Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Study Design
2.2. Liver Function Biomarkers Analysis
2.3. Liver Pro-Oxidant/Antioxidant Biomarkers Analysis
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Liver Function Biomarkers
3.2. Liver Pro-Oxidant/Antioxidant Biomarkers
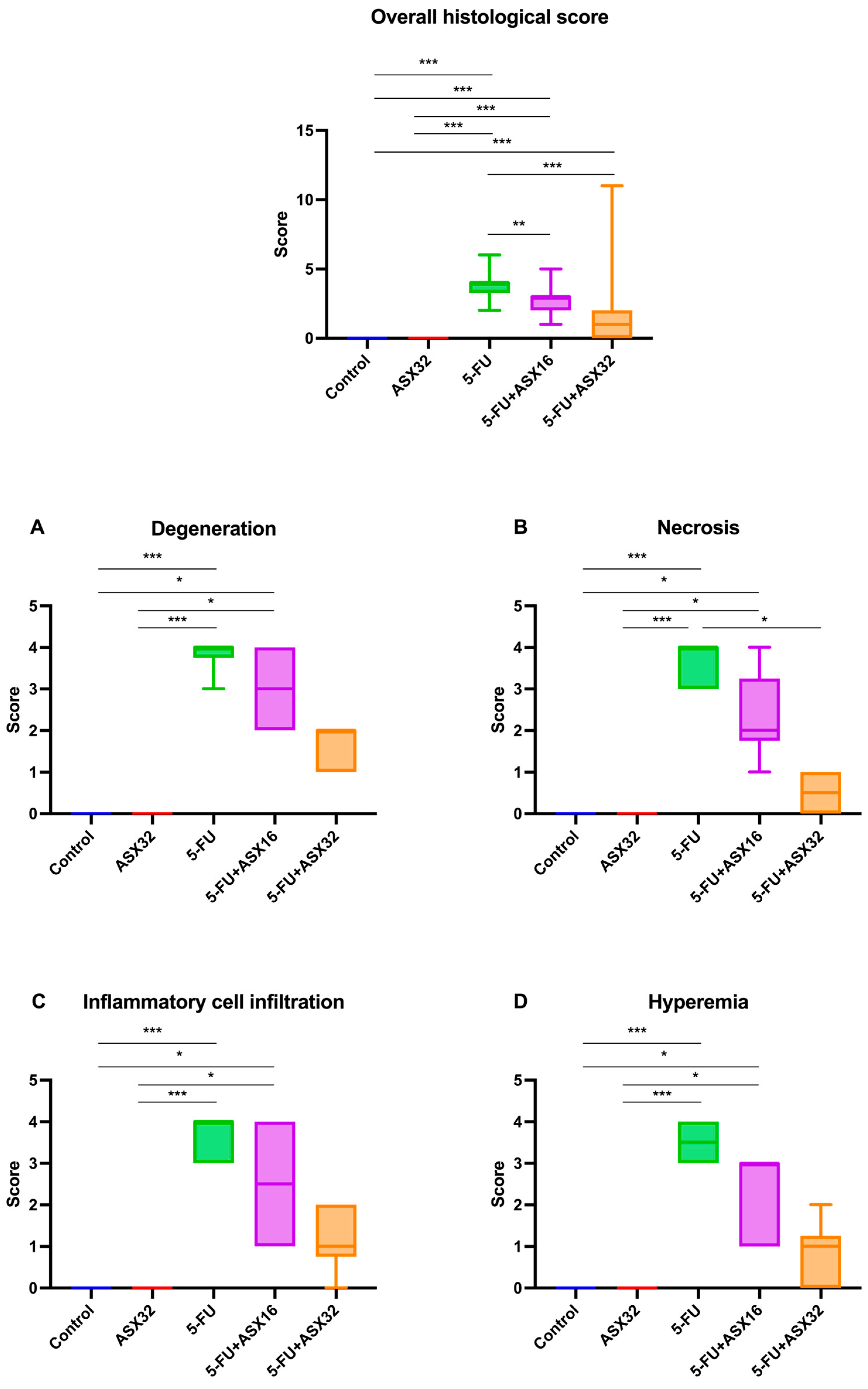
3.3. Histopathological Analysis
3.4. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| AST | Aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| GSR | Glutathione reductase |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| TP | Total protein |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| ASX | Astaxanthin |
| 8-OHDG | 8-Hydroxyguanosine |
References
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelen, V.; Sengul, E.; Yildirim, S.; Atila, G. The protective effects of naringin against 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemula, S.; Mylaram, J.; Yadala, R.; Alla, G.; Banothu, A.; Durga Veera, H.D. Protective Effects of Naringenin on 5-Fluorouracil Induced Pulmonary Toxicity Via Modulation of NF-κB and Nrf2 Pathway. Pak. Vet. J. 2024, 44, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelen, V.; Şengül, E.; Gedikli, S.; Atila, G.; Uslu, H.; Makav, M. The protective effect of rutin and quercetin on 5-FU-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2017, 7, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, S.M.; AbuBakr, H.O.; Mohamed, M.A.; El-Bahrawy, A. Ameliorative effect of pumpkin seed oil against emamectin induced toxicity in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukibe, K.; Hashida, K.; Yoshida, N.; Takagi, H. Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for astaxanthin production and oxidative stress tolerance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7205–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cerbo, A.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Palmieri, B.; Pezzuto, F.; Cocco, R.; Flores, G.; Iannitti, T. Functional foods in pet nutrition: Focus on dogs and cats. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 112, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidetti, G.; Di Cerbo, A.; Giovazzino, A.; Rubino, V.; Palatucci, A.T.; Centenaro, S.; Fraccaroli, E.; Cortese, L.; Bonomo, M.G.; Ruggiero, G.; et al. In Vitro Effects of Some Botanicals with Anti-Inflammatory and Antitoxic Activity. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 5457010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Zeid, S.M.; Aljuaydi, S.H.; AbuBakr, H.O.; Tahoun, E.A.; Di Cerbo, A.; Alagawany, M.; Khalil, S.R.; Farag, M.R. Astaxanthin Mitigates Thiacloprid-Induced Liver Injury and Immunotoxicity in Male Rats. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: Applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, S.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Dargahi, L.; Jorjani, M. Astaxanthin: A mechanistic review on its biological activities and health benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destefanis, S.; Giretto, D.; Muscolo, M.C.; Di Cerbo, A.; Guidetti, G.; Canello, S.; Giovazzino, A.; Centenaro, S.; Terrazzano, G. Clinical evaluation of a nutraceutical diet as an adjuvant to pharmacological treatment in dogs affected by Keratoconjunctivitis sicca. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, P.N.; Ashokkumar, P.; Sudhandiran, G. Antioxidative and antiproliferative effects of astaxanthin during the initiation stages of 1,2-dimethyl hydrazine-induced experimental colon carcinogenesis. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 23, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Chyun, J.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Line, L.L.; Chew, B.P. Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelli, E.; Ferrari, L.; Borghetti, P.; Candela, F.; Abiakam, N.S.; Bianchera, A.; Buttini, F.; Magi, G.E.; Sonvico, F.; Martelli, P.; et al. Nano-adjuvanted dry powder vaccine for the mucosal immunization against airways pathogens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1116722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, G.E.; Mariotti, F.; Pallotta, L.; Di Cerbo, A.; Venanzi, F.M. Immunohistochemical Expression of p62 in Feline Mammary Carcinoma and Non-Neoplastic Mammary Tissue. Animals 2022, 12, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.-H.M.N. Protective Effect of Captopril against 5- Fluorouracil-Induced Hepato and Nephrotoxicity in Male Albino Rats. J. Am. Sci. 2012, 8, 680–685. [Google Scholar]
