was discovered by Kimishige Ishizaka’s group in Denver Colorado, USA as the “regain” antibody [6], which was confirmed to be identical to the unknown myeloma protein studied by Bennich and Johansson’s group in Sweden [7]. Human TRX was first identified as a secretory autocrine and IL-2 receptor inducing protein, adult T cell leukemia (ATL)-derived factor (ADF) from the culture supernatant of human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I)-transformed T cell lines [8]. ATL characterized by abnormal leukemia cells having multi-convoluted nuclei and T cell properties was reported in Japan in the early 1970s. ATL cases were frequent in the southern regions of Japan, and soon proved to be associated with retrovirus HTLV-I [9,10].
The human TRX gene is located on chromosome 9 (9q31), and the coding sequence of TRX consists of five exons. The promoter region contains several regulatory elements, such as antioxidant responsive element (ARE), which enable the gene to be responsive to various external stimuli [11]. The TRX gene encodes the protein of 105 amino acids, and TRX resides mainly in a cytosolic compartment. Although TRX lacks an N-terminal signal peptide for the vesicular secretion pathway, it is released by cells under various stress conditions, where it exhibits cytokine and chemokine-like activities [12]. It seems that the extracellular function of TRX is not mediated through the canonical ligand–receptor interaction, and no specific cell surface receptors for TRX have been identified. It has been shown that TRX regulates the redox status of target cell surface molecules, such as CD4, CD30, and a type of transient potential channel, thereby controlling the downstream signaling [13,14,15]. Extracellular TRX may also be taken up by cells through membrane lipid rafts, and exert its effect intracellularly [16].
TRX is exported to the extracellular space by an unconventional ER/Golgi-independent pathway, which has been poorly characterized. No interaction has been found between TRX and any membranous elements or vesicles [17,18]. There was a report suggesting the partial involvement of inflammatory caspase-1 in the release of TRX [19], but the precise mechanism that mediates the secretion of TRX still remains unknown.
Increased levels of extracellular TRX have been reported in many pathological conditions associated with oxidative stress (Table 1) [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51]. The elevation of TRX in plasma or serum suggests the potential utility of TRX as a useful clinical parameter for inflammatory disorders. It has also been reported that TRX is highly expressed in salivary glands of Sjögren’s syndrome patients [48]. TRX was secreted into saliva, and the levels of salivary TRX were correlated well with the severity of the disease, implying that TRX could be used as a noninvasive marker to reflect the oxidative tissue damage.

Table 1.
Thioredoxin as a marker for inflammatory disorders.
Transgenic overexpression of TRX and the systemic administration of recombinant human thioredoxin (rhTRX) are effective in a wide variety of in vivo inflammatory disease models, such as viral pneumonia, acute lung injury, pancreatitis, myocarditis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and indomethacin-induced gastric injury (Figure 2). Elevated TRX levels in several primary tumors may suggest that TRX up-regulation in the cytosol can overwhelm the benefits of antioxidant/anti-inflammatory properties in a particular pathological condition, where compounds targeting TRX and TRX reductase can be effective [52,53,54,55]. However, a number of preclinical studies have demonstrated that extracellular TRX has a cytoprotective function under oxidative and inflammatory conditions, and no apparent evidence of adverse effects or undesirable symptoms have yet been found. The protective effects of TRX against inflammation and its potential clinical utility have been extensively reviewed elsewhere [56,57,58,59]. In this review, we describe the recent findings regarding the therapeutic applications of TRX and the strategies for TRX supplementation. In addition to the clinical use of TRX, we also discuss its potential utility as an attractive functional component of cosmetic products and dietary supplements.
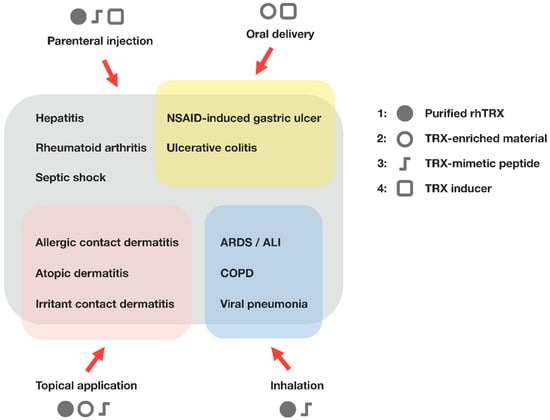
Figure 2.
