Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus ST-G30 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Preparation of Experimental Samples
2.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. Giemsa Staining
2.7. Determination of Myotube Diameter, Fusion Index, and Myotube Length
2.8. Determination of Total Protein Concentrations
2.9. Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
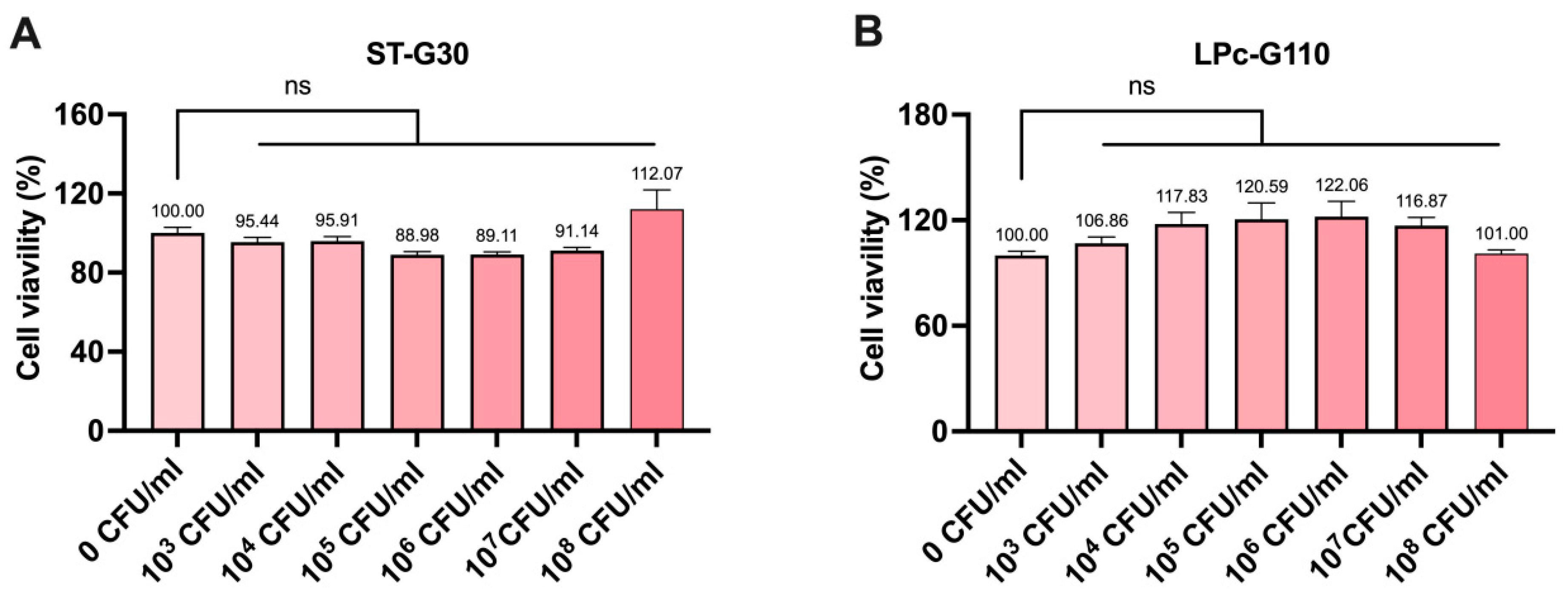
3.1. Effect of ST-G30 and LPc-G110 on Cell Viability in C2C12 Cells
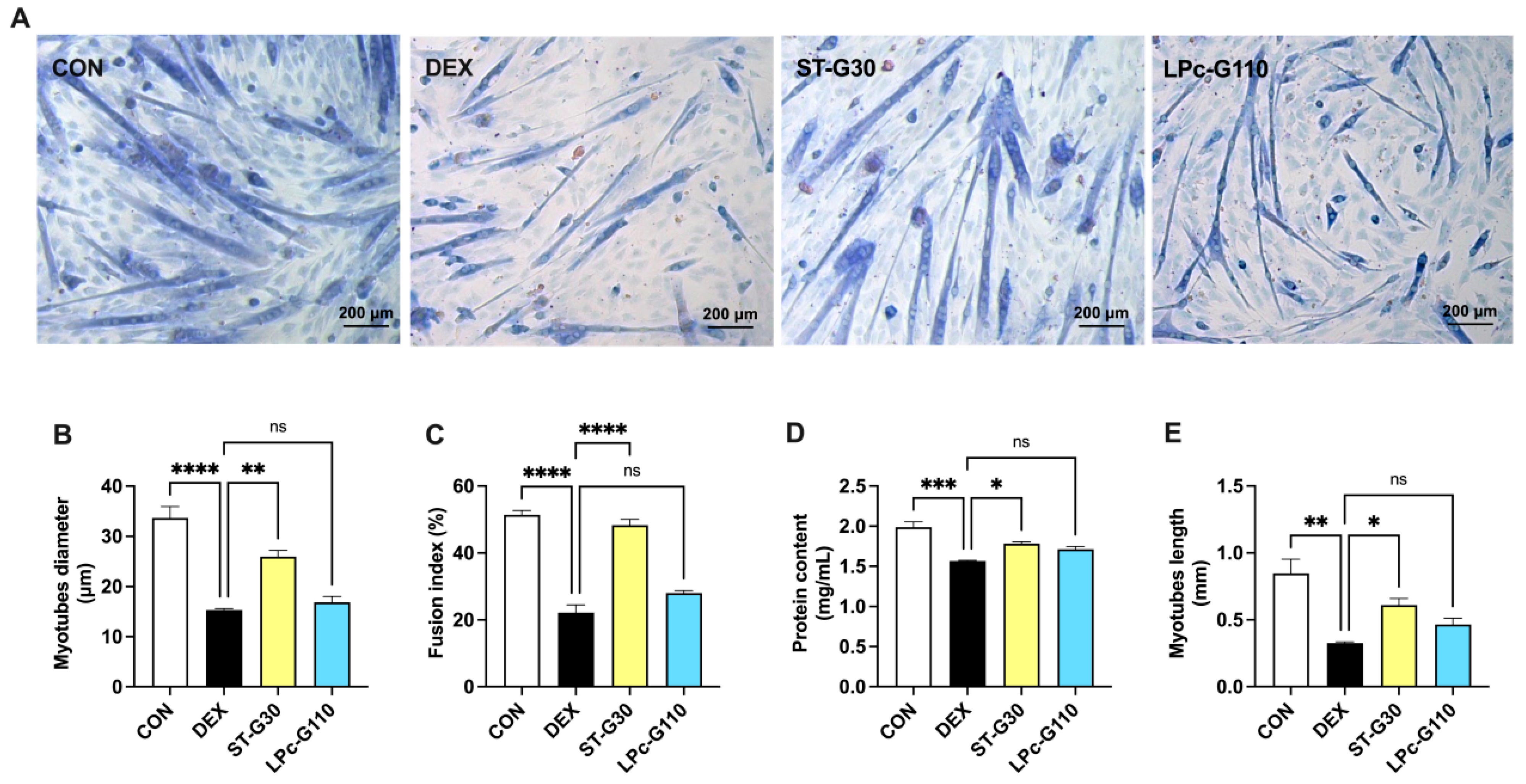
3.2. Effect of ST-G30 and LPc-G110 on Myotube Formation in DEX-Induced Muscle Atrophy
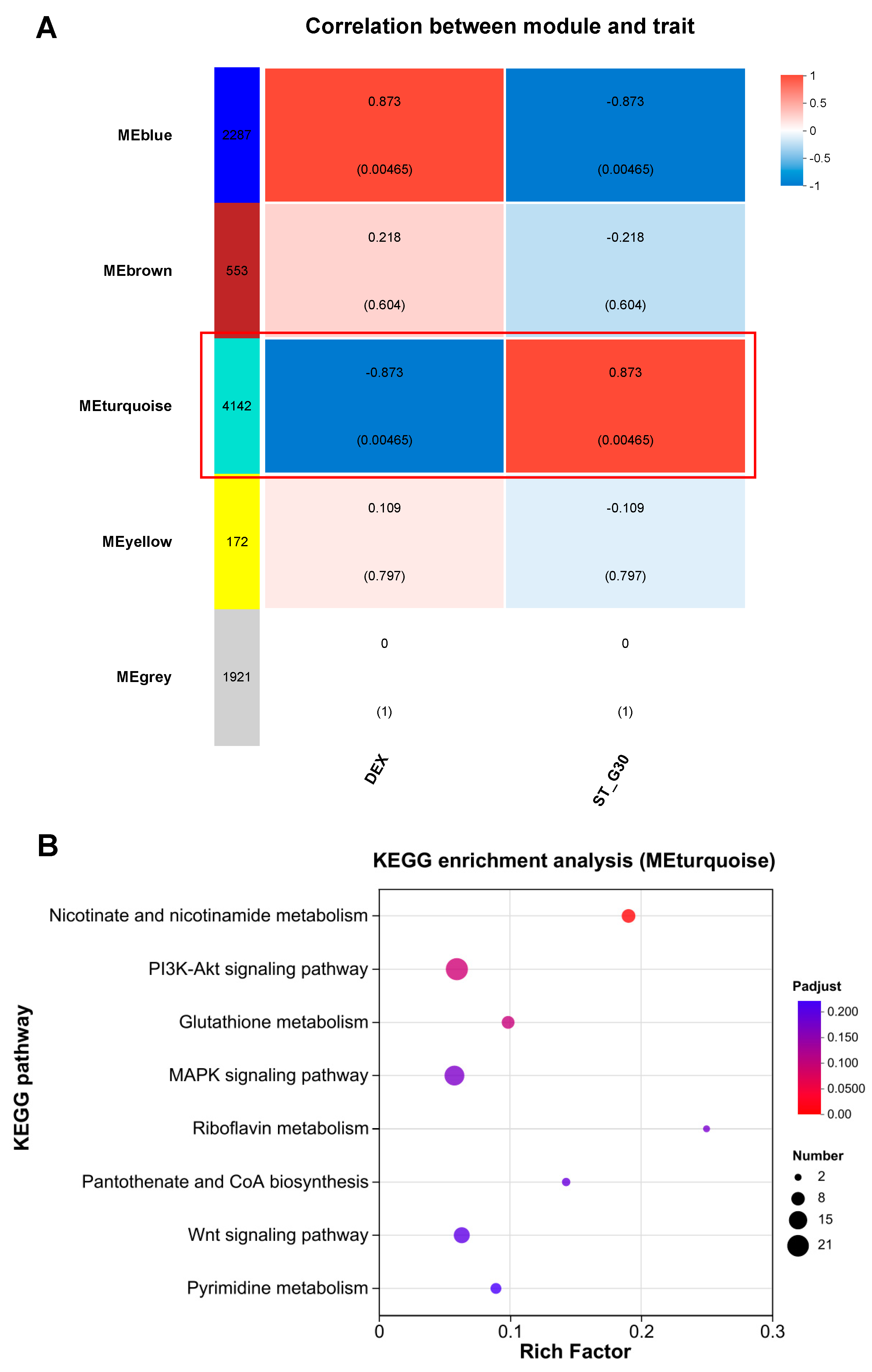
3.3. Effect of ST-G30 on Transcriptomic Profiles of DEX-Treated C2C12 Myotubes
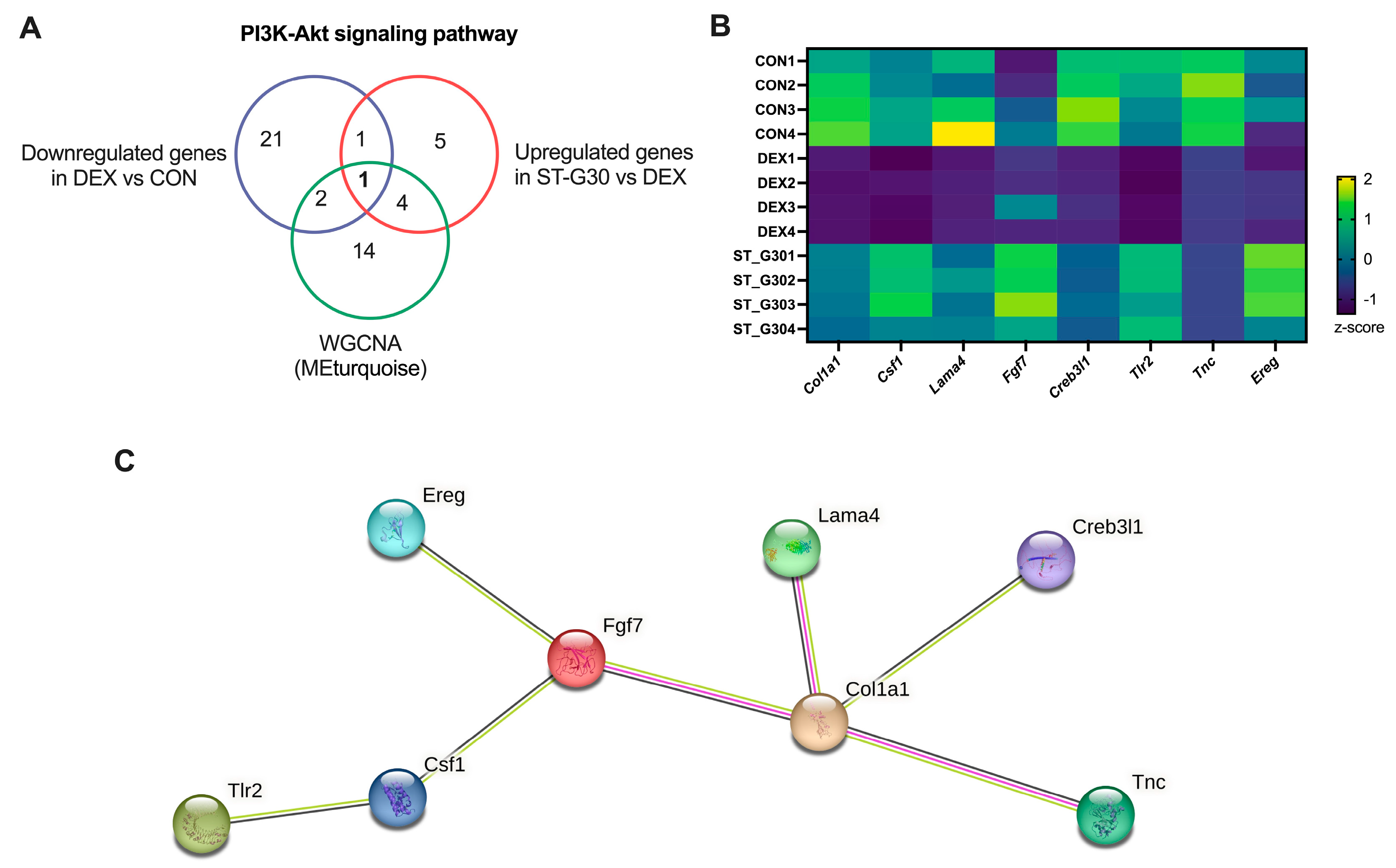
3.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis Uncovers the Signaling Pathways Regulated by ST-G30
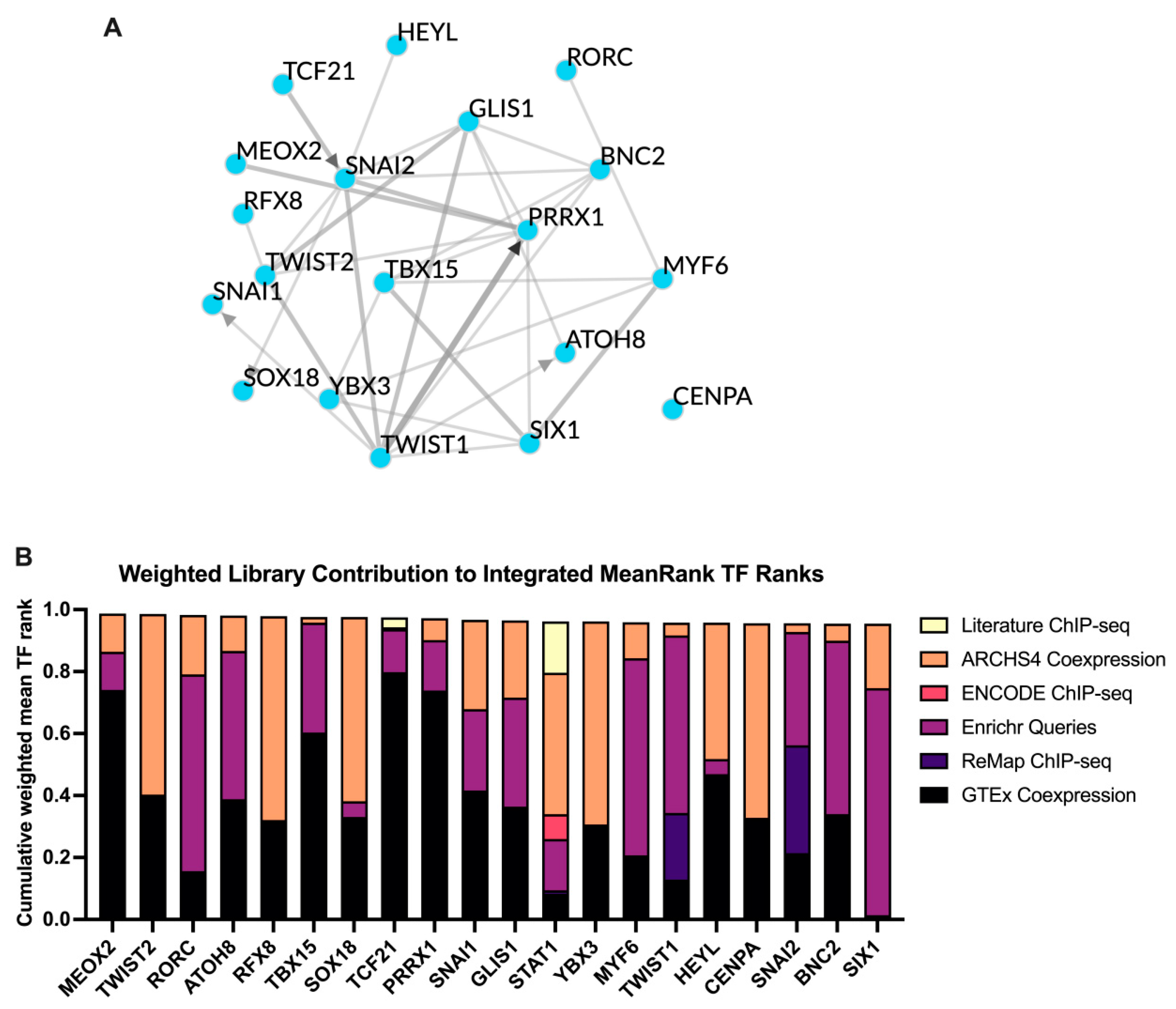
3.5. TF Target Enrichment Analysis
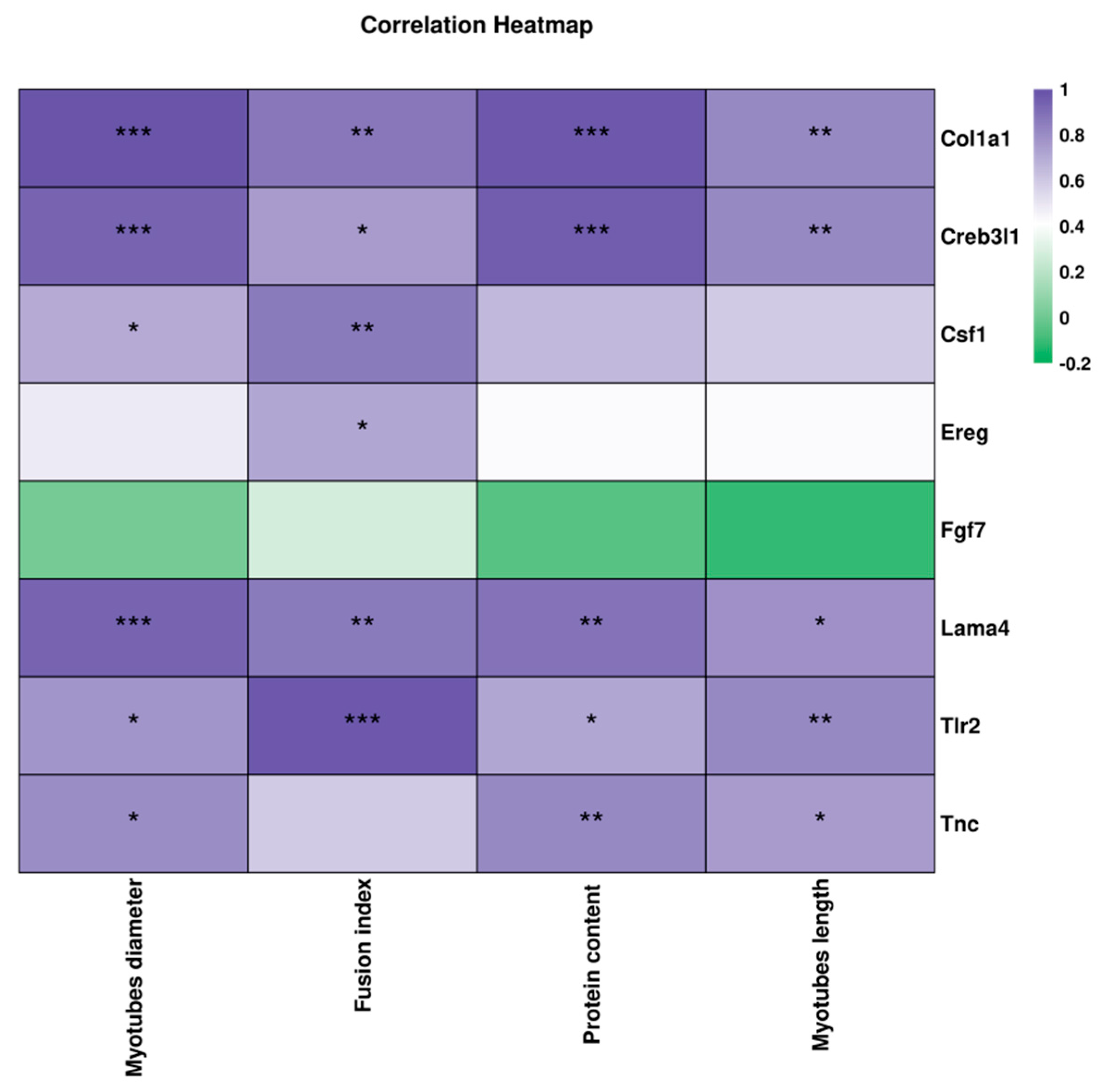
3.6. Correlation Between the Key DEGs and Muscle Atrophy-Related Indexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LABs | Lactic acid bacteria |
| S. thermophilus | Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus |
| L. paracasei | Lacticaseibacillus paracasei |
| ST-G30 | S. thermophilus ST-G30 |
| LPc-G110 | L. paracasei LPc-G110 |
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| WGCNA | Weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| TFs | Transcription factor |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
References
