Luminal Sweet Sensing and Enteric Nervous System Participate in Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Transporter, GLUT2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.1.1. Piglets, Dietary Trials, Tissue Collection
2.1.2. Effect of Sweeteners, with Differential Effect on Activating Pig T1R2–T1R3, on Activity and Expression of GLUT2
2.1.3. Tissue Collection and Usage
2.1.4. Large-Scale Feeding Trial
2.1.5. Mice, Diets and Tissue Collection
2.2. Taste Receptor Constructs
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Heterologous Expression Assay
2.5. Electric Field Stimulation (EFS)
2.6. Isolation of Brush Border Membrane Vesicles
2.7. Isolation of Basolateral Membrane Vesicles
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Glucose Transport into Membrane Vesicles
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Morphometric Analysis
2.12. Quantitative PCR
2.13. Statistics
3. Results
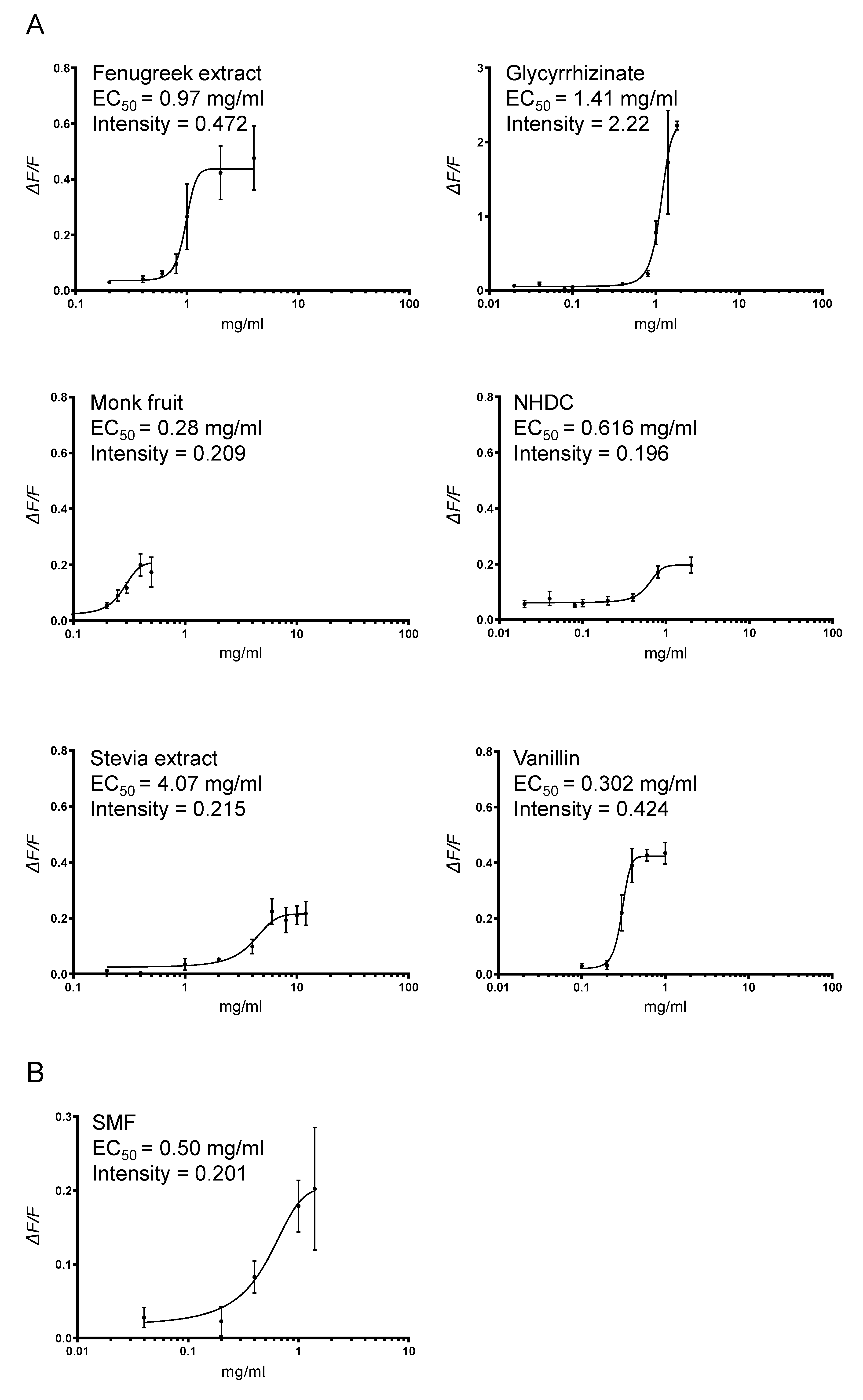
3.1. Heterologous Expression of Pig T1R2–T1R3 and Response to Sweetener SMF
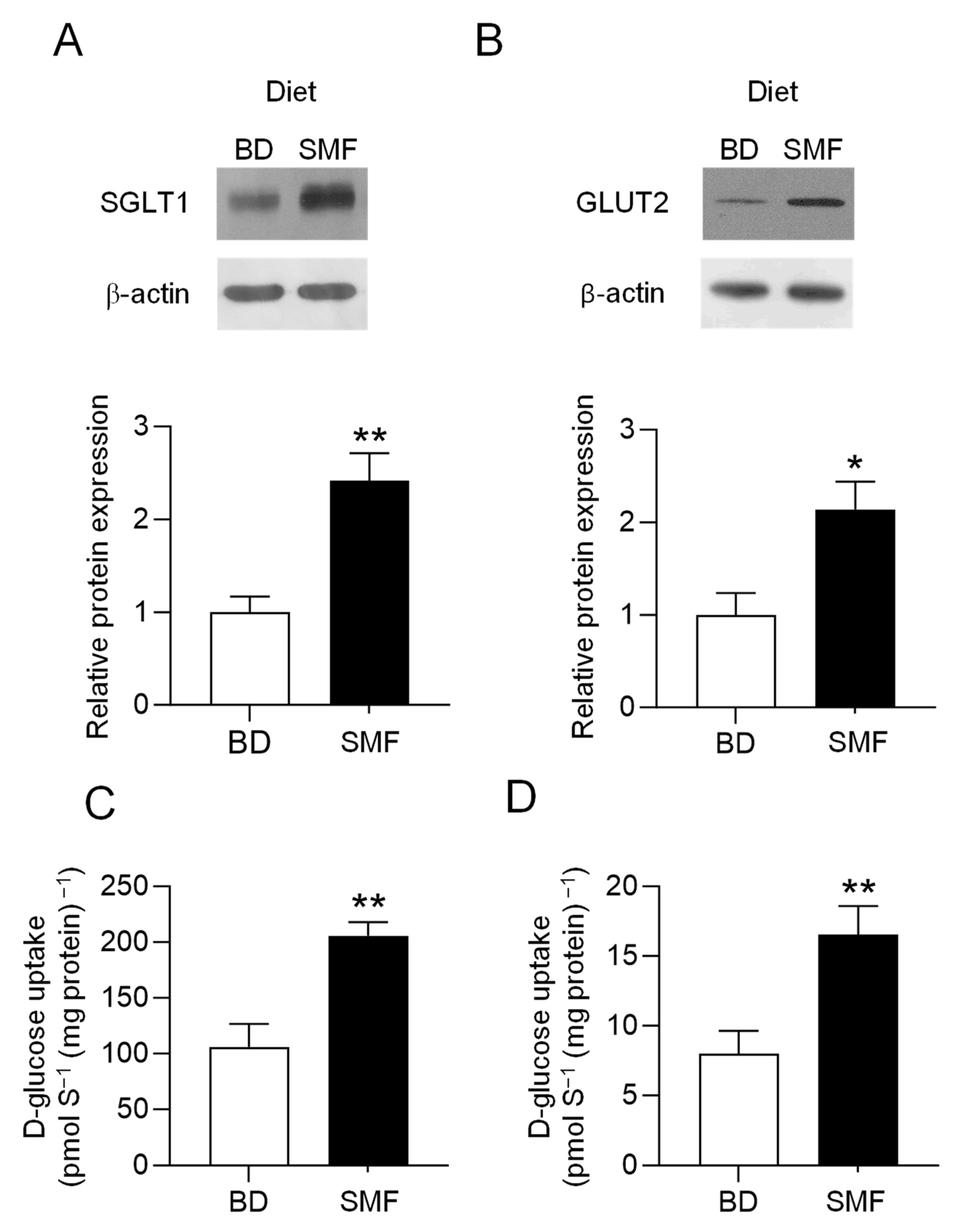
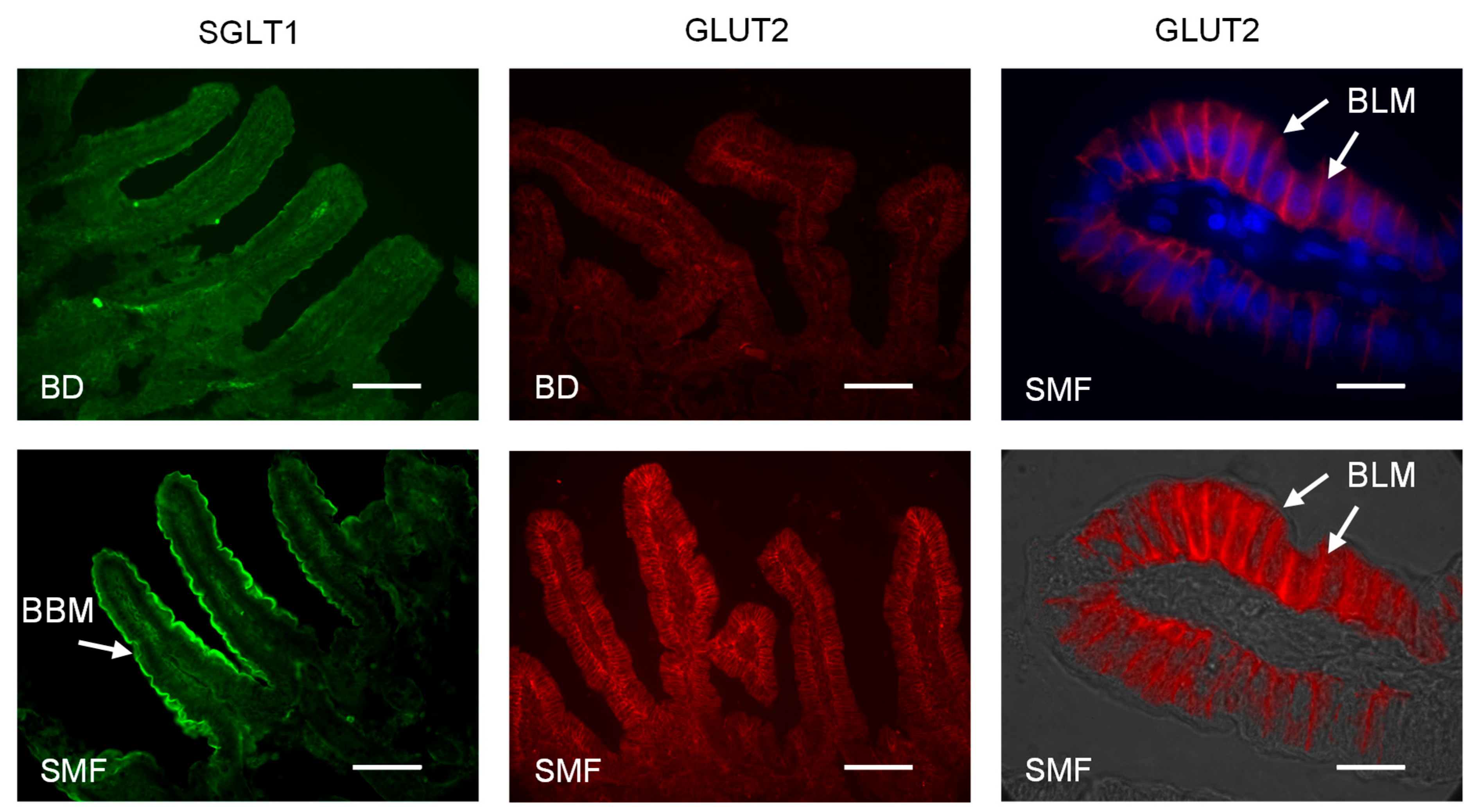
3.2. SMF Included in the Feed of Weaning Piglets Upregulates GLUT2 and SGLT1 Expression with a Similar Magnitude
3.3. Inclusion of SMF in the Feed of Weaning Piglets Enhances Animal Performance
3.4. Addition of SMF in the Feed of Weaning Piglets Results in Increased Villus Height
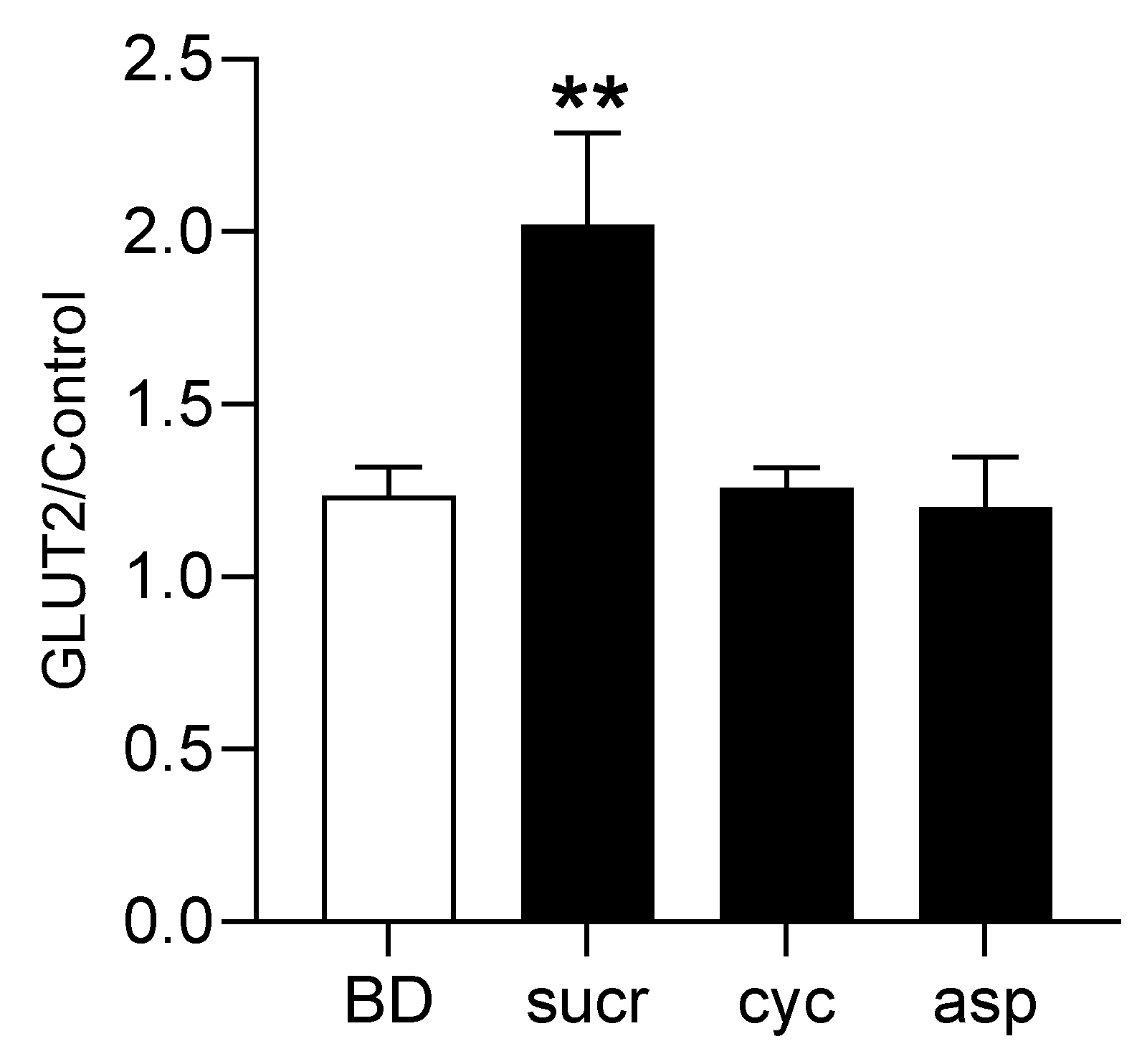
3.5. Direct Involvement of T1R2–T1R3 in Sweetener-Induced Upregulation of GLUT2 Expression
3.6. Expression of GLUT2 in the Intestine of T1R3, Gα-Gustducin Knockout Mice Is Not Responsive to Sweetener Intake Compared to Wild-Type Mice
3.7. Glucagon-like Peptide-2 Participates in the Pathway Regulating GLUT2 Expression
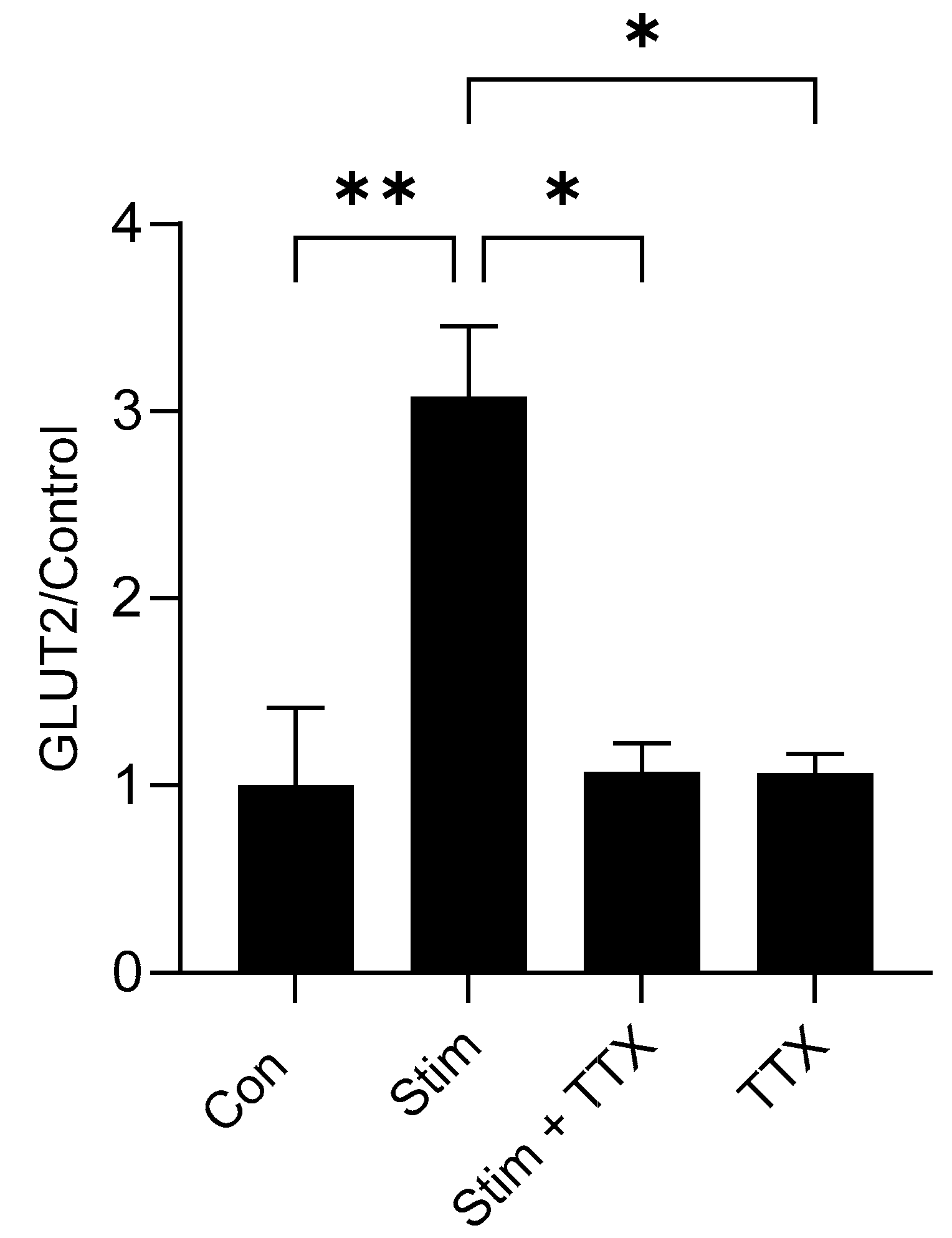
3.8. Electric Field Stimulation of Mouse Small Intestine Enhanced GLUT2 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTB | β-actin |