Therapeutic applications of thioredoxin. Administration of TRX suppresses the excessive inflammatory response and any associated tissue injury, indicating the benefits of TRX for the treatment of inflammatory conditions. Four different types of thioredoxin-based therapeutics and the possible routes of administration are shown. (1) Recombinant human TRX (rhTRX). Expression systems for producing rhTRX have been established in E. coli and transgenic plants; (2) TRX-enriched material. Yeast cells secrete TRX in response to ethanol treatment, and the yeast-derived protein extracts with high TRX content retain anti-inflammatory activity; (3) TRX-mimetic peptide [60]. Smaller peptide mimetics may have a potential advantage over rhTRX, with respect to production cost and delivery efficiency; (4) TRX inducer. TRX-inducing compounds that increase endogenous TRX levels may also offer protection against inflammation and oxidative stress. ALI, acute lung injury; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; NSAID, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
3. Mucosa and Skin Inflammation
In TRX-transgenic mice, allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) and ultraviolet light-induced dermatitis were unequivocally suppressed [61,62]. Transgenic overexpression of TRX in mice suppressed the allergic reaction and inflammation in an experimental ACD model. The migratory function of cutaneous dendritic cells and the subsequent antigen-specific proliferation of lymph node cells after dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) sensitization were equivalent in both TRX-transgenic mice and wild type mice [61]. Thus, the overproduction of TRX in mice did not affect the primary immune response in the induction phase of ACD, whereas skin inflammation was suppressed by diminishing the infiltration of neutrophils in TRX-transgenic mice after elicitation challenge with DNFB. There were no apparent differences in immune cell populations between TRX-transgenic and wild type animals [63]. These findings indicate that TRX exerts an anti-inflammatory effect in the elicitation phase of ACD, suggesting that the anti-inflammatory mechanism of TRX is different from the mechanisms associated with other anti-inflammatory agents, such as the glucocorticoids, which regulate the inflammatory reaction in association with the suppression of immune responses.
The protective effects of exogenously applied TRX have also been demonstrated in an irritant contact dermatitis (ICD) model. The ICD mouse model induced by croton oil has been widely accepted as a useful pharmacological model for the investigation of new anti-inflammatory drugs [64]. Croton oil contains phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) and other phorbol esters as main irritant agents. Croton oil is known to cause significant inflammatory responses by inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines produced by keratinocytes, as characterized by edema, neutrophil infiltration, prostaglandins production, and increases in vascular permeability. Topically applied rhTRX inhibited the production and release of pro-inflammatory mediators at the site of the inflammation, thereby suppressing ICD [65]. The local application of TRX proteins may be a promising therapeutic strategy to prevent a variety of skin and mucosal inflammatory disorders. Based on these findings, skincare products are being developed that take advantage of the anti-allergic and anti-aging action of TRX.
4. Oral Delivery of TRX
Transcription factors containing sulfhydryl groups, such as the activator protein 1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), increase DNA-binding activity through the change in the redox state of the cysteine residues by TRX directly or indirectly [66,67]. Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1), a MAP kinase kinase kinase, is inhibited by being bound to reduced TRX [68]. These functions suggested that TRX plays a defensive role against several diseases, including gastrointestinal disease. Previous studies have shown attenuation of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis [37], Helicobacter felis-induced gastritis [69] and indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury [70] in TRX-overexpressing transgenic mice or mice after systemic administration of rhTRX. Recently, Nakajima et al. reported that oral administration of sake yeast extracts with a high TRX content reduced indomethacin-induced gastric injury [71], suggesting that orally administered TRX, and not merely endogenous TRX or injected rhTRX, can protect the gastric mucosa. However, no studies have been conducted to investigate how long orally administered TRX remains in the stomach. Taketani et al. demonstrated that orally administered TRX derived from yeast, which is commonly used in fermented foods, has a protective effect on the gastric mucosa both in in vitro and in vivo models (water-immersion restraint stress and HCl/ethanol-induced gastric ulcer models) [72]. DNA microarray analysis revealed the upregulation of genes related to tissue repair in ulcer regions of rats administered with yeast TRX. These results demonstrated that oral administration could be an alternative option for targeted delivery of TRX to the sites of inflammation. We are now engaged in the highly efficient production of TRX in several plants, such as lettuce [73], grain and rice, and they should provide a feasible source for oral delivery of TRX.
5. TRX-Inducing Principles
Given its nature to respond to oxidative stresses, TRX expression can be induced by a variety of physiochemical stimuli, including virus infection, mitogen, UV-irradiation, hydrogen peroxide and ischemia-reperfusion, which we have extensively reviewed [58,74,75]. Natural metabolic or endocrine substances including hemin, estrogen, prostaglandins, sulforaphane, and cAMP can also induce the expression and secretion of TRX [76,77,78]. Geranylgeranylacetone (GGA), an acyclic polyisoprenoid used as an anti-ulcer drug, and tert-butylhydroquinone (tBHQ), an electrophile stressor, can also induce TRX expression [79,80,81]. A series of stress-responsive elements in the promoter region have been identified, including the oxidative stress response element (ORE), antioxidant responsive element (ARE), cAMP responsive element (CRE), xenobiotics responsive element (XRE) and Sp1 [76,77,81,82,83]. Recently, we showed that fragrant unsaturated aldehydes from edible plants are novel TRX inducers, through the activation of the ARE element in the promoter region, and that they may be beneficial for protection against oxidative stress-induced cellular damage [84].
6. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (Txnip/TBP-2/VDUP1)
Thioredoxin interacting protein (Txnip) was originally cloned as a vitamin D3 target gene (named the vitamin D3 upregulated protein, VDUP1). This molecule has emerged as a key component of the cellular redox-regulation, since it was identified as a binding partner of TRX and further, suggested as an endogenous TRX inhibitor (named the thioredoxin binding protein-2, TBP-2) [85]. Two Txnip cysteines are important for thioredoxin binding through a disulfide exchange reaction between oxidized Txnip and reduced TRX [86]. This clear evidence suggests that the TRX–Txnip complex is important for various redox-dependent cell functions. Interestingly, Txnip is a member of the α-arrestin protein family (ARRDC1-5 and Txnip) containing two characteristic arrestin-like domains with the PxxP sequence, which is a binding motif for SH3-domain containing proteins, and the PPxY sequence, which is known as the binding motif for the WW-domain [86,87,88,89,90]. Since Txnip has specific arrestin-like domains that are responsible for protein–protein binding, a number of studies have identified various interacting partners for Txnip, such as the importin-α, SMRT-mSin3-HDAC corepressor, JAB1, E3 ubiquitin ligase itch, Mybbp1a and NLRP3, as well as TRX [91,92,93,94,95]. These findings raise the possibility that Txnip may play a scaffolding role in the signal complex. Txnip is highlighted in the metabolic regulation, since the molecule was identified as a nonsense mutation gene in Hcb-19 mice, which is known as the familial combined hyperlipidemic model [96]. Hcb-19 mice have decreased CO2 production, but increased ketone body synthesis, and the evidence highlighted the fact that altered redox status by TRX/Txnip down-regulates the lipid metabolism, such as the citric-acid cycle, sparing fatty acids for triglyceride and ketone body production [97].
Previously, we reported that gene targeting disruption of Txnip (Txnip KO) in mice resulted in a predisposition to death with severe bleeding, hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia and liver steatosis during fasting [98]. Txnip gene expression is induced in fasting, and the key transcription regulator peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) and sterol response element-binding protein (SREBP) signaling are dysregulated in the liver of Txnip KO during feeding–fasting nutritional transition [99]. Txnip expression is widely regulated by nutritional status, obesity, high glucose, amino acids, nuclear receptor signal and AMPK [87,94,99,100,101,102,103,104,105]. These results clearly suggest that Txnip is an important molecule to regulate glucose and lipid homeostasis.
7. TRX/Txnip; Redoxisome, a Redox-Related Signal Complex
The TRXs system plays an important role in maintaining a reducing environment in cells. We first identified Txnip/TBP-2/VDUP1 as an endogenous TRX binding and inhibiting protein [85]. Interestingly, Txnip bound to reduced TRX, but not to oxidized TRX, nor to mutant TRX, in which two redox-active cysteine residues were substituted by serine [85]. Since the disulfide exchange reaction between oxidized Txnip and reduced TRX (Txnip and TRX form a stable disulfide-linked complex) is known as the essential event for the interaction between Txnip and TRX [86], these two Txnip cysteines are important for TRX binding. These cysteines are not conserved in the broader family of arrestin domain-containing proteins, suggesting that the TRX-binding property of Txnip is unique [86]. Thus, the catalytic center of TRX seems to be important for the interaction. This interaction is important for cellular redox regulation, since the protein reducing activity of TRX is actually inhibited by the Txnip interaction [85,86]. In COS-7 and HEK293 cells transiently transfected with Txnip expression vector, a decrease in the insulin reducing activity of TRX and a diminishment of TRX expression was observed. In addition, treatment of HL-60 cells with 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 caused an increase in the Txnip expression and down-regulation of the expression and the reducing activity of TRX.
These results suggest that Txnip serves as a negative regulator of the biological function and expression of TRX by direct interaction, providing new insight into the redox-dependent signaling mechanism. We propose that this signal complex, composed of TRXs and Txnip as redox-dependent signal complexes, be known as “redoxisome”. We believe this signal complex could be a key regulatory mechanism for controlling various kinds of harmful stress (biostress) and preventing the progression or aggravation of stress diseases.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to Kiichi Hirota and Akira Yamauchi for their valuable comments on this paper and David Lee Vancil for English language editing. This work was partly supported by Japan Biostress Research Promotion Alliance (JBPA).
