Nutritional Strategies for Intestinal Rehabilitation in Children with Short Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
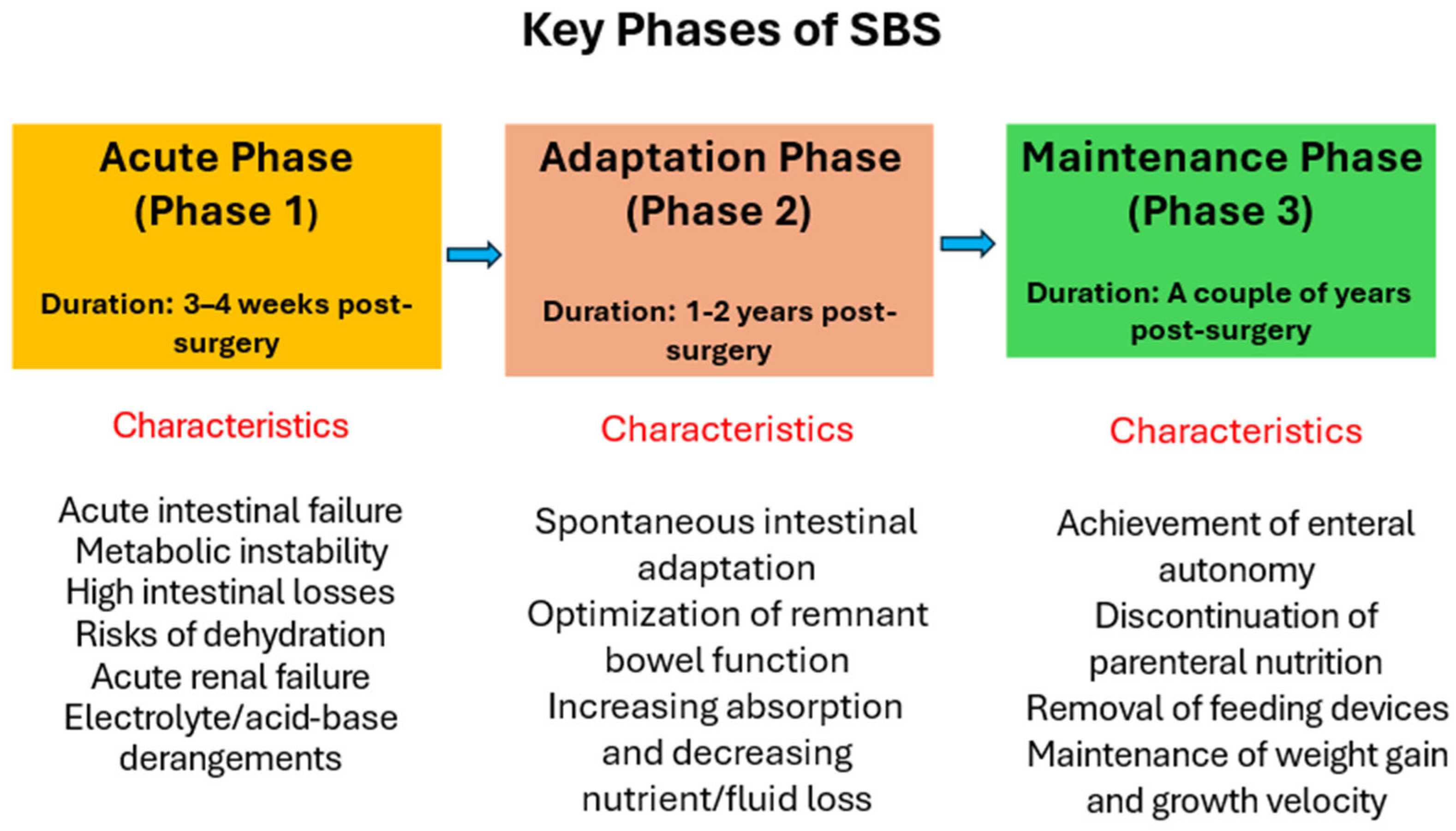
Postoperative Phases of SBS
2. Methods
- At what time should enteral nutrition (EN) be initiated? How should EN be advanced and administered?
