Targeting the Gut–Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Gut–Brain Axis Overview
3.1. Anatomy and Physiology of the Gut–Brain Axis
3.2. Mechanisms of Interaction
- Neural Pathways
- 2.
- Hormonal Signaling
- 3.
- Immune-Mediated Communication
- 4.
- Microbial pathways
- GABA, other neurotransmitters, and neurotransmitter derivatives: certain bacteria can produce or stimulate the production of neurotransmitters. For instance, Lactobacillus produces acetylcholine and γ-GABA; Bifidobacterium produces γ-GABA; Bacillus and Escherichia coli produce norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine; and Streptococcus, Enterococcus, and Candida produce serotonin, which directly affects brain function [17,48];
- Trimethylamines and amino acid derivatives: these metabolites have systemic effects, influencing host metabolism and potentially impacting brain health [47].
- 5.
- Integrated System
3.3. Essential Oils and the GBA
3.3.1. Cannabis EOs on GBA
3.3.2. Other EOs Modulating the GBA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
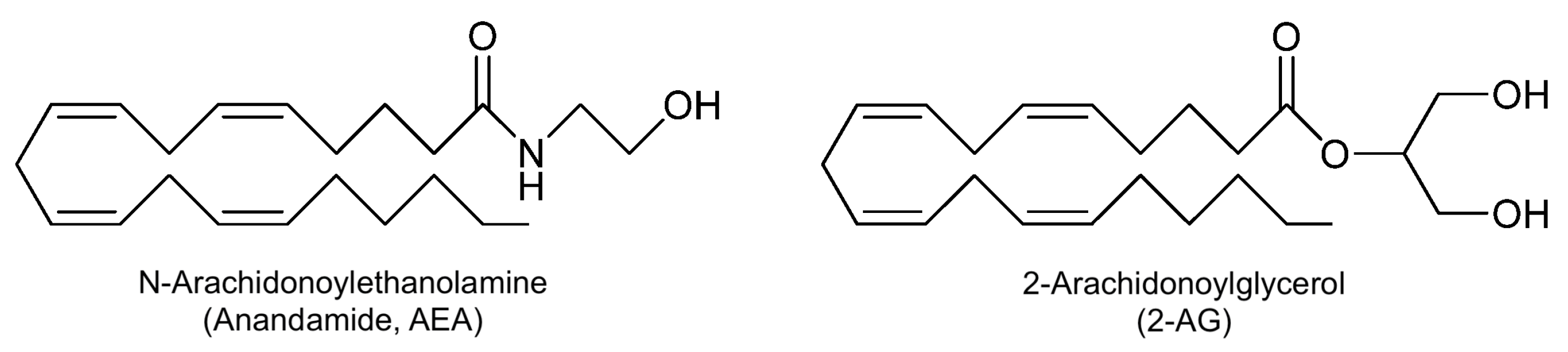
| AEA | Anandamide |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| CD | Crohn’s Disease |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DGBIs | Disorders of Gut–Brain Interaction |
| ECB | Endocannabinoid |
| ECS | Endocannabinoid System |
| ENS | Enteric Nervous System |
| EO | Essential Oil |
| GBA | Gut–Brain Axis |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HPA | Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal |
| IBD | Irritable Bowel Disease |
| IBS | Irritable Bowel Syndrome |
| OEO | Oregano Oil |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acids |
| SEO | Solid Essential Oil |
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinol |
| UC | Ulcerative Colitis |
| 2-AG | 2-arachidonoylglycerol |
References
- Twenge, J.M.; Cooper, A.B.; Joiner, T.E.; Duffy, M.E.; Binau, S.G. Age, Period, and Cohort Trends in Mood Disorder Indicators and Suicide-Related Outcomes in a Nationally Representative Dataset, 2005–2017. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2019, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qiao, L.; Li, M.; Wen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Global, Regional, National Epidemiology and Trends of Parkinson’s Disease from 1990 to 2021: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1498756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Better, M.A. 2024 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 3708–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarlata, G.G.M.; Abenavoli, L. Gut Microbiota: The Pathogenetic Bridge between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Turpin, W.; Olivera Sendra, P.; Xue, M.; Griffiths, A.; Panaccione, R.; Dieleman, L.; Steinhart, A.; Jacobson, K.; Lee, S.; et al. A73 Microbial Contribution to the Risk of Future Crohn’s Disease: Stratification by Subclinical Inflammation Levels Measured by Fecal Calprotectin. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2025, 8, i29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvey, S.; Dolovich, C.L.; Bernstein, C.N. A176 Serological Heavy Metal Assessment in Persons with IBD. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2025, 8, i73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, H.; Keefer, L. Psychological Comorbidity in Gastrointestinal Diseases: Update on the Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 107, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut Feelings: The Emerging Biology of Gut-Brain Communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershon, M.D.; Margolis, K.G. The Gut, Its Microbiome, and the Brain: Connections and Communications. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-Altering Microorganisms: The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Brain and Behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The Gut-Brain Axis: Interactions between Enteric Microbiota, Central and Enteric Nervous Systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enayati, A.; Soghi, A.; Butler, A.E.; Rizzo, M.; Sahebkar, A. The Effect of Curcumin on the Gut-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Implications. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 29, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shandilya, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar Jha, N.; Kumar Kesari, K.; Ruokolainen, J. Interplay of Gut Microbiota and Oxidative Stress: Perspective on Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 38, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant Polyphenols as Dietary Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.; Mayer, D.E.; Chen, S.; Mayer, E.A. Role of Diet and Its Effects on the Gut Microbiome in the Pathophysiology of Mental Disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-J.; Heinbockel, T. Essential Oils and Their Constituents Targeting the GABAergic System and Sodium Channels as Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Molecules 2018, 23, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.S.; Mak, W.Q.; Tan, L.K.S.; Ng, C.X.; Chan, H.H.; Yeow, S.H.; Foo, J.B.; Ong, Y.S.; How, C.W.; Khaw, K.Y. Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis and Its Therapeutic Applications in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, H.D. Dietary Fiber and Prebiotics and the Gastrointestinal Microbiota. Gut Microbes 2017, 8, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallamaci, R.; Budriesi, R.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Biotti, G.; Micucci, M.; Ragusa, A.; Curci, F.; Muraglia, M.; Corbo, F.; Franchini, C. Olive Tree in Circular Economy as a Source of Secondary Metabolites Active for Human and Animal Health Beyond Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Molecules 2021, 26, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential Oils: A Short Review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tit, D.M.; Bungau, S.G. Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezantes-Orellana, C.; German Bermúdez, F.; Matías De la Cruz, C.; Montalvo, J.L.; Orellana-Manzano, A. Essential Oils: A Systematic Review on Revolutionizing Health, Nutrition, and Omics for Optimal Well-Being. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1337785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsghyan, L.M.; Moghrovyan, A.V.; Poghosyan, S.S.; Babajanyan, M.A.; Gaboyan, M.A.; Voskanyan, A.V.; Darbinyan, A.A. The Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Combined Preparation Based on the Blunt-Nosed Viper’s Venom and Oregano Essential Oil. Korean J. Pain 2025, 38, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, D.P.; Damasceno, R.O.S.; Amorati, R.; Elshabrawy, H.A.; de Castro, R.D.; Bezerra, D.P.; Nunes, V.R.V.; Gomes, R.C.; Lima, T.C. Essential Oils: Chemistry and Pharmacological Activities. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saljoughian, S.; Roohinejad, S.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Greiner, R.; Omidizadeh, A.; Nikmaram, N.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. The Effects of Food Essential Oils on Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1688–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Amin, S.; Raana, S.; Zahid, M.; Naeem, M.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Aadil, R.M. Recent Advances in the Implementation of Ultrasound Technology for the Extraction of Essential Oils from Terrestrial Plant Materials: A Comprehensive Review. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2024, 107, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori Tamburlin, I.; Roux, E.; Feuillée, M.; Labbé, J.; Aussaguès, Y.; El Fadle, F.E.; Fraboul, F.; Bouvier, G. Toxicological Safety Assessment of Essential Oils Used as Food Supplements to Establish Safe Oral Recommended Doses. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 157, 112603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Deng, W.; Sun, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J. Extract Toolkit for Essential Oils: State of the Art, Trends, and Challenges. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadgrove, N.; Jones, G. A Contemporary Introduction to Essential Oils: Chemistry, Bioactivity and Prospects for Australian Agriculture. Agriculture 2015, 5, 48–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Nance, K.; Chen, S. The Gut-Brain Axis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.A.; Rinaman, L.; Cryan, J.F. Stress & the Gut-Brain Axis: Regulation by the Microbiome. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 7, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, P.P.; Tavares-Gomes, A.L.; Stockler-Pinto, M.B. Relaxing the “Second Brain”: Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds as a Therapeutic and Preventive Strategy to Alleviate Oxidative Stress in the Enteric Nervous System. Nutr. Rev. 2022, 80, 2206–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Almanzar, N.; Chiu, I.M. The Role of Cellular and Molecular Neuroimmune Crosstalk in Gut Immunity. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, R.; Gunnigle, E.; Geissen, V.; Clarke, G.; Nagpal, J.; Cryan, J.F. Pesticide Exposure and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharvin, B.L.; Aburto, M.R.; Cryan, J.F. Decoding the Neurocircuitry of Gut Feelings: Region-Specific Microbiome-Mediated Brain Alterations. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 179, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörkl, S.; Butler, M.I.; Wagner-Skacel, J. Gut-Brain-Crosstalk—The Vagus Nerve and the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Depression: A Narrative Review. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2023, 13, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, S.M.; Zisman, T.L.; Suskind, D.L.; Damman, C.J. The intestinal microbiome, barrier function, and immune system in inflammatory bowel disease: A tripartite pathophysiological circuit with implications for new therapeutic directions. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botschuijver, S.; Welting, O.; Levin, E.; Maria-Ferreira, D.; Koch, E.; Montijn, R.C.; Seppen, J.; Hakvoort, T.B.M.; Schuren, F.H.J.; de Jonge, W.J.; et al. Reversal of visceral hypersensitivity in rat by Menthacarin®, a proprietary combination of essential oils from peppermint and caraway, coincides with mycobiome modulation. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 30, e13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fülling, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut Microbe to Brain Signaling: What Happens in Vagus…. Neuron 2019, 101, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmensen, C.; Müller, T.D.; Woods, S.C.; Berthoud, H.-R.; Seeley, R.J.; Tschöp, M.H. Gut-Brain Cross-Talk in Metabolic Control. Cell 2017, 168, 758–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, P.; Thornberry, N.A.; Pinto, S. The Gut-Brain Axis: Identifying New Therapeutic Approaches for Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, and Related Disorders. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.-J.; Li, J.-N.; Nie, Y.-Z. Gut Hormones in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Cross-Talk. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.; Bonomi, C.G.; Ricci, F.; Di Donna, M.G.; Mercuri, N.B.; Koch, G.; Martorana, A.; Motta, C. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Is Associated with Different Neuroinflammatory Profiles in Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, C.; Rothhammer, V.; Karow, M.; Neurath, M.; Winner, B. The Gut-Brain Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Current and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut Microbes and Metabolites as Modulators of Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity and Brain Health. Gut Microbes 2019, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, K.; Su, N.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, F. Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Health and Neurological Disease: Interactions between Gut Microbiota and the Nervous System. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powder-George, Y.L.; Ludwiczuk, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Georgiev, M.I. Chapter 10—Terpenoids. In Pharmacognosy, 2nd ed.; McCreath, S.B., Clement, Y.N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 253–294. ISBN 978-0-443-18657-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Advances in Controllable Release Essential Oil Microcapsules and Their Promising Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, Z.D.; Bošnjak-Neumüller, J.; Pajić-Lijaković, I.; Raj, J.; Vasiljević, M. Essential Oils as Feed Additives-Future Perspectives. Molecules 2018, 23, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely-Szentmiklósi, I.; Rédai, E.M.; Szabó, Z.-I.; Kovács, B.; Albert, C.; Gergely, A.-L.; Székely-Szentmiklósi, B.; Sipos, E. Microencapsulation by Complex Coacervation of Lavender Oil Obtained by Steam Distillation at Semi-Industrial Scale. Foods 2024, 13, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Shen, D.; Li, C. Effects of Microencapsulated Essential Oils on Growth and Intestinal Health in Weaned Piglets. Animals 2024, 14, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, W.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, D. Dual Cross-Linking with Tannic Acid and Transglutaminase Improves Microcapsule Stability and Encapsulates Lemon Essential Oil for Food Preservation. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, K.A.; Wiley, J.W. The Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Brain–Gut Axis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K. Distribution of Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. In Cannabinoids; Pertwee, R.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 299–325. ISBN 978-3-540-26573-3. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, M.; Davison, J.S.; Sharkey, K.A. Review Article: Endocannabinoids and Their Receptors in the Enteric Nervous System. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralevic, V. Cannabinoid Modulation of Peripheral Autonomic and Sensory Neurotransmission. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 472, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Gertsch, J.; Grether, U.; Howlett, A.C.; Hua, T.