Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in the 21st Century—An Overview of 1415 Consecutive Dysphagic Adult Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Underlying Conditions
- Neurological disorders with a progressive course (such as neurodegenerative diseases);
- Neurological disorders with a potentially regressive course (conditions resulting from sudden aggression, such as stroke or head trauma, where patients tend to improve over time);
- Head and neck cancer/esophageal cancer (HNC/EC);
- Other conditions that do not fit in the three previous groups.
2.4. Clinical Outcome
2.5. Anthropometric Evaluation
2.6. Laboratory Evaluation
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Underlying Conditions
3.3. Anthropometric and Laboratory Evaluation
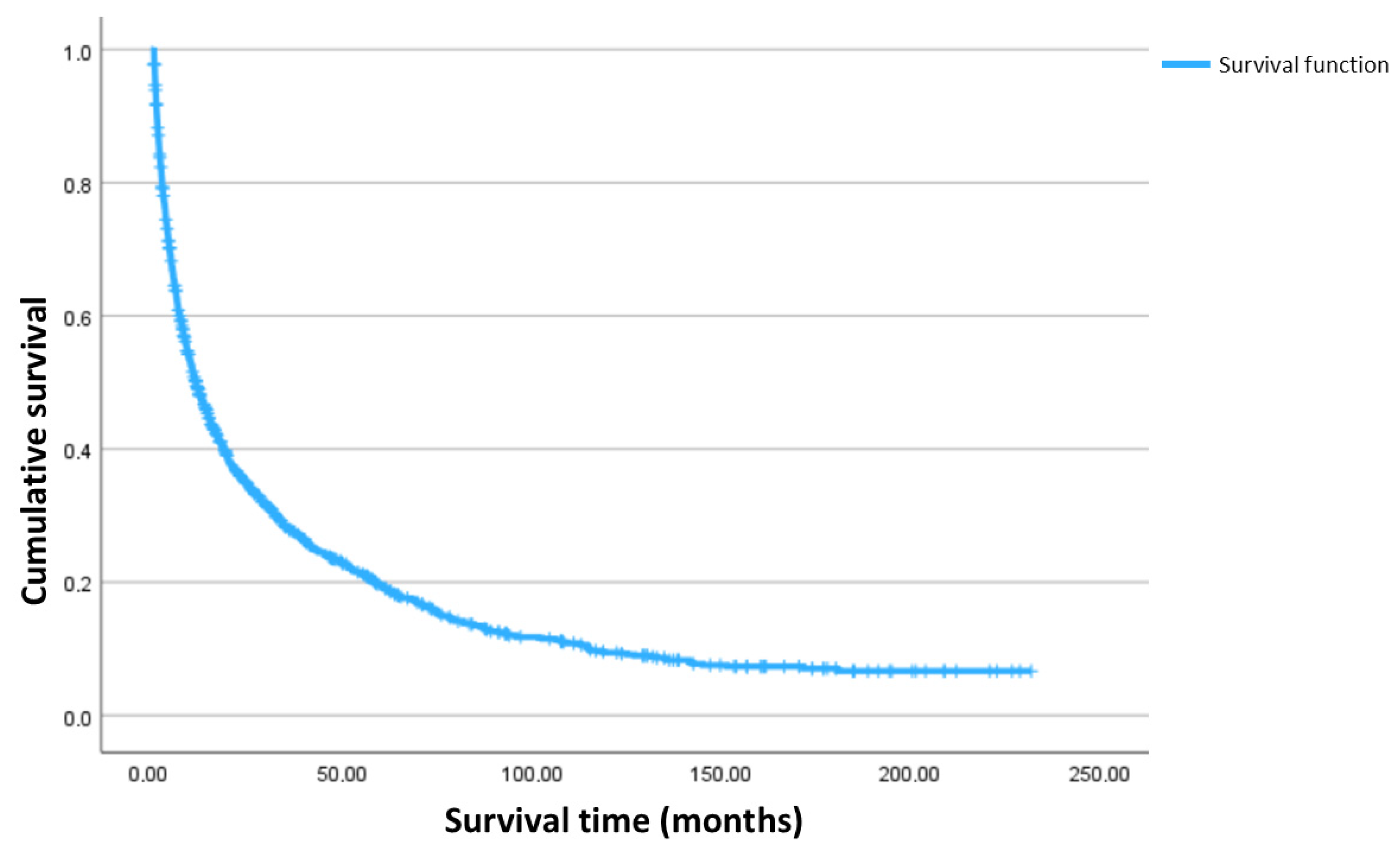
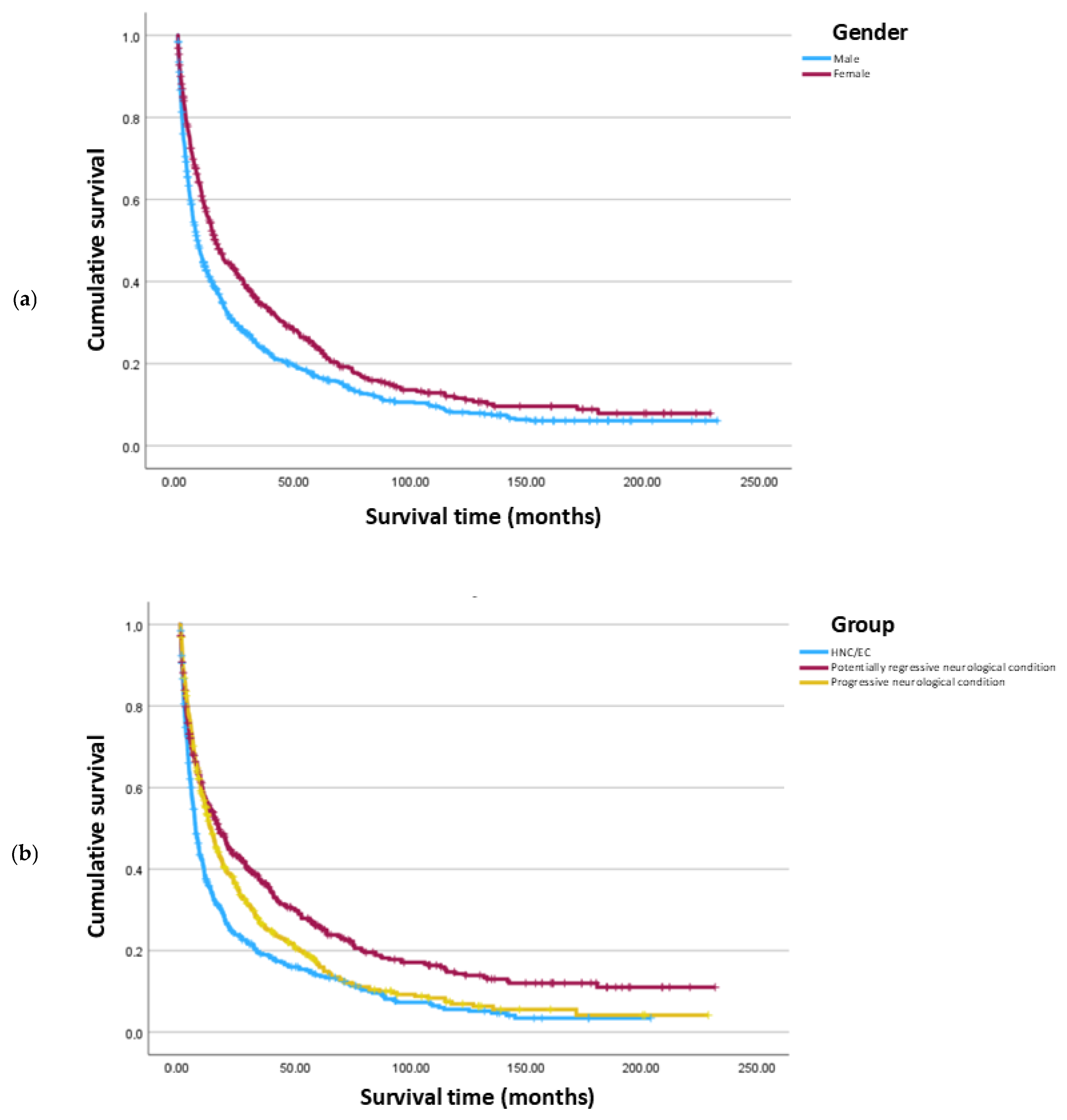
3.4. Clinical Outcome
- Being female is associated with a 60.4% lower risk of death, indicating a significantly reduced hazard compared to males.