| BBMV | Brush border membrane vesicle |
| BD | Basal diet |
| BLMV | Basolateral membrane vesicle |
| B2M | β2-microglobulin |
| CD | Control diet |
| DAPI | 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| GLP-2 | Glucagon-like peptide 2 |
| GLUT2 | Glucose transporter 2 |
| OCT | Optimal cutting temperature |
| PACAP | Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide |
| PMSF | Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride |
| POLR2A | RNA polymerase 2 subunit RPB1 |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene difluoride |
| SDS | Sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| SGLT1 | Sodium/glucose co-transporter 1 |
| TTX | Tetrodotoxin |
| T1R2 | Taste 1 receptor 2 |
| T1R3 | Taste 1 receptor 3 |
| VIP | Vasoactive intestinal peptide |
References
- Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Molecular biology of intestinal glucose transport. Nutr. Res. Rev. 1995, 8, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.M.; Martin, M.G.; Turk, E. Intestinal absorption in health and disease-sugars. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 17, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, R.P.; Choe, J.Y.; Patel, C.R. Intestinal Absorption of Fructose. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koepsell, H. Glucose transporters in the small intestine in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020, 472, 1207–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueckler, M.; Kruse, M.; Strube, M.; Riggs, A.C.; Chiu, K.C.; Permutt, M.A. A mutation in the Glut2 glucose transporter gene of a diabetic patient abolishes transport activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17765–17767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santer, R.; Groth, S.; Kinner, M.; Dombrowski, A.; Berry, G.T.; Brodehl, J.; Leonard, J.V.; Moses, S.; Norgren, S.; Skovby, F.; et al. The mutation spectrum of the facilitative glucose transporter gene SLC2A2 (GLUT2) in patients with Fanconi-Bickel syndrome. Hum. Genet. 