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Ueda, N.; van der Stelt, M. Goods and Bads of the Endocannabinoid System as a Therapeutic Target: Lessons Learned after 30 Years. Pharmacol. Rev. 2023, 75, 885–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Cannabis, Cannabinoid Receptors, and Endocannabinoid System: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M. Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersani, G.; Pacitti, F.; Iannitelli, A.; Caroti, E.; Quartini, A.; Xenos, D.; Marconi, M.; Cuoco, V.; Bigio, B.; Bowles, N.P.; et al. Inverse Correlation between Plasma 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Levels and Subjective Severity of Depression. Human. Psychopharmacol. 2021, 36, e2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassir Nia, A.; Bender, R.; Harpaz-Rotem, I. Endocannabinoid System Alterations in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: A Review of Developmental and Accumulative Effects of Trauma. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks) 2019, 3, 2470547019864096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospéro-García, O.; Ruiz Contreras, A.E.; Ortega Gómez, A.; Herrera-Solís, A.; Méndez-Díaz, M. Endocannabinoids as Therapeutic Targets. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgeman, M.B.; Abazia, D.T. Medicinal Cannabis: History, Pharmacology, and Implications for the Acute Care Setting. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Hinds, N.M.; Ullrich, K.; Smid, S.D. Cannabinoid 1 (CB1) Receptors Coupled to Cholinergic Motorneurones Inhibit Neurogenic Circular Muscle Contractility in the Human Colon. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 148, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, A.A.; Sharkey, K.A. Cannabinoids and the gut: New developments and emerging concepts. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalo, R.; Chen, C.; Vera, G.; Fichna, J.; Thakur, G.A.; López-Pérez, A.E.; Makriyannis, A.; Martín-Fontelles, M.I.; Storr, M. In vitro and non-invasive in vivo effects of the cannabinoid-1 receptor agonist AM841 on gastrointestinal motor function in the rat. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M. Cannabinoids and Gastrointestinal Motility: Pharmacology, Clinical Effects and Potential Therapeutics in Humans. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018, 30, e13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: A therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, R.; Cong, Y.; Liu, Z. Critical Roles of G Protein-Coupled Receptors in Regulating Intestinal Homeostasis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinapati, K.K.; Vidya, S.; Khan, M.F.; Mandal, D.; Banerjee, S. Gut Bacteria, Endocannabinoid System, and Marijuana Addiction: Novel Therapeutic Implications. Health Sci. Rev. 2024, 10, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoly, H.C.; Mueller, R.L.; Bidwell, L.C.; Hutchison, K.E. Cannabinoids and the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis: Emerging Effects of Cannabidiol and Potential Applications to Alcohol Use Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Fitting, S.; Robinson, C.; Benitez, A.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Fu, X.; Amato, D.; Ning, W.; Funderburg, N.; et al. Chronic Cannabis Smoking-Enriched Oral Pathobiont Drives Behavioral Changes, Macrophage Infiltration, and Increases β-Amyloid Protein Production in the Brain. eBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansma, J.; Brinkman, F.; van Hemert, S.; El Aidy, S. Targeting the Endocannabinoid System with Microbial Interventions to Improve Gut Integrity. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 106, 110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panee, J.; Gerschenson, M.; Chang, L. Associations Between Microbiota, Mitochondrial Function, and Cognition in Chronic Marijuana Users. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, H.; Hu, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, C.; Fan, Y.; Wu, B.; Zou, T.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Gut Bacterial Profiles in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 140–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; Yan, J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhong, J.; et al. Prevotella Copri Transplantation Promotes Neurorehabilitation in a Mouse Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2024, 21, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, R.; Gomes, A.P.; Pereira-Leite, C.; Marques-da-Costa, A.; Monteiro Rodrigues, L.; Sassano, M.; Rijo, P.; Costa, M.d.C. The Entourage Effect in Cannabis Medicinal Products: A Comprehensive Review. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Choi, S.; Park, A.Y.; Ju, S.; Kweon, B.; Kim, D.-U.; Bae, G.-S.; Han, D.; Kwon, E.; Hong, J.