Abstract
Increasing evidence has suggested an association between dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome. However, previous research examining dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome has produced mixed results. Our objective was to determine the relationship between dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome in the adult population using a dose-response meta-analysis. We searched the PubMed, Embase and the Cochrane Library databases from August, 1965, to May, 2014. Observational studies reporting risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for metabolic syndrome in ≥3 categories of dietary magnesium intake levels were selected. The data extraction was performed independently by two authors, and the quality of the studies was evaluated using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Nonrandomized Studies (RoBANS). Based on eight cross-sectional studies and two prospective cohort studies, the pooled relative risks of metabolic syndrome per 150 mg/day increment in magnesium intake was 0.88 (95% CI, 0.84–0.93; I2 = 36.3%). The meta-regression model showed a generally linear, inverse relationship between magnesium intake (mg/day) and metabolic syndrome. This dose-response meta-analysis indicates that dietary magnesium intake is significantly and inversely associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome. However, randomized clinical trials will be necessary to address the issue of causality and to determine whether magnesium supplementation is effective for the prevention of metabolic syndrome.
1. Introduction
Metabolic syndrome is characterized by hyperinsulinemia with underlying insulin resistance, as well as a variety of other cardiovascular risk factors, including impaired glucose regulation, elevated levels of triglycerides, decreased levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, increased blood pressure and centrally-distributed obesity [1]. Metabolic syndrome [2] has received increased attention in the past year. Given that metabolic syndrome is strongly linked to cardiovascular events [3], cancer and mortality [4], preventing metabolic syndrome is important to public health.
Dietary and lifestyle modifications are widely perceived to play an important role in reducing metabolic syndrome [5]. Magnesium is an essential trace mineral for the human body that plays a key role in all energy-dependent transport systems, glycolysis and oxidative energy metabolism [6,7]. Foods rich in magnesium include whole grains, spinach, nuts, legumes and potatoes [8]. Magnesium deficiency, either from inadequate intake, excess excretion or altered homeostasis, is often suspected to be associated with the initiation of many symptoms and diseases [9]. Lifestyle factors (e.g., poor nutrition and excess alcohol intake), certain types of medications (e.g., diuretics) and lower mineral content [10,11] in commonly-eaten foods (e.g., fruits and vegetables) have led to an increase in studies evaluating the potential link between magnesium deficiency and numerous health conditions [12].
Low serum magnesium levels have been associated with risk factors of metabolic syndrome, such as hyperglycemia, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia and insulin resistance [13]. Additionally, waist circumference is independently associated with hypomagnesemia [14]. Furthermore, several studies [15,16,17] suggested that serum magnesium levels are independently associated with metabolic syndrome. Hence, a high dietary magnesium intake may potentially reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome. However, recent epidemiological studies have been conducted to investigate the association between magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome, with inconsistent results. Several epidemiological studies [18,19,20] indicated that deficient magnesium intake may be an independent risk factor for metabolic syndrome; however, other studies [21,22] have reported no significant association.
Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis of observational studies for the following purposes: (1) to assess the association between dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome; (2) to evaluate a dose-response pattern of dietary magnesium intake on the risk of metabolic syndrome; and (3) to examine the association according to the characteristics of study designs and populations.
2. Materials and Methods
Following generally-accepted methodology recommendations, the meta-analysis was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses statement (Table S1: PRISMA checklist) [23]. This study was registered at both the ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration System (NCT02151227), https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02151227?term=NCT02151227&rank=1 and the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review, www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/ (CRD42014010545).
2.1. Literature Search
A medical librarian with a Master’s degree and experience in systematic reviews participated in the search strategy design process. We searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library and Embase databases via Elsevier from August, 1965, to May, 2014. A PubMed search for studies on magnesium and metabolic syndrome was conducted without restrictions, by combining synonymous or related search terms for magnesium and metabolic syndrome. The keywords used in the PubMed search were converted to search tags for the Cochrane Library and EMBASE (Table S2: search strategies). Furthermore, manual searches of the bibliographies of relevant articles were performed to identify additional studies.
2.2. Excluded Studies
In total, 452 articles were found in our initial search. Using an automated reference manager facility, 128 duplicates were removed, leaving a database containing 324 references. In the first round of screening on the basis of the title or abstract, we excluded 266 articles for at least one of the following reasons: did not study magnesium exposure or use metabolic syndrome as an outcome; was a duplicate study; was a nonhuman study; was a non-original study, such as a review, editorial, letters or commentary. In the second round of screening on the basis of full-text articles, we excluded 49 articles because these did not meet the inclusion criteria: no full text available (4 articles), no relevant studies (25 articles), no original articles (13 articles), data not available (3 articles) and duplicates (4 articles) (Table S3: excluded studies). Lastly, 10 independent observational studies (extracted from 9 articles), including 8 cross-sectional studies and 2 prospective cohort studies, were included in the meta-analysis (Figure S1: flow diagram for the search strategy and study selection process). Furthermore, manual searches of the bibliographies of relevant articles were performed to identify additional studies.