Author Contributions
J.Y. conducted the literature search and wrote the manuscript. Y.M. conducted the literature search, prepared the table and figures, and wrote the manuscript. H.T. conducted the literature search and proofread the paper. H.M. and T.I. drafted and revised the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holmgren, A.; Lu, J. Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase: Current research with special reference to human disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 396, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillig, C.H.; Holmgren, A. Thioredoxin and related molecules—From biology to health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, D.F.; Abderrazak, A.; El Hadri, K.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. The thioredoxin system as a therapeutic target in human health and disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1266–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, S.G.; Chae, H.Z.; Kim, K. Peroxiredoxins: A historical overview and speculative preview of novel mechanisms and emerging concepts in cell signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, T.C.; Moore, E.C.; Reichard, P. Enzymatic Synthesis of Deoxyribonucleotides. IV. Isolation and Characterization of Thioredoxin, the Hydrogen Donor from Escherichia Coli B. J. Biol. Chem. 1964, 239, 3436–3444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishizaka, K.; Ishizaka, T.; Hornbrook, M.M. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. V. Correlation of reaginic activity wth gamma-E-globulin antibody. J. Immunol. 1966, 97, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johansson, S.G.; Bennich, H. Immunological studies of an atypical (myeloma) immunoglobulin. Immunology 1967, 13, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tagaya, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Mitsui, A.; Kondo, N.; Matsui, H.; Hamuro, J.; Brown, N.; Arai, K.; Yokota, T.; Wakasugi, H.; et al. ATL-derived factor (ADF), an IL-2 receptor/Tac inducer homologous to thioredoxin; possible involvement of dithiol-reduction in the IL-2 receptor induction. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yodoi, J.; Takatsuki, K.; Masuda, T. Letter: Two cases of T-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia in Japan. N. Engl. J. Med. 1974, 290, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, T.; Yodoi, J.; Sagawa, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Uchino, H. Adult T-cell leukemia: Clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood 1977, 50, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masutani, H.; Hirota, K.; Sasada, T.; Ueda-Taniguchi, Y.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sono, H.; Yodoi, J. Transactivation of an inducible anti-oxidative stress protein, human thioredoxin by HTLV-I Tax. Immunol. Lett. 1996, 54, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Nakamura, H.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J. Redox regulation of human thioredoxin network. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, L.J.; Yam, P.T.; Jiang, X.M.; Vandegraaff, N.; Li, P.; Poumbourios, P.; Donoghue, N.; Hogg, P.J. Disulfide exchange in domain 2 of CD4 is required for entry of HIV-1. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwertassek, U.; Balmer, Y.; Gutscher, M.; Weingarten, L.; Preuss, M.; Engelhard, J.; Winkler, M.; Dick, T.P. Selective redox regulation of cytokine receptor signaling by extracellular thioredoxin-1. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3086–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.Z.; Sukumar, P.; Zeng, F.; Li, J.; Jairaman, A.; English, A.; Naylor, J.; Ciurtin, C.; Majeed, Y.; Milligan, C.J.; et al. TRPC channel activation by extracellular thioredoxin. Nature 2008, 451, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, N.; Ishii, Y.; Kwon, Y.W.; Tanito, M.; Sakakura-Nishiyama, J.; Mochizuki, M.; Maeda, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kojima, M.; Kim, Y.C.; et al. Lipid raft-mediated uptake of cysteine-modified thioredoxin-1: Apoptosis enhancement by inhibiting the endogenous thioredoxin-1. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manabe, Y.; Takagi, M.; Nakamura-Yamada, M.; Goto-Inoue, N.; Taoka, M.; Isobe, T.; Fujii, N.L. Redox proteins are constitutively secreted by skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 64, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubartelli, A.; Bajetto, A.; Allavena, G.; Wollman, E.; Sitia, R. Secretion of thioredoxin by normal and neoplastic cells through a leaderless secretory pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 24161–24164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.; Ruegg, A.; Werner, S.; Beer, H.D. Active caspase-1 is a regulator of unconventional protein secretion. Cell 2008, 132, 818–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; De Rosa, S.; Roederer, M.; Anderson, M.T.; Dubs, J.G.; Yodoi, J.; Holmgren, A.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Elevation of plasma thioredoxin levels in HIV-infected individuals. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; De Rosa, S.C.; Yodoi, J.; Holmgren, A.; Ghezzi, P.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Chronic elevation of plasma thioredoxin: Inhibition of chemotaxis and curtailment of life expectancy in AIDS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2688–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, C.; Shioji, K.; Nakamura, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Yodoi, J.; Sasayama, S. Serum thioredoxin (TRX) levels in patients with heart failure. Jpn. Circ. J. 2001, 65, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Soejima, H.; Shimomura, H.; Kajiwara, I.; Kojima, S.; Hokamaki, J.