- What type of EN should be used (focusing on specific macronutrients and micronutrients) during each post-surgical phase?
- What are the features of nutritional management depending on the type of SBS (e.g., site of resection and colon-in-continuity)?
Definitions
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Enteral Nutrition at the First Phase of SBS (Acute Phase, Typically Lasts Weeks to Months)
4.1.1. Parenteral Nutrition (PN)
4.1.2. Timing of EN Initiation
4.1.3. Route of Delivery
Oral vs. Tube Feeding
4.1.4. Gastric vs. Post-Pyloric Feeding
4.1.5. Feeding Modality: Bolus vs. Continuous
4.1.6. Choice of Feed
4.1.7. Advancement of Enteral Feeding
4.2. Enteral Nutrition at the Second Phase of SBS (Acute Phase, Typically Lasts Weeks to 18 Months)
4.2.1. Role of PN and Rationale for Progressive EN
4.2.2. Type of Enteral Nutrition
4.2.3. Lipid Composition
4.2.4. Carbohydrate Quality
4.2.5. Electrolyte and Fluid Considerations in Older Infants/Children
4.2.6. Hyperoxaluria
4.2.7. Blenderized Feeds
4.3. Enteral Nutrition at the Third Phase of SBS (Maintenance Phase, Typically Lasts from 18–24 Months to Several Years)
4.3.1. Stepwise Weaning and Feeding Advancement
4.3.2. Pharmacologic Support for PN Weaning
4.3.3. Oral Aversion
4.3.4. Nutritional Status Monitoring
4.3.5. Hydration Monitoring
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations and Future Perspectives
6.1. Limitations
6.2. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Modi, B.P.; Galloway, D.P.; Gura, K.; Nucci, A.; Plogsted, S.; Tucker, A.; Wales, P.W. ASPEN definitions in pediatric intestinal failure. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L. Definitions of intestinal failure and the short bowel syndrome. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, C.P.; Jaksic, T. Pediatric intestinal failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, I.R.; de Silva, N.; Pencharz, P.B.; Kim, J.H.; Wales, P.W.; Group for the Improvement of Intestinal Function Treatment. Neonatal short bowel syndrome outcomes after the establishment of the first Canadian multidisciplinary program. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.H.; Soraisham, A.; Bagga, N.; Massieu, L.A.; Maheshwari, A. Nutritional management of short bowel syndrome. Clin. Perinatol. 2022, 49, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive proteins in human milk—Potential benefits for preterm infants. Clin. Perinatol. 2017, 44, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksic, T. Current short bowel syndrome management: An era of improved outcomes and continued challenges. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2023, 58, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolapio, J.S.; Fleming, C.R. Short bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 27, 467–479. [Google Scholar]
- Gattini, D.; Roberts, A.J.; Wales, P.W.; Beath, S.V.; Evans, H.M.; Hind, J.; Mercer, D.; Wong, T.; Yap, J.; Belza, C.; et al. Trends in pediatric intestinal failure: A multicenter, multinational study. J. Pediatr. 2021, 237, 16–23.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bines, J.E.; Taylor, R.G.; Justice, F.; Paris, M.C.; Sourial, M.; Nagy, E.; Emselle, S.; Catto-Smith, A.G.; Fuller, P.J. Influence of diet complexity on intestinal adaptation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Ohyama, T.; Yokota, N.; Sugai, Y.; Takano, S.; Hamasaki, Y.; Kaneko, U.; et al. A rare case of eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders with short bowel syndrome after strangulated obstruction. Surg. Case Rep. 2022, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, O.; Abi Nader, E.; Pigneur, B.; Lambe, C. Short bowel syndrome as the leading cause of intestinal failure in early life. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2019, 22, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bines, J.; Francis, D.; Hill, D. Reducing parenteral requirement with amino acid–based formula. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1998, 26, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ksiazyk, J.; Piena, M.; Kierkus, J.; Lyszkowska, M. Hydrolyzed versus nonhydrolyzed protein diet in children with short bowel syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2002, 35, 615–618. [Google Scholar]