2.3. Validity Assessment
The quality of the primary studies was evaluated using the Risk of Bias Assessment Tool for Nonrandomized Studies (RoBANS), which showed moderate reliability, promising feasibility and validity [24]. RoBANS consists of the following 6 domains: the selection of the participants, confounding variables, measurement of exposure, blinding of outcome assessments, incomplete outcome data and selective outcome reporting.
2.4. Data Extraction
Two investigators (Sang-Yhun Ju and Do-Hoon Kim, co-authors of the present study, independently extracted the data from the original reports. The adjusted risk estimates that reflected the most comprehensive control were extracted to avoid potential confounding variables. The following information was extracted: study characteristics (study name, study design and location, first author’s surname, publication year and adjusted covariates), participants’ characteristics (age, sex, sample size and sample source), methods of dietary magnesium assessment and the definition of metabolic syndrome used.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Summary risk ratios were calculated by pooling the study-specific estimates using a random-effects model, which considered both within-study and between-study variations [25]. We also performed a random-effects meta-regression model to assess the overall linear relationship between dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome with weights, based on the inverse of variances [26].
For the dose-response meta-analysis, we used generalized least-squares regression (Stata GLST command), which considered the correlation between estimates for different exposure levels [27], to compute study-specific slopes (linear trends). This method required that the number of cases and controls and the risk ratio with its variance estimate for at least three quantitative exposure categories were known. For the studies that did not provide this information, we estimated the dose-response slopes using variance-weighted least-squares regression (Stata VWLS command). Both methods (GLST and VWLS) required median or mean exposure for each category of magnesium intake level. The mid-point of each category of magnesium intake was calculated, and half the width of the adjacent category was used to define the corresponding point for open-ended categories.
The reported HRs and ORs were assumed to approximate the same measure of RRs [28]. Where studies reported RRs with differing degrees of adjustment for other risk factors, the maximum adjusted estimate was used. Dose responses of dietary magnesium were standardized across studies to 150 mg/day, based on the interquartile range between the bottom and top quartiles across all studies of 148 mg/day for dietary magnesium. The RRs for different increments can be calculated from our data. Although the magnesium intake in our included studies was expressed in different units, we rescaled it to milligrams (mg) per day. When the exposures were expressed in mg/1000 kcal, we converted it to mg/day using the average energy intake (kcal/day) reported in that article [19]. For the study reporting intakes in mg/kg/day [29], the intakes in mg/day were estimated using the average body weight of Taiwan elderly individuals reported in that article [30].
The subgroup meta-analyses were conducted according to the pre-specified study-level characteristics using a fixed-effects meta-analysis. The sources included location, study design (cohort, cross-sectional), sex, age, sample size, sample source (population-based, hospital-based), the dietary assessment method, the definition of metabolic syndrome used and the risk of bias.
The statistical heterogeneity among the studies was assessed using I2 statistics [31]. We defined low, moderate and high heterogeneity as I2 values of 25%, 50% and 75%, respectively. Heterogeneity was assessed by comparing the results from studies grouped according to the pre-specified study-level characteristics using meta-regression. We also conducted sensitivity analyses to evaluate the potential sources of heterogeneity in the analyses. The publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test and Begg’s test. In the presence of publication bias, the p-values for Egger’s test and Begg’s test are less than 0.05. All of the statistical analyses were performed using Stata software, version 13.0 (Stata Corp., College Station, TX, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics, Quality and Bias Assessment
We identified 10 articles, including nine [18,19,20,21,22,29,32,33,34] that investigated the association between dietary magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome and one article [33] that reported results separately for gender (men and women).
The studies included in this meta-analysis are summarized in Table 1. A total of 30,092 participants were reported in 10 observational studies, including eight cross-sectional studies [18,20,21,29,32,33,34] and two prospective cohort studies [19,22]. Eight population-based studies [18,19,20,21,32,33,34] involving healthy populations were included, and two hospital-based studies recruited patients with elderly type 2 diabetes [29] and recipients of living-donor kidney transplant [22]. Four studies were conducted in the United States [18,19,20,34], four in Asia [22,29,32,33] and one in Europe [21]; all of the studies were published in the 2000s. The participants’ mean age ranged from 18 years to 72 years. Four studies [18,19,21,22] defined metabolic syndrome using the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (ATP-III), and six studies [20,29,32,33,34] assessed metabolic syndrome using the modified NCEP ATP-III and International Diabetes Foundation. The assay method of dietary magnesium intake varied across the studies. Four studies [19,20,21,22] used the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ); five studies [18,29,32,33] used 24-h dietary recalls; and one study [34] used a consecutive three-day food record.
