Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
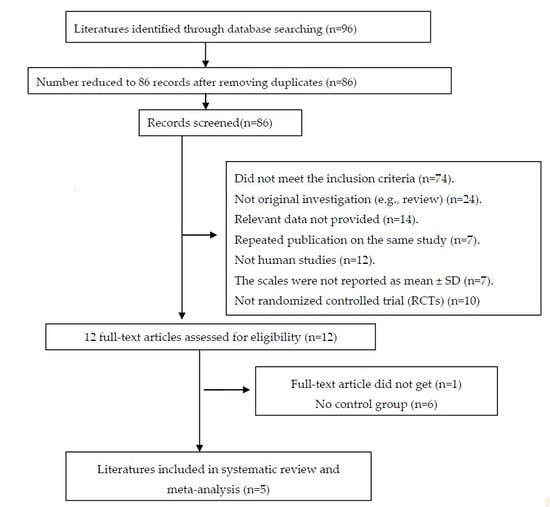
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies
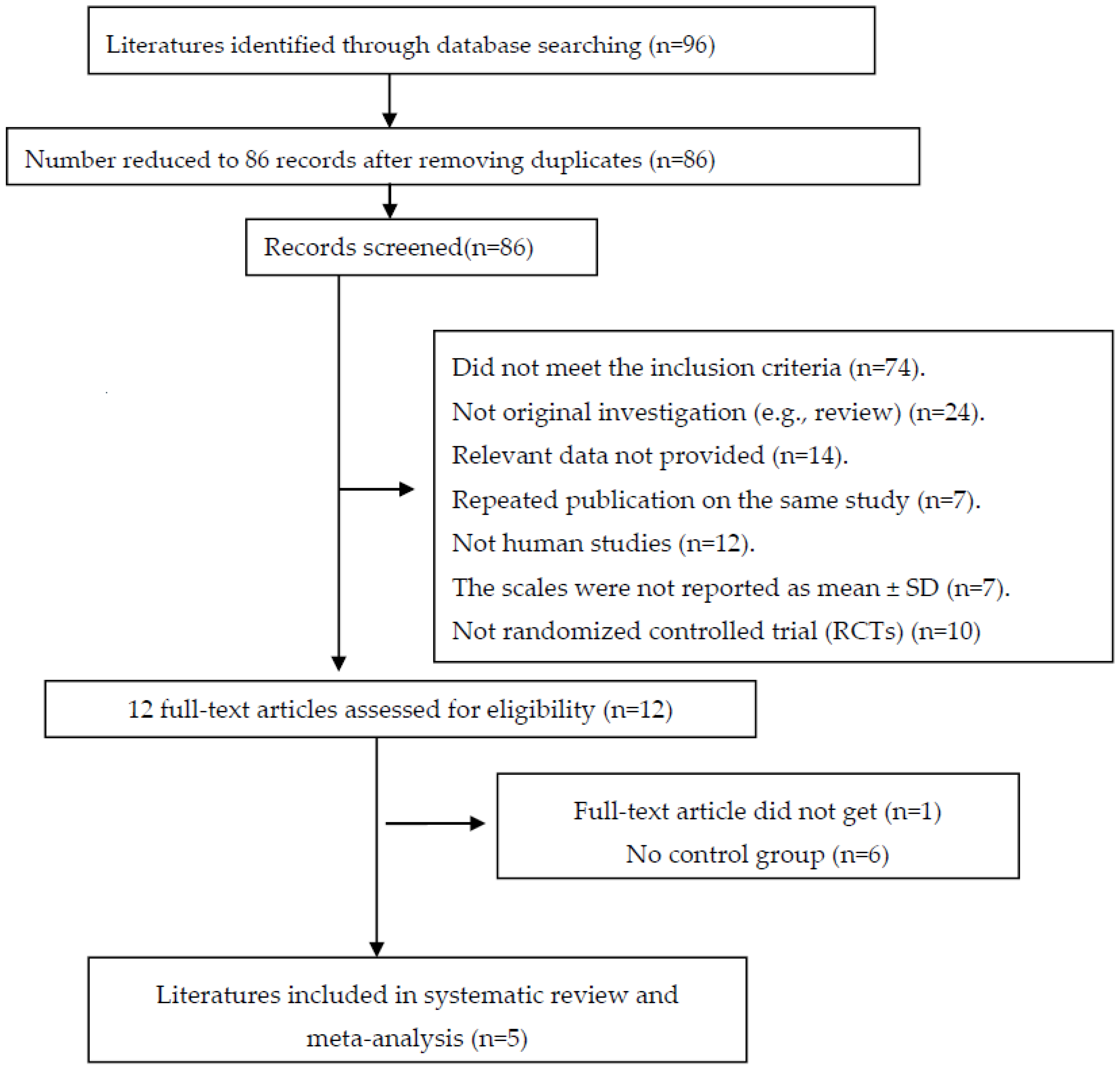
3.2. Quality Assessment
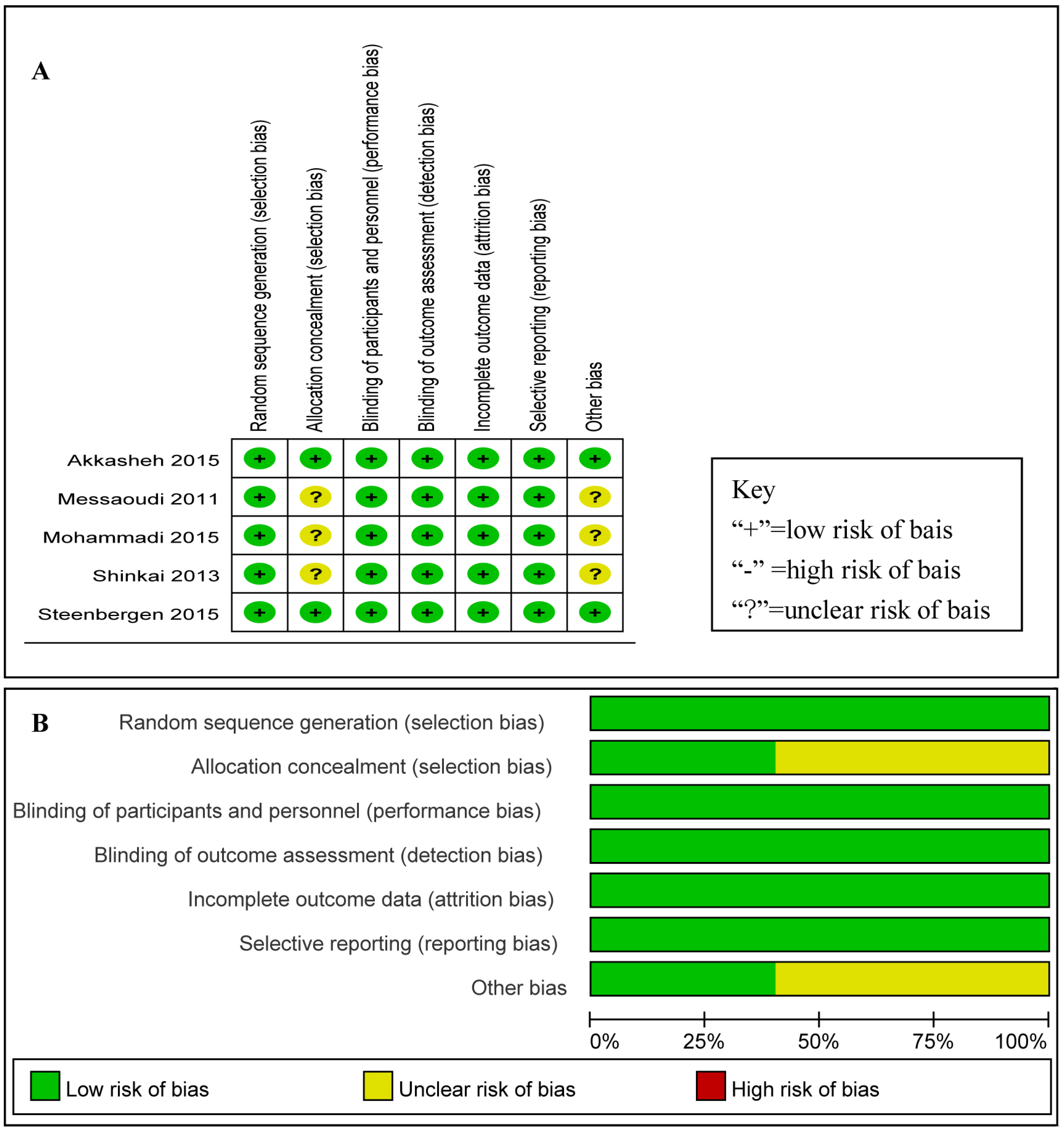
3.3. Efficacy of Probiotics
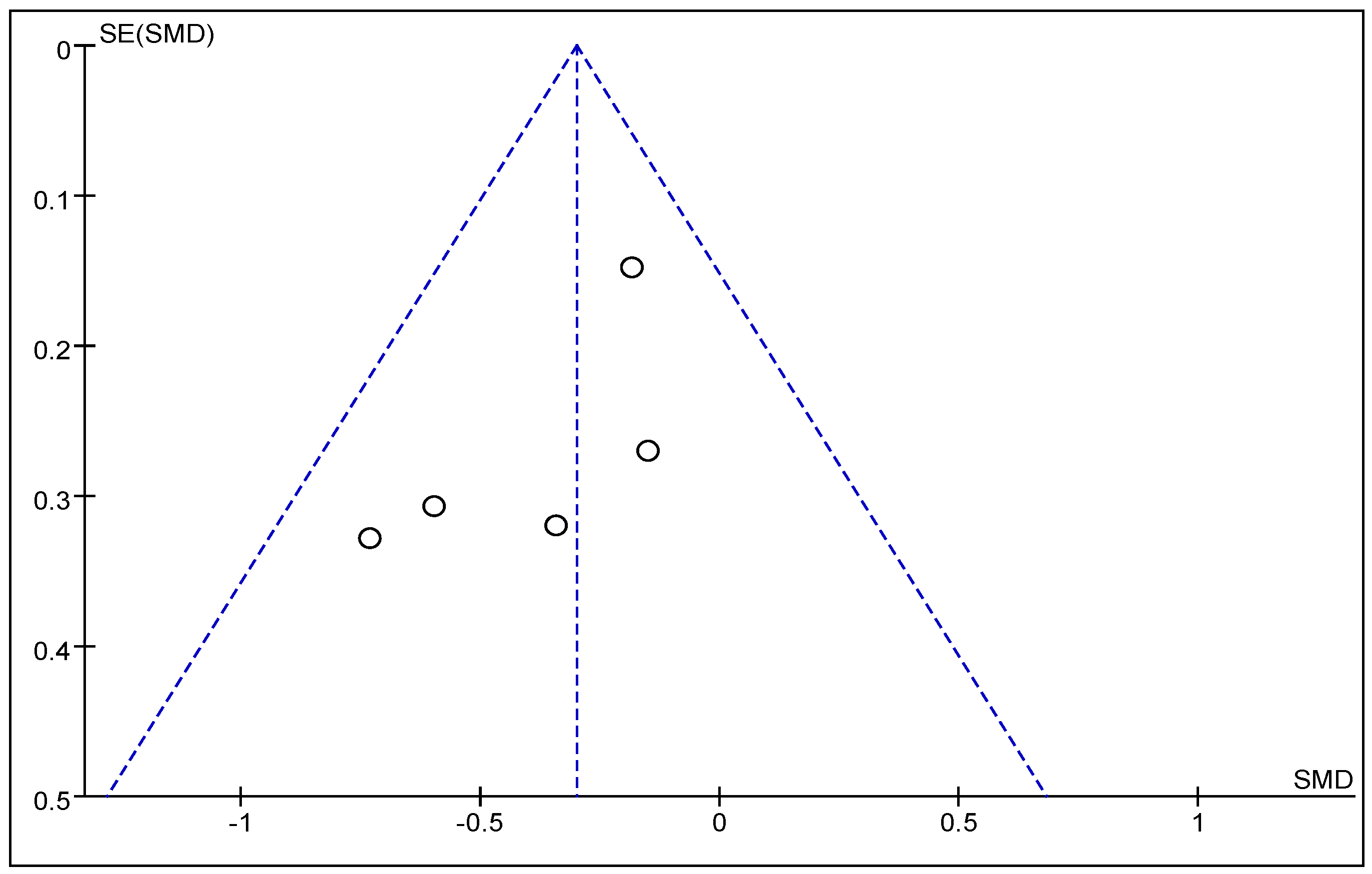
3.4. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilagut, G.; Forero, C.G.; Barbaglia, G.; Alonso, J. Screening for Depression in the General Population with the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression (CES-D): A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e155431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.L.; Cho, J.; Park, S.; Park, E.C. Depression symptom and professional mental health service use. BMC Psychiatry 2015, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawlik, S.; Waldeier, L.; Muller, M.; Szabo, A.; Sohn, C.; Reck, C. Subclinical depressive symptoms during pregnancy and birth outcome—A pilot study in a healthy German sample. Arch. Womens Ment. Health 2013, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Berglund, P.; Demler, O.; Jin, R.; Merikangas, K.R.; Walters, E.E. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solem, S.; Hagen, R.; Wang, C.E.; Hjemdal, O.; Waterloo, K.; Eisemann, M.; Halvorsen, M. Metacognitions and mindful attention awareness in depression: a comparison of currently depressed, previously depressed and never depressed individuals. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, R.J.; Kirk, S.J.; Gardiner, K.R. Probiotics (Br. J. Surg. 2001; 88: 161-2). Br. J. Surg. 2001, 88, 1018–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gismondo, M.R.; Drago, L.; Lombardi, A. Review of probiotics available to modify gastrointestinal flora. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1999, 12, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cabezas, R.; Davideau, J.L.; Tenenbaum, H.; Huck, O. Clinical efficacy of probiotics as an adjunctive therapy to non-surgical periodontal treatment of chronic periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Fei, X. Effect of probiotics on body weight and body-mass index: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 67, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruner, D.; Paris, S.; Schwendicke, F. Probiotics