Impact of Alcohol Intake on Body Composition in Patients with Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients and Our Study
2.2. Group Classification Based on Alcohol Intake
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Features
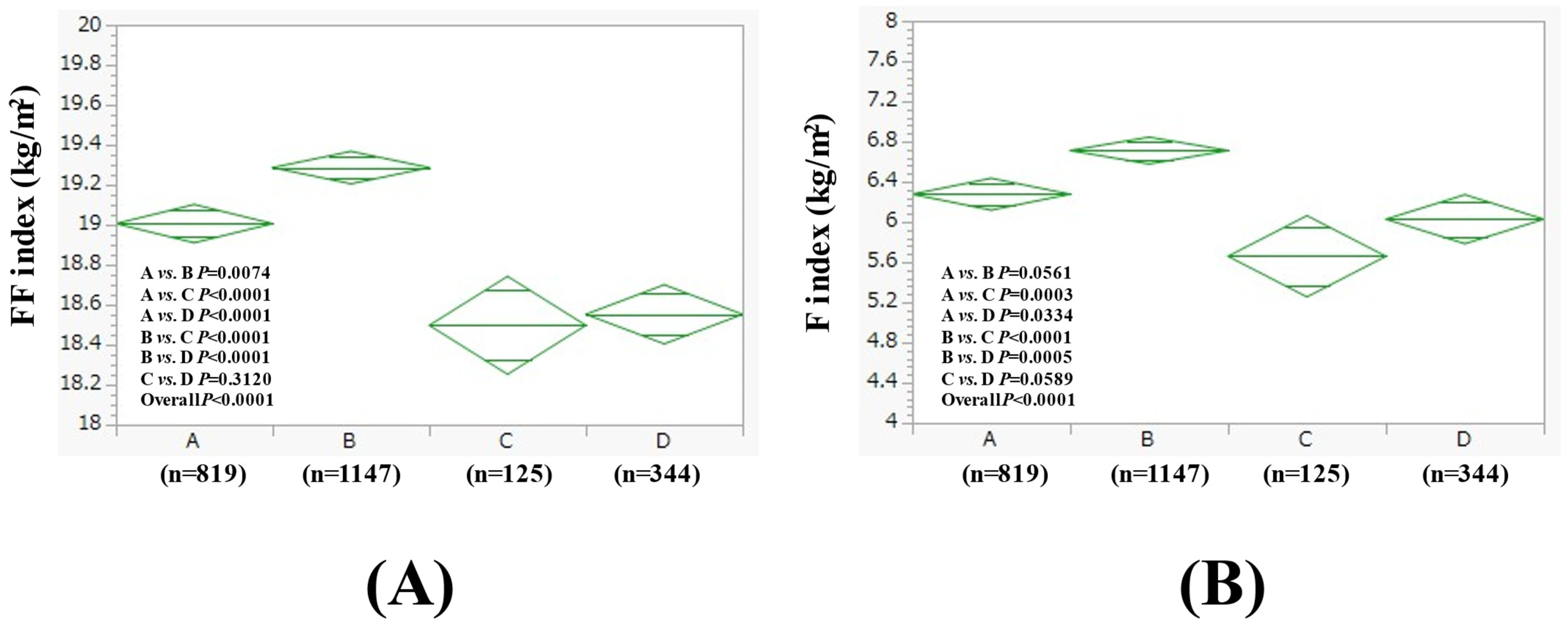
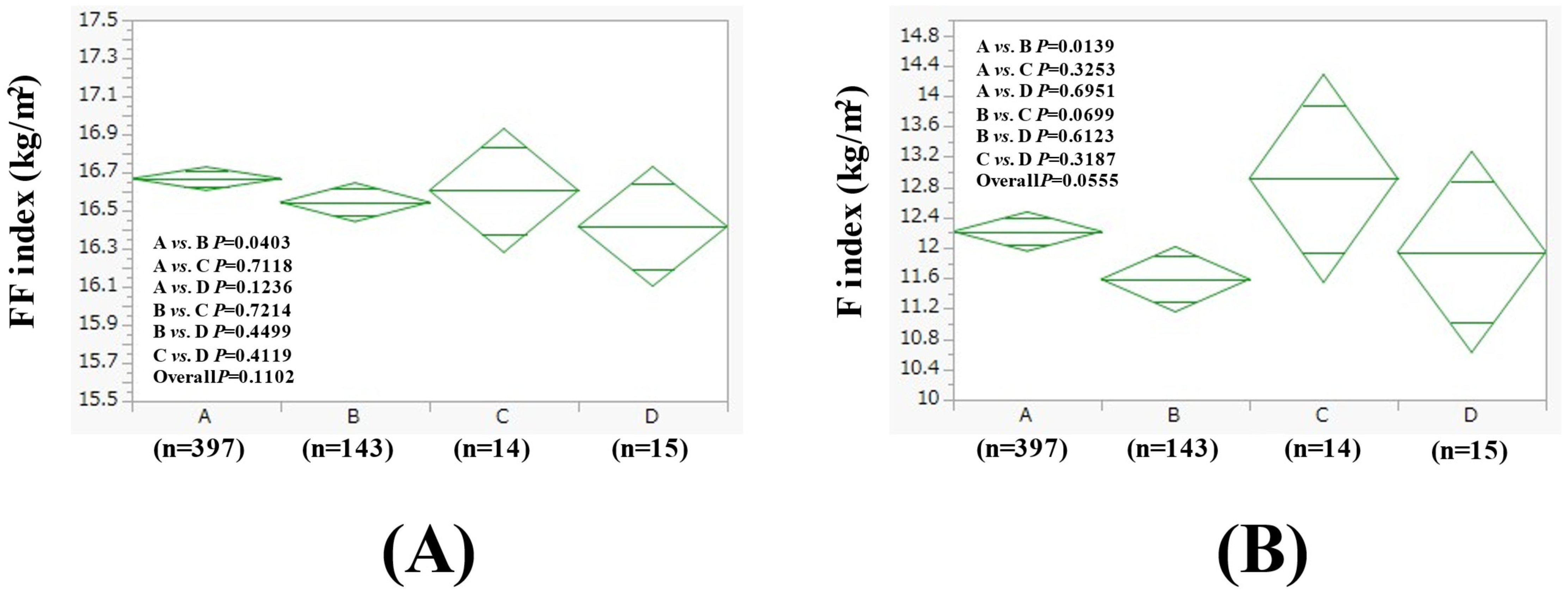
3.2. Comparison of FF Index and F Index Between Four Groups in Men
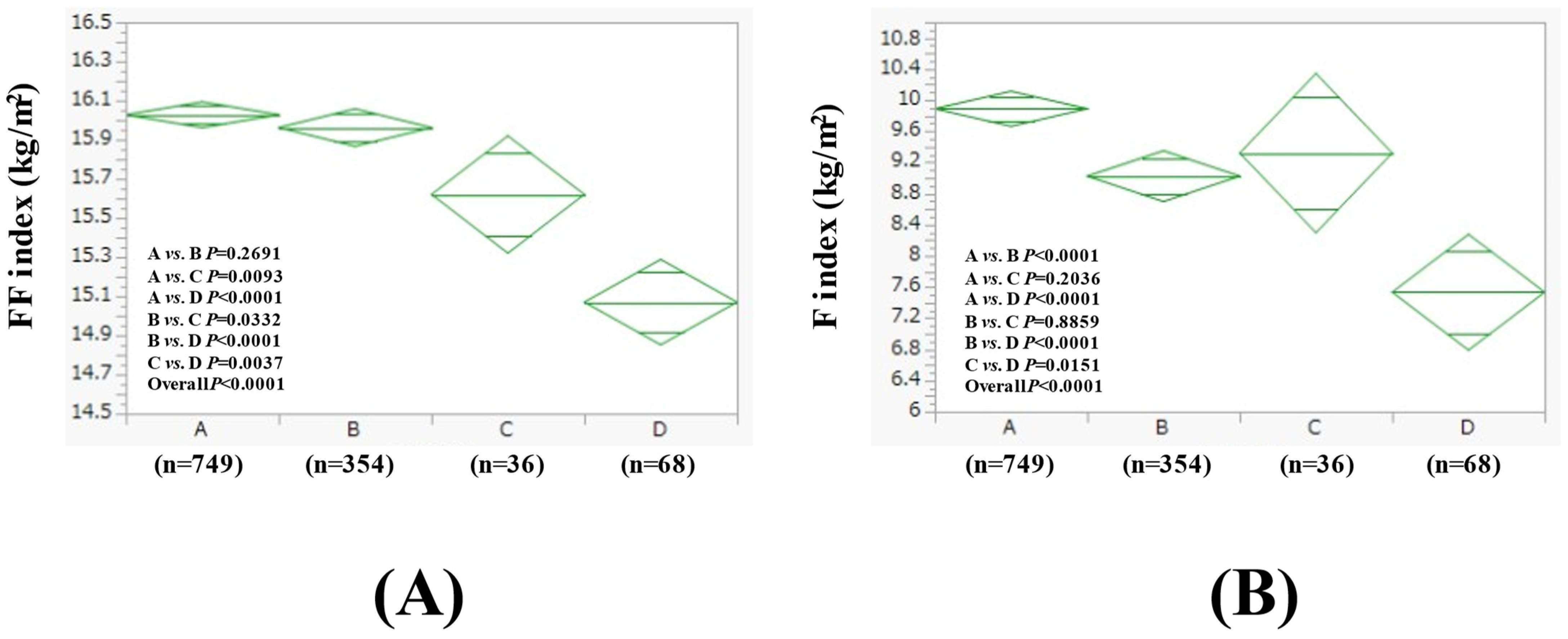
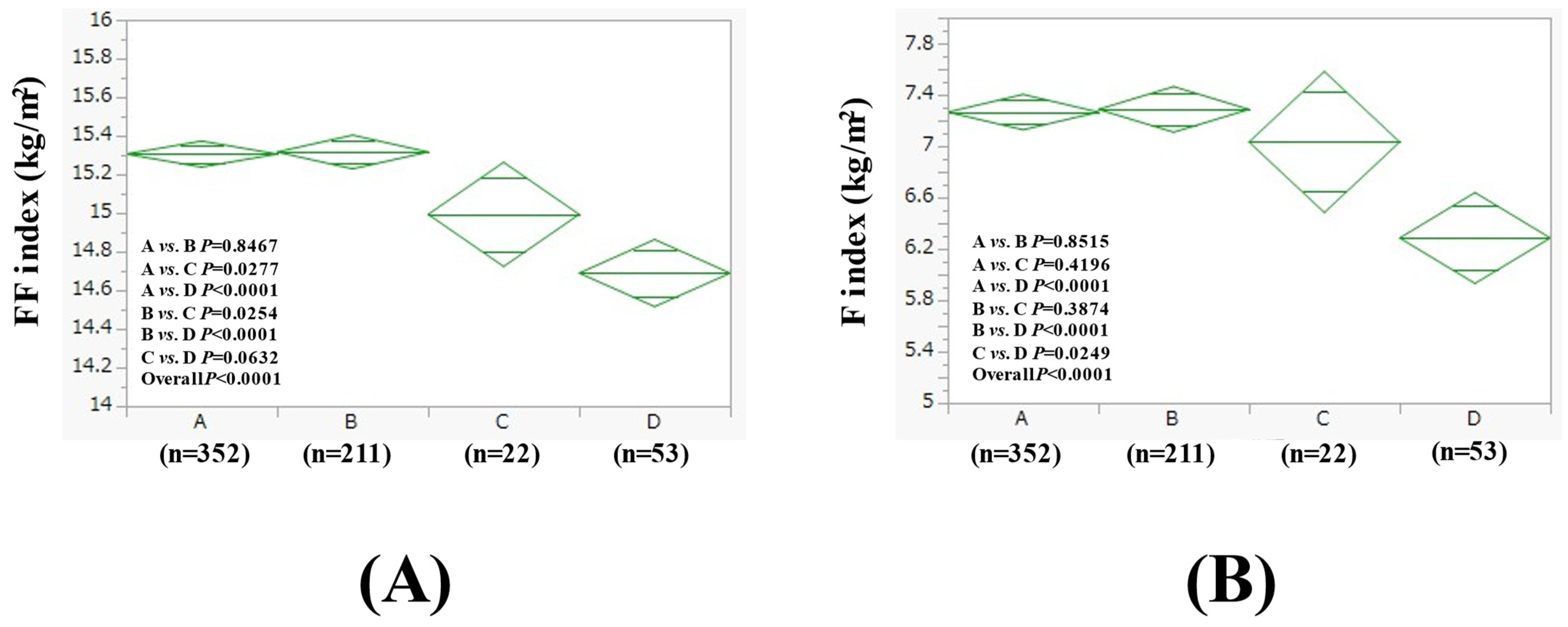
3.3. Comparison of FF Index and F Index Between Four Groups in Women
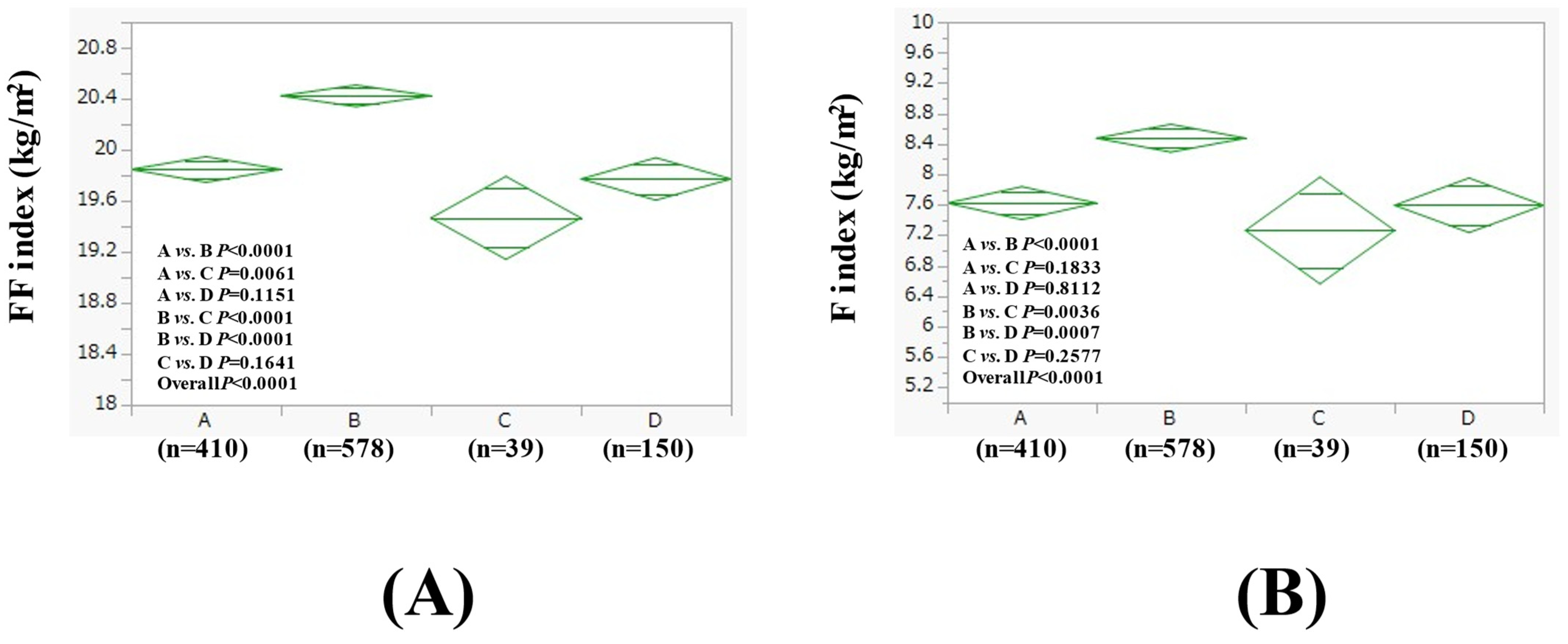
3.4. Subgroup Analysis 1: Comparison of FF Index and F Index Between Four Groups in Men with BMI > 25 kg/m2 and BMI ≤ 25 kg/m2
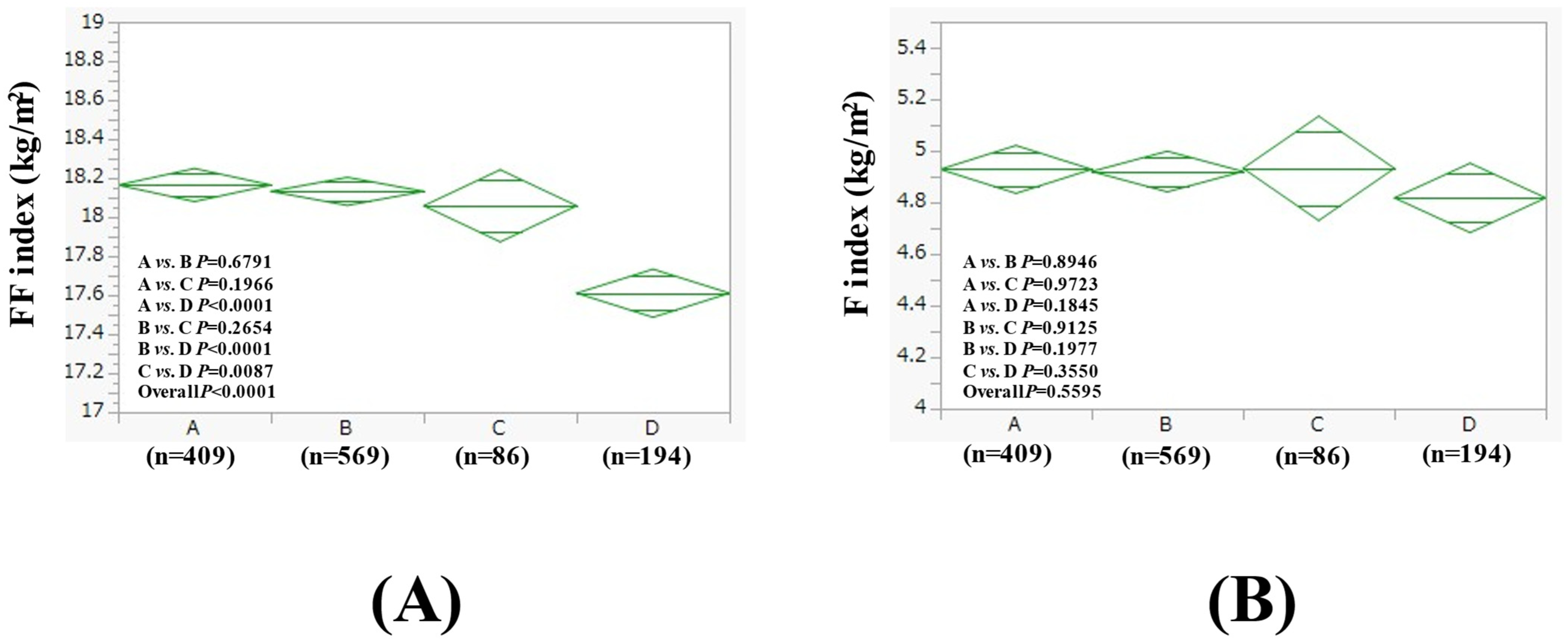
3.5. Subgroup Analysis 2: Comparison of FF Index and F Index Among Four Groups in Women with BMI > 25 kg/m2 and BMI ≤ 25 kg/m2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Higuchi, S.; Parrish, K.M.; Dufour, M.C.; Towle, L.H.; Harford, T.C. Relationship between age and drinking patterns and drinking problems among Japanese, Japanese-Americans, and Caucasians. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1994, 18, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_38541.html (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Osaki, Y.; Kinjo, A.; Higuchi, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Yuzuriha, T.; Horie, Y.; Kimura, M.; Kanda, H.; Yoshimoto, H. Prevalence and Trends in Alcohol Dependence and Alcohol Use Disorders in Japanese Adults; Results from Periodical Nationwide Surveys. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krittanawong, C.; Isath, A.; Rosenson, R.S.; Khawaja, M.; Wang, Z.; Fogg, S.E.; Virani, S.S.; Qi, L.; Cao, Y.; Long, M.T.; et al. Alcohol Consumption and Cardiovascular Health. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 1213–1230.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llamosas-Falcón, L.; Rehm, J.; Bright, S.; Buckley, C.; Carr, T.; Kilian, C.; Lasserre, A.M.; Lemp, J.M.; Zhu, Y.; Probst, C. The Relationship Between Alcohol Consumption, BMI, and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar]