The reported risk estimates for the association of dietary magnesium intake levels with metabolic syndrome are illustrated in Figure 1. There appeared to be an approximately inverse linear relationship of magnesium intake levels and metabolic syndrome in all of the studies, except for the studies of Al-Daghri et al. [32], Bo et al. [21] and Noori et al. [22], which found no association between magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome. For all other studies, the group with the highest magnesium intake levels had the lowest metabolic syndrome risk.

Table 1.
Characteristics of studies included in the meta-analysis on the association of dietary magnesium intake with metabolic syndrome.
| Author, Year | Country (Study) | Population | Baseline Population | Participant Cases | Sex | Assessment (Exposure) | Key Set of Covariates 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Mean Age | Definition (Outcome) | |||||
| Song et al., 2005 [20] | USA (WHS) | Population-based | Healthy | 9907 | F | FFQ | + |
| Cross-sectional | 2418 | 52 | Modified NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| Bo et al., 2006 [21] | Italy | Population-based | Healthy | 1653 | M and F | FFQ | + |
| Cross-sectional | 384 | 54 | NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| He et al., 2006 [19] | USA (CARDIA) | Population-based | Healthy | 4637 | M and F | FFQ | ++ |
| Prospective cohort | 608 | 25 | NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| Ford et al., 2007 [18] | USA (NHANES III) | Population-based | Healthy | 7669 | M and F | 24-h recall | + |
| Cross-sectional | 4965 | 44 | NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| McKeown et al., 2008 [34] | USA | Population-based | Healthy | 535 | M and F | 3-D food record | ++ |
| Cross-sectional | 212 | 72 | Modified NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| Noori, 2010 [22] | Iran | Hospital-based | Renal-transplant recipient | 160 | M and F | FFQ | + |
| Prospective cohort | 58 | 40 | NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| Huang et al., 2012 [29] | Taiwan | Hospital-based | Diabetes | 210 | M and F | 24-h recall | ++ |
| Cross-sectional | 156 | 72 | NCEP-ATP III | ||||
| Al-Daghri et al., 2013 [32] | Saudi Arabia | Population-based | Healthy | 185 | M and F | 24-h recall | + |
| Cross-sectional | 72 | 26 | IDF | ||||
| Choi et al., 2013 [33] | Korea (KNHANES IV) | Population-based | Healthy | 2084 | M | 24-h recall | + |
| 540 | 44 | Modified NCEP-ATP III | |||||
| Cross-sectional | 3052 | F | |||||
| 748 | 49 |
Abbreviations: CARDIA, Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults; CDS, Chinese Diabetes Society; FFQ, food-frequency questionnaire; IDF, International Diabetes Foundation; KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; NCEP-ATP III, National Cholesterol Education Program and Adult Treatment Panel III; NHANES III, The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; TLGS, Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study; WHS, Women’s Health Study; 1 Key set of covariates indicates age, sex, obesity, smoking, alcohol intake, exercise and calories intake: ++, the key sets of covariates were adequately confirmed and adjusted for during the analysis phase; +, although the existence of major confounding variables were confirmed, the key sets of covariates were not adequately considered during the design and analytic phases.
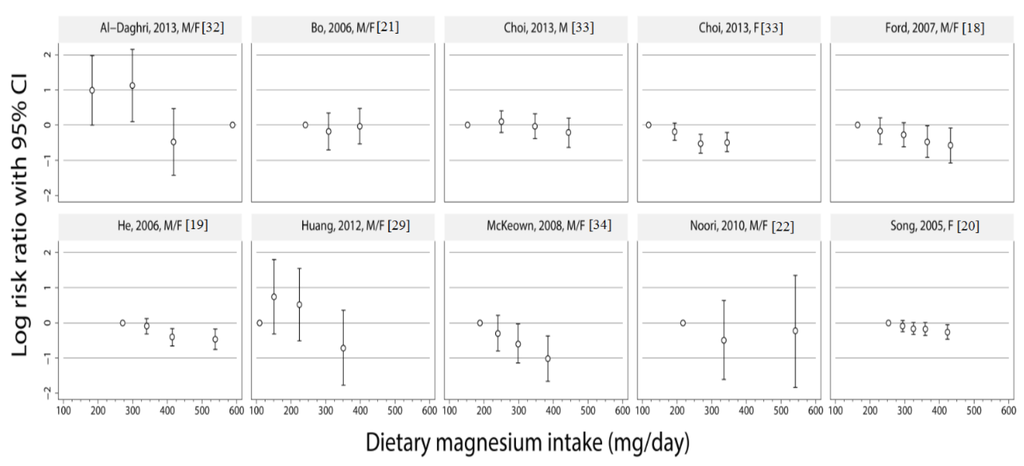
Figure 1.
Study-specific risks ratios (RRs) and 95% CIs of metabolic syndrome risk according to study-specific levels of dietary magnesium intake. Depending on available information, the median, midpoints or means of the categories were used for defining study-specific levels of magnesium intake categories (mg/day). The vertical axis is on a log scale.
The risk of bias analysis revealed several areas of concern (Figure S2: assessment of the risk of bias), particularly with regard to confounding variables in two studies [32,33] that did not adjust for the key covariates, including age, sex, obesity, smoking, alcohol intake, exercise and calorie intake.