for managing caries and periodontitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2016, 48, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarnejad, S.; Shab-Bidar, S.; Speakman, J.R.; Parastui, K.; Daneshi-Maskooni, M.; Djafarian, K. Probiotics reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhea in adults (18–64 years) but not the elderly (>65 years): A meta-analysis. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emge, J.R.; Huynh, K.; Miller, E.N.; Kaur, M.; Reardon, C.; Barrett, K.E.; Gareau, M.G. Modulation of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis by Probiotics in a Murine Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Melancholic microbes: A link between gut microbiota and depression? Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C. Mental health: Thinking from the gut. Nature 2015, 518, S12–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, W. Gut Microbiota: The Brain Peacekeeper. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.R.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Brain-gut-microbiota axis: Challenges for translation in psychiatry. Ann. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseribafrouei, A.; Hestad, K.; Avershina, E.; Sekelja, M.; Linlokken, A.; Wilson, R.; Rudi, K. Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and depression. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Ling, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, H.; Ma, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Tan, Z.; Shi, J.; et al. Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 4, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Kiely, B.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Effects of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis in the maternal separation model of depression. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouault-Holowacz, S.; Bieuvelet, S.; Burckel, A.; Cazaubiel, M.; Dray, X.; Marteau, P. A double blind randomized controlled trial of a probiotic combination in 100 patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2008, 32, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.M.; Moeller, M.J.; Chey, W.D.; Schoenfeld, P.S. The utility of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, M.; Lalonde, R.; Violle, N.; Javelot, H.; Desor, D.; Nejdi, A.; Bisson, J.F.; Rougeot, C.; Pichelin, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; et al. Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.A.; Jazayeri, S.; Khosravi-Darani, K.; Solati, Z.; Mohammadpour, N.; Asemi, Z.; Adab, Z.; Djalali, M.; Tehrani-Doost, M.; Hosseini, M.; et al. The effects of probiotics on mental health and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in petrochemical workers. Nutr. Neurosci. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, D.; Williams, C.; Brown, A. Impact of consuming a milk drink containing a probiotic on mood and cognition. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkasheh, G.; Kashani-Poor, Z.; Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M.; Jafari, P.; Akbari, H.; Taghizadeh, M.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Clinical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in patients with major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition 2016, 32, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evrensel, A.; Ceylan, M.E. The Gut-Brain Axis: The Missing Link in Depression. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2015, 13, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Moher, D.; Cameron, C. The PRISMA Extension Statement. Ann. Int. Med. 2015, 163, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenbergen, L.; Sellaro, R.; van Hemert, S.; Bosch, J.A.; Colzato, L.S. A randomized controlled trial to test the effect of multispecies probiotics on cognitive reactivity to sad mood. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, S.; Toba, M.; Saito, T.; Sato, I.; Tsubouchi, M.; Taira, K.; Kakumoto, K.; Inamatsu, T.; Yoshida, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. Immunoprotective effects of oral intake of heat-killed Lactobacillus pentosus strain b240 in elderly adults: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1856–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Zamora, E.; Macias-de, L.T.A.; Higareda-Almaraz, M.A. Depression prevalence among end stage renal disease patients in maintenance hemodialysis. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2016, 54, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joo, J.; Hwang, S.; Gallo, J.J. Death Ideation and Suicidal Ideation in a Community Sample Who Do Not Meet Criteria for Major Depression. Crisis 2016, 37, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, S.; Beadle, J.N.; Raymont, V.; Grafman, J. Suicidal thoughts and emotion competence. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2016, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, A.; Khan, M.; Shah, S.R.; Fatima, K.; Tunio, S.A.; Hussain, M.; Khan, M.A.; Shaikh, M.A.; Arshad, M.H. Sociodemographic Pattern of Depression in Urban Settlement of Karachi, Pakistan. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, C9–C13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, X. Depression among Low-Income Female Muslim Uyghur and Kazakh Informal Caregivers of Disabled Elders in Far Western China: Influence on the Caregivers' Burden and the Disabled Elders’ Quality of Life. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e156382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, R.F.; Bunge, E.L. Prevention of depression worldwide: a wake-up call. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitsur, R.; Grinshpahet, R.; Goren, N.; Weinstein, I.; Kirshenboim, O.; Chlebowski, N. Prenatal SSRI alters the hormonal and behavioral responses to stress in female mice: Possible role for glucocorticoid resistance. Horm. Behav. 2016, 84, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, G.W.; Makmor-Bakry, M.; Omar, M.S. Long term use of lithium and factors associated with treatment response among patients with bipolar disorder. Psychiatr. Danub. 2016, 28, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, D.L.; Leibu, E.; Aloysi, A.S.; Kopell, B.H.; Goodman, W.K.; Kellner, C.H. Safety and efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy for depression in the presence of deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borre, Y.E.; Moloney, R.D.; Clarke, G.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The impact of microbiota on brain and behavior: mechanisms & therapeutic potential. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 373–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savignac, H.M.