- Hanai, T.; Nishimura, K.; Unome, S.; Miwa, T.; Nakahata, Y.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M. Alcohol-associated liver disease increases the risk of muscle loss and mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 932–940. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnardi, V.; Rota, M.; Botteri, E.; Tramacere, I.; Islami, F.; Fedirko, V.; Scotti, L.; Jenab, M.; Turati, F.; Pasquali, E.; et al. Alcohol consumption and site-specific cancer risk: A comprehensive dose-response meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 580–593. [Google Scholar]
- Rumgay, H.; Murphy, N.; Ferrari, P.; Soerjomataram, I. Alcohol and Cancer: Epidemiology and Biological Mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, E.; Rudd, J.H.F. Alcohol use disorders and the heart. Addiction 2019, 114, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, H.; Akuta, N.; Hikita, H.; Suda, G.; Inoue, J.; Tamaki, N.; Ito, K.; Akahane, T.; Kawaoka, T.; Morishita, A.; et al. Etiological changes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma-complicated liver cirrhosis in Japan: Updated nationwide survey from 2018 to 2021. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 54, 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, L.; Bourgeois, B.L.; Molina, P.E. Alcohol and Skeletal Muscle in Health and Disease. Alcohol Res. 2023, 43, 04. [Google Scholar]
- Oba, T.; Maeno, Y.; Ishida, K. Differential contribution of clinical amounts of acetaldehyde to skeletal and cardiac muscle dysfunction in alcoholic myopathy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Davuluri, G.; Alchirazi, K.A.; Welch, N.; Heit, C.; Kumar, A.; Gangadhariah, M.; Kim, A.; McMullen, M.R.; Willard, B.; et al. Ethanol sensitizes skeletal muscle to ammonia-induced molecular perturbations. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7231–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elamin, E.E.; Masclee, A.A.; Dekker, J.; Jonkers, D.M. Ethanol metabolism and its effects on the intestinal epithelial barrier. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, J.