- Arosio, B.; Calvani, R.; Ferri, E.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Carandina, A.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V.; Marzetti, E.; Picca, A. Sarcopenia and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults: Targeting the Muscle–Brain Axis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cheng, J.-K.; Hu, Y.-M. Gut microbiota as a promising therapeutic target for age-related sarcopenia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 81, 101739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Fang, J.; Geng, R.; Kang, S.-G.; Huang, K.; Tong, T. Diabetes-induced muscle wasting: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapeutic targets. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewska, M.; Przekop, Z.; Szostak-Węgierek, D.; Chrzanowska, M.; Raciborski, F.; Traczyk, I.; Sińska, B.I.; Samoliński, B. Prevalence of Risk of Sarcopenia in Polish Elderly Population—A Population Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petermann-Rocha, F.; Balntzi, V.; Gray, S.R.; Lara, J.; Ho, F.K.; Pell, J.P.; Celis-Morales, C. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, C.S.; Ktoris, K.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Sarcopenia Is Associated with Mortality in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gerontology 2021, 68, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.L.; Elmassry, M.M.; Grue, K.; Joiner, H.E.; Jacobo, A.U.; Hamood, A.; Chung, E. Geranylgeraniol and Green Tea Polyphenols Mitigate Negative Effects of a High-Fat Diet on Skeletal Muscle and the Gut Microbiome in Male C57BL/6J Mice. Metabolites 2022, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K.; Jeong, H.H.; Kim, M.-J.; Ryu, H.; Baek, J.; Lee, B. Nutrients against Glucocorticoid-Induced Muscle Atrophy. Foods 2022, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaniku, A.; Bilgic, S.N.; Kir, S. Muscle wasting: Emerging pathways and potential drug targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Yadav, S.S.; Singh, S.; Dabur, R. Natural products: Potential therapeutic agents to prevent skeletal muscle atrophy. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 925, 174995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Shehzad, A.; Niazi, S.; Zahid, A.; Ashraf, W.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Riaz, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Khan, I.M. Probiotics: Mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216674. [Google Scholar]
- Giron, M.; Thomas, M.; Dardevet, D.; Chassard, C.; Savary-Auzeloux, I. Gut microbes and muscle function: Can probiotics make our muscles stronger? J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1460–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, R.; Sakata, S.; Nakao, R.; Oishi, K.; Nakamura, Y. Lactobacillus curvatus CP2998 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandraki, V.; Kazou, M.; Blom, J.; Pot, B.; Papadimitriou, K.; Tsakalidou, E. Comparative Genomics of Streptococcus thermophilus Support Important Traits Concerning the Evolution, Biology and Technological Properties of the Species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards; Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 15: Suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until September 2021. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Huang, D.; Liu, X.-D.; Chan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, J.-D.; Coker, O.O.; et al. Streptococcus thermophilus Inhibits Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Secreting β-Galactosidase. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1179–1193.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, A.; Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Amati, L.; Lavermicocca, P.; Guerra, V.; Russo, F. Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects of Viable or Heat-Killed Lactobacillus paracasei IMPC2.1 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in HGC-27 Gastric and DLD-1 Colon Cell Lines. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Pan, Y.; Pei, Z.; Guo, M.; Yang, B.; Lee, Y.-K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Influence of Lactose Supplementation on Regulation of Streptococcus thermophilus on Gut Microbiota. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Lan, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Tian, P.; Chen, W. Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus CCFM1312 enhanced mice resilience to activity-based anorexia. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, G.; Phillips, M.; Jones, M.; Kailasapathy, K. Immune enhancing effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus LAFTI L10 and Lactobacillus paracasei LAFTI L26 in mice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, R.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, R.; Zhuang, K.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Man, C. Administration of Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates type 2 diabetes in mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3630–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, P.; Sun, Y.; Xia, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Yang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, W. Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus CCFM1095 alleviates age-related muscle mass loss and function decline via gut-muscle axis. Food Biosci. 2025, 63, 105686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-H.; Cheng, S.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Huang, C.-L.; Wen, P.-J.; Chang, M.