Diagnosis of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): The Salerno Experts’ Criteria
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Frequency | Intestinal | Extra-Intestinal |
|---|---|---|
| Very Common | Bloating | Lack of wellbeing |
| Abdominal pain | Tiredness | |
| Common | Diarrhea | Headache |
| Epigastric pain | Anxiety | |
| Nausea | Foggy mind | |
| Aerophagia | Numbness | |
| GER | Joint/muscle pain | |
| Aphthous stomatitis | Skin rash/dermatitis | |
| Alternating bowel habits | ||
| Constipation | ||
| Undetermined | Hematochezia | Weight loss |
| Anal fissures | Anemia | |
| Loss of balance | ||
| Depression | ||
| Rhinitis/asthma | ||
| Weight increase | ||
| Interstitial cystitis | ||
| Ingrown hairs | ||
| Oligo or polymenorrhea | ||
| Sensory symptoms | ||
| Disturbed sleep pattern | ||
| Hallucinations | ||
| Mood swings | ||
| Autism | ||
| Schizophrenia |
2. NCGS Diagnostic Protocol
2.1. Step 1: Definition of a Patient Responsive to the GFD (Patient on a Gluten-Containing Diet)
- At baseline the patient has to be on a normal gluten containing diet for at least six weeks. The patient is assessed by the Table 2 diagnostic questionnaire at week-2, -1 and 0 to establish baseline symptoms;
- At time 0 the GFD is started after detailed explanation (preferably by a dietitian);
- Timeline: at least six weeks of verified GFD. Although the amelioration of symptoms is expected shortly after starting the GFD, a prolonged observation is needed to properly investigate the causal relationship, particularly for fluctuating symptoms (e.g., headache);
- Data recording: weekly completion of the Table 2 questionnaire from week 0 to 6. The patient will identify one to three main symptoms. The response parameters are those with an initial score of at least 3 on the numerical rating scale (NRS).
| Intestinal Symptoms | Baseline | 1 Week | 2 Week | 3 Week | 4 Week | 5 Week | 6 Week |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdominal pain or discomfort | |||||||
| Heartburn | |||||||
| Acid regurgitation | |||||||
| Bloating | |||||||
| Nausea and vomiting | |||||||
| Borborygmus | |||||||
| Abdominal distension | |||||||
| Eructation | |||||||
| Increased flatus | |||||||
| Decreased passage of stools | |||||||
| Increased passage of stools | |||||||
| Loose stools | |||||||
| Hard stools | |||||||
| Urgent need for defecation | |||||||
| Feeling of incomplete evacuation | |||||||
| Extra-intestinal symptoms | |||||||
| Dermatitis | |||||||
| Headache | |||||||
| Foggy mind | |||||||
| Fatigue | |||||||
| Numbness of the limbs | |||||||
| Joint/muscle pains | |||||||
| Fainting | |||||||
| Oral/tongue lesions | |||||||
| Other (specify) |
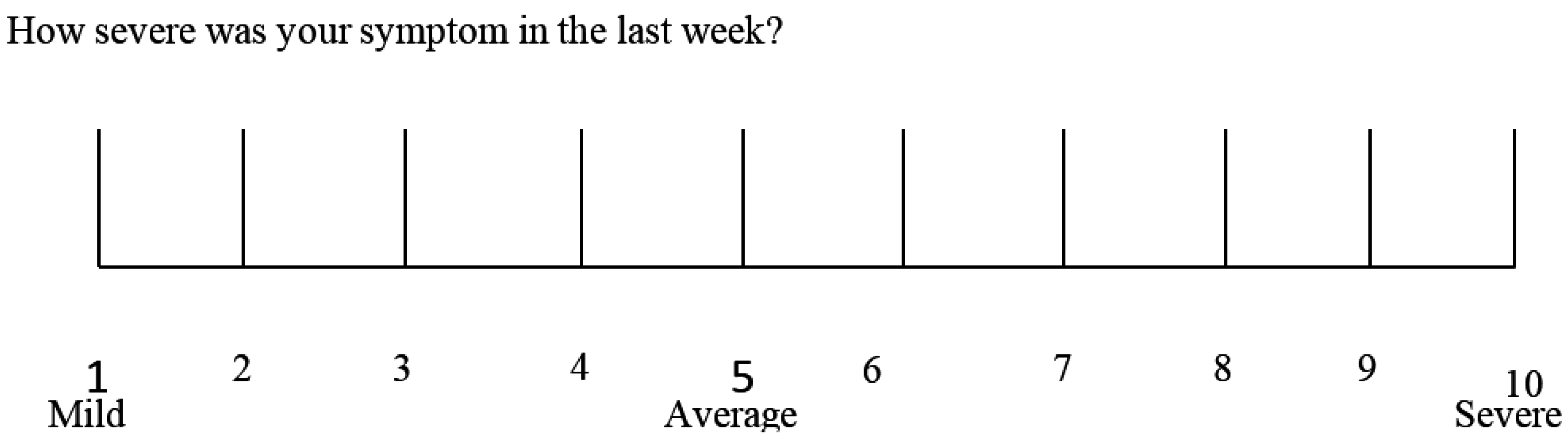
2.2. Step 2: the Gluten Challenge (Patient on the GFD)
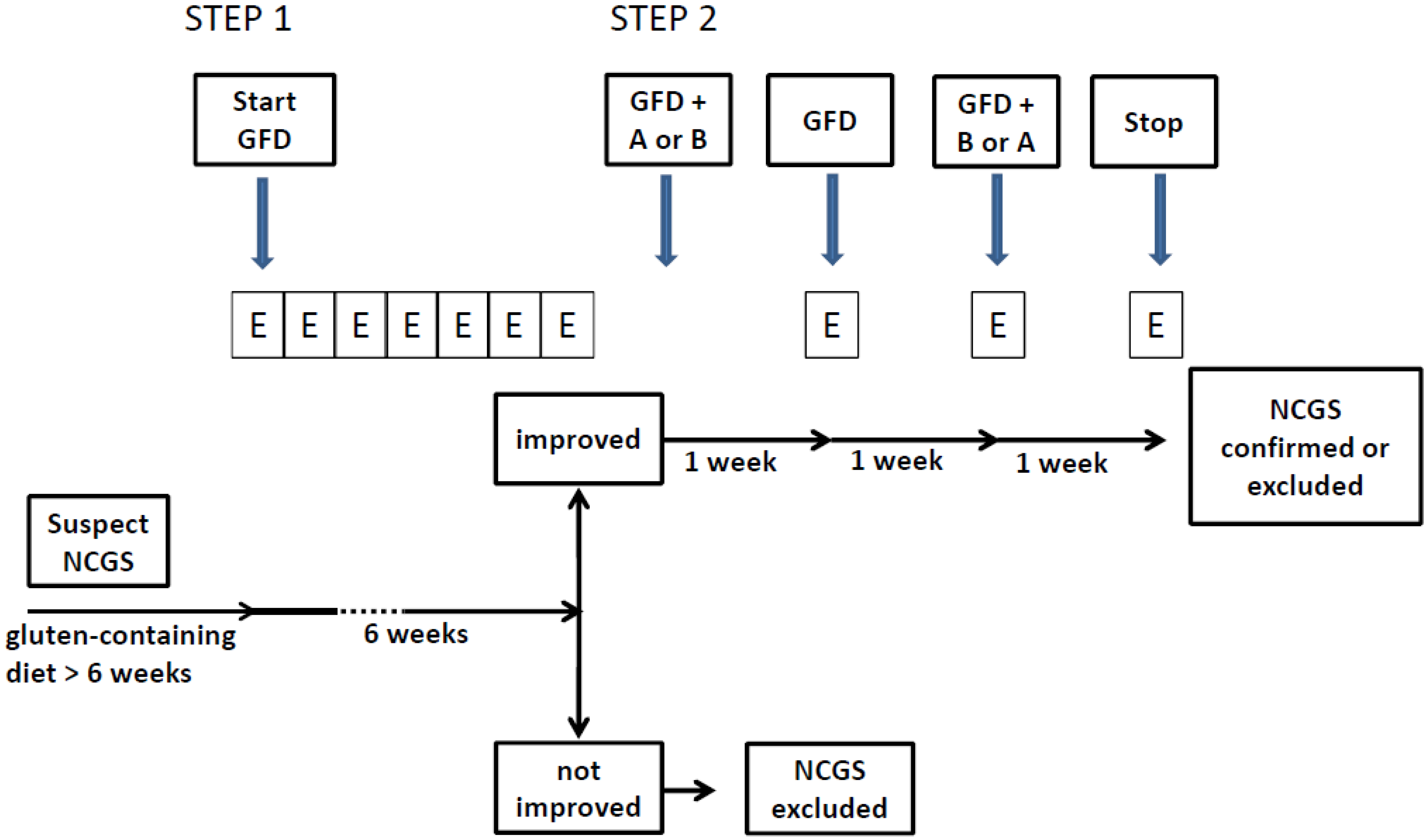