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease: Clinical and Molecular Advances. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.; Grossmann, M.; Hoermann, R.; Angus, P.W.; Gow, P.J. Testosterone therapy increases muscle mass in men with cirrhosis and low testosterone: A randomised controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentler, J.J.; LaPaglia, N.; Steiner, J.; Williams, D.; Castelli, M.; Kelley, M.R.; Emanuele, N.V.; Emanuele, M.A. Ethanol, growth hormone and testosterone in peripubertal rats. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 152, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, J.; Shepstone, L.; Hickson, M.; Welch, A.A. Alcohol Consumption and Measures of Sarcopenic Muscle Risk: Cross-Sectional and Prospective Associations Within the UK Biobank Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2023, 113, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, D.T. The effect of ethanol and its metabolites on carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1988, 18, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- You, M.; Arteel, G.E. Effect of ethanol on lipid metabolism. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.L.; Brady, G.F. Recent advances in MASLD genetics: Insights into disease mechanisms and the next frontiers in clinical application. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0618. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onishi, S.; Fukuda, A.; Matsui, M.; Ushiro, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Asai, A.; Kim, S.K.; Nishikawa, H. Body Composition Analysis in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiro, K.; Matsui, M.; Fukuda, A.; Onishi, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Asai, A.; Kim, S.K.; Nishikawa, H. Fatty liver index and somatic composition in subjects receiving medical health checkup. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 55, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, M.; Kojima, T.; Itoh, Y.; Harano, Y.; Fujii, K.; Nakajima, T.; Kato, T.; Takeda, N.; Okuda, J.; Ida, K.; et al. The severity of ultrasonographic findings in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease reflects the metabolic syndrome and visceral fat accumulation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar]
