Production of Hesperetin Glycosides by Xanthomonas campestris and Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Their Anti-allergic Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
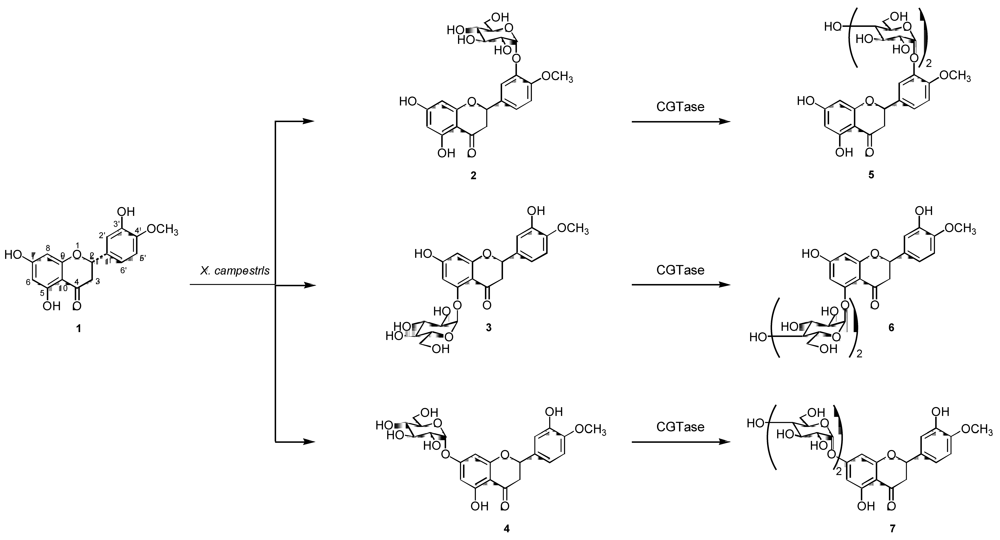
2.1. Production of Hesperetin α-glycosides
2.2. Anti-allergic Activity of Hesperetin α-glycosides
| Compound | IgE levela |
|---|---|
| None | 393.1 ± 188.7 |
| 2 | 356.6 ± 186.9 |
| 3 | 338.3 ± 163.0 |
| 4 | 155.4 ± 67.2* |
| 5 | 365.7 ± 126.7 |
| 6 | 374.9 ± 169.1 |
| 7 | 164.6 ± 57.8* |
| Compound | %Inhibition a |
|---|---|
| 2 | 12 |
| 3 | 17 |
| 4 | 59 |
| 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 |
| 7 | 46 |
| Mequitazine | 62 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
3.3. Production of Hesperetin α-glucosides by X. Campestris
3.4. Production of Hesperetin α-maltosides by CGTase
3.5. Suppressive Action on IgE Antibody Formation
3.6. Inhibitory Action on O2- Generation from Rat Neutrophils
4. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Formica, J.V.; Regelson, W. Review of the biology of quercetin and related bioflavonoids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 1061–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez, J.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Miranda, N.D.; Vega-Villa, K.R.; Andrews, P.K.; Davies, N.M. Pharmacokinetics of selected chiral flavonoids: hesperetin, naringenin and eriodictyol in rats and their content in fruit juices. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2008, 29, 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- So, F.V.; Guthrie, N.; Chambers, A.F.; Carroll, K.K. Inhibition of proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by flavonoids in the presence and absence of excess estrogen. Cancer lett. 1997, 112, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsunaga, Y.; Takanaga, H.; Matsuo, H.; Naito, M.; Tsuruo, T.; Ohtani, H.; Sawada, Y. Effect of bioflavonoids on vinicristine transport across blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 395, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- O’Prey, J.; Brown, J.; Fleming, J.; Harrison, P.R. Effects of dietary flavonoids on major signal transduction pathways in human epithelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 2075–2088. [Google Scholar]
- Youdim, K.A.; Dobbie, M.S.; Kuhnle, G.; Proteggente, A.R.; Abbott, N.J.; Rice-Evans, C. Interaction between flavonoids and the blood-brain barrier: in vitro study. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 180–192. [Google Scholar]
- Kaminaga, Y.; Nagatsu, A.; Akiyama, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamazaki, T.; Maitani, T.; Mizukami, H. Production of unnaturalglycosides of curcumin with drastically enhanced water solubility by cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. FEBS Lett. 2003, 555, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrissoud, D.; Testa, B. Inhibiting or potentiating effects of flavonoids on carbon tetrachloride-induced toxicity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1986, 36, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, J.P.; Ji, H.T.; Wang, J.S.; Qian, D.H. Effect of six flavonoids on proliferation of hepatic stellate cells in Vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2000, 21, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Garg, S.; Zaneveld, L.J.D.; Singla, A.K. Chemistry and pharmacology of the Citrus bioflavonoid hesperidin. Phytother.Res. 2001, 15, 655–669. [Google Scholar]
- Chiba, H.; Uehara, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Masuyama, R.; Suzuki, K.; Kanazawa, K.; Ishimi, Y. Hesperidin, a citrus flavonoid, inhibits bone loss and decreases serum and hepatic lipids in ovariectomized mice. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1892–1897. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.C.; Ong, T.T.; Fu, P.; Ching, C.B. Enantiomer separation of flavour and fragrance compounds by liquid chromatography using novel urea-covalent bonded methylated beta-cyclodextrins on silica. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 968, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Asztemborska, M.; Miśkiewicz, M.; Sybilska, D. Separation of some chiral flavanones by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 2527–2531. [Google Scholar]
- Caccamese, S.; Caruso, C.; Parrinello, N.; Savarino, A. High-performance liquid chromatographic separation and chiroptical properties of the enantiomers of naringenin and other flavanones. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1076, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, C.; Park, H.; Jung, S. Enantioseparation of some chiral flavanones using microbial cyclic beta-(1-->3),(1-->6)-glucans as novel chiral additives in capillary electrophoresis. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 762–766. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez, J.A.; Remsberg, C.M.; Miranda, N.D.; Vega-Villa, K.R.; Andrews, P.K.; Davies, N.M. Pharmacokinetics of selected chiral flavonoids: hesperetin, naringenin and eriodictyol in rats and their content in fruit juices. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2008, 29, 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, C.; Paik, S.R.; Jung, S. Enantiomeric separation of some flavanones using shinorhizobial linear octasaccharides in CE. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 4284–4290. [Google Scholar]