2002, 110, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolskee, R.F.; Dyer, J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Salmon, K.S.; Ilegems, E.; Daly, K.; Maillet, E.L.; Ninomiya, Y.; Mosinger, B.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15075–15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stearns, A.T.; Balakrishnan, A.; Rhoads, D.B.; Tavakkolizadeh, A. Rapid upregulation of sodium-glucose transporter SGLT1 in response to intestinal sweet taste stimulation. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.J.; Kokrashvili, Z.; Theodorakis, M.J.; Carlson, O.D.; Kim, B.J.; Zhou, J.; Kim, H.H.; Xu, X.; Chan, S.L.; Juhaszova, M.; et al. Gut-expressed gustducin and taste receptors regulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15069–15074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, A.W.; Al-Rammahi, M.A.; Batchelor, D.J.; Bravo, D.M.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 and the Enteric Nervous System Are Components of Cell-Cell Communication Pathway Regulating Intestinal Na+/Glucose Co-transport. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.E.; Gerspach, A.C.; Gutmann, H.; Asarian, L.; Drewe, J.; Beglinger, C. The functional involvement of gut-expressed sweet taste receptors in glucose-stimulated secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY). Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ørskov, C.; Hartmann, B.; Poulsen, S.S.; Thulesen, J.; Hare, K.J.; Holst, J.J. GLP-2 stimulates colonic growth via KGF, released by subepithelial myofibroblasts with GLP-2 receptors. Regul. Pept. 2005, 124, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, K.J.; Hartmann, B.; Kissow, H.; Holst, J.J.; Poulsen, S.S. The intestinotrophic peptide, glp-2, counteracts intestinal atrophy in mice induced by the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor, gefitinib. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5170–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.B.; Hjollund, K.R.; Johnsen, A.H.; Orskov, C.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J. Porcine glucagon-like peptide-2: Structure, signaling, metabolism and effects. Regul. Pept. 2008, 146, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehfeld, J.F. A centenary of gastrointestinal endocrinology. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottrell, J.J.; Stoll, B.; Buddington, R.K.; Stephens, J.E.; Cui, L.; Chang, X.; Burrin, D.G. Glucagon-like peptide-2 protects against TPN-induced intestinal hexose malabsorption in enterally refed piglets. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G293–G300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangild, P.T.; Tappenden, K.A.; Malo, C.; Petersen, Y.M.; Elnif, J.; Bartholome, A.L.; Buddington, R.K. Glucagon-like peptide 2 stimulates intestinal nutrient absorption in parenterally fed newborn pigs. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2006, 43, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Koehler, J.; Yusta, B.; Bahrami, J.; Matthews, D.; Rafii, M.; Pencharz, P.B.; Drucker, D.J. Enteroendocrine-derived glucagon-like peptide-2 controls intestinal amino acid transport. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, C.I. Upregulation of SGLT-1 transport activity in rat jejunum induced by GLP-2 infusion in vivo. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1997, 273, R1965–R1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrin, D.; Guan, X.; Stoll, B.; Petersen, Y.M.; Sangild, P.T. Glucagon-like peptide 2: A key link between nutrition and intestinal adaptation in