3.2. Meta-Regression and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis
As shown in Figure 2a, for the ten epidemiological studies that assessed dietary magnesium intake, the pooled estimate indicated that magnesium intake (mg/day) was significantly and inversely associated with metabolic syndrome based on the meta-regression model, as follows:
The estimated RRs of metabolic syndrome for an increase in magnesium intake of 150 mg/day for each of the 10 observational studies are shown in Figure 2b. A significant inverse association between magnesium intake and metabolic syndrome was observed in five studies [18,19,20,33,34], and a nonsignificant inverse association was found in five studies [21,22,29,32,33]. In the analysis of all of the studies, the overall RR demonstrated a statistically significant inverse association between dietary magnesium intake of an increase in 150 mg/day and metabolic syndrome (RR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.84–0.93). There was moderate heterogeneity across studies (I2 = 36.3%). In a sensitivity analysis in which one study at a time was removed and the remaining studies were analyzed, the RR ranged from 0.87 (95% CI, 0.82–0.92) when the study by Song et al. [20] was excluded to 0.90 (95% CI, 0.87–0.94) when the study (on women) by Choi et al. [33] was excluded. No publication bias was detected with Egger’s test (p for bias = 0.352) or Begg’s test (p for bias = 0.655) (Figure S3: Begg’s funnel plots in the meta-analysis of observational studies).
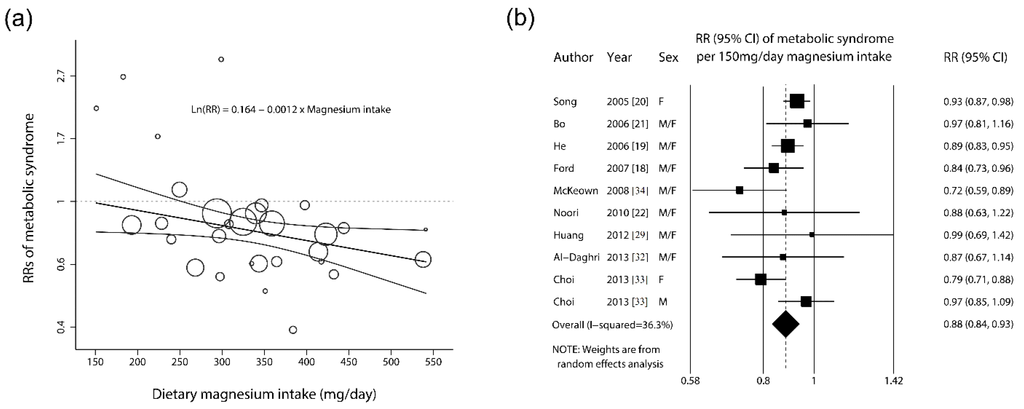
Figure 2.
(a) Association between the risk of metabolic syndrome and dietary magnesium intake: dose-response meta-regression. The levels of magnesium intake (mg/day) were modeled using a linear trend with random-effects meta-regression models. The solid black line represents the weighted regression line based on variance-weighted least squares. The gray line shows the 95% CI around the regression line. The circles indicate RRs in each study. The circle size is proportional to the precision of the RR. The vertical axis is on a log scale. (b) Forest plots of the risks ratios (RRs) of metabolic syndrome per 150 mg/day increment in dietary magnesium intake (n = 30,092) using a random-effects analysis. The squares represent study-specific RR (the square sizes are proportional to the weight of each study in the overall estimate); the horizontal lines represent 95% confidence intervals (CIs); and the diamond represents the overall RR estimate with the 95% CI.
3.3. Subgroup Analyses and Publication Bias
The subgroup analyses using fixed effects are shown in Figure 3. There were significant differences in dietary magnesium assessment (p = 0.04 for heterogeneity between groups). The corresponding RRs for studies based on FFQ, 24-h recall and 3-D food records were 0.91 (95% CI, 0.88–0.95), 0.86 (95% CI, 0.81–0.92) and 0.72 (95% CI, 0.59–0.89), respectively. In contrast, no significant group difference was found for study design, location, population base, sex, age, definition of outcome, number of cases and key sets of covariates (p > 0.1 for heterogeneity between groups). The univariate meta-regression analyses indicated no influence of the difference in dietary assessment, study design, location, population base, sex, age, definition of outcome, number of case and key sets of covariates on the inverse association between dietary magnesium intake and the risk of metabolic syndrome (p > 0.05 for all).