- Sumida, Y.; Shima, T.; Mitsumoto, Y.; Katayama, T.; Umemura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Itoh, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Okanoue, T. Epidemiology: Pathogenesis, and Diagnostic Strategy of Diabetic Liver Disease in Japan. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, P.K.; Wright, N.; Yang, L.; Chan, K.H.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Du, H.; Yang, X.; Avery, D.; Wang, S.; et al. Alcohol consumption and risks of more than 200 diseases in Chinese men. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Giovannucci, E.L. Body composition and mortality in the general population: A review of epidemiologic studies. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Wong, G.; Lee, E.I.; Akhtar, O.; Lopes, R.; Sumida, Y. Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in Japan: A focused literature review. JGH Open 2020, 4, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopidis, K.; Witard, O.C. Understanding the role of smoking and chronic excess alcohol consumption on reduced caloric intake and the development of sarcopenia. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2022, 35, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.A.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. Association of Sarcopenia and NAFLD: An Overview. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 16, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Jung, Y. Energy Metabolism Changes and Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism in Postmenopausal Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, J.; Huang, D.Q.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Kam, L.Y.; Tan, X.X.E.; et al. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shida, T.; Oshida, N.; Suzuki, H.; Okada, K.; Watahiki, T.; Oh, S.; Kim, T.; Isobe, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Ariizumi, S.I.; et al. Clinical and anthropometric characteristics of non-obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease subjects in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, N.; Hiraoka, A.; Nakai, M.; Shiraki, M.; Namisaki, T.; Miyaaki, H.; Hisanaga, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ohama, H.; Tada, F.; et al. Brief intervention for chronic liver disease patients with alcohol use disorder in a hepatology outpatient unit: Effects and limitations. Hepatol. Res. 2024, 54, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammock, K.; Velasquez, M.M.; Alwan, H.; von Sternberg, K. Alcohol Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT) for Girls and Women. Alcohol Res. 2020, 40, 07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, A.; Jensen, N.; Havighurst, T. Meta-analysis of randomized control trials addressing brief interventions in heavy alcohol drinkers. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 1997, 12, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palpacuer, C.; Duprez, R.; Huneau, A.; Locher, C.; Boussageon, R.; Laviolle, B.; Naudet, F. Pharmacologically controlled drinking in the treatment of alcohol dependence or alcohol use disorders: A systematic review with direct and network meta-analyses on nalmefene, naltrexone, acamprosate, baclofen and topiramate. Addiction 2018, 113, 220–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, S.; Takahashi, M.; Murai, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, K.; Nakamura, I.; Meulien, D.; Miyata, H. Long-term safety and efficacy of nalmefene in Japanese patients with alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 74, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Takahashi, M.; Murai, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, K.; Hayashi, T.; Meulien, D.; Sørensen, P.; Higuchi, S. Nalmefene in alcohol-dependent patients with a high drinking risk: Randomized controlled trial. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, D.; Curran, J.; Somerville, M.; Sinclair, D.; Wozney, L.; MacPhee, S.; Rose, A.E.; Boulos, L.; Caudrella, A. Harm reduction strategies in acute care for people who use alcohol and/or drugs: A scoping review. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Men (n = 2435) | Women (n = 1207) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 55.3 ± 10.9 | 56.8 ± 10.1 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.5 ± 3.5 | 25.4 ± 4.0 | 0.2110 |