- Elbanan, M.E.; Amer, M.E.; El-Missiry, M.A.; Othman, A.I.; Shabana, S.M. Melatonin protects mice from 5-FU hepatotoxicity and improves 5-FU antitumor effects by an apoptotic pathway dependent on cell cycle arrest in A549 human lung cancer cells. RPS Pharm. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 2, rqad034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandrino, F.; Qin, L.; Cruz, G.; Sahu, S.; Rosenthal, M.H.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Shinagare, A.B. 5-Fluorouracil induced liver toxicity in patients with colorectal cancer: Role of computed tomography texture analysis as a potential biomarker. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molander, D.W.; Sheppard, E.; Payne, M.A. Serum Transaminase in Liver Disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1957, 163, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Xiao, H.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Angelica Polysaccharide Antagonizes 5-FU-Induced Oxidative Stress Injury to Reduce Apoptosis in the Liver Through Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 720620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.; Kang, W.; Roh, J.; Jung, Y.; Lee, H.; Park, T. Acetyl tributyl citrate attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in human keratinocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 230, 116606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Kang, H.E.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, M.G.; Shin, W.G. Pharmacokinetics and first-pass metabolism of astaxanthin in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 105, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, J.; Punja, Z.K. Transgenic carrot plants accumulating ketocarotenoids show tolerance to UV and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adikwu, E.; Ebinyo, N.; Adogbo Ejovwoke, C. Resveratrol abrogates 5-flourouracil -induced hepatotoxicity: A preclinical study. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medoro, A.; Davinelli, S.; Milella, L.; Willcox, B.J.; Allsopp, R.C.; Scapagnini, G.; Willcox, D.C. Dietary Astaxanthin: A Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Agent for Brain Aging and Adult Neurogenesis. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-kappaB response pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Koh, H.-K.; Kim, D.-S. Down-regulation of IL-6 production by astaxanthin via ERK-, MSK-, and NF-κB-mediated signals in activated microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Qiu, H.; Lin, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Jin, D. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signalling Pathway Activates Autophagy and Suppresses Peritoneal Fibrosis in the Process of Peritoneal Dialysis. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 778479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-H.; Qu, J.; Shen, X. NF-κB/p65 antagonizes Nrf2-ARE pathway by depriving CBP from Nrf2 and facilitating recruitment of HDAC3 to MafK. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, M. Pathogenesis of arthritis: Recent research progress. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davinelli, S.; Saso, L.; D’Angeli, F.; Calabrese, V.; Intrieri, M.; Scapagnini, G. Astaxanthin as a Modulator of Nrf2, NF-κB, and Their Crosstalk: Molecular Mechanisms and Possible Clinical Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chen, S.; Xiong, H.; Wang, M.; Hang, W.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Ge, B.; Li, R.; Cui, H. Astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis ameliorates the chemotherapeutic drug (doxorubicin) induced liver injury through the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4659–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadi, C.K.; Howells, L.M.; Atherfold, P.A.; Manson, M.M. Involvement of Nrf2, p38, B-Raf, and nuclear factor-kappaB, but not phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, in induction of hemeoxygenase-1 by dietary polyphenols. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdo, J.