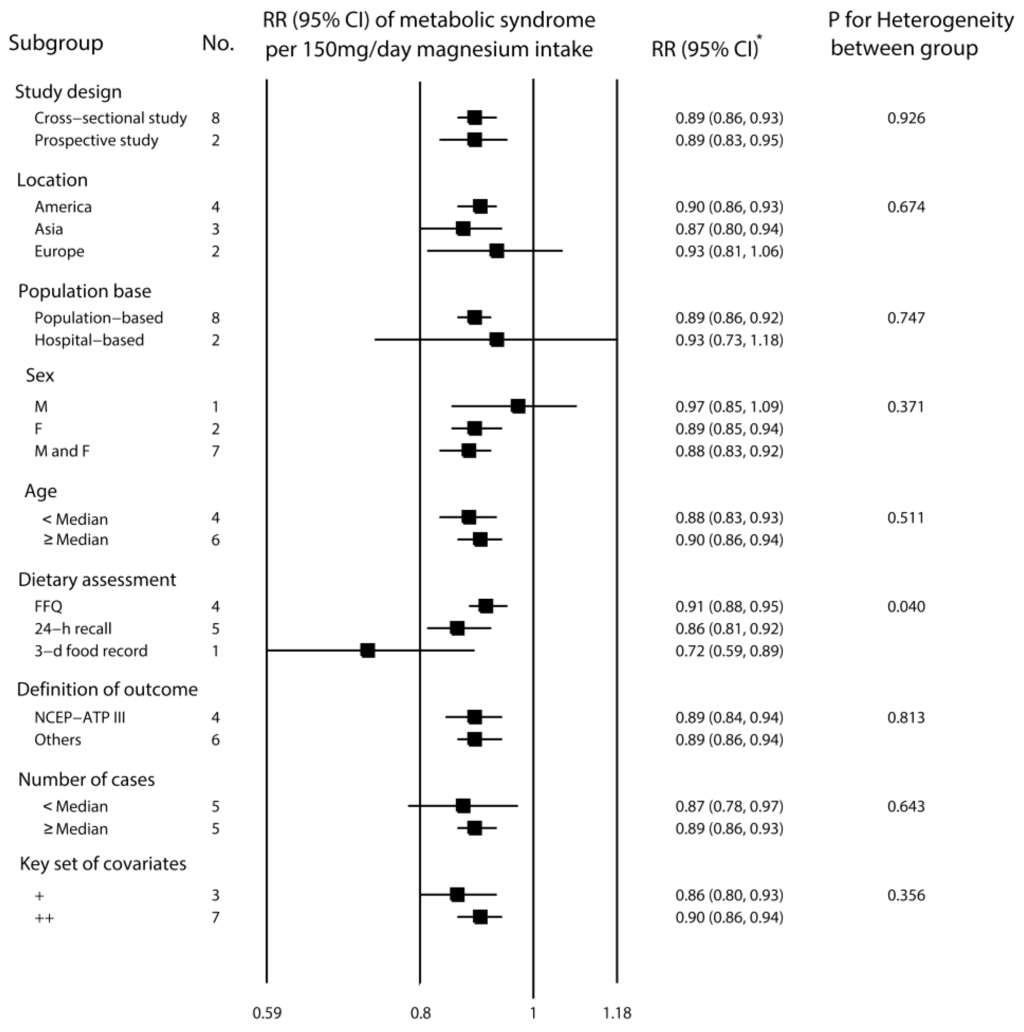
Figure 3.
Relative risk for metabolic syndrome per 150 mg/day increment in dietary magnesium intake according to different study-level characteristics. * p > 0.05 from meta-regression analyses on each of the covariates; FFQ, food frequency questionnaires; NCEP-ATP III, National Cholesterol Education Program and Adult Treatment Panel III; the key sets of covariates indicate age, sex, obesity, smoking, alcohol intake, exercise and calorie intake: ++, the key sets of covariates were adequately confirmed and adjusted for during the analysis phase; +, although the existence of major confounding variables were confirmed, the key sets of covariates were not adequately considered during the design and analytic phases.
4. Discussion
This meta-analysis of observational studies showed a statistically significant inverse association between dietary magnesium intake and the risk of metabolic syndrome based on cross-sectional studies and prospective cohort studies published between 2005 and 2013. The overall estimate indicated a 12% reduction in the risk of metabolic syndrome for an increment in magnesium intake of 150 mg/day, which is approximately equivalent to the magnesium content in 2 oz. of dry roasted almonds, one cup of cooked spinach, 1.5 cup of beans, two cups of brown, long-grained cooked rice, three medium baked potatoes with skin, five medium bananas or six tablespoons of peanut butter per day [35]. Moreover, using the data on magnesium intake levels, a progressively decreasing relationship was observed for low levels of magnesium intake in the pooled analysis. There was some heterogeneity among the studies, although there were no publication bias and no differences between the subgroups, including dietary assessment, study design, location, cohort-based, sex, age, definition of outcome, number of case and key sets of covariates using meta-regression.
This dose-response meta-analysis allowed us to evaluate the risk across the entire spectrum of observed magnesium intake levels. We found a monotonically decreasing association between magnesium intake levels and the risk of metabolic syndrome in the adult population, which suggested that any incremental increase in the magnesium intake level was associated with a decreased risk in the metabolic syndrome. However, because the range of magnesium intake levels was centered at approximately 200 mg/day to 450 mg/day, the apparent dose relationship at higher levels of magnesium intake might have been weak. Therefore, this result should be interpreted cautiously.