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Ozaki, Y.; et al. Plasma thioredoxin levels and platelet aggregability in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am. Heart J. 2003, 146, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejima, H.; Suefuji, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Kajiwaram, I.; Kojima, S.; Hokamaki, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; et al. Increased plasma thioredoxin in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Cardiol. 2003, 26, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, S.; Nishio, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kido, M.; Kiriya, K.; Asada, M.; Tamaki, H.; Fukui, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Clinical significance of serum thioredoxin 1 levels in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2006, 32, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callister, M.E.; Burke-Gaffney, A.; Quinlan, G.J.; Nicholson, A.G.; Florio, R.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; Evans, T.W. Extracellular thioredoxin levels are increased in patients with acute lung injury. Thorax 2006, 61, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Adachi, T.; Sannohe, S.; Oyamada, H.; Kayaba, H.; Yodoi, J.; Chihara, J. Elevated serum levels of thioredoxin in patients with acute exacerbation of asthma. Immunol. Lett. 2003, 86, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal-Matute, J.; Fernandez-Garcia, C.E.; Blanco-Colio, L.M.; Burillo, E.; Fortuno, A.; Martinez-Pinna, R.; Llamas-Granda, P.; Beloqui, O.; Egido, J.; Zalba, G.; et al. Thioredoxin-1/peroxiredoxin-1 as sensors of oxidative stress mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in atherosclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdiu, A.; Nakamura, H.; Sahaf, B.; Yodoi, J.; Holmgren, A.; Rosen, A. Thioredoxin blood level increases after severe burn injury. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2000, 2, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Vaage, J.; Valen, G.; Padilla, C.A.; Bjornstedt, M.; Holmgren, A. Measurements of plasma glutaredoxin and thioredoxin in healthy volunteers and during open-heart surgery. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekell, A.; Hossain, A.; Alehagen, U.; Dahlstrom, U.; Rosen, A. Elevated circulating levels of thioredoxin and stress in chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2004, 6, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakisaka, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Sumida, Y.; Yoh, T.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; Senmaru, H. Elevation of serum thioredoxin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2002, 34, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Kawano, H.; Hokamaki, J.; Soejima, H.; Kojima, S.; Kudoh, T.; Nagayoshi, Y.; Sugiyama, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Yoshimura, M.; et al. Increased plasma levels of thioredoxin in patients with glucose intolerance. Intern. Med. 2005, 44, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Z.J.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.L.; Wang, K.; Wu, D.; Wan, X.Y.; Xia, Y.; Lau, W.Y.; Wu, M.C.; et al. Serum thioredoxin is a diagnostic marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9551–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Noda, N.; Okada, S.; Hagiwara, Y.; Miyata, M.; Sakurabayashi, I.; Yamaguchi, N.; Sugimura, T.; Terada, M.; Wakasugi, H. Elevated serum level of thioredoxin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Biotherapy 1998, 11, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Yoh, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Okanoue, T.; Kashima, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Serum thioredoxin levels as an indicator of oxidative stress in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, H.; Nakamura, H.; Nishio, A.; Nakase, H.; Ueno, S.; Uza, N.; Kido, M.; Inoue, S.; Mikami, S.; Asada, M.; et al. Human thioredoxin-1 ameliorates experimental murine colitis in association with suppressed macrophage inhibitory factor production. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, K.; Nakamura, H.; Nakamura, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Ueda, S.; Ichikawa, M.; Tabata, C.; Fujita, S.; Masago, K.; Yodoi, J.; et al. Elevation of serum thioredoxin in patients with gefitinib-induced interstitial lung disease. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1905–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, Y.; Nakashima, T.; Yoh, T.; Furutani, M.; Hirohama, A.; Kakisaka, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Mitsuyoshi, H.; Okanoue, T.; et al. Serum thioredoxin levels as a predictor of steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Azuma, K.; Hoshino, T.; Imaoka, H.; Ikeda, J.; Kinoshita, T.; Takamori, S.; Ohshima, K.; Edakuni, N.; Kato, S.; et al. Correlation of decreased survival and IL-18 in bone metastasis. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Chin, K.; Nakamura, H.; Morita, S.; Sumi, K.; Oga, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Niimi, A.; Fukuhara, S.; Yodoi, J.; et al. Plasma thioredoxin, a novel oxidative stress marker, in patients with obstructive sleep apnea before and after nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csosz, E.; Labiscsak, P.; Kallo, G.; Markus, B.; Emri, M.; Szabo, A.; Tar, I.; Tozser, J.; Kiss, C.; Marton, I. Proteomics investigation of OSCC-specific salivary biomarkers in a Hungarian population highlights the importance of identification of population-tailored biomarkers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Bai, J.; Nishinaka, Y.; Ueda, S.; Sasada, T.; Ohshio, G.; Imamura, M.; Takabayashi, A.; Yamaoka, Y.; Yodoi, J. Expression of thioredoxin and glutaredoxin, redox-regulating proteins, in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2000, 24, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koura, T.; Gon, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Azuma, A.; Kudoh, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Sugawara, I.; Yodoi, J.; Horie, T. Expression of thioredoxin in granulomas of sarcoidosis: Possible role in the development of T lymphocyte activation. Thorax 2000, 55, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jikimoto, T.; Nishikubo, Y.; Koshiba, M.; Kanagawa, S.; Morinobu, S.; Morinobu, A.; Saura, R.; Mizuno, K.; Kondo, S.; Toyokuni, S.; et al. Thioredoxin as a biomarker for oxidative stress in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, M.M.; Nakamura, H.; Gringhuis, S.; Okamoto, T.; Yoshida, S.; Kullmann, F.; Lechner, S.; van der Voort, E.A.; Leow, A.; Versendaal, J.; et al. Expression of the thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system in the inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1999, 42, 2430–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Katoh, T.; Tetsuka, T.; Uno, K.; Matsui, N.; Okamoto, T. Involvement of thioredoxin in rheumatoid arthritis: Its costimulatory roles in the TNF-alpha-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8 from cultured synovial fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurimoto, C.; Kawano, S.; Tsuji, G.; Hatachi, S.; Jikimoto, T.; Sugiyama, D.; Kasagi, S.; Komori, T.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; et al. Thioredoxin may exert a protective effect against tissue damage caused by oxidative stress in salivary glands of patients with Sjogren’s syndrome. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 2035–2043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.X.; Cai, J.Y.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.D.; Lu, C.; Sun, J.; Ba, H.J. Thioredoxin as a marker for severity and prognosis of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 363, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, J.; Gidlof, A.; Eriksson, M.; Larsson, E.; Brattstrom, O.; Oldner, A. Thioredoxin a novel biomarker of post-injury sepsis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hokamaki, J.; Kawano, H.; Soejima, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Kajiwara, I.; Kojima, S.; Sakamoto, T.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Plasma thioredoxin levels in patients with unstable angina. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 99, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke-Gaffney, A.; Callister, M.E.; Nakamura, H. Thioredoxin: Friend or foe in human disease? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 26, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhar, M.; Shytaj, I.L.; Stamler, J.S.; Savarino, A. Dual targeting of the thioredoxin and glutathione systems in cancer and HIV. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Holmgren, A. A novel antioxidant mechanism of ebselen involving ebselen diselenide, a substrate of mammalian thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39456–39462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Masayasu, H.; Holmgren, A. Ebselen: A substrate for human thioredoxin reductase strongly stimulating its hydroperoxide reductase activity and a superfast thioredoxin oxidant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8579–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Yodoi, J. Extracellular thioredoxin: A therapeutic tool to combat inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Okuyama, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin 1 delivery as new therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J. Extracellular thioredoxin and thioredoxin-binding protein 2 in control of cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yodoi, J.; Tian, H.; Masutani, H.; Nakamura, H. Thiol redox barrier; local and systemic surveillance against stress and inflammatory diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 595, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachnoff, N.; Trus, M.; Atlas, D. Alleviation of oxidative stress by potent and selective thioredoxin-mimetic peptides. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, A.; Horikawa, T.; Ogura, K.; Taguchi, K.; Yu, X.; Funasaka, Y.; Takeda, M.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J.; Nishigori, C. Thioredoxin suppresses the contact hypersensitivity response by inhibiting leukocyte recruitment during the elicitation phase. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, R.; Masaki, T.; Dien, S.; Yu, X.; Fukunaga, A.; Yodoi, J.; Nishigori, C. Suppressive effect of recombinant human thioredoxin on ultraviolet light-induced inflammation and apoptosis in murine skin. J. Dermatol. 2012, 39, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kondo, N.; Matsuo, Y.; Liu, W.; Oka, S.; Ishii, Y.; Yodoi, J. Redox regulation of mast cell histamine release in thioredoxin-1 (TRX) transgenic mice. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabor, M. Models of acute inflammation in the ear. Methods Mol. Biol. 2003, 225, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Fukunaga, A.; Ono, R.; Nishigori, C.