2.3. Monitoring the Gluten Elimination/Reintroduction Effects by Biomarkers
3. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sapone, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Mazzarella, G.; Mikhailenko, I.; Cartenì, M.; Casolaro, V.; Fasano, A. Differential mucosal IL-17 expression in two gliadin-induced disorders: Gluten sensitivity and the autoimmune enteropathy celiac disease. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 152, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesiekierski, J.R.; Newnham, E.D.; Irving, P.M.; Barrett, J.S.; Haines, M.; Doecke, J.D.; Shepherd, S.J.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Gluten causes gastrointestinal symptoms in subjects without celiac disease: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junker, Y.; Zeissig, S.; Kim, S.J.; Barisani, D.; Wieser, H.; Leffler, D.A.; Zevallos, V.; Libermann, T.A.; Dillon, S.; Freitag, T.L.; et al. Wheat amylase trypsin inhibitors drive intestinal inflammation via activation of toll-like receptor 4. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 2395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volta, U.; Bardella, M.T.; Calabrò, A.; Troncone, R.; Corazza, G.R. Study Group for Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity. An Italian prospective multicenter survey on patients suspected of having non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catassi, C.; Gatti, S.; Fasano, A. The new epidemiology of celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 59, S7–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A.; Sapone, A.; Zevallos, V.; Schuppan, D. Non-celiac Gluten Sensitivity. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroccio, A.; Mansueto, P.; Iacono, G.; Soresi, M.; D’Alcamo, A.; Cavataio, F.; Brusca, I.; Florena, A.M.; Ambrosiano, G.; Seidita, A.; et al. Non-celiac wheat sensitivity diagnosed by double-blind placebo-controlled challenge: exploring a new clinical entity. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesiekierski, J.R.; Peters, S.L.; Newnham, E.D.; Rosella, O.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. No effects of gluten in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity after dietary reduction of fermentable, poorly absorbed, short-chain carbohydrates. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja-Bulsa, G. Non coeliac gluten sensitivity—A new disease with gluten intolerance. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 34, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, I.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Coeliac disease: Noncoeliac gluten sensitivity—Food for thought. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 398–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.; Eaton, W.; Cascella, N.; Fasano, A.; Santora, D.; Sullivan, K.; Feldman, S.; Raley, H.; McMahon, R.P.; Carpenter, W.T., Jr.; et al. Gluten sensitivity and relationship to psychiatric symptoms in people with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 159, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catassi, C.; Bai, J.C.; Bonaz, B.; Bouma, G.; Calabrò, A.; Carroccio, A.; Castillejo, G.; Ciacci, C.; Cristofori, F.; Dolinsek, J.; et al. Non-Celiac Gluten sensitivity: the new frontier of gluten related disorders. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3839–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genuis, S.J.; Lobo, R.A. Gluten sensitivity presenting as a neuropsychiatric disorder. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 293206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.L.; Biesiekierski, J.R.; Yelland, G.W.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Randomised clinical trial: Gluten may cause depression in subjects with non-coeliac gluten sensitivity—An exploratory clinical study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Magistris, L.; Familiari, V.; Pascotto, A.; Sapone, A.; Frolli, A.; Iardino, P.; Carteni, M.; de Rosa, M.; Francavilla, R.; Riegler, G.; et al. Alterations of the intestinal barrier in patients with autism spectrum disorders and in their first-degree relatives. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J.; Kunze, W.A. Vagal pathways for microbiome-brain-gut axis communication. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glasziou, P.; Rose, P.; Heneghan, C.; Balla, J. Diagnosis using “test of treatment”. BMJ 2009, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulich, K.R.; Madisch, A.; Pacini, F.; Piqué, J.M.; Regula, J.; van Rensburg, C.J.; Ujszászy, L.; Carlsson, J.; Halling, K.; Wiklund, I.K. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: A six-country study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapone, A.; Bai, J.C.; Ciacci, C.; Dolinsek, J.; Green, P.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Rostami, K.; Sanders, D.S.; Schumann, M.; et al. Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: consensus on new nomenclature and classification. BMC Med. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Overbeek, F.M.; Uil-Dieterman, I.G.; Mol, I.W.; Köhler-Brands, L.; Heymans, H.S.; Mulder, C.J. The daily gluten intake in relatives of patients with coeliac disease compared with that of the general Dutch population. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 9, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caio, G.; Volta, U.; Tovoli, F.; De Giorgio, R. Effect of gluten free diet on immune response to gliadin in patients with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, F.; Pearson, D.A.; Fatheree, N.; Mansour, R.; Hashmi, S.S.; Rhoads, J.M. Are “leaky gut” and behavior associated with gluten and dairy containing diet in children with autism spectrum disorders? Nutr. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapone, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Casolaro, V.; Cammarota, M.; Giuliano, M.T.; de Rosa, M.; Stefanile, R.; Mazzarella, G.; Tolone, C.; Russo, M.I.; et al. Divergence of gut permeability and mucosal immune gene expression in two gluten-associated conditions: celiac disease and gluten sensitivity. BMC Med. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollon, J.; Puppa, E.L.; Greenwald, B.; Goldberg, E.; Guerrerio, A.; Fasano, A. Effect of gliadin on permeability of intestinal biopsy explants from celiac disease patients and patients with non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brottveit, M.; Beitnes, A.C.; Tollefsen, S.; Bratlie, J.E.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Johansen, F.E.; Sollid, L.M.; Lundin, K.E. Mucosal cytokine response after short-term gluten challenge in celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, B.T.; Holmes, G.K.; Ferguson, R.; Thompson, R.A.; Allan, R.N.; Cooke, W.T. Gluten-sensitive diarrhea without evidence of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 1980, 79, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catassi, C.; Elli, L.; Bonaz, B.; Bouma, G.; Carroccio, A.; Castillejo, G.; Cellier, C.; Cristofori, F.; De Magistris, L.; Dolinsek, J.; et al. Diagnosis of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): The Salerno Experts’ Criteria. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4966-4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064966
Catassi C, Elli L, Bonaz B, Bouma G, Carroccio A, Castillejo G, Cellier C, Cristofori F, De Magistris L, Dolinsek J, et al. Diagnosis of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): The Salerno Experts’ Criteria. Nutrients. 2015; 7(6):4966-4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064966
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatassi, Carlo, Luca Elli, Bruno Bonaz, Gerd Bouma, Antonio Carroccio, Gemma Castillejo, Christophe Cellier, Fernanda Cristofori, Laura De Magistris, Jernej Dolinsek, and et al. 2015. "Diagnosis of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): The Salerno Experts’ Criteria" Nutrients 7, no. 6: 4966-4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064966
APA StyleCatassi, C., Elli, L., Bonaz, B., Bouma, G., Carroccio, A., Castillejo, G., Cellier, C., Cristofori, F., De Magistris, L., Dolinsek, J., Dieterich, W., Francavilla, R., Hadjivassiliou, M., Holtmeier, W., Körner, U., Leffler, D. A., Lundin, K. E. A., Mazzarella, G., Mulder, C. J., ... Fasano, A. (2015). Diagnosis of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS): The Salerno Experts’ Criteria. Nutrients, 7(6), 4966-4977. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7064966