neonates? J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3712–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsanahie, A.; Duxbury, M.S.; Grikscheit, T.C.; Perez, A.; Rhoads, D.B.; Gardner-Thorpe, J.; Ogilvie, J.; Ashley, S.W.; Vacanti, J.P.; Whang, E.E. Effect of GLP-2 on mucosal morphology and SGLT1 expression in tissue-engineered neointestine. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G1345–G1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.Y.; Loftin, P.; Clancy, C.J.; Peng, H.; Lever, J.E. Cyclic nucleotide regulation of Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) mRNA stability; Interaction of a nucleocytoplasmic protein with a regulatory domain in the 3’-untranslated region critical for stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33998–34008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftin, P.; Lever, J.E. HuR binds a cyclic nucleotide-dependent, stabilizing domain in the 3’untranslated region of Na (+)/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) mRNA. FEBS Lett. 2001, 509, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, D.; Wanner, M.; Tinti, J.M.; Nofre, C. Gustatory responses of pigs to various natural and artificial compounds known to be sweet in man. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.; Li, K.K.; Holland, D.; Maughan, H.; Guttman, D.S.; Yusta, B.; Drucker, D.J. Disruption of the murine Glp2r impairs Paneth cell function and increases susceptibility to small bowel enteritis. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, K.; Moran, A.W.; Al-Rammahi, M.; Weatherburn, D.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Non-nutritive sweetener activation of the pig sweet taste receptor T1R2-T1R3 in vitro mirrors sweetener stimulation of the gut-expressed receptor in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 542, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Brockhoff, A.