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-C. Lactobacillus paracasei PS23 dietary supplementation alleviates muscle aging via ghrelin stimulation in d-galactose-induced aging mice. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 85, 104651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-S.; Shin, Y.-J.; Ma, X.; Park, H.-S.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus paracasei alleviate sarcopenia and cognitive impairment in aged mice by regulating gut microbiota-mediated AKT, NF-κB, and FOXO3a signaling pathways. Immun. Ageing 2023, 20, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Kim, M.; Park, T. α-Ionone attenuates high-fat diet-induced skeletal muscle wasting in mice via activation of cAMP signaling. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, J.; Park, S.-D.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-L. Lactobacillus plantarum HY7715 Ameliorates Sarcopenia by Improving Skeletal Muscle Mass and Function in Aged Balb/c Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Kim, M.; Park, T. α-Cedrene, a Newly Identified Ligand of MOR23, Increases Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1800173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Han, F.; Ge, C.; Mao, W.; Chen, L.; Hu, H.; Chen, G.; Lang, Q.; Fang, C. OmicStudio: A composable bioinformatics cloud platform with real-time feedback that can generate high-quality graphs for publication. iMeta 2023, 2, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madamsetty, V.S.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Uzieliene, I.; Nabavi, N.; Dehshahri, A.; García-Couce, J.; Tavakol, S.; Moghassemi, S.; Dadashzadeh, A.; Makvandi, P.; et al. Dexamethasone: Insights into Pharmacological Aspects, Therapeutic Mechanisms, and Delivery Systems. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 1763–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Joung, J.Y.; Pack, S.P.; Oh, N.S. Preventive effect of fermented whey protein mediated by Lactobacillus gasseri IM13 via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO pathway in muscle atrophy. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 2606–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y.I.; Nirmala, F.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Seo, H.-D.; Ha, T.Y.; Jung, C.H.; Ahn, J. Chrysanthemum zawadskil Herbich attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy through the regulation of proteostasis and mitochondrial function. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Jung, Y.-J.; Kwak, M.-S.; Sung, M.-H.; Imm, J.-Y. KL-Biome (Postbiotic Formulation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KM2) Improves Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kang, C.-H. Limosilactobacillus fermentum MG5091 and Lactococcus lactis MG4668 and MG5474 Suppress Muscle Atrophy by Regulating Apoptosis in C2C12 Cells. Fermentation 2023, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.P.; Chanyi, R.M.; Schultz, M. Chapter 19—Common Organisms and Probiotics: Streptococcus thermophilus (Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus). In The Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology; Floch, M.H., Ringel, Y., Allan Walker, W., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lü, F.X.; Lu, Z.X.; Bie, X.M.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, L.J.; Yu, B. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid by Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus Y2 under submerged fermentation. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, W.; Gong, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Ji, M.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Cai, C.; et al. The Regulatory Role of CircAGGF1 in Myogenic Differentiation and Skeletal Muscle Development. Animals 2025, 15, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Meng, Y.; An, Y.; Han, P.; Zhang, C.; Yue, Y.; Wen, C.; Shi, X.e.; Jin, J.; Yang, G.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals novel interaction between muscle satellite cells and fibro-adipogenic progenitors mediated with FGF7 signalling. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 1388–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chou, L.-Y.; Chou, H.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Kang, L.; Cheng, T.-L.; Wang, C.-Z. The Essential Role of Stathmin in Myoblast C2C12 for Vertical Vibration-Induced Myotube Formation. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Locht, M.; Borsboom, T.C.; Winter, J.M.; Ottenheijm, C.A.C. Troponin Variants in Congenital Myopathies: How They Affect Skeletal Muscle Mechanics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.; Wan Zurinah, W.N.; Mouly, V.; Norwahidah, A.K. Tocotrienol-Rich Fraction (TRF) Treatment Promotes Proliferation Capacity of Stress-Induced Premature Senescence Myoblasts and Modulates the Renewal of Satellite Cells: Microarray Analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9141343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantinato, V.; Camargo, H.R.; Sousa, A.L.O.P.D. Probiotics study with Streptococcus salivarius and its ability to produce bacteriocins and adherence to KB cells. Rev. De Odontol. Da UNESP 2019, 48, e20190029. [Google Scholar]
