Recovery of Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Vegetarians Consuming the Upper and Lower Ends of Protein Recommendations for Athletes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Visit 1: Diet Recall
2.3. Visits 2–5: Start of Phase One/Baseline Measurements/Familiarization
2.4. Power
2.5. Isometric Contractions
2.6. Concentric Contractions at 60, 180, and 240 Degrees per Second
2.7. Supplements
2.8. Visit 6: Supplement/Muscle Damage Protocol
2.9. 10 cm Visual Analog Scale
2.10. Pain Upon Use Test
2.11. Visits: 7–11
2.12. Washout Period
2.13. Visit 12: Start of Phase Two/Reestablishing Baseline
2.14. Visit 13
2.15. Visit 14–18
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Strength: Isometric
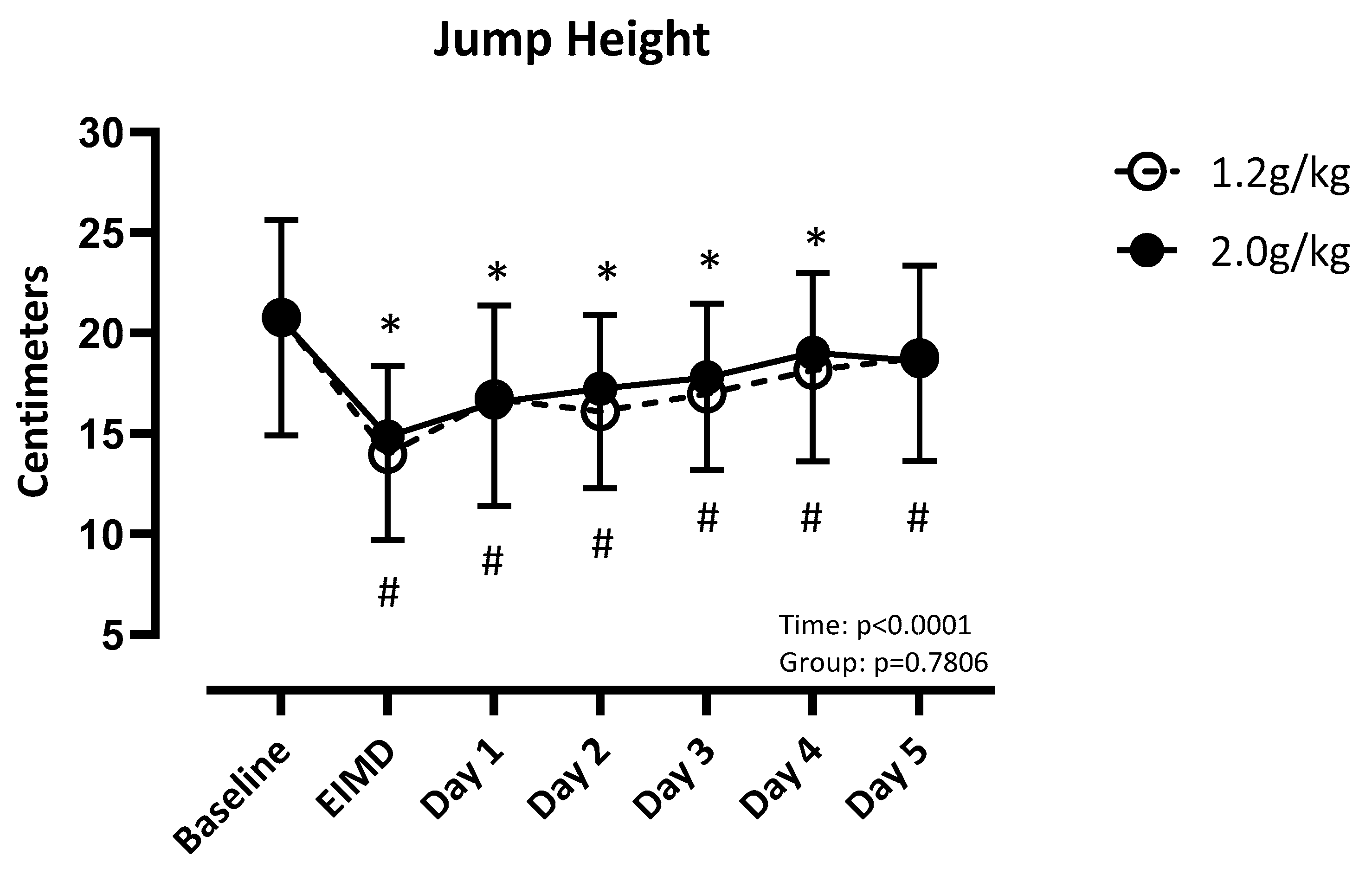
3.2. Power: Vertical Jump
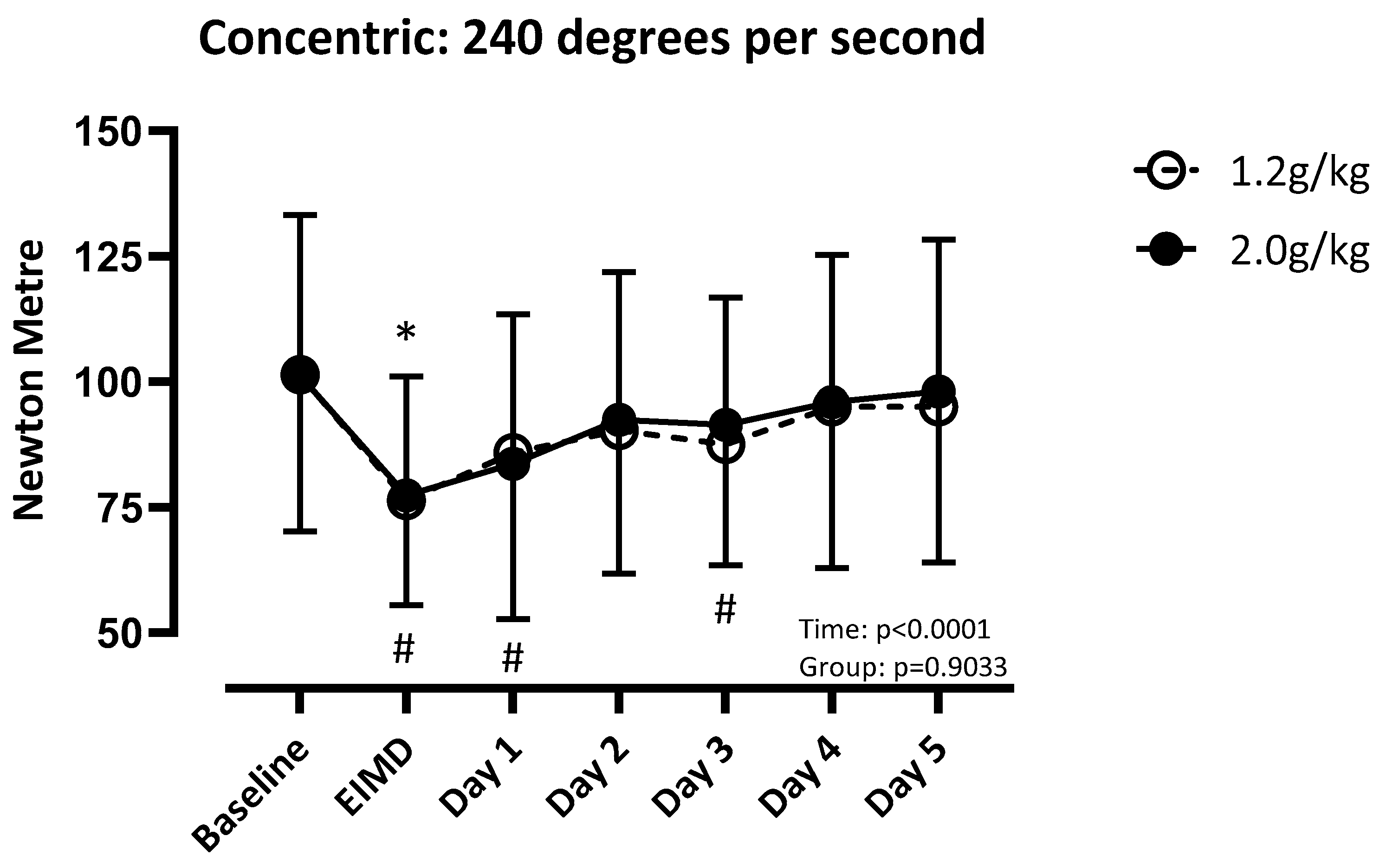
3.3. Concentric Strength
3.4. Soreness
3.5. Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kon, M.; Tanabe, K.; Lee, H.; Kimura, F.; Akimoto, T.; Kono, I. Eccentric muscle contractions induce greater oxidative stress than concentric contractions in skeletal muscle. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damas, F.; Nosaka, K.; Libardi, C.A.; Chen, T.C.; Ugrinowitsch, C. Susceptibility to Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Cluster Analysis with a Large Sample. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.; Eston, R.G.; Edwards, R.H. Characteristics of isometric and dynamic strength loss following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2001, 11, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twist, C.; Eston, R. The effects of exercise-induced muscle damage on maximal intensity intermittent exercise performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 94, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hody, S.; Croisier, J.L.; Bury, T.; Rogister, B.; Leprince, P. Eccentric Muscle Contractions: Risks and Benefits. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHugh, M.P.; Connolly, D.A.; Eston, R.G.; Gleim, G.W. Electromyographic analysis of exercise resulting in symptoms of muscle damage. J. Sports Sci. 2000, 18, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, L.M. Chapter 15: Elite Athletes. In Sports Nutrition: A Handbook for Professionals, 6th ed.; Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Chicago: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Köhne, J.L.; Ormsbee, M.J.; McKune, A.J. Supplementation strategies to reduce muscle damage and improve recovery following exercise in females: A systematic review. Sports 2016, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranchordas, M.K.; Dawson, J.T.; Russell, M. Practical nutritional recovery strategies for elite soccer players when limited time separates repeated matches. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicine, I.O. Dietary Reference Intakes: The Essential Guide to Nutrient Requirements; Otten, J.H.J.J., Meyers, L.D., Eds.; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pinckaers, P.J.; Trommelen, J.; Snijders, T.; van Loon, L.J. The anabolic response to plant-based protein ingestion. Sports Med. 2021, 51 (Suppl. S1), 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kniskern, M.A.; Johnston, C.S. Protein dietary reference intakes may be inadequate for vegetarians if low amounts of animal protein are consumed. Nutrition 2011, 27, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson-Meyer, D.E. Chapter 16: Vegetarian Athletes 2017. In Sports Nutrition, 6th ed.; Karpinski, C., Ed.; Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Chicago: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ciuris, C.; Lynch, H.M.; Wharton, C.; Johnston, C.S. A Comparison of Dietary Protein Digestibility, Based on DIAAS Scoring, in Vegetarian and Non-Vegetarian Athletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, A. An overview of anti-nutritional factors in food. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Smulikowska, S.; Pastuszewska, B.; Swiech, E.; Ochtabinska, A.; Mieczkowska, A.; Nguyen, V.; Buraczewska, L. Tannin content affects negatively nutritive value of pea for monogastrics. J. Anim. Feed. Sci. 2001, 10, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomoskozi, S.; Lasztity, R.; Haraszi, R.; Baticz, O. Isolation and study of the functional properties of pea proteins. Nahrung 2001, 45, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Anthropometrics | |
|---|---|
| Height | 170 ± 6.8 cm |
| Mass | 68.2 ± 10 kg |
| BMI | 23.5 ± 2.5 kg/m2 |
| Age | 23.5 ± 2.4 yr |
| Sex | |
| Female | n = 7 |
| Male | n = 9 |
| Race | |
| Asian | n = 9 |
| White | n = 5 |
| Black | n = 1 |
| Mix | n = 1 |
| Diet (g) | Average | 1.2 g/kg | 2.0 g/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 1833.2 ± 523.5 | 1824.6 ± 483.3 | 1841.8 ± 576.8 |
| Fat | 65.0 ± 29.9 | 63.0 ± 25.9 | 67.0 ± 34.2 |
| Carbohydrates | 255.0 ± 85.5 | 258.3 ± 88.5 | 251.7 ± 85.1 |
| Protein | 62.4 ± 20.3 | 60.8 ± 16.1 | 64.0 ± 24.3 |
| Animal protein | 19.5 ± 13.8 | 19.4 ± 11.8 | 19.5 ± 16 |
| Plant protein | 42.9 ± 16.4 | 41.4 ± 15.5 | 44.5 ± 17.7 |
| Diet (g/kg) | Average | 1.2 g/kg | 2.0 g/kg |
| Energy | 27.2 ± 7.8 | 27.2 ± 7.8 | 27.2 ± 8.2 |
| Fat | 1.1 ± 0.5 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.6 |
| Carbohydrates | 3.8 ± 1.3 | 3.9 ± 1.4 | 3.7 ± 1.3 |
| Protein | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.9 ± 0.3 |
| Animal protein | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 |
| Plant protein | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.3 |
| Essential Amino Acids (g) | Average | 1.2 g/kg | 2.0 g/kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tryptophan | 0.8 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.3 | 0.8 ± 0.3 |
| Threonine | 2.3 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 0.9 |
| Isoleucine | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 1.0 |
| Leucine | 4.8 ± 1.6 | 4.7 ± 1.2 | 5.0 ± 1.9 |
| Lysine | 3.3 ± 1.3 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 1.6 |
| Methionine | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.5 |