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin ameliorates cutaneous inflammation by regulating the epithelial production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, K.; Matsui, M.; Iwata, S.; Nishiyama, A.; Mori, K.; Yodoi, J. AP-1 transcriptional activity is regulated by a direct association between thioredoxin and Ref-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3633–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.R.; Wakasugi, N.; Virelizier, J.L.; Yodoi, J.; Hay, R.T. Thioredoxin regulates the DNA-binding activity of NF-kappa B by reduction of a disulphide bond involving cysteine 62. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, M.; Nishitoh, H.; Fujii, M.; Takeda, K.; Tobiume, K.; Sawada, Y.; Kawabata, M.; Miyazono, K.; Ichijo, H. Mammalian thioredoxin is a direct inhibitor of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK) 1. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Nishio, A.; Nakamura, H.; Uchida, K.; Fukui, T.; Ohana, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Ohashi, S.; Tamaki, H.; Matsuura, M.; et al. Helicobacter felis-induced gastritis was suppressed in mice overexpressing thioredoxin-1. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 1104–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Nakamura, H.; Kondo, N.; Tanito, M.; Kwon, Y.W.; Ahsan, M.K.; Matsui, H.; Narita, M.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-1 attenuates indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury in mice. Free Radic. Res. 2007, 41, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, A.; Fukui, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Kishimoto, M.; Yamashina, M.; Nakayama, S.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Uchida, K.; Nishio, A.; et al. Attenuation of indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury by prophylactic administration of sake yeast-derived thioredoxin. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketani, Y.; Kinugasa, K.; Kitajima, R.; Nishiumi, S.; Ashida, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fujita, T.; Kanzaki, K.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J. Protective effects of oral administration of yeast thioredoxin against gastric mucosal injury. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Ashida, H.; Watanabe, R.; Inai, K.; Kim, Y.S.; Mukougawa, K.; Fukuda, H.; Tomizawa, K.; Ushiyama, K.; Asao, H.; et al. Production of biologically active human thioredoxin 1 protein in lettuce chloroplasts. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Nakamura, K.; Yodoi, J. Redox regulation of cellular activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, H.; Ueda, S.; Yodoi, J. The thioredoxin system in retroviral infection and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12 (Suppl. 1), 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.; Nakamura, H.; Kwon, Y.W.; Hattori, I.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Kondo, N.; Oka, S.; Ueda, S.; Masutani, H.; et al. Critical roles of thioredoxin in nerve growth factor-mediated signal transduction and neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Masutani, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Yodoi, J. Hemin-induced activation of the thioredoxin gene by Nrf2. A differential regulation of the antioxidant responsive element by a switch of its binding factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18399–18406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanito, M.; Masutani, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Nishikawa, M.; Ohira, A.; Yodoi, J. Sulforaphane induces thioredoxin through the antioxidant-responsive element and attenuates retinal light damage in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekigai, H.; Nakamura, H.; Bai, J.; Tanito, M.; Masutani, H.; Hirota, K.; Matsui, H.; Murakami, M.; Yodoi, J. Geranylgeranylacetone promotes induction and secretion of thioredoxin in gastric mucosal cells and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Free Radic. Res. 2001, 35, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, K.; Nakamura, H.; Arai, T.; Ishii, H.; Bai, J.; Itoh, T.; Fukuda, K.; Yodoi, J. Geranylgeranylacetone enhances expression of thioredoxin and suppresses ethanol-induced cytotoxicity in cultured hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kondo, N.; Masutani, H.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-dependent redox regulation of the antioxidant responsive element (ARE) in electrophile response. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1860–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonissen, K.F.; Wells, J.R. Isolation and characterization of human thioredoxin-encoding genes. Gene 1991, 102, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodoi, J.; Nakamura, H.; Masutani, H. Redox regulation of stress signals: Possible roles of dendritic stellate TRX producer cells (DST cell types). Biol. Chem. 2002, 383, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, H.; Otsuki, R.