| Group A/B/C/D | 819/1147/125/344 | 749/354/36/68 | <0.0001 |
| Severity of fatty liver through US mild/moderate/severe | 1150/975/310 | 643/437/127 | 0.0021 |
| WC (cm) | 90.2 ± 8.9 | 88.2 ± 9.6 | <0.0001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.1 ± 1.1 | 13.5 ± 1.1 | <0.0001 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 32.2 ± 22.4 | 24.8 ± 17.0 | <0.0001 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 56.2 ± 62.9 | 35.2 ± 41.7 | <0.0001 |
| Platelet count | 25.0 ± 5.4 | 27.3 ± 6.3 | <0.0001 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 146.8 ± 105.1 | 119.3 ± 69.2 | <0.0001 |
| Fatty liver index | 46.4 ± 25.0 | 36.1 ± 24.4 | <0.0001 |
| FIB4 index | 1.15 ± 0.58 | 1.11 ± 0.48 | 0.5322 |
| FBS (mg/dL) | 100.2 ± 20.1 | 96.6 ± 17.0 | <0.0001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.4 ± 1.3 | 5.3 ± 1.1 | <0.0001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 69.7 ± 13.2 | 72.0 ± 13.5 | <0.0001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 126.2 ± 15.8 | 125.9 ± 17.2 | 0.1795 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 82.1 ± 11.6 | 77.3 ± 11.6 | <0.0001 |
| FF index (kg/m2) | 19.0 ± 1.4 | 15.9 ± 0.9 | <0.0001 |
| F index (kg/m2) | 6.4 ± 2.3 | 9.5 ± 3.2 | <0.0001 |
| Men (n = 2435) | Group A (n = 819) | Group B (n = 1147) | Group C (n = 125) | Group D (n = 344) | Overall p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 55.1 ± 11.6 | 54.9 ± 10.4 | 55.8 ± 11.6 | 56.7 ± 10.0 | 0.0226 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.3 ± 2.8 | 26.0 ± 4.1 | 24.2 ± 2.2 | 24.6 ± 3.2 | <0.0001 |
| Severity of fatty liver on US, mild/moderate/severe | 368/121/330 | 526/161/460 | 67/6/52 | 189/22/133 | <0.0001 |
