Infant Colic Symptoms and Amino Acid Formula: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
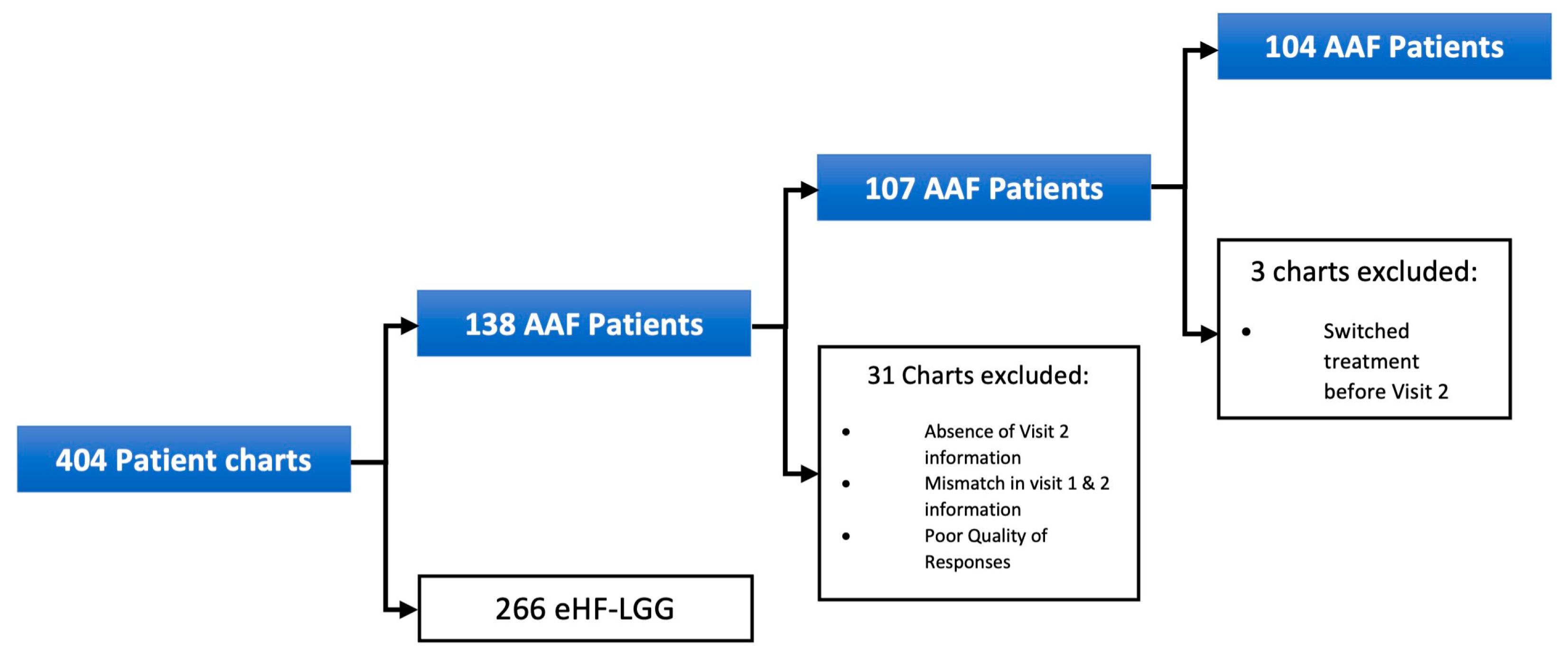
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
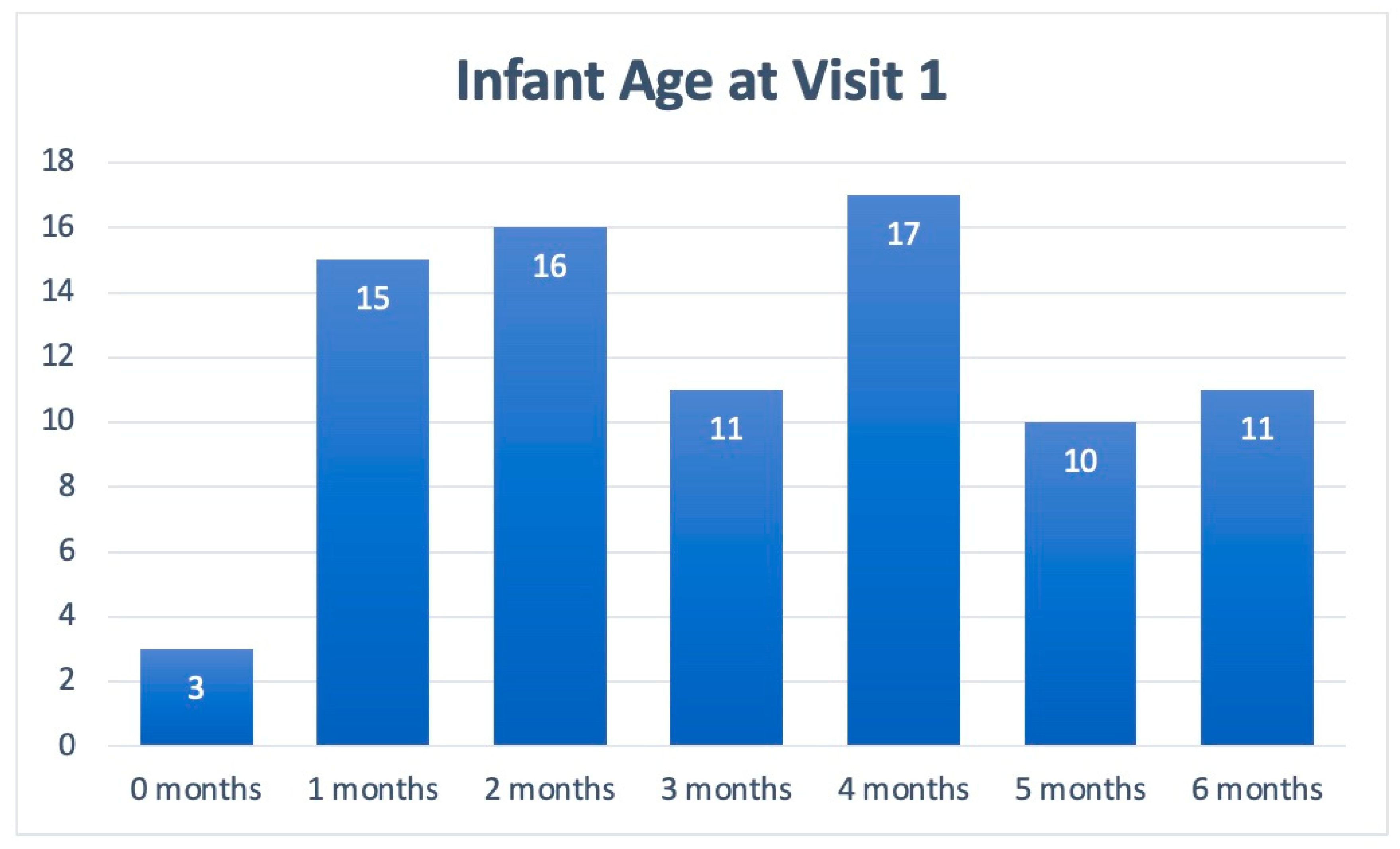
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMPA | Cow’s milk protein allergy |
| eHF | Extensively hydrolyzed formula |
| AAF | Amino acid formula |
| HCP | Healthcare provider |
| GI | Gastroenterology |
| LGG | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG |
References
- Nocerino, R.; Pezzella, V.; Cosenza, L.; Amoroso, A.; Di Scala, C.; Amato, F.; Iacono, G.; Canani, R.B. The controversial role of food allergy in infantile colic: Evidence and clinical management. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevenhooven, J.; Browne, P.D.; L’Hoir, M.P.; de Weerth, C.; Benninga, M.A. Infant colic: Mechanisms and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppen, I.J.; Nurko, S.; Saps, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Benninga, M.A. The pediatric Rome IV criteria: What’s new? Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeevenhooven, J.; Koppen, I.J.; Benninga, M.A. The New Rome IV Criteria for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders in Infants and Toddlers. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2017, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, P.E.; Milla, P.J.; Benninga, M.A.; Davidson, G.P.; Fleisher, D.F.; Taminiau, J. Childhood functional gastrointestinal disorders: Neonate/toddler. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benninga, M.A.; Faure, C.; Hyman, P.E.; St James Roberts, I.; Schechter, N.L.; Nurko, S. Childhood Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Neonate/Toddler. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1443–1455.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Cocker, K.; Chang, E. Infantile Colic: Recognition and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, G.L.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, D.D.; Kang, W.Q.; Tang, M.Q.; Xu, J.K. Effectiveness of Lactobacillus reuteri in infantile colic and colicky induced maternal depression: A prospective single blind randomized trial. Antonie Van. Leeuwenhoek 2015, 107, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwood, J.; Draper-Rodi, J.; Carnes, D. Comparison of common interventions for the treatment of infantile colic: A systematic review of reviews and guidelines. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, V.; Hiscock, H.; Tang, M.; Mensah, F.K.; Heine, R.G.; Stock, A.; York, E.; Barr, R.G.; Wake, M. Probiotics to improve outcomes of colic in the community: Protocol for the Baby Biotics randomised controlled trial. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.; James-Roberts, I.S.; Sleep, J.; Gillham, P. Economic evaluation of strategies for managing crying and sleeping problems. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 84, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haiden, N.; Savino, F.; Hill, S.; Kivelä, L.; De Koning, B.; Kӧglmeier, J.; Luque, V.; Moltu, S.J.; Norsa, L.; De Pipaon, M.S.; et al. Infant formulas for the treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders: A position paper of the ESPGHAN Nutrition Committee. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2024, 79, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, D.; Alp, H.; Gözüm, S.; Orbak, Z.; Cifçi, E.K. Effectiveness of massage, sucrose solution, herbal tea or hydrolysed formula in the treatment of infantile colic. J. Clin. Nurs. 2008, 17, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, V.; D’Amico, F.; Cabana, M.D.; Chau, K.; Koren, G.; Savino, F.; Szajewska, H.; Deshpande, G.; Dupont, C.; Indrio, F.; et al. Lactobacillus reuteri to Treat Infant Colic: A Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2018, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C. Diagnosis of cow’s milk allergy in children: Determining the gold standard? Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.J.; Roy, N.; Heine, R.G.; Hosking, C.S.; Francis, D.E.; Brown, J.; Speirs, B.; Sadowsky, J.; Carlin, J.B. Effect of a low-allergen maternal diet on colic among breastfed infants: A randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e709–e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Gutierrez-Castrellon, P.; Velasco-Benitez, C.; Palacios, J.; Jaen, D.; Ribeiro, H.; Shek, L.P.; Lee, B.W.; Alarcon, P. Practical algorithms for managing common gastrointestinal symptoms in infants. Nutrition 2013, 29, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berseth, C.L.; Johnston, W.H.; Stolz, S.I.; Harris, C.L.; Mitmesser, S.H. Clinical response to 2 commonly used switch formulas occurs within 1 day. Clin Pediatr 2009, 48, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beacker, J.; Brown, J.M.; Florio, J.; Baran, J.V.; Lamos, L.; Oliveros, L.; Vanderhoof, J.A.; Sriaroon, P.; Wilsey, M.J. Clinician Experience with Using Hypoallergenic Formulas to Treat Infants with Suspected Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy: A Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Survey Cohort. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2023, 26, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Baran, J.V.; Lamos, L.; Beacker, J.; Florio, J.; Oliveros, L.V.; Fabbrini, A.L.; Farrar, A.A.; Vanderhoof, J.A.; Wilsey, M.J. Extensively Hydrolyzed Formula and Infant Colic Symptoms: Secondary Analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Pediatr. 2024, 63, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.V.; Brown, J.M.; Farrar, A.A.; Oliveros, L.V.; Beacker, J.; Lamos, L.; Florio, J.; Fabbrini, A.L.; Wilsey, M.J. Impact of the 2022 national formula shortage on clinical decision-making of healthcare providers in switching amino acid formulas for infants with cow’s milk protein allergy: A survey-based study. Front Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1328506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsey, M.J.; Florio, J.; Beacker, J.; Lamos, L.; Baran, J.V.; Oliveros, L.; Sriaroon, P.; Brown, J.M.; Vanderhoof, J.A. Extensively