| Phenylalanine | 3.0 ± 1.1 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 3.0 ± 1.3 |
| Valine | 3.3 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 1.3 |
| Histidine | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.7 |
| Essential Amino Acids (g/kg) | Average | 1.2 g/kg | 2.0 g/kg |
| Tryptophan | 0.01 ± 0 | 0.01 ± 0 | 0.01 ± 0 |
| Threonine | 0.03 ± 0 | 0.03 ± 0 | 0.03 ± 0 |
| Isoleucine | 0.04 ± 0 | 0.04 ± 0 | 0.04 ± 0 |
| Leucine | 0.07 ± 0 | 0.07 ± 0 | 0.07 ± 0 |
| Lysine | 0.05 ± 0 | 0.05 ± 0 | 0.05 ± 0 |
| Methionine | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.5 |
| Phenylalanine | 0.04 ± 0 | 0.04 ± 0 | 0.04 ± 0 |
| Valine | 0.05 ± 0 | 0.05 ± 0 | 0.05 ± 0 |
| Histidine | 0.02 ± 0 | 0.02 ± 0 | 0.02 ± 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Presti, N.; Rideout, T.C.; Temple, J.L.; Bratta, B.; Hostler, D. Recovery of Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Vegetarians Consuming the Upper and Lower Ends of Protein Recommendations for Athletes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061046
Presti N, Rideout TC, Temple JL, Bratta B, Hostler D. Recovery of Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Vegetarians Consuming the Upper and Lower Ends of Protein Recommendations for Athletes. Nutrients. 2025; 17(6):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061046
Chicago/Turabian StylePresti, Nicole, Todd C. Rideout, Jennifer L. Temple, Brian Bratta, and David Hostler. 2025. "Recovery of Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Vegetarians Consuming the Upper and Lower Ends of Protein Recommendations for Athletes" Nutrients 17, no. 6: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061046
APA StylePresti, N., Rideout, T. C., Temple, J. L., Bratta, B., & Hostler, D. (2025). Recovery of Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage in Vegetarians Consuming the Upper and Lower Ends of Protein Recommendations for Athletes. Nutrients, 17(6), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17061046