- Shores, D.R.; Bullard, J.E.; Aucott, S.W.; Stewart, F.D.; Haney, C.; Tymann, H.; Miller, M.R.; Nonyane, B.A.; Schwarz, K.B. Implementation of feeding guidelines in infants at risk of intestinal failure. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Greef, E.; Mahler, T.; Janssen, A.; Cuypers, H.; Veereman-Wauters, G. Influence of Neocate in pediatric short bowel syndrome on PN weaning. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 2010, 297575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andorsky, D.J.; Lund, D.P.; Lillehei, C.W.; Jaksic, T.; Dicanzio, J.; Richardson, D.S.; Collier, S.B.; Lo, C.; Duggan, C. Nutritional and Other Postoperative Management of Neonates with Short Bowel Syndrome Correlates with Clinical Outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2001, 139, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Goudoever, J.B.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Sainz de Pipaon, M. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Amino acids. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriati, T.; Nobili, V.; Stronati, L.; Cucchiara, S.; Laureti, F.; Liguori, A.; Tyndall, E.; Diamanti, A. Enteral nutrition in pediatric intestinal failure: Impact of initial feeding on adaptation. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappenden, K.A. Anatomical and physiological considerations in short bowel syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Beyec, J.; Billiauws, L.; Bado, A.; Joly, F.; Le Gall, M. Short bowel syndrome: A paradigm for intestinal adaptation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2020, 40, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venick, R.S. Predictors of intestinal adaptation in children. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappenden, K.A. Mechanisms of enteral nutrient-enhanced intestinal adaptation. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S93–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Siplovich, L.; Shiloni, E.; Mor-Vaknin, N.; Harmon, C.M.; Coran, A.G. Intestinal adaptation in infants and children with SBS. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2002, 18, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L. Definition, classification, and causes of short bowel syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2023, 38, S9–S16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muto, M.; Kaji, T.; Onishi, S.; Yano, K.; Yamada, W.; Ieiri, S. Current management of pediatric short-bowel syndrome. Surg. Today 2022, 52, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Puoti, M.G.; Köglmeier, J. Nutritional management of intestinal failure due to short bowel syndrome in children. Nutrients 2023, 15, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondheimer, J.M.; Cadnapaphornchai, M.; Sontag, M.; Zerbe, G.O. Predicting PN duration after neonatal intestinal resection. J. Pediatr. 1998, 132, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tappenden, K.A. Intestinal adaptation following resection. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 23S–31S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshel Fuhrer, A.; Sukhotnik, S.; Moran-Lev, H.; Kremer, K.; Ben-Shahar, Y.; Sukhotnik, I. Motility disorders in children with intestinal failure. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2022, 38, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkinen, M.; Mutanen, A.; Pakarinen, M.P. Small bowel dilation and risk of mucosal injury in SBS. Surgery 2017, 162, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA-ScR extension. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Lisy, K.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; et al. Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. JBI Man. Evid. Synth. 2020, 1, 217–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, J.E.; Kennedy, K.A. Minimal enteral feeding for feeding tolerance. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2000, CD000504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, E.; King, L.M. Techniques for advancing feeds in pediatric intestinal failure. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.; Olieman, J.; Ksiazyk, J.; Spolidoro, J.; Tibboe, D.; Köhler, H.; Yagci, R.V.; Falconer, J.; Grimble, G.; Beattie, R.M. Neonatal short bowel syndrome as a model of intestinal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltu, S.J.; Bronsky, J.; Embleton, N.; Gerasimidis, K.; Indrio, F.; Köglmeier, J.; de Koning, B.; Lapillonne, A.; Norsa, L.; Verduci, E.; et al. Nutritional management of the critically ill neonate. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 73, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsa, L.; Goulet, O.; Alberti, D.; DeKooning, B.; Domellöf, M.; Haiden, N.; Hill, S.; Indrio, F.; Köglmeier, J.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Nutrition and intestinal rehabilitation of children with SBS: Part 1. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 77, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.; DiBaise, J.K.; Rubio-Tapia, A. AGA clinical practice update on SBS. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2185–2194.