Fermentation of Alginate and Its Oligosaccharides by the Human Gut Microbiota: Structure–Property Relationships and New Findings Focusing on Bacteroides xylanisolvens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Fermentation of Alginate and AOS by the Human Gut Microbiota and the Keystone Bacterium B. xylanisolvens
2.3. Carbohydrate Utilization and Fermentation Products Analysis
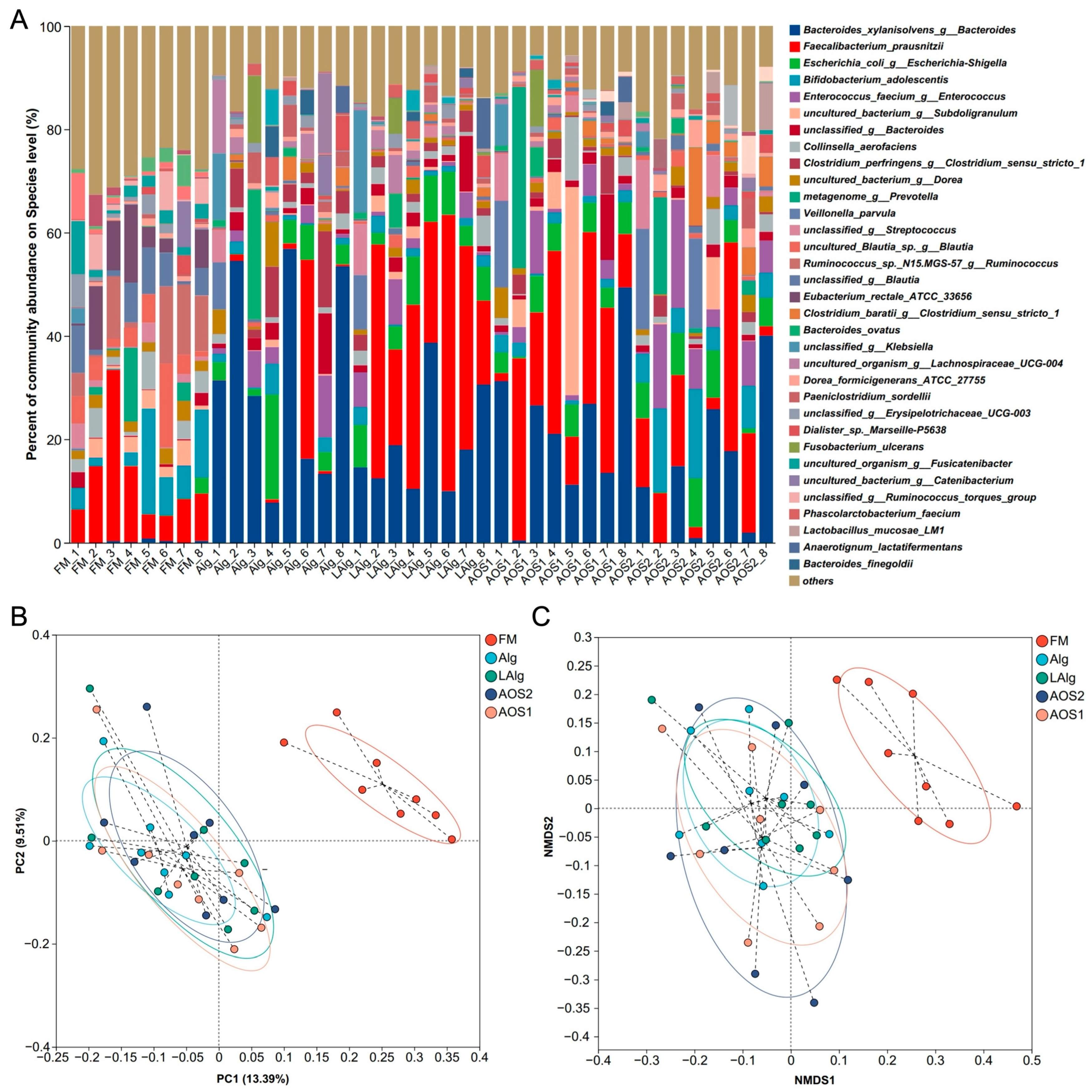
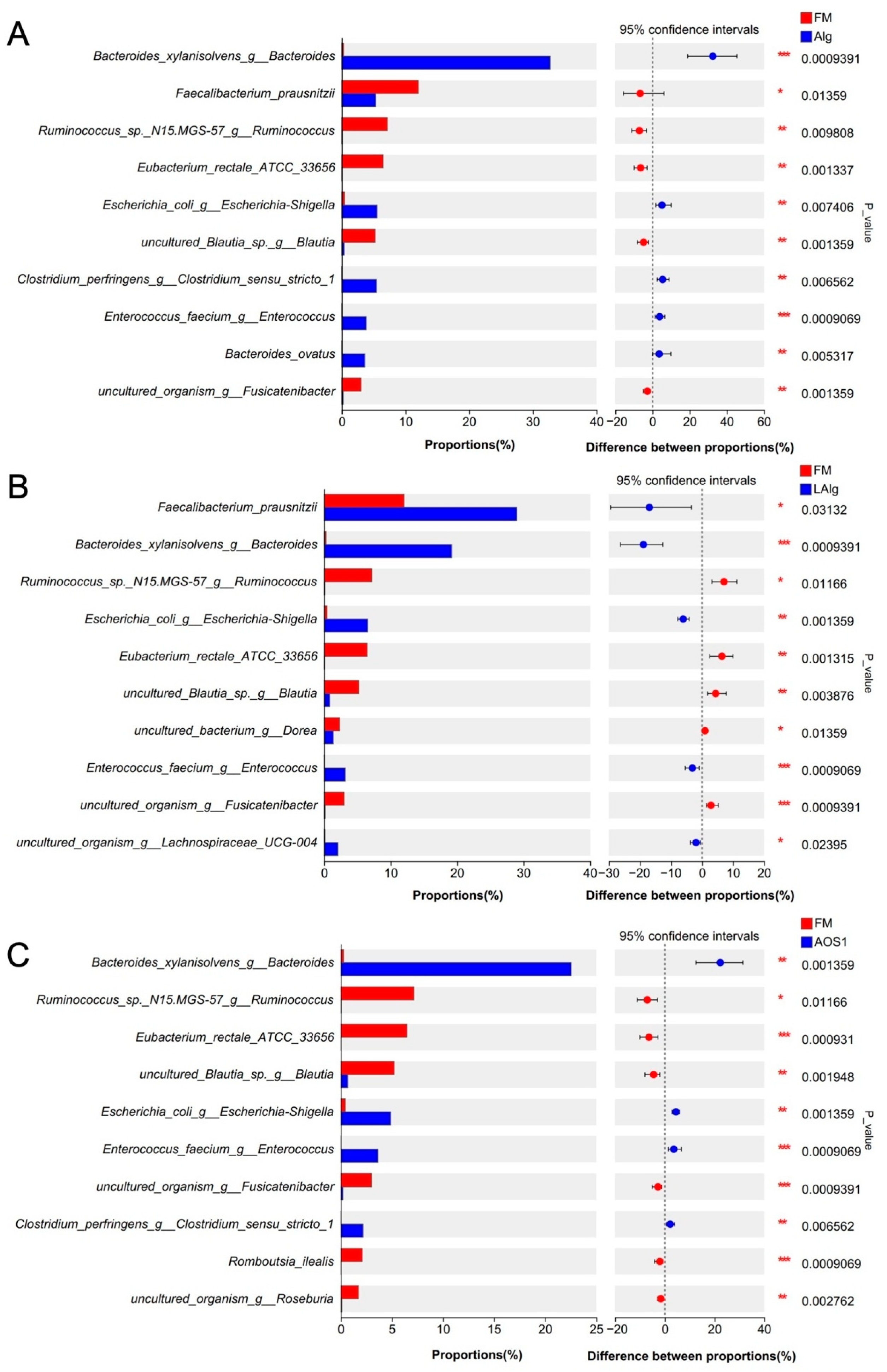
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon High-Throughput Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
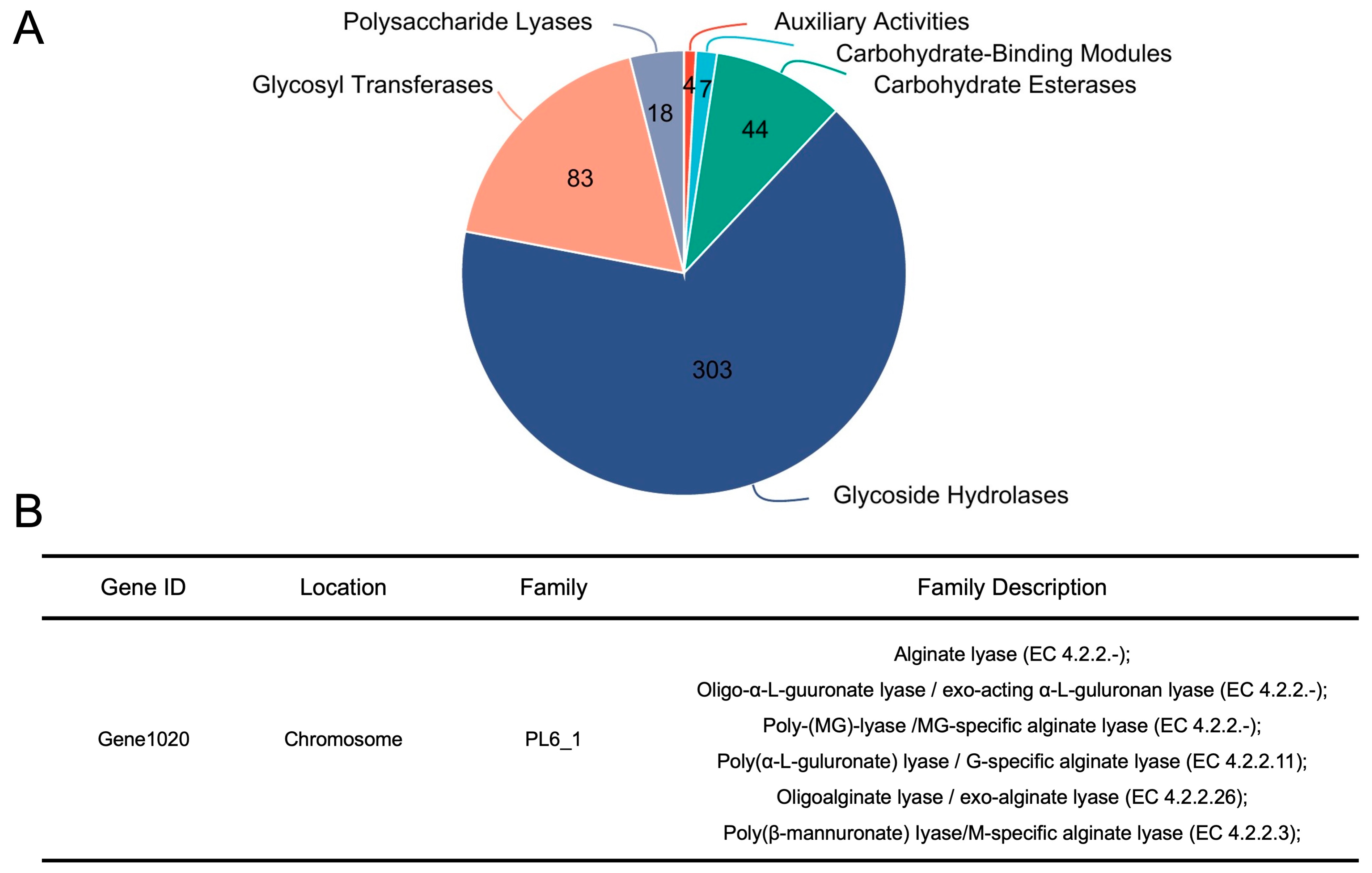
2.5. Whole Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Metabolome Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
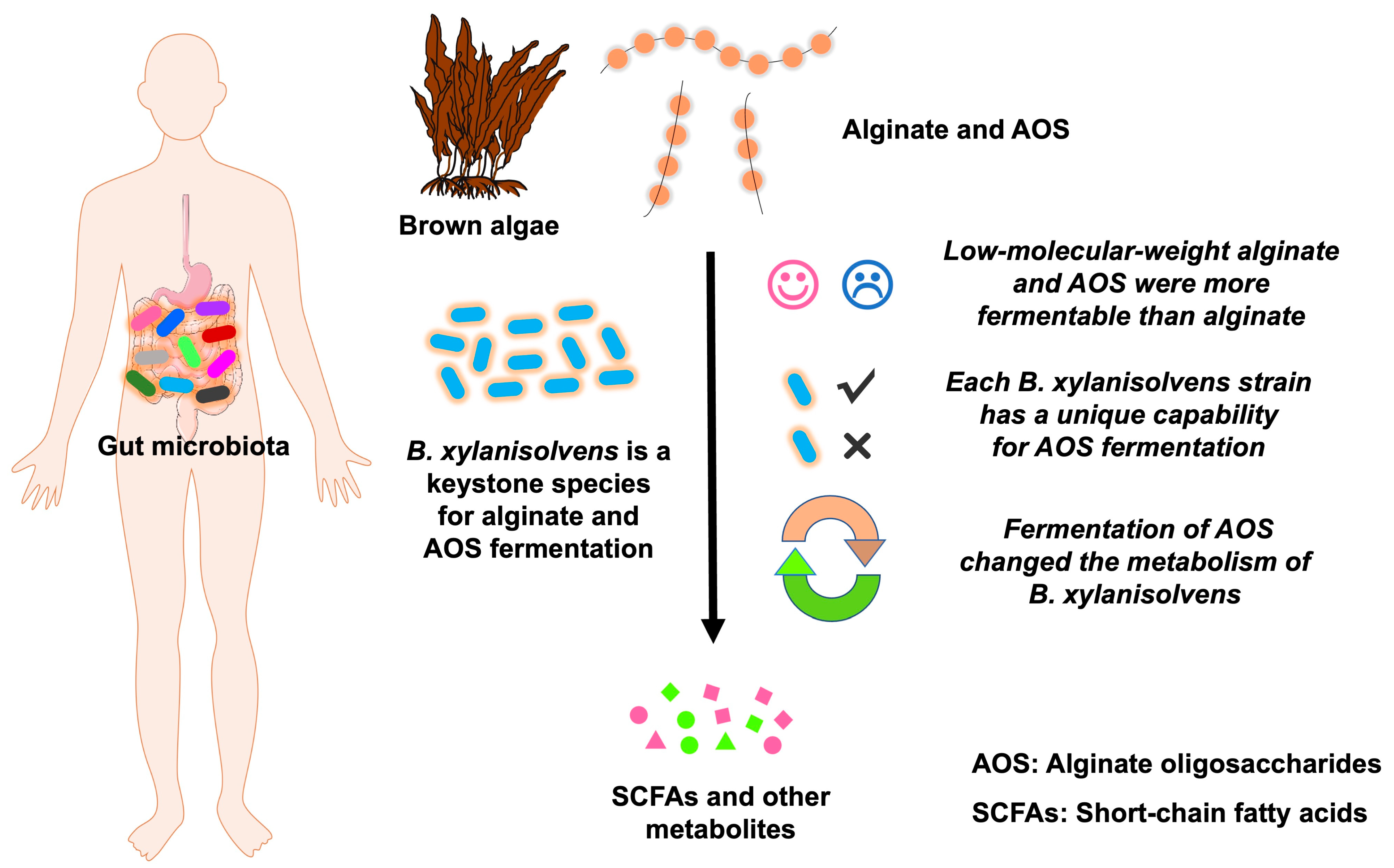
3.1. Low-Molecular-Weight Alginate and AOS Are More Fermentable than Alginate by the Human Gut Microbiota
3.2. B. xylanisolvens Is a Keystone Species for the Fermentation of Alginate and AOS in the Human Gut Microbiota
3.3. Each B. xylanisolvens Strain Is Characterized with a Unique Capability for AOS Fermentation
3.4. B. xylanisolvens Is Armed with a Plethora of CAZymes, and PL 6_1 Is Identified as a Candidate Enzyme Responsible for the Utilization of AOS
3.5. Fermentation of AOS by B. xylanisolvens Is Associated with Significant Changes in Bacterial Metabolites and Metabolic Pathways
4. Discussion
4.1. Major Findings and Strengths of the Study
4.2. Future Directions in This Field
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bi, D.; Yang, X.; Yao, L.; Hu, Z.; Li, H.; Xu, X.; Lu, J. Potential food and nutraceutical applications of alginate: A review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, U.M.; Lee, O.K.; Lee, E.Y. Alginate derived functional oligosaccharides: Recent developments, barriers, and future outlooks. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Rauf, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Shan, Z.; Chen, C.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Wan, C. Process and applications of alginate oligosaccharides with emphasis on health beneficial perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 303–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, S.; Touvreyloiodice, M.; Poulet, L.; Drouillard, S.; Vincentelli, R.; Henrissat, B.; Braek, G.S.; Helbert, W. Ancient acquisition of “alginate utilization loci” by human gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudlo, N.A.; Pereira, G.V.; Parnami, J.; Cid, M.; Markert, S.; Tingley, J.P.; Unfried, F.; Ali, A.; Varghese, N.J.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Diverse events have transferred genes for edible seaweed digestion from marine to human gut bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 314–328.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cai, C.; Hao, J.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Gut microbiota fermentation of marine polysaccharides and its effects on intestinal ecology: An overview. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Zhou, L.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Pan, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Q.; Shang, Q.; Yu, G. Enterotype-specific effect of human gut microbiota on the fermentation of marine algae oligosaccharides: A preliminary proof-of-concept in vitro study. Polymers 2022, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Pan, L.; Shang, Q.; Yu, G. Fermentation of alginate and its derivatives by different enterotypes of human gut microbiota: Towards personalized nutrition using enterotype-specific dietary fibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Dai, W.; Pan, L.; Shang, Q.; Yu, G. Isolation of alginate-degrading bacteria from the human gut microbiota and discovery of Bacteroides xylanisolvens AY11-1 as a novel anti-colitis probiotic bacterium. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Stombaugh, J.I.; Gordon, J.I.; Jansson, J.K.; Knight, R. Diversity, stability and resilience of the human gut microbiota. Nature 2012, 489, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, G.; Tropini, C. The gut microbiota and its biogeography. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.S.; Zhao, S.J.; Yin, Y.H.; Zhang, H.D.; Needham, D.M.; Evans, E.D.; Dai, C.L.; Lu, P.J.; Alm, E.J.; Weitz, D.A. High-throughput, single-microbe genomics with strain resolution, applied to a human gut microbiome. Science 2022, 376, eabm148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S. Understanding competition and cooperation within the mammalian gut microbiome. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R538–R544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Blaser, M.J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jansson, J.K.; Lynch, S.V.; Knight, R. Current understanding of the human microbiome. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, M.; Dai, W.; Shang, Q.; Yu, G. Bacteroides salyersiae is a potent chondroitin sulfate-degrading species in the human gut microbiota. Microbiome 2024, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghita Puscaselu, R.; Lobiuc, A.; Dimian, M.; Covasa, M. Alginate: From food industry to biomedical applications and management of metabolic disorders. Polymers 2020, 12, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; Van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaoutari, A.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrissat, B. The abundance and variety of carbohydrate-active enzymes in the human gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardman, J.F.; Bains, R.K.; Rahfeld, P.; Withers, S.G. Carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) in the gut microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dong, S.; Li, F.L.; Ma, X.Q. Structural basis for the exolytic activity of polysaccharide lyase family 6 alginate lyase BcAlyPL6 from human gut microbe Bacteroides clarus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 547, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodmann, T.; Endo, A.; Gueimonde, M.; Vinderola, G.; Kneifel, W.; de Vos, W.M.; Salminen, S.; Gómez-Gallego, C. Safety of novel microbes for human consumption: Practical examples of assessment in the European Union. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Investigations of Bacteroides spp. towards next-generation probiotics. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulsemer, P.; Toutounian, K.; Kressel, G.; Goletz, C.; Schmidt, J.; Karsten, U.; Hahn, A.; Goletz, S. Impact of oral consumption of heat-treated Bacteroides xylanisolvens DSM 23964 on the level of natural TFα-specific antibodies in human adults. Benef. Microbes. 2016, 7, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Bao, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, S.; Liao, M.; Liu, C.; Zhou, N.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Activation of a specific gut Bacteroides-folate-liver axis benefits for the alleviation of nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Sun, L.; Zeng, G.; Shen, Z.; Wang, K.; Yin, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, P.; Ding, Y.; Nie, Q.; et al. Gut bacteria alleviate smoking-related NASH by degrading gut nicotine. Nature 2022, 610, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo-Rodrigues, H.; Sousa, A.S.; Relvas, J.B.; Tavaria, F.K.; Pintado, M. An overview on mushroom polysaccharides: Health-promoting properties, prebiotic and gut microbiota modulation effects and structure-function correlation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 333, 121978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Zuo, S.; Chen, C.; Lin, Q.; Nie, S. Targeted modification of gut microbiota and related metabolites via dietary fiber. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 316, 120986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Shen, M.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Review of the relationships among polysaccharides, gut microbiota, and human health. Food Res. Int. 2020, 140, 109858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; Tan, Y.; Feng, W.; Peng, C. Interactions between polysaccharides and gut microbiota: A metabolomic and microbial review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Santamarina, A.; Sinisterra-Loaiza, L.; Mondragón-Portocarrero, A.; Ortiz-Viedma, J.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Abuín, C.M.F.; Cepeda, A. Potential prebiotic effect of two Atlantic whole brown seaweeds, Saccharina japonica and Undaria pinnatifida, using in vitro simulation of distal colonic fermentation. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1170392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-chain fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Peng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, S.; Wen, Y.; Gao, J.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; et al. Weight reduction effect of alginate associated with gut microbiota and bile acids: A double-blind and randomized trial. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 108, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Nigam, A.; Mishra, R.; Gupta, S.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Khan, S.-U.-D.; almuqri, E.A.; Ahmed, Z.H.; Rustagi, S.; Singh, D.P.; et al. Novel therapeutic approach for obesity: Seaweeds as an alternative medicine with the latest conventional therapy. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhernakova, D.V.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Andreu-Sanchez, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ruiz-Moreno, A.J.; Peng, H.; Plomp, N.; Del Castillo-Izquierdo, A.; Gacesa, R.; et al. Host genetic regulation of human gut microbial structural variation. Nature 2024, 625, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joos, R.; Boucher, K.; Lavelle, A.; Arumugam, M.; Blaser, M.J.; Claesson, M.J.; Clarke, G.; Cotter, P.D.; De Sordi, L.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; et al. Examining the Healthy Human Microbiome Concept. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Lv, Y.; Shao, M.; Lv, D.; Fu, Z.; Guo, P.; Li, Q.; Shang, Q. Fermentation of Alginate and Its Oligosaccharides by the Human Gut Microbiota: Structure–Property Relationships and New Findings Focusing on Bacteroides xylanisolvens. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091424
Li J, Lv Y, Shao M, Lv D, Fu Z, Guo P, Li Q, Shang Q. Fermentation of Alginate and Its Oligosaccharides by the Human Gut Microbiota: Structure–Property Relationships and New Findings Focusing on Bacteroides xylanisolvens. Nutrients. 2025; 17(9):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091424
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiayi, Youjing Lv, Meng Shao, Depeng Lv, Zhiliang Fu, Peng Guo, Quancai Li, and Qingsen Shang. 2025. "Fermentation of Alginate and Its Oligosaccharides by the Human Gut Microbiota: Structure–Property Relationships and New Findings Focusing on Bacteroides xylanisolvens" Nutrients 17, no. 9: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091424
APA StyleLi, J., Lv, Y., Shao, M., Lv, D., Fu, Z., Guo, P., Li, Q., & Shang, Q. (2025). Fermentation of Alginate and Its Oligosaccharides by the Human Gut Microbiota: Structure–Property Relationships and New Findings Focusing on Bacteroides xylanisolvens. Nutrients, 17(9), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17091424