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Antidepressant-like Effects of Cannabis sativa L. Extracts. Plants 2024, 13, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyemni, M.; Louaste, B.; Nechad, I.; Elkamli, T.; Bouia, A.; Taleb, M.; Chaouch, M.; Eloutassi, N. Extraction of Essential Oils of Rosmarinus Officinalis L. by Two Different Methods: Hydrodistillation and Microwave Assisted Hydrodistillation. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 3659432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Gallardo, K.; Quintero-Rincón, P.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Aromatherapy and Essential Oils: Holistic Strategies in Complementary and Alternative Medicine for Integral Wellbeing. Plants 2025, 14, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. The Therapeutic Potential of Rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis) Diterpenes for Alzheimer’s Disease. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 2680409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebei, K.; Sakouhi, F.; Herchi, W.; Khouja, M.L.; Boukhchina, S. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activities of Seven Eucalyptus Species Essential Oils Leaves. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, G.A.B.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Chakrabarti, T.; Tagde, P.; Cavalu, S. Exploring Pharmacological Mechanisms of Essential Oils on the Central Nervous System. Plants 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Quintero, M.J.; Delgado, J.; Medina-Vera, D.; Becerra-Muñoz, V.M.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Estévez, M.; Plaza-Andrades, I.; Rodríguez-Capitán, J.; Sánchez, P.L.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Essential Oils from the Mediterranean Diet on Gut Microbiota and Their Metabolites in Ischemic Heart Disease and Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Wei, H. Oregano Essential Oil Improves Intestinal Morphology and Expression of Tight Junction Proteins Associated with Modulation of Selected Intestinal Bacteria and Immune Status in a Pig Model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5436738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micucci, M.; Protti, M.; Aldini, R.; Frosini, M.; Corazza, I.; Marzetti, C.; Mattioli, L.B.; Tocci, G.; Chiarini, A.; Mercolini, L.; et al. Thymus vulgaris L. Essential Oil Solid Formulation: Chemical Profile and Spasmolytic and Antimicrobial Effects. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Sharma, G.; Dai, C. Thymol as a Potential Neuroprotective Agent: Mechanisms, Efficacy, and Future Prospects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 6803–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, W.E.; Sillani, G.; Schuwald, A.; Friedland, K. Pharmacological Basis of the Anxiolytic and Antidepressant Properties of Silexan®, an Essential Oil from the Flowers of Lavender. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 143, 104899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupalak, J.K.; Rajput, P.; Gupta, G.L. Gut Microbiota and Alzheimer’s Disease: Exploring Natural Product Intervention and the Gut–Brain Axis for Therapeutic Strategies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 984, 177022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, C.M.; Nookaew, I.; Ewing, L.E.; Wongsurawat, T.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Quick, C.M.; Yee, E.U.; Piccolo, B.D.; ElSohly, M.; Walker, L.A.; et al. Potential Probiotic or Trigger of Gut Inflammation—The Janus-Faced Nature of Cannabidiol-Rich Cannabis Extract. J. Diet. Suppl. 2020, 17, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| EOs | Main Effects | References |
|---|---|---|
| Rosemary | Anxiolytic, ↑ cognitive function, antioxidant, metal-chelating, and anti-inflammatory. | [82] |
| Eucalyptus | ↑ Memory function, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial. | [84,85] |
| Oregano | ↑ Intestinal barrier integrity, and ↓ proinflammatory cytokines. | [87] |
| Thymus | Intestinal smooth muscle relaxation, antimicrobial, and neuroprotective. | [88,89] |
| Silexan® | Anxiolytic effects. | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camarda, L.; Mattioli, L.B.; Corazza, I.; Marzetti, C.; Budriesi, R. Targeting the Gut–Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091578
Camarda L, Mattioli LB, Corazza I, Marzetti C, Budriesi R. Targeting the Gut–Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091578
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamarda, Luca, Laura Beatrice Mattioli, Ivan Corazza, Carla Marzetti, and Roberta Budriesi. 2025. "Targeting the Gut–Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091578
APA StyleCamarda, L., Mattioli, L. B., Corazza, I., Marzetti, C., & Budriesi, R. (2025). Targeting the Gut–Brain Axis with Plant-Derived Essential Oils: Phytocannabinoids and Beyond. Nutrients, 17(9), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091578