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Appendino, G.; Meyerhof, W. The human bitter taste receptor hTAS2R50 is activated by the two natural bitter terpenoids andrographolide and amarogentin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9860–9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, J.S.; Pearson, G.T.; Petersen, O.H. Mouse Pancreatic Acinar Cells: Effects of Electric Field Stimulation on Membrane Potential and Resistance. J. Physiol. 1980, 301, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi-Beechey, S.P.; Davies, A.G.; Tebbutt, K.; Dyer, J.; Ellis, A.; Taylor, C.J.; Fairclough, P.; Beechey, R.B. Preparation and properties of brush-border membrane vesicles from human small intestine. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.; Wood, I.S.; Palejwala, A.; Ellis, A.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Expression of monosaccharide transporters in intestine of diabetic humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G241–G248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, G.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 2001, 106, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuBois, G.E. Molecular mechanism of sweetness sensation. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 164 Pt B, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschhorn, N.; Greenough, W.B. Progress in oral rehydration therapy. Sci. Am. 1991, 264, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, H.L.; Robert, K. Crane-Na(+)-glucose cotransporter to cure? Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallès, J.P.; Bosi, P.; Smidt, H.; Stokes, C.R. Nutritional management of gut health in pigs during weaning. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2007, 66, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, I.; Earley, B.; Gilmore, J.; Hogan, I.; Kennedy, E.; More, S.J. Calf health from birth to weaning. Ir. Vet. J. 2011, 64, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stass, V.L. A Method to Determine the Feed Conversion Coefficient in Farm Pigs. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerknes, M.; Cheng, H. Modulation of specific intestinal epithelial progenitors by enteric neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12497–12502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.; Pedersen, N.B.; Brix, S.W.; Grunddal, K.V.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Ørskov, C.; Poulsen, S.S.; Holst, J.J. The glucagon-like peptide 2 receptor is expressed in enteric neurons and not in the epithelium of the intestine. Peptides 2015, 67, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.L.; Sutherland, K.; Pezos, N.; Brierley, S.M.; Horowitz, M.; Rayner, C.K.; Blackshaw, L.A. Expression of taste molecules in the upper gastrointestinal tract in humans with and without type 2 diabetes. Gut 2009, 58, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.; Salmon, K.S.; Zibrik, L.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Expression of sweet taste receptors of the T1R family in the intestinal tract and enteroendocrine cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, O.J.; Affleck, J.; Patel, N.; Kellett, G.L. Sweet taste receptors in rat small intestine stimulate glucose absorption through apical GLUT2. J. Physiol. 2007, 582 Pt 1, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.; Karimian Azari, E.; LaMoia, T.E.; Hussain, T.; Vargova, V.; Karolyi, K.; Veldhuis, P.P.; Arnoletti, J.P.; de la Fuente, S.G.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. T1R2 receptor-mediated glucose sensing in the upper intestine potentiates glucose absorption through activation of local regulatory pathways. Mol. Metab. 