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olieman, J.; Kastelijn, W. Nutritional feeding strategies in pediatric intestinal failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olieman, J.F.; Penning, C.; IJsselstijn, H.; Escher, J.C.; Joosten, K.F.; Hulst, J.M.; Tibboel, D. Enteral nutrition in children with short-bowel syndrome. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlato, G.; Hill, S.; Jonkers-Schuitema, C.; Macdonald, S.; Guimber, D.; Echochard-Dugelay, E.; Pulvirenti, R.; Lambe, C.; Tabbers, M. European Reference Network on Rare Inherited Congenital Anomalies (ERNICA) International survey on feeding in infants with SBS. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 73, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitzur, Y.; Courtney-Martin, G. Enteral approaches in malabsorption. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvadia, J.K.; Keswani, S.G.; Vaikunth, S.; Maldonado, A.R.; Marwan, A.; Stehr, W.; Erwin, C.; Uzvolgyi, E.; Warner, B.W.; Yamano, S.; et al. VEGF and bowel adaptation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G591–G598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micic, D.; Martin, J.A.; Fang, J. AGA clinical update on endoscopic enteral access. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channabasappa, N.; Girouard, S.; Nguyen, V.; Piper, H. Enteral Nutrition in Pediatric Short-Bowel Syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.M.; Skillman, H.E.; Irving, S.Y.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Vermilyea, S.; Farrington, E.A.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Goday, P.S.; Braunschweig, C. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 706–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, L.; Coopman, S.; Guimber, D.; Sfeir, R.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Percutaneous gastrojejunostomy in children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2012, 97, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Dias, J.A.; Hartman, C.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Koletzko, S.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.; Puntis, J.; et al. ESPGHAN comment on pediatric enteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 110–122. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, P.; Stroop, S.; Greene, H. Continuous vs. intermittent feeding in infants with intestinal disease. J. Pediatr. 1981, 99, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.; Frileux, P.; Sandrucci, S.; Ollivier, J.M.; Masini, J.P.; Cosnes, J.; Hannoun, L.; Parc, R. Continuous enteral nutrition during early adaptation in SBS. Br. J. Surg. 1988, 75, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizman, Z.; Schmueli, A.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Continuous nasogastric elemental feeding for prolonged diarrhea. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1983, 137, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.; Dray, X.; Corcos, O.; Barbot, L.; Kapel, N.; Messing, B. Tube Feeding Improves Intestinal Absorption in Short Bowel Syndrome Patients. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanler, R.J.; Shulman, R.J.; Lau, C.; Smith, E.O.; Heitkemper, M.M. Feeding strategies for premature infants: Randomized trial of GI priming and tube-feeding method. Pediatrics 1999, 103, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premji, S.S.; Chessell, L. Continuous nasogastric milk feeding versus intermittent bolus feeding for premature infants <1500 g. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2002, CD001819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.G.; Stellwagen, L.M.; Noble, L.; Kim, J.H.; Poindexter, B.B.; Puopolo, K.M. Promoting human milk and breastfeeding for the very low birth weight infant. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021054272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manea, A.; Boia, M.; Iacob, D.; Dima, M.; Iacob, R.E. Benefits of early enteral nutrition in extremely low birth weight infants. Singapore Med. J. 2016, 57, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Mercado, V.; Rios, M.; Arboleda, R.; Gomara, R.; Muinos, W.; Reeves-Garcia, J.; Hernandez, E. Breast milk vs. formula in preventing PN-associated liver disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Meader, N.; McGuire, W. Donor human milk for preventing NEC in very preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, CD002971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chi, C.