| WC (cm) | 89.6 ± 7.8 | 91.2 ± 9.9 | 87.6 ± 6.6 | 89.0 ± 8.3 | <0.0001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.1 ± 1.1 | 15.2 ± 1.0 | 15.1 ± 1.0 | 15.1 ± 1.1 | 0.2241 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 31.7 ± 19.6 | 33.1 ± 25.1 | 28.6 ± 17.0 | 31.7 ± 20.2 | 0.1300 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 40.0 ± 31.3 | 54.2 ± 55.4 | 59.8 ± 53.7 | 100.0 ± 109.1 | <0.0001 |
| Platelet count (/μL) | 25.2 ± 5.4 | 25.1 ± 5.6 | 24.3 ± 5.4 | 24.5 ± 5.2 | 0.1458 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 4.4 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.3 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 139.8 ± 104.1 | 144.6 ± 99.2 | 164.0 ± 112.5 | 164.7 ± 120.7 | 0.0172 |
| Fatty liver index | 41.9 ± 22.6 | 48.2 ± 26.0 | 43.5 ± 24.2 | 52.0 ± 25.9 | <0.0001 |
| FIB4 index | 1.08 ± 0.58 | 1.13 ± 0.51 | 1.23 ± 0.61 | 1.35 ± 0.72 | <0.0001 |
| FBS (mg/dL) | 98.0 ± 16.7 | 101.1 ± 21.6 | 100.9 ± 18.8 | 102.1 ± 22.5 | 0.0013 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 6.2 ± 1.3 | 6.5 ± 1.2 | 6.4 ± 1.1 | 6.4 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 68.8 ± 12.9 | 69.6 ± 13.1 | 71.5 ± 11.7 | 71.8 ± 14.2 | 0.0015 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 123.6 ± 15.6 | 126.7 ± 15.4 | 126.1 ± 15.4 | 130.8 ± 16.8 | <0.0001 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 79.8 ± 11.5 | 82.7 ± 11.4 | 82.3 ± 11.2 | 85.5 ± 11.7 | <0.0001 |
| Women (n = 1207) | Group A (n = 749) | Group B (n = 354) | Group C (n = 36) | Group D (n = 68) | Overall p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 56.2 ± 9.9 | 57.8 ± 9.9 | 52.5 ± 8.8 | 59.3 ± 12.0 | 0.0007 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.9 ± 4.0 | 24.8 ± 3.6 | 24.9 ± 4.7 | 22.6 ± 3.8 | <0.0001 |
| Severity of fatty liver on US, mild/moderate/severe | 375/93/281 | 204/27/123 | 21/5/10 | 43/2/23 | 0.0203 |
| WC (cm) | 89.1 ± 9.7 | 87.3 ± 9.1 | 87.2 ± 9.5 | 83.6 ± 8.7 | <0.0001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5 ± 1.1 | 13.4 ± 1.0 | 13.3 ± 1.3 | 13.4 ± 1.3 | 0.5860 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 25.7 ± 18.2 | 23.8 ± 15.9 | 23.1 ± 9.6 | 21.3 ± 11.1 | 0.0952 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 32.1 ± 29.8 | 34.9 ± 34.6 | 38.7 ± 27.9 | 69.1 ± 116.0 | <0.0001 |