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P. Glutathione production is regulated via distinct pathways in stressed and non-stressed cortical neurons. Brain Res. 2008, 1189, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liao, Y.; Peng, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Nussler, A.K.; Liu, L.; et al. The Protective Effect of Heme Oxygenase-1 on Liver Injury Caused by DON-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cytotoxicity. Toxins 2021, 13, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zou, K.; Xie, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Seabuckthorn berry polysaccharide extracts protect against acetaminophen induced hepatotoxicity in mice via activating the Nrf-2/HO-1-SOD-2 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 38, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Singh, D.; Patel, S.; Singh, M.R. Role of enzymatic free radical scavengers in management of oxidative stress in autoimmune disorders. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias-Rodriguez, R.U.; Inzaugarat, M.E.; Ruiz-Margain, A.; Nelson, L.J.; Trautwein, C.; Cubero, F.J. Reclassifying Hepatic Cell Death during Liver Damage: Ferroptosis-A Novel Form of Non-Apoptotic Cell Death? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugden, P.H.; Clerk, A. Oxidative stress and growth-regulating intracellular signaling pathways in cardiac myocytes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 2111–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X. Astaxanthin Inhibits Acetaldehyde-Induced Cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells by Modulating Akt/CREB and p38MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Xuan, R.; Jiang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhen, Z.; Song, Y.; Hong, L.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; et al. Astaxanthin Induces the Nrf2/HO-1 Antioxidant Pathway in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells by Generating Trace Amounts of ROS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Krill oil: Nutraceutical potential in skin health and disease. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1388155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, B.; Nice, E.C.; Xu, J.; Huang, C. Antioxidant Therapy in Cancer: Rationale and Progress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Sun, S.; Iijima, K.; Gross, M.D. Antitumor activity of astaxanthin and its mode of action. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 36, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Song, G.-G.; Park, J.-J.; Chang, H.-I. Protective effect of astaxanthin on naproxen-induced gastric antral ulceration in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 514, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W. The Origin of the Antioxidant Capacity Against Oxidative and Photooxidative Stress, Singlet Oxygen Reactivity, and the Excited States in Skin and Eye Related Diseases of Astaxanthin and Other Carotenoids, Isomers and Esters in the Cell Membrane and Cytosol. 2023. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-04211840/document (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Han, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q. Astaxanthin in microalgae: Pathways, functions and biotechnological implications. ALGAE 2013, 28, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J. Ferroptosis: Bug or feature? Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, M.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Wen, R.; Pei, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. Astaxanthin attenuates doxorubicin-induced liver injury via suppression of ferroptosis in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 121, 106437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hua, S.; Deng, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Khan, N.U.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Z. Astaxanthin Activated the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway to Enhance Autophagy and Inhibit Ferroptosis, Ameliorating Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 42887–42903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, C.-Y.; Wang, T.; Yu, H.-M.; Ouyang, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-P.; Gong, H.-B.; Ma, X.-H.; Jiao, G.-L.; Fu, L.-L.; et al. (+)-Clausenamide protects against drug-induced liver injury by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; He, S.; Guo, N.; Tian, W.; Zhang, W.; Luo, L. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 72, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Li, K.; Zheng, G. Astaxanthin ameliorates oxidative stress in lens epithelial cells by regulating GPX4 and ferroptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 383, 110684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2054–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monmeesil, P.; Fungfuang, W.; Tulayakul, P.; Pongchairerk, U. The effects of astaxanthin on liver histopathology and expression of superoxide dismutase in rat aflatoxicosis. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.S.; Aschele, C.; Sobrero, A.; Chang, Y.M.; Bertino, J.R. Decreased folylpolyglutamate synthetase expression: A novel mechanism of fluorouracil resistance. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3677–3680. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, M.; Tanaka, T.; Sawada, H. Increased sensitivity to long-term 5-fluorouracil exposure of human colon cancer HT-29 cells resistant to short-term exposure. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radenković, N.; Nikodijević, D.; Jovankić, J.; Blagojević, S.; Milutinović, M. Resistance to 5-fluorouracil: The molecular mechanisms of development in colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 983, 176979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, K.; Kinouchi, M.; Ishida, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Naitoh, T.; Ogawa, H.; Ando, T.; Yazaki, N.; Watanabe, K.; Haneda, S.; et al. 5-fu metabolism in cancer and orally-administrable 5-fu drugs. Cancers 2010, 2, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, U.; Barbour, K.W.; Clinton, S.A.; Berger, F.G. Oxidative Stress and Response to Thymidylate Synthase-Targeted Antimetabolites. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, K.; Kowshik, J.; Kishore, T.K.; Baba, A.B.; Nagini, S. Astaxanthin inhibits NF-kappaB and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways via inactivation of Erk/MAPK and PI3K/Akt to induce intrinsic apoptosis in a hamster model of oral cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4433–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta: Can it be a target for oral cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.M.; Jimenez-Fonseca, P.; Galan-Moral, R.; Coca-Membribes, S.; Fernandez-Montes, A.; Sorribes, E.; Garcia-Torralba, E.; Punti-Brun, L.; Gil-Raga, M.; Cano-Cano, J.; et al. Toxicities and Quality of Life during Cancer Treatment in Advanced Solid Tumors. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9205–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitchumroonchokchai, C.; Failla, M.L. Bioaccessibility and intestinal cell uptake of astaxanthin from salmon and commercial supplements. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Liu, T.; Diao, J.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y. Preparation and characterization of astaxanthin-loaded liposomes by phytosterol oleate instead of cholesterol. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 141008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Histological Feature | Score | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Degenerative changes in the hepatocytes | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Hepatocellular necrosis in the periacinar zone | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Inflammatory cell infiltration | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe | |
| Hyperemia and hemorrhages | 0 | none |
| 1 | minimal | |
| 2 | mild | |
| 3 | moderate | |
| 4 | severe |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Öztürk, Y.; Öztürk, M.; Dörtbudak, M.B.; Mariotti, F.; Magi, G.E.; Di Cerbo, A. Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071230
Öztürk Y, Öztürk M, Dörtbudak MB, Mariotti F, Magi GE, Di Cerbo A. Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071230
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖztürk, Yasin, Merve Öztürk, Muhammet Bahaeddin Dörtbudak, Francesca Mariotti, Gian Enrico Magi, and Alessandro Di Cerbo. 2025. "Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071230
APA StyleÖztürk, Y., Öztürk, M., Dörtbudak, M. B., Mariotti, F., Magi, G. E., & Di Cerbo, A. (2025). Astaxanthin Mitigates 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats. Nutrients, 17(7), 1230. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071230