The inverse association found in our study is supported by evidence from randomized controlled studies [36,37] that cite the role of magnesium as an important component in improving insulin resistance, a central feature of metabolic syndrome. In addition, one case-control study [15] reported an inverse association between low serum magnesium levels and metabolic syndrome. A dietary intervention study [38] found that magnesium intake was inadequate among non-diabetic individuals with metabolic syndrome and that a higher level of magnesium intake from food had a beneficial effect on insulin resistance.
The potential protective role of magnesium intake against the risk of metabolic syndrome may be related to its beneficial effects on individual components of metabolic syndrome. The experimental data suggest that magnesium is a necessary cofactor for several enzymes that play an important role in glucose metabolism, especially those involved in autophosphorylation of the β-subunit of the insulin receptor and the activity of muscle insulin tyrosine kinase [39]. A recent meta-analysis suggested that higher dietary magnesium intake was inversely associated with fasting glucose and fasting insulin in individuals free of diabetes, generally, irrespective of genetic variation at the glycemia and magnesium-related loci investigated [40].
The findings from a current meta-analysis of 22 randomized clinical trials (mean duration, 11.3 weeks) have shown that magnesium supplementation (mean dose, 410 mg) significantly decreased blood pressure by 3–4 mmHg for systolic pressure and 2–3 mmHg for diastolic pressure, which is more evident at the higher dose (≥370 mg/day) [41]. An animal study of streptozocin-induced diabetic rats found that administering magnesium sulfate for eight weeks can improve the lipid profile, decrease mesenteric fat and also decrease systolic and diastolic blood pressure, suggesting that magnesium sulfate administration decreases cardiovascular risk factors [42]. The beneficial effect of magnesium supplementation on lipid parameters has also been attributed to improving insulin sensitivity, because it normalized total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which were impaired by a high fructose diet in rats [43].
Evidence that magnesium is directly involved in body weight regulation is lacking. The association between magnesium intake and obesity is a matter of controversy [44]. Two population-based studies have reported either a negative or no relationship between magnesium and body mass index [19,20], whereas a cross-sectional study [45] found a significant inverse association between magnesium intake and obesity or central obesity, which suggests that the inverse association may be attributable to dietary magnesium’s ability to form bonds with fatty acids in the intestine and, thus, reduce the digestible energy content of the diet [46]. Additionally, a recent study demonstrated that higher dietary magnesium intake is associated with improved insulin sensitivity and that this effect is particularly beneficial for overweight and obese individuals in the general population [47].
Within the subgroup analysis, we found that the association was attenuated in studies that assessed dietary magnesium intake with an FFQ only at baseline, which generally leads to bias in observed relative risks and loss of power to detect diet-disease relationships [48,49]. Additionally, some degree of misclassification of exposure may have weakened the strength of the association [50,51]. As an instrument for quantifying nutrient intakes, FFQ is relatively rough, although the majority of FFQs have been validated before application [52]. Such errors may have been present in other studies [53,54] that assessed dietary magnesium at baseline only, which could lead to an underestimation of the relative risk estimates. Therefore, the observed reduction in metabolic syndrome is likely a conservative estimate.
Although our meta-analysis included only multivariable adjusted risk ratios, there was evidence of moderate heterogeneity across the observational studies. This heterogeneity could be attributable to differences in study designs, sample sizes, analytic strategies, the participants’ characteristics, the diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome, study quality and the measurement of magnesium intake. To account for this heterogeneity, we used random-effects models of the meta-analyses and performed subgroup analyses using fixed-effects models; however, the results were not significantly altered. Additionally, the meta-regression did not identify any statistically significant sources of heterogeneity, although statistical power for identifying heterogeneity was limited given the number of studies.
This meta-analysis had several strengths and limitations. The primary strength was that it was the first dose-response meta-analysis that examined the relationship between the various magnesium intake levels and metabolic syndrome based on a comprehensive literature survey. Furthermore, our dose-response meta-analysis revealed a linear relationship between the magnesium intake and the risk of metabolic syndrome, despite the heterogeneous categorization of magnesium intake levels in individual studies. We found no publication bias in any of the analyses. A limitation of this approach is that it depended on the means, median or midpoints of the magnesium intake categories. The estimates of risk in this approach were therefore slightly less accurate than in the individual patient data meta-analyses. Second, despite the calculation of risk estimates that reflected the greatest degrees of controlling for potential confounders, several limitations must be considered when interpreting the meta-analysis results. Because it is impossible to adjust for general health status completely, residual confounders must always be considered when interpreting the results from observational studies. Third, one limitation was the evidence of heterogeneity across the studies, particularly resulting from heterogeneous magnesium intake measurement methods. Thus, the results of this analysis should be interpreted cautiously. We lastly were not able to assess the impact of magnesium from the supplement use on metabolic syndrome because such data are limited. Furthermore, because nearly all of the dietary magnesium in the identified studies was from foods, our findings support recommendations for increasing the consumption of magnesium-rich foods rather than taking supplements.