| Platelet count (/μL) | 27.6 ± 6.4 | 26.9 ± 5.6 | 27.9 ± 6.9 | 27.0 ± 8.4 | 0.4337 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 0.2766 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 118.2 ± 62.4 | 119.3 ± 58.7 | 126.4 ± 74.6 | 126.7 ± 147.2 | 0.7194 |
| Fatty liver index | 37.6 ± 24.9 | 34.0 ± 23.0 | 38.3 ± 27.8 | 29.9 ± 22.8 | 0.0183 |
| FIB4 index | 1.07 ± 0.45 | 1.14 ± 0.46 | 0.95 ± 0.31 | 1.47 ± 0.77 | <0.0001 |
| FBS (mg/dL) | 97.1 ± 18.6 | 96.1 ± 14.1 | 94.8 ± 13.5 | 94.4 ± 13.5 | 0.4886 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.2 ± 1.0 | 5.3 ± 1.1 | 5.3 ± 1.1 | 5.4 ± 1.1 | 0.5568 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 71.8 ± 13.3 | 71.3 ± 13.2 | 75.1 ± 13.3 | 75.6 ± 16.6 | 0.0463 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 125.9 ± 16.8 | 125.0 ± 17.3 | 123.4 ± 18.4 | 131.5 ± 19.1 | 0.0289 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 77.6 ± 11.3 | 76.4 ± 11.5 | 79.7 ± 15.1 | 78.7 ± 13.3 | 0.1720 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matsui, M.; Fukuda, A.; Onishi, S.; Ushiro, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Asai, A.; Kim, S.K.; Nishikawa, H. Impact of Alcohol Intake on Body Composition in Patients with Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061092
Matsui M, Fukuda A, Onishi S, Ushiro K, Nishikawa T, Asai A, Kim SK, Nishikawa H. Impact of Alcohol Intake on Body Composition in Patients with Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061092
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatsui, Masahiro, Akira Fukuda, Saori Onishi, Kosuke Ushiro, Tomohiro Nishikawa, Akira Asai, Soo Ki Kim, and Hiroki Nishikawa. 2025. "Impact of Alcohol Intake on Body Composition in Patients with Steatotic Liver Disease" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061092
APA StyleMatsui, M., Fukuda, A., Onishi, S., Ushiro, K., Nishikawa, T., Asai, A., Kim, S. K., & Nishikawa, H. (2025). Impact of Alcohol Intake on Body Composition in Patients with Steatotic Liver Disease. Nutrients, 17(6), 1092. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061092