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Bifidobacteria exert strain-specific effects on stress-related behavior and physiology in BALB/c mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study, Year, Country | Subjects, Total Number of Cases | Take Medications; Duration | Species, Dosage | Scale of Depression |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohammadi, 2015, Iran | 20–60 years old healthy petrochemical workers, 45 (20/25) | 6 weeks | Actobacillus casei 3 × 103 CFU/g, L. acidophilus 3 × 107 CFU/g, L. rhamnosus 7 × 109 CFU/g, L. bulgaricus 5 × 108 CFU/g, Bifidobacterium breve 2 × 1010 CFU/g, B. longum 1 × 109 CFU/g, S. thermophilus 3 × 108 CFU/g. | Depression Anxiety and Stress Scale (DASS) |
| Akkasheh, 2015, Iran | 20–55 years old patients with MDD, 40 (20/20) | One capsule per day; 8 weeks | L. acidophilus 2 × 109 CFU/g, L. casei 2 × 109 CFU/g, Bifidobacterium bifidum 2 × 109 CFU/g. | Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) |
| Steenbergen, 2015, The Netherlands | Around 20 years old; healthy young adults, 40 (20/20) | One sachet per day; 4 weeks | Bifidobacterium bifidum W23, Bifidobacterium lactis W52, L. acidophilus W37, L. brevis W63, L. casei W56, L. salivarius W24, Lactococcus lactis (W19 and W58), 2.5 × 109 CFU/g. | BDI |
| Messaoudi, 2011, France | 30–60 years old healthy human volunteers, 55 (29/26) | 1.5 g/day; 30 days | Lactobacillus helveticus R0052, Bifidobacterium longum R0175, 3 × 109 CFU. | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS-D) |
| Shinkai, 2013, Japan | Adults aged 65 years or older, 278 (93/92/93) | One capsule per day, 20 weeks | Lactobacillus pentosus strain b240, Low-dose group 2 × 109 cells, High-dose group 2 × 1010 cells. | Profile of Mood States (POMS): Depression-dejection |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, R.; Wang, K.; Hu, J. Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2016, 8, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080483
Huang R, Wang K, Hu J. Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2016; 8(8):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080483
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ruixue, Ke Wang, and Jianan Hu. 2016. "Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 8, no. 8: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080483
APA StyleHuang, R., Wang, K., & Hu, J. (2016). Effect of Probiotics on Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 8(8), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080483