- Sausa, M.; Fucarino, A.; Paladino, L.; Zummo, F.P.; Fabbrizio, A.; Di Felice, V.; Rappa, F.; Barone, R.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Macaluso, F. Probiotics as Potential Therapeutic Agents: Safeguarding Skeletal Muscle against Alcohol-Induced Damage through the Gut–Liver–Muscle Axis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-C.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-J.; Huang, C.-C. Enhancement of Lower Limb Muscle Strength and Reduction of Inflammation in the Elderly: A Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Trial Comparing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei PS23 Probiotic with Heat-Treated Supplementation. Nutrients 2025, 17, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Muhammad, T.; Shahid Iqbal, M.; Qaisar, R. A multistrain probiotic improves handgrip strength and functional capacity in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2022, 102, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Kang, S.-G.; Huang, K.; Tong, T. Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus ST-G30 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071141
Li M, Kang S-G, Huang K, Tong T. Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus ST-G30 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes. Nutrients. 2025; 17(7):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengjie, Seong-Gook Kang, Kunlun Huang, and Tao Tong. 2025. "Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus ST-G30 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes" Nutrients 17, no. 7: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071141
APA StyleLi, M., Kang, S.-G., Huang, K., & Tong, T. (2025). Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophilus ST-G30 Prevents Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy in C2C12 Myotubes. Nutrients, 17(7), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17071141