- Si-Ahmed, K.; Tazerouti, F.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Aturki, Z.; D'Orazio, G.; Rocco, A.; Fanali, S. Optical isomer separation of flavanones and flavanone glycosides by nano-liquid chromatography using a phenyl-carbamate-propyl-beta-cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Si-Ahmed, K.; Tazerouti, F.; Badjah-Hadj-Ahmed, A.Y.; Aturki, Z.; D'Orazio, G.; Rocco, A.; Fanali, S. Analysis of hesperetin enantiomers in human urine after ingestion of blood orange juice by using nano-liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Yáñez, J.A.; Andrews, P.K.; Davies, N.M. Methods of analysis and separation of chiral flavonoids. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 848, 159–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.-J.; Giridhar, R.; Wu, W.-T. Regioselective formation of kojic acid-7-o-alpha-D-glucopyranoside by whole cells of mutated Xanthomonas campestris. Enz. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadykov, A.A.; Isaev, K.I.; Ismailov, A.I. Polyphenols in the bark of Persica vulgaris roots and flowers. Khim. Prirod. Soed. 1975, 11, 281–282. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseff, R.L.; Martin, S.F.; Youtsey, C.O. Quantitative survey of narirutin, naringin, hesperidin and neohesperidin in citrus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1987, 35, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, J.A.; Fuster, M.D.; Sabater, F.; Porras, I.; Garcia-Lidon, A.; Ortuno, A. Effect of benzylaminopurine on the flavanones hesperidin, hesperetin 7-O-glucoside and pruning in tangelo nova fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 2030–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, E.; Berman, E.; Mazur, Y.; Gressel, J. Glucosylation of exogenous flavanones by grapefruit (Citrus paradisi) cell cultures. Phytochemistry 1986, 25, 2531–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, E.; Berman, E.; Mazur, Y.; Gressel, J. Glucosylation and (1-6) rhamnosylation of exogenous flavanones by undifferentiated Citrus cell cultures. Plant Science 1989, 61, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koda, A.; Miura, T.; Inagaki, N.; Sakamoto, O.; Arimura, A.; Nagai, H.; Mori, H. A method for evaluating anti-allergic drugs by simultaneously induced passive cutaneous anaphylaxis and mediator cutaneous reactions. Int. Arch. Allergy. Appl. Immunol. 1990, 92, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Akagi, M.; Katakuse, Y.; Fukuishi, N.; Kan, T.; Akagi, R. Superoxide anion-induced histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 732–734. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Akagi, M.; Hamada, H.; Hamada, H. Synthesis of oligosaccharides of genistein and quercetin as potential anti-inflammatory agents. Chem. Lett. 2008, 37, 876–877. [Google Scholar]
- Saija, A.; Scalese, M.; Lanza, M.; Marzullo, D.; Bonina, F.; Castelli, F. Flavonoids as antioxidant agents: importance of their interaction with biomembranes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 19, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Ficarra, R.; Tommasini, S.; Raneri, D.; Calabrò, M.L.; Di Bella, M.R.; Rustichelli, C.; Gamberini, M.C.; Ficarra, P. Study of flavonoids/beta-cyclodextrins inclusion complexes by NMR, FT-IR, DSC, X-ray investigation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 29, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasini, S.; Calabrò, M.L.; Stancanelli, R.; Donato, P.; Costa, C.; Catania, S.; Villari, V.; Ficarra, P.; Ficarra, R. The inclusion complexes of hesperetin and its 7-rhamnoglucoside with (2-hydroxypropyl)-beta-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 572–580. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.R.; Al Shaal, L.; Müller, R.H.; Keck, C.M. Production and characterization of Hesperetin nanosuspensions for dermal delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 371, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda, K.; Kondo, Y.; Akagi, M.; Abe, K.; Hamada, H.; Hamada, H. Synthesis of α-tocopheryl disaccharides as potential antiallergic agents. Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 570–571. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shimoda, K.; Hamada, H. Production of Hesperetin Glycosides by Xanthomonas campestris and Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Their Anti-allergic Activities. Nutrients 2010, 2, 171-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2020171
Shimoda K, Hamada H. Production of Hesperetin Glycosides by Xanthomonas campestris and Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Their Anti-allergic Activities. Nutrients. 2010; 2(2):171-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleShimoda, Kei, and Hiroki Hamada. 2010. "Production of Hesperetin Glycosides by Xanthomonas campestris and Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Their Anti-allergic Activities" Nutrients 2, no. 2: 171-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2020171
APA StyleShimoda, K., & Hamada, H. (2010). Production of Hesperetin Glycosides by Xanthomonas campestris and Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Their Anti-allergic Activities. Nutrients, 2(2), 171-180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu2020171