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Takenaka, M.; Kanoh, N.; Takatera, K.; Kunimoto, Y.; Yodoi, J. Fragrant unsaturated aldehydes elicit activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 system leading to the upregulation of thioredoxin expression and protection against oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 949–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Matsui, M.; Iwata, S.; Hirota, K.; Masutani, H.; Nakamura, H.; Takagi, Y.; Sono, H.; Gon, Y.; Yodoi, J. Identification of thioredoxin-binding protein-2/vitamin D(3) up-regulated protein 1 as a negative regulator of thioredoxin function and expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21645–21650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwari, P.; Higgins, L.J.; Chutkow, W.A.; Yoshioka, J.; Lee, R.T. The interaction of thioredoxin with Txnip. Evidence for formation of a mixed disulfide by disulfide exchange. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21884–21891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Masutani, H.; Liu, W.; Horita, H.; Wang, D.; Kizaka-Kondoh, S.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-binding protein-2-like inducible membrane protein is a novel vitamin D3 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)gamma ligand target protein that regulates PPARgamma signaling. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwari, P.; Chutkow, W.A.; Cummings, K.; Verstraeten, V.L.; Lammerding, J.; Schreiter, E.R.; Lee, R.T. Thioredoxin-independent regulation of metabolism by the alpha-arrestin proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24996–25003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, C.E. On the origins of arrestin and rhodopsin. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masutani, H.; Yoshihara, E.; Masaki, S.; Chen, Z.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin binding protein (TBP)-2/Txnip and alpha-arrestin proteins in cancer and diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 50, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, K.N.; Hwang, C.Y.; Kwon, K.S.; You, K.H.; Choi, I. Tumor suppressor VDUP1 increases p27(kip1) stability by inhibiting JAB1. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishinaka, Y.; Masutani, H.; Oka, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Nishio, K.; Ishii, Y.; Yodoi, J. Importin alpha1 (Rch1) mediates nuclear translocation of thioredoxin-binding protein-2/vitamin D(3)-up-regulated protein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37559–37565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, F.; Takata, M.; Kamitori, K.; Nonaka, M.; Dong, Y.; Sui, L.; Tokuda, M. Rare sugar D-allose induces specific up-regulation of TXNIP and subsequent G1 cell cycle arrest in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilization of p27kip1. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, E.; Fujimoto, S.; Inagaki, N.; Okawa, K.; Masaki, S.; Yodoi, J.; Masutani, H. Disruption of TBP-2 ameliorates insulin sensitivity and secretion without affecting obesity. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Tardivel, A.; Thorens, B.; Choi, I.; Tschopp, J. Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodnar, J.S.; Chatterjee, A.; Castellani, L.W.; Ross, D.A.; Ohmen, J.; Cavalcoli, J.; Wu, C.; Dains, K.M.; Catanese, J.; Chu, M.; et al. Positional cloning of the combined hyperlipidemia gene Hyplip1. Nat. Genet. 2002, 30, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Margosian, M.R.; Sheth, S.S.; Lusis, A.J.; Parks, E.J. Increased lipogenesis and fatty acid reesterification contribute to hepatic triacylglycerol stores in hyperlipidemic Txnip-/- mice. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Liu, W.; Masutani, H.; Hirata, H.; Shinkai, Y.; Yamada, S.; Yoshida, T.; Nakamura, H.; Yodoi, J. Impaired fatty acid utilization in thioredoxin binding protein-2 (TBP-2)-deficient mice: A unique animal model of Reye syndrome. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, S.; Yoshihara, E.; Bizen-Abe, A.; Liu, W.; Watanabe, M.; Yodoi, J.; Masutani, H. Thioredoxin binding protein-2/thioredoxin-interacting protein is a critical regulator of insulin secretion and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor function. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lopez-Ramos, D.A.; Yoshihara, E.; Maeda, Y.; Masutani, H.; Sugie, K.; Maeda, M.; Yodoi, J. Thioredoxin-binding protein-2 (TBP-2/VDUP1/TXNIP) regulates T-cell sensitivity to glucocorticoid during HTLV-I-induced transformation. Leukemia 2011, 25, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yoshihara, E.; Son, A.; Matsuo, Y.; Masutani, H.; Sugie, K.; Maeda, M.; Yodoi, J. Differential roles of Annexin A1 (ANXA1/lipocortin-1/lipomodulin) and thioredoxin binding protein-2 (TBP-2/VDUP1/TXNIP) in glucocorticoid signaling of HTLV-I-transformed T cells. Immunol. Lett. 2010, 131, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Ling, X.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, D. Molecular characterization of differentially expressed TXNIP gene and its association with porcine carcass traits. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 10439–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Rong, Y.P.; Malone, M.H.; Davis, M.C.; Zhong, F.; Distelhorst, C.W. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (txnip) is a glucocorticoid-regulated primary response gene involved in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Zheng, B.; Shaywitz, A.; Dagon, Y.; Tower, C.; Bellinger, G.; Shen, C.H.; Wen, J.; Asara, J.; McGraw, T.E.; et al. AMPK-dependent degradation of TXNIP upon energy stress leads to enhanced glucose uptake via GLUT1. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.S.; DeLuca, H.F. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA from HL-60 cells treated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-3. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1219, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).