5. Conclusions
In summary, lower levels of magnesium intake were associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome in observational studies, which is consistent with the results from an analysis using linear regression methods. However, the data available for levels greater than 450 mg/day of magnesium intake were sparse, and additional studies, particularly longitudinal studies, are needed to provide more in-depth analyses, more precise and stable estimates of association and a better understanding of the potential role of magnesium intake in the risk of metabolic syndrome. Randomized clinical trials will also be necessary to address the issue of causality and to determine whether magnesium supplementation is effective for preventing metabolic syndrome.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
We thank So-Na Jeong, from the Medical Library, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, for performing database searches and preparing the manuscript. The authors appreciate the financial support provided by the College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 22 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-701, Republic of Korea.
Author Contributions
The authors’ responsibilities were as follows: S.-Y.J. had full access to all of the study data, took responsibility for the study integrity and the accuracy of data analyses, designed the study, reviewed and revised the final manuscript and contributed to the conception, design, statistical analyses, data interpretation and manuscript drafting for this study. D.-H.K. contributed to the data extraction and evaluated the methodological quality of the study using criteria that had been previously established. W.-S.C., S.-M.O. and C.-M.K. contributed to administrative, technical or material support. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Conflicts of Interest
All of the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
References
- Reaven, G.M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 1988, 37, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M.; Cleeman, J.I.; Daniels, S.R.; Donato, K.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Franklin, B.A.; Gordon, D.J.; Krauss, R.M.; Savage, P.J.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: An american heart association/national heart, lung, and blood institute scientific statement. Circulation 2005, 112, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottillo, S.; Filion, K.B.; Genest, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Rinfret, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; Liu, Z.; Ho, S.C. Metabolic syndrome and all-cause mortality: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, C.J.; Fernandez, M.L. Dietary strategies to reduce metabolic syndrome. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J.; Galioto, A.; Ferlisi, A.; Cani, C.; Malfa, L.; Pineo, A.; Busardo, A.; Paolisso, G. Role of magnesium in insulin action, diabetes and cardio-metabolic syndrome X. Mol. Asp. Med. 2003, 24, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elin, R.J. Magnesium: The fifth but forgotten electrolyte. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 102, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katcher, H.I.; Legro, R.S.; Kunselman, A.R.; Gillies, P.J.; Demers, L.M.; Bagshaw, D.M.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. The effects of a whole grain-enriched hypocaloric diet on cardiovascular disease risk factors in men and women with metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guerrera, M.P.; Volpe, S.L.; Mao, J.J. Therapeutic uses of magnesium. Am. Fam. Phys. 2009, 80, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D. The mineral depletion of foods available to us as a nation (1940–2002)—A review of the 6th edition of mccance and widdowson. Nutr. Health 2007, 19, 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.E.; Langkamp-Henken, B.; Littell, R.C.; Lukowski, M.J.; Suarez, M.F. Comparing nutrient intake from food to the estimated average requirements shows middle- to upper-income pregnant women lack iron and possibly magnesium. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2003, 103, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volpe, S.L. Magnesium, the metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corica, F.; Corsonello, A.; Ientile, R.; Cucinotta, D.; Di Benedetto, A.; Perticone, F.; Dominguez, L.J.; Barbagallo, M. Serum ionized magnesium levels in relation to metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Low serum magnesium levels and metabolic syndrome. Acta Diabetol. 2002, 39, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Hypomagnesemia, oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2006, 22, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.F.; Li, D. Serum levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids are low in Chinese men with metabolic syndrome, whereas serum levels of saturated fatty acids, zinc, and magnesium are high. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, E.S.; Li, C.; McGuire, L.C.; Mokdad, A.H.; Liu, S. Intake of dietary magnesium and the prevalence of the metabolic syndrome among U.S. Adults. Obesity 2007, 15, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Liu, K.; Daviglus, M.L.; Morris, S.J.; Loria, C.M.; van Horn, L.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Savage, P.J. Magnesium intake and incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation 2006, 113, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Ridker, P.M.; Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Liu, S. Magnesium intake, C-reactive protein, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged and older U.S. women. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Durazzo, M.; Guidi, S.; Carello, M.; Sacerdote, C.; Silli, B.; Rosato, R.; Cassader, M.; Gentile, L.; Pagano, G. Dietary magnesium and fiber intakes and inflammatory and metabolic indicators in middle-aged subjects from a population-based cohort. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noori, N.; Nafar, M.; Poorrezagholi, F.; Ahmadpoor, P.; Samadian, F.; Firouzan, A.; Einollahi, B. Dietary intakes of fiber and magnesium and incidence of metabolic syndrome in first year after renal transplantation. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, J.E.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.J.; Sheen, S.S.; Hahn, S.; Jang, B.H.; Son, H.J. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013, 66, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.G.; Higgins, J.P. How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, S.; Longnecker, M.P. Methods for trend estimation from summarized dose-response data, with applications to meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1992, 135, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Symons, M.J.; Moore, D.T. Hazard rate ratio and prospective epidemiological studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2002, 55, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.H.; Lu, Y.F.; Cheng, F.C.; Lee, J.N.; Tsai, L.C. Correlation of magnesium intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly type 2 diabetes patients: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, M.T. Metabolic syndrome in metabolic obese, non-obese elderly in northern Taiwan. Adv. Aging Res. 2012, 1, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Daghri, N.M.; Khan, N.; Alkharfy, K.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S.; Alfawaz, H.A.; Alothman, A.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Selected dietary nutrients and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult males and females in saudi arabia: A pilot study. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4587–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.K.; Bae, Y.J. Relationship between dietary magnesium, manganese, and copper and metabolic syndrome risk in korean adults: The Korea National Health And Nutrition Examination Survey (2007–2008). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, N.M.; Jacques, P.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Juan, W.; Sahyoun, N.R. Dietary magnesium intake is related to metabolic syndrome in older Americans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2008, 47, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, S.L. Magnesium in disease prevention and overall health. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 378S–383S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjistavri, L.S.; Sarafidis, P.A.; Georgianos, P.I.; Tziolas, I.M.; Aroditis, C.P.; Hitoglou-Makedou, A.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Pikilidou, M.I.; Lasaridis, A.N. Beneficial effects of oral magnesium supplementation on insulin sensitivity and serum lipid profile. Med. Sci. Monit. 2010, 16, CR307–CR312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; He, K.; Levitan, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Liu, S. Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized double-blind controlled trials. Diabet. Med. 2006, 23, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Persuitte, G.; Olendzki, B.C.; Wedick, N.M.; Zhang, Z.; Merriam, P.A.; Fang, H.; Carmody, J.; Olendzki, G.F.; Ma, Y. Dietary magnesium intake improves insulin resistance among non-diabetic individuals with metabolic syndrome participating in a dietary trial. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3910–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, A.; Pulido, N.; Casla, A.; Casanova, B.; Arrieta, F.J.; Rovira, A. Impaired tyrosine-kinase activity of muscle insulin receptors from hypomagnesaemic rats. Diabetologia 1995, 38, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, A.; Ngwa, J.S.; Renström, F.; Wojczynski, M.K.; Ganna, A.; Hallmans, G.; Houston, D.K.; Jacques, P.F.; Kanoni, S.; Lehtimäki, T.; et al. Higher magnesium intake is associated with lower fasting glucose and insulin, with no evidence of interaction with select genetic loci, in a meta-analysis of 15 charge consortium studies. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, L.; Weekes, J.; Carpenter, L. Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarz, M.; Dehpour, A.R. Effect of oral magnesium sulfate administration on blood pressure and lipid profile in streptozocin diabetic rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 560, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunji, L.A.; Soladoye, A.O. Increased magnesium intake prevents hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance and reduces lipid peroxidation in fructose-fed rats. Pathophysiology 2007, 14, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Pisu, E. Role of dietary magnesium in cardiovascular disease prevention, insulin sensitivity and diabetes. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, M.A.; Gary, T.L.; Caballero, B.H.; Lawrence, R.S.; Cheskin, L.J.; Wang, Y. Ethnic differences in dairy and related nutrient consumption among us adults and their association with obesity, central obesity, and the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drenick, E.J. The influence of ingestion of calcium and other soap-forming substances on fecal fat. Gastroenterology 1961, 41, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cahill, F.; Shahidi, M.; Shea, J.; Wadden, D.; Gulliver, W.; Randell, E.; Vasdev, S.; Sun, G. High dietary magnesium intake is associated with low insulin resistance in the newfoundland population. PLoS One 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, L.S.; Schatzkin, A.; Wax, Y. The impact of dietary measurement error on planning sample size required in a cohort study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 132, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freudenheim, J.L.; Marshall, J.R. The problem of profound mismeasurement and the power of epidemiological studies of diet and cancer. Nutr. Cancer 1988, 11, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höfler, M. The effect of misclassification on the estimation of association: A review. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2005, 14, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, K.T.; Checkoway, H.; McMichael, A.J.; Holbrook, R.H. Bias due to misclassification in the estimation of relative risk. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1977, 105, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, F.E.; Kipnis, V.; Midthune, D.; Freedman, L.S.; Carroll, R.J.; Subar, A.F.; Brown, C.C.; Butcher, M.S.; Mouw, T.; Leitzmann, M.; et al. Performance of a food-frequency questionnaire in the US NIH-AARP (National Institutes of Health-American Association of Retired Persons) diet and health study. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Y.; Xun, P.; He, K.; Qin, L.Q. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes: Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2116–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Jin, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, T.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Dai, K. Magnesium and the risk of cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS One 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).