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; Sun, J. Efficacy of donated milk in early nutrition of preterm infants: A meta-analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, R.; Khatri, S.; Patel, A.; Unger, S.L. Supplementation of mother’s own milk with donor milk in infants with gastroschisis or intestinal atresia. Nutrients 2020, 12, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, K.; Vieira, F.; Eckert, J.; Chaaban, H. Lipid composition and absorption differences among neonatal feeding strategies: Potential Implications for Intestinal Inflammation in Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2021, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, C.; Moro, G.E.; Bertino, E.; Cavallarin, L.; Giribaldi, M.; Giuliani, F.; Cresi, F.; Coscia, A. Effect of Holder pasteurization on donor human milk nutrients and bioactive components. Nutrients 2016, 8, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaizy, T.T. Effects of milk banking procedures on donor human milk components. Semin. Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskes, L.; Chamzas, A.; Ma, B.; Medina, A.E.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Viscardi, R.M.; Sundararajan, S. Early human milk feeding: Intestinal barrier maturation and growth. Pediatr. Res. 2025, 97, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Llorca, A.; Gormaz, M.; Alcántara, C.; Cernada, M.; Nuñez-Ramiro, A.; Vento, M.; Collado, M.C. Preterm gut microbiome depending on feeding type: Significance of donor milk. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezoff, E.A.; Hawkins, J.A.; Ollberding, N.J.; Karns, R.; Morrow, A.L.; Helmrath, M.A. 2’-Fucosyllactose augments adaptive response to intestinal resection. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G427–G438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Akkerman, R.; Kong, C.; Walvoort, M.T.C.; de Vos, P. Human milk oligosaccharides as essential bioactive molecules. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1184–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; van der Molen, J.; Kuipers, F.; van Leeuwen, S.S. Quantitation of bioactive components in infant formulas. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, V.; Klein, L.D.; Brown, R.; Sulfaro, C.; Hoad, V.; Gosbell, I.B.; Pink, J. Donor and recipient safety in human milk banking. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutsoudis, I.; Adhikari, M.; Nair, N.; Coutsoudis, A. Feasibility of donor breastmilk bank in resource-limited neonatal units. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhisivam, B.; Vishnu Bhat, B.; Rao, K.; Kingsley, S.M.; Plakkal, N.; Palanivel, C. Effect of Holder pasteurization on macronutrients and immunoglobulin profile of pooled donor human milk. J. Matern.-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 3016–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemontese, P.; Mallardi, D.; Liotto, N.; Tabasso, C.; Menis, C.; Perrone, M.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. Macronutrient content of pooled donor human milk before and after Holder pasteurization. BMC. Pediatr. 2019, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreissl, A.; Zwiauer, V.; Repa, A.; Binder, C.; Haninger, N.; Jilma, B.; Berger, A.; Haiden, N. Effect of fortifiers and protein on human milk osmolarity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnappan, A.; Sharma, A.; Agarwal, R.; Thukral, A.; Deorari, A.; Sankar, M.J. Breast milk fortification with preterm formula vs. HMF. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz Barbero, A.; Rico, N.; Oller-Salvia, B.; Aldecoa-Bilbao, V.; Macías-Muñoz, L.; Wijngaard, R.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Salvia-Roigés, M. Fortifier selection and dosage enables control of breast milk osmolarity. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Turner, J.M.; Mager, D.R.; Sigalet, D.L.; Wizzard, P.R.; Nation, P.N.; Ball, R.O.; Pencharz, P.B.; Wales, P.W. Polymeric vs. elemental formula in neonatal piglets with SBS. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hassani, A.; Michaud, L.; Chartier, A.; Penel-Capelle, D.; Sfeir, R.; Besson, R.; Turck, D.; Gottrand, F. Cow’s milk protein allergy after neonatal intestinal surgery. Arch. Pediatr. 2005, 12, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, A.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Capriati, T.; Panetta, F.; Pucci, N.; Bellucci, F.; Torre, G. Cow’s milk allergy and neonatal SBS. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamm, D.A.; Hait, E.; Litman, H.J.; Mitchell, P.D.; Duggan, C. High prevalence of eosinophilic GI disease in intestinal failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masumoto, K.; Esumi, G.; Teshiba, R.; Nagata, K.; Hayashida, M.; Nakatsuji, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishimoto, Y.; Taguchi, T. Cow’s milk allergy in extremely short bowel syndrome. e-SPEN 2008, 3, e147–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelis, E.G.; Olieman, J.F.; Hulst, J.M.; de Koning, B.A.; Wijnen, R.M.; Rings, E.H. Promoting intestinal adaptation by nutrition and medication. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, L.E. Nutrition and fluid optimization for short bowel syndrome. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigoni, E.; Marteau, P.; Briet, F.; Pochart, P.; Rambaud, J.C.; Messing, B. Lactose tolerance and absorption in short bowel syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteau, P.; Messing, B.; Arrigoni, E.; Briet, F.; Flourié, B.; Morin, M.C.; Rambaud, J.C. Do SBS patients need a lactose-free diet? Nutrition 1997, 13, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, P.B.; Mortensen, P.B. Influence of preserved colon on medium-chain fat absorption. Gut 1998, 43, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhoof, J.A.; Grandjean, C.J.; Kaufman, S.S.; Burkley, K.T.; Antonson, D.L. Effect of high percentage medium-chain triglyceride diet on mucosal adaptation following massive bowel resection in rats. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1984, 8, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, M.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fidler Mis, N.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.M.; Indrio, F.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Complementary feeding: ESPGHAN guidelines. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Mor-Vaknin, N.; Drongowski, R.A.; Miselevich, I.; Coran, A.G.; Harmon, C.M. Effect of dietary fat on intestinal adaptation in SBS rats. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2004, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, P.M.; Sun, R.C.; Guo, J.; Erwin, C.R.; Warner, B.W. High-fat diet enhances villus growth after massive resection. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2014, 18, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Shiloni, E.; Krausz, M.M.; Yakirevich, E.; Sabo, E.; Mogilner, J.; Coran, A.G.; Harmon, C.M. Low-fat diet impairs postresection adaptation. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003, 38, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhotnik, I.; Gork, A.S.; Chen, M.; Drongowski, R.A.; Coran, A.G.; Harmon, C.M. Low-fat diet and fatty-acid transport after resection. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2001, 17, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovesen, L.; Chu, R.; Howard, L. Influence of dietary fat on jejunostomy output in severe SBS. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 38, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, J.T.; Schulz-Heise, S.; Rueckel, A.; Rauh, M.; Juengert, J.; Galiano, M.; Meier, N.; Woelfle, J.; Schiffer, M.; Hoerning, A. Enteric hyperoxaluria in pediatric SBS. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1157696. [Google Scholar]
- Atia, A.; Girard-Pipau, F.; Hébuterne, X.; Spies, W.G.; Guardiola, A.; Ahn, C.W.; Fryer, J.; Xue, F.; Rammohan, M.; Sumague, M.; et al. Macronutrient absorption in SBS with jejunocolonic anastomosis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenckpohl, D.; Hocker, J.; Shareef, M.; Vegunta, R.; Colgan, C. Green beans resolving diarrhea after neonatal bowel surgery: Case study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2005, 20, 674–677. [Google Scholar]
- Brindle, M.E.; McDiarmid, C.; Short, K.; Miller, K.; MacRobie, A.; Lam, J.Y.K.; Brockel, M.; Raval, M.V.; Howlett, A.; Lee, K.S.; et al. ERAS guidelines for neonatal intestinal surgery. World J. Surg. 2020, 44, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, M.; Teitelbaum, D.H.; Harris, M.B. Sodium depletion and poor weight gain in ileostomy patients. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2014, 29, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, K.B.; Ternberg, J.L.; Bell, M.J.; Keating, J.P. Sodium needs in infants with ileostomy. J. Pediatr. 1983, 102, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, B.; Leumann, E.; von Unruh, G.; Laube, N.; Hesse, A. Diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in secondary hyperoxaluria. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, e437–e443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, M.; Millar, E.C.; Deans, K.A.; Torreggiani, M.; Moroni, F. Nutrition and CKD-related hyperoxaluria in SBS. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3441. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, A.; Koutkia, P.; Apovian, C.M. Nutritional management of short bowel syndrome in adults. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2002, 5, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, S.; Algotar, A.; Karjoo, S.; Gabel, M.; Kruszewski, P.; Duro, D.; Sankararaman, S.; Wendel, D.; Namjoshi, S.S.; Abdelhadi, R.A.; et al. State-of-the-art review of blenderized diets. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2025, 81, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Troutt, R.; Merves, J. Blenderized enteral nutrition in pediatric short gut syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2022, 37, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaula, B.; Mitchell, P.D.; Reese, E.; Gray, M.; Duggan, C.P. Parenteral nutrition dependence and growth in pediatric intestinal failure after transition to blenderized feeds: Case series. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samela, K.; Mokha, J.; Emerick, K.; Davidovics, Z.H. Transition to real-food ingredient tube formulas in pediatric intestinal failure. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2017, 32, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, I.M.; Kang, K.H.; Jaksic, T. Neonatal short bowel syndrome. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 16, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, S. Practical management of home parenteral nutrition in infancy. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 138, 104876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enman, M.A.; Wilkinson, L.T.; Meloni, K.B.; Shroyer, M.C.; Jackson, T.F.; Aban, I.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Martin, C.A.; Galloway, D.P. Determinants of enteral autonomy and reduced PN exposure in pediatric intestinal failure. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsa, L.; Goulet, O.; Alberti, D.; DeKooning, B.; Domellöf, M.; Haiden, N.; Hill, S.; Indrio, F.; Köglmeier, J.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Nutrition and intestinal rehabilitation in children with SBS: Part 2, long-term follow-up on home PN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2023, 77, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Squires, R.H.; Litman, H.J.; Balint, J.; Carter, B.A.; Fisher, J.G.; Horslen, S.P.; Jaksic, T.; Kocoshis, S.; Martinez, J.A.; et al. Predictors of enteral autonomy in pediatric intestinal failure: Multicenter cohort. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 29–34.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, W.N. Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Hum. Nutr. Clin. Nutr. 1985, 39, 5–41. [Google Scholar]
- Abi Nader, E.; Lambe, C.; Talbotec, C.; Acramel, A.; Pigneur, B.; Goulet, O. Metabolic bone disease in pediatric intestinal failure is not associated with PN dependency. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proli, F.; Faragalli, A.; Talbotec, C.; Bucci, A.; Zemrani, B.; Chardot, C.; Abi Nader, E.; Goulet, O.; Lambe, C. Plasma citrulline variation predicts PN-weaning in neonatal short bowel syndrome. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4941–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belza, C.; Fitzgerald, K.; de Silva, N.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W. Early predictors of enteral autonomy in pediatric intestinal failure: Development of a severity scoring tool. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 961–969. [Google Scholar]
- Roggero, P.; Liotto, N.; Piemontese, P.; Menis, C.; Perrone, M.; Tabasso, C.; Menis, C.; Perrone, M.; Tabasso, C.; Amato, O.; et al. Neonatal intestinal failure: Growth pattern and nutrition during PN weaning. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2023, 47, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, P.; Balint, J.; Bechtold, M.; Bingham, A.; Chan, L.N.; Durfee, S.; Jevenn, A.K.; Malone, A.; Mascarenhas, M.; Robinson, D.T.; et al. When is parenteral nutrition appropriate? J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 324–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannuri, U.; de Barros, F.; Tannuri, A.C.A. Treatment of short bowel syndrome in children: Value of intestinal rehabilitation program. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2016, 62, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntis, J.W.L.; Hojsak, I.; Ksiazyk, J.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN working group on pediatric parenteral nutrition. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Organizational aspects. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanner, H.; Zelig, R.; Rigassio Radler, D. Impact of infusion frequency on quality of life in home PN patients. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2022, 46, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaise, J.K.; Matarese, L.E.; Messing, B.; Steiger, E. Strategies for PN weaning in adult SBS. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, S94–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaenkumchorn, T.K.; Lampone, O.; Huebner, K.; Cramer, J.; Karls, C. When PN is the answer: Pediatric intestinal rehabilitation case series. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2024, 39, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.; Cermak, S.A.; Merritt, R.J. Oral feeding difficulties in children with short bowel syndrome: Narrative review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boctor, D.L.; Jutteau, W.H.; Fenton, T.R.; Shourounis, J.; Galante, G.J.; Eicher, I.; Goulet, O.; Lambe, C. Feeding difficulties and risk factors in pediatric intestinal failure. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5399–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubesie, A.C.; Kocoshis, S.A.; Mezoff, A.G.; Henderson, C.J.; Helmrath, M.A.; Cole, C.R. Multiple micronutrient deficiencies during and after transition to enteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelis, E.; Olieman, J.; Rizopoulos, D.; Wijnen, R.; Rings, E.; de Koning, B.; Hulst, J. Growth, body composition, and micronutrient abnormalities after weaning off home PN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, e95–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuokkola, J.; Olkkonen, E.; Gunnar, R.; Pakarinen, M.; Merras-Salmio, L. Vitamin and trace element status in children with SBS being weaned off PN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2025, 80, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.F.; Duro, D.; Zurakowski, D.; Lee, M.; Jaksic, T.; Duggan, C. High prevalence of multiple micronutrient deficiencies in children with intestinal failure: A longitudinal study. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, Q.; Feng, Y.; Huang, J.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Shi, C. Nutrition assessment in children with short bowel syndrome weaned off parenteral nutrition: A long-term follow-up study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.; Vu, L.; Matarese, L.E. Bacteria, Bones, and Stones: Managing Complications of Short Bowel Syndrome. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnar, R.; Lumia, M.; Pakarinen, M.; Merras-Salmio, L. Essential fatty acid deficiency risk during intestinal rehabilitation. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2018, 42, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| PICOS Category | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| P (Population) | Neonates, infants, and older children with SBS | Children with intestinal failure due to motility disorders; children with SBS > 5 years of follow-up |
| I (Intervention) | Full-text papers, including RCTs, prospective cohort, analytical cross-sectional, case–control, longitudinal, case series, and retrospective cross-sectional studies | Studies using incompatible virtual methods; studies primarily focused on medical or surgical management of SBS |
| C (Comparators) | Studies comparing outcomes of nutritional management during different SBS phases or between anatomical SBS types | Studies comparing nutritional management in children vs. adults with SBS |
| O (Outcomes) | Survival, achievement of EA (weaning off PN), and complication rates | Incomplete results |
| S (Study Design) | Studies published in English between January 1974 and December 2024, indexed in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, CENTRAL, SciELO, and Google Scholar | Duplicates, conference papers, abstracts, and non-English case reports |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Spector Cohen, I.; Moran-Lev, H.; Levi, R.; Golden, H.; Sukhotnik, I. Nutritional Strategies for Intestinal Rehabilitation in Children with Short Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2026, 18, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18020180
Spector Cohen I, Moran-Lev H, Levi R, Golden H, Sukhotnik I. Nutritional Strategies for Intestinal Rehabilitation in Children with Short Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2026; 18(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpector Cohen, Inna, Hadar Moran-Lev, Reut Levi, Hofit Golden, and Igor Sukhotnik. 2026. "Nutritional Strategies for Intestinal Rehabilitation in Children with Short Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review" Nutrients 18, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18020180
APA StyleSpector Cohen, I., Moran-Lev, H., Levi, R., Golden, H., & Sukhotnik, I. (2026). Nutritional Strategies for Intestinal Rehabilitation in Children with Short Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 18(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu18020180