Hydrolyzed Formula Improves Allergic Symptoms in the Short Term in Infants with Suspected Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsey, M.J.; Baran, J.V.; Lamos, L.; Beacker, J.; Florio, J.; Oliveros, L.; Sriaroon, P.; Brown, J.M.; Vanderhoof, J.A. Short-term symptom improvement in infants with suspected cow’s milk protein allergy using amino acid formula: A prospective cohort analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, e1208334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W. Methods for testing statistical differences between groups in medical research: Statistical standard and guideline of Life Cycle Committee. Life Cycle 2022, 2, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Biagioli, E.; Sorrenti, M.; Lingua, C.; Moja, L.; Banks, S.S.; Ceratto, S.; Savino, F. Dietary modifications for infantile colic. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, CD011029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, D.C.; Kulczycki, A., Jr. Treatment of infant colic with amino acid-based infant formula: A preliminary study. Acta Paediatr. 2000, 89, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Weerth, C.; Fuentes, S.; de Vos, W.M. Crying in infants: On the possible role of intestinal microbiota in the development of colic. Gut Microbes 2013, 4, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savino, F.; Montanari, P.; Galliano, I.; Daprà, V.; Bergallo, M. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) for the Management of Infantile Colic: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, e1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, K.; Lau, E.; Greenberg, S.; Jacobson, S.; Yazdani-Brojeni, P.; Verma, N.; Koren, G. Probiotics for infantile colic: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigating Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianifar, H.; Ahanchian, H.; Grover, Z.; Jafari, S.; Noorbakhsh, Z.; Khakshour, A.; Sedaghat, M.; Kiani, M. Synbiotic in the management of infantile colic: A randomised controlled trial. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2014, 50, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatheree, N.Y.; Liu, Y.; Taylor, C.M.; Hoang, T.K.; Cai, C.; Rahbar, M.H.; Hessabi, M.; Ferris, M.; McMurtry, V.; Wong, C.; et al. Lactobacillus reuteri for Infants with Colic: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Pediatr. 2017, 191, 170–178.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocerino, R.; De Filippis, F.; Cecere, G.; Marino, A.; Micillo, M.; Di Scala, C.; De Caro, C.; Calignano, A.; Bruno, C.; Paparo, L.; et al. The therapeutic efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12® in infant colic: A randomised, double blind, placebo-controlled trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, G.; Xie, H.; You, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, C.; Xu, S.; Melsaether, C.; Yuan, S. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis, BB-12® on infant colic—A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes. 2021, 12, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenplas, Y.; Abkari, A.; Bellaiche, M.; Benninga, M.; Chouraqui, J.P.; Çokura, F.; Harb, T.; Hegar, B.; Lifschitz, C.; Ludwig, T.; et al. Prevalence and Health Outcomes of Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Infants From Birth to 12 Months of Age. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolke, D.; Bilgin, A.; Samara, M. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Fussing and Crying Durations and Prevalence of Colic in Infants. J. Pediatr 2017, 185, 55–61.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Population |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Male, n (%) | 64 (60) |
| Female, n (%) | 43 (40) |
| Mean age at enrollment, months (Range) | 3 (1–6) |
| Median time between visits, weeks (IQR) | 5 (4–6) |
| Visit 1 | Visit 2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptom | n | Severe | Moderate | Mild | Not Present | n | Severe | Moderate | Mild | Not Present |
| Colic | 104 | 17% | 36% | 27% | 20% | 103 | 0% | 2% | 19% | 79% |
| Fussiness | 101 | 7% | 26% | 30% | 38% | 101 | 0% | 1% | 19% | 80% |
| Gassiness | 101 | 10% | 17% | 45% | 29% | 102 | 0% | 3% | 20% | 77% |
| Sleep Difficulties | 100 | 7% | 21% | 28% | 44% | 101 | 0% | 1% | 9% | 90% |
| Symptom | Severe in Visit 1 - > Total Resolution in Visit 2 | Moderate in Visit 1 - > Total Resolution in Visit 2 | Mild in Visit 1 - > Total Resolution in Visit 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colic | 14 (78%) | 24 (65%) | 23 (82%) |
| Fussiness | 4 (57%) | 20 (77%) | 22 (73%) |
| Gassiness | 6 (60%) | 12 (71%) | 32 (71%) |
| Sleeping Difficulties | 7 (100%) | 19 (90%) | 22 (79%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brown, J.M.; Baran, J.V.; Lamos, L.; Beacker, J.; Florio, J.; Oliveros, L.V.; Fabbrini, A.L.; Farrar, A.A.; Wilsey, M.J. Infant Colic Symptoms and Amino Acid Formula: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081302
Brown JM, Baran JV, Lamos L, Beacker J, Florio J, Oliveros LV, Fabbrini AL, Farrar AA, Wilsey MJ. Infant Colic Symptoms and Amino Acid Formula: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(8):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081302
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrown, Jerry M., Jessica V. Baran, Luke Lamos, Jesse Beacker, Jared Florio, Lea V. Oliveros, Abigail L. Fabbrini, Andrew A. Farrar, and Michael J. Wilsey. 2025. "Infant Colic Symptoms and Amino Acid Formula: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 17, no. 8: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081302
APA StyleBrown, J. M., Baran, J. V., Lamos, L., Beacker, J., Florio, J., Oliveros, L. V., Fabbrini, A. L., Farrar, A. A., & Wilsey, M. J. (2025). Infant Colic Symptoms and Amino Acid Formula: Insights from a Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 17(8), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17081302