2018, 17, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, E.; Zabel, B.; Mundlos, S.; Dyer, J.; Wright, E.M. Glucose/galactose malabsorption caused by a defect in the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Nature 1991, 350, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R.; Wallace, L.E.; Sigalet, D.L. Glucagon-like peptide-2 induces intestinal adaptation in parenterally fed rats with short bowel syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G964–G972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrin, D.G.; Petersen, Y.; Stoll, B.; Sangild, P. Glucagon-like peptide 2: A nutrient-responsive gut growth factor. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moran, A.W.; Alrammahi, M.; Daly, K.; Weatherburn, D.; Ionescu, C.; Blanchard, A.; Shirazi-Beechey, S.P. Luminal Sweet Sensing and Enteric Nervous System Participate in Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Transporter, GLUT2. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091547
Moran AW, Alrammahi M, Daly K, Weatherburn D, Ionescu C, Blanchard A, Shirazi-Beechey SP. Luminal Sweet Sensing and Enteric Nervous System Participate in Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Transporter, GLUT2. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091547
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoran, Andrew W., Miran Alrammahi, Kristian Daly, Darren Weatherburn, Catherine Ionescu, Alexandra Blanchard, and Soraya P. Shirazi-Beechey. 2025. "Luminal Sweet Sensing and Enteric Nervous System Participate in Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Transporter, GLUT2" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091547
APA StyleMoran, A. W., Alrammahi, M., Daly, K., Weatherburn, D., Ionescu, C., Blanchard, A., & Shirazi-Beechey, S. P. (2025). Luminal Sweet Sensing and Enteric Nervous System Participate in Regulation of Intestinal Glucose Transporter, GLUT2. Nutrients, 17(9), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091547