- Older age is associated with an increased hazard. Each additional year increases the risk of death by 2.0%.
- Compared to those with a progressive neurological condition, patients with potentially regressive neurological conditions have a decreased hazard, with a 20.9% lower risk of death, while patients with HNC/EC have an increased hazard, with a 39.1% higher risk of death. Patients in the HNC/EC group have an increased hazard compared to patients with potentially regressive neurological conditions, with 75.8% higher risk of death. Patients with other conditions do not differ significantly from the neurological and HNC/EC groups.
- Higher BMI is associated with a reduced hazard. Each unit increase in BMI decreases the risk of death by 3.7%.
- Higher albumin levels are associated with a decreased hazard. Each unit increase in albumin decreases the risk of death by 31.3%.
- A significant interaction between gender, BMI and albumin was observed, indicating that the combined effect of BMI and albumin on survival varies by gender. Specifically, for every one-unit increase in the product of albumin and BMI, the risk of death is approximately 0.8% higher in females when compared to males. This suggests that higher BMI and albumin levels provide greater protection against mortality in males than in females (although they remain protective in females, their effect is slightly attenuated).
- Transferrin and total cholesterol were not significantly associated with survival (p > 0.05).
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malagelada, J.R.; Bazzoli, F.; Boeckxstaens, G.; De Looze, D.; Fried, M.; Kahrilas, P.; Lindberg, G.; Malfertheiner, P.; Salis, G.; Sharma, P.; et al. World gastroenterology organisation global guidelines: Dysphagia—Global guidelines and cascades update September 2014. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 40, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueshima, J.; Momosaki, R.; Shimizu, A.; Motokawa, K.; Sonoi, M.; Shirai, Y.; Uno, C.; Kokura, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Nishiyama, A.; et al. Nutritional Assessment in Adult Patients with Dysphagia: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión, S.; Cabré, M.; Monteis, R.; Roca, M.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M.; Rofes, L.; Clavé, P. Oropharyngeal dysphagia is a prevalent risk factor for malnutrition in a cohort of older patients admitted with an acute disease to a general hospital. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanar, V.; Lohrmann, C.; Amir, Y.; Eglseer, D. Dysphagia and factors associated with malnutrition risk: A 5-year multicentre study. J. Adv. Nurs. 2019, 75, 3566–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, B.; Zirtil, C.; Erten, S.N.; Akpinar, T.S.; Altinkaynak, M.; Akyuz, F.; Cavus, B.; Ozmen, B.; Buyukdemir, S.; Tascıoglu, C. Indications, effectiveness and safety of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: A single center experience and literature review. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 30, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Arvanitakis, M.; Despott, E.J.; Ballarin, A.; Beyna, T.; Boeykens, K.; Elbe, P.; Gisbertz, I.; Hoyois, A.; Mosteanu, O.; et al. Endoscopic management of enteral tubes in adult patients—Part 2: Peri- and post-procedural management. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 178–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, E.; Pitts, N.; Latchford, A.; Lewis, S. A large prospective audit of morbidity and mortality associated with feeding gastrostomies in the community. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Austin, P.; Boeykens, K.; Chourdakis, M.; Cuerda, C.; Jonkers-Schuitema, C.; Lichota, M.; Nyulasi, I.; Schneider, S.M.; Stanga, Z.; et al. ESPEN guideline on home enteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friginal-Ruiz, A.B.; Lucendo, A.J. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy: A Practical Overview on Its Indications, Placement Conditions, Management, and Nursing Care. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2015, 38, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnemai-Azar, A.A.; Rahnemaiazar, A.A.; Naghshizadian, R.; Kurtz, A.; Farkas, D.T. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: Indications, technique, complications and management. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 28, 7739–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Friginal-Ruiz, A.B. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: An update on its indications, management, complications, and care. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2014, 106, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, J.; Santos, C.A.; Brito, J. Predicting survival of endoscopic gastrostomy candidates using the underlying disease, serum cholesterol, albumin and transferrin levels. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Welbank, T.; Kurien, M. To PEG or not to PEG that is the question. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.L.; Miranda, L.E.C.; Lima, R.N.C.L.; Romero-Velez, G.; Chin, R.; Shadduck, P.P.; Sreeramoju, P. Factors Associated with Mortality after Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy. JSLS J. Soc. Laparosc. Robot. Surg. 2023, 27, e2023.00005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.; Santos, C.A.; Brito, J. Malnutrition and Clinical Outcome of 234 Head and Neck Cancer Patients who Underwent Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Catita, D.; Ferreira-Santos, C.; Mascarenhas, P.; Oliveira, C.; Madeira, R.; Santos, C.A.; André, C.; Godinho, C.; Antunes, L.; Fonseca, J. Malnutrition, Cancer Stage and Gastrostomy Timing as Markers of Poor Outcomes in Gastrostomy-Fed Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderloni, A.; Di Leo, M.; Barzaghi, F.; Semeraro, R.; Meucci, G.; Marino, R.; Amato, L.; Frigerio, M.; Saladino, V.; Toldi, A.; et al. Complications and early mortality in percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement in lombardy: A multicenter prospective cohort study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zopf, Y.; Maiss, J.; Konturek, P.; Rabe, C.; Hahn, E.G.; Schwab, D. Predictive factors of mortality after PEG insertion: Guidance for clinical practice. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udd, M.; Lindström, O.; Mustonen, H.; Bäck, L.; Halttunen, J.; Kylänpää, L. Assessment of indications for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy–development of a predictive model. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbeit, W.; Kadah, A.; Mari, A.; Mahamid, M.; Khoury, T. Simple bedside predictors of survival after percutaneous gastrostomy tube insertion. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 1532918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cúrdia, G.T.; Marinho, C.; Magalhães, J.; Barbosa, M.; Monteiro, S.; Dias de Castro, F.; Boal Carvalho, P.; Rosa, B.; Figueiredo, L.; Cotter, J. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: Confirming the clinical benefits far beyond anthropometry. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limpias Kamiya, K.J.L.; Hosoe, N.; Takabayashi, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Mutaguchi, M.; Nakamura, R.; Kawakubo, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Ogata, H.; et al. Factors predicting major complications, mortality, and recovery in percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. JGH Open 2021, 5, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumaste, V.V.; Bhamidimarri, K.R.; Bansal, R.; Sidhu, L.; Baum, J.; Walfish, A. Factors predicting early discharge and mortality in post-percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy patients. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duzenli, T.; Ketenci, M.; Akyol, T.; Koseoglu, H.; Tanolu, A.; Kaplan, M.; Yazgan, Y. Predictive factors of complications and 30-day mortality in patients undergoing percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: The utility of c-reactive protein to albumin ratio. Acta Gastro-Enterol. Belg. 2021, 84, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Im, J.P.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.E.; Ryu, D.Y.; Cha, J.M.; Kim, E.Y.; Kim, E.R.; Chang, D.K. Risk factors for complications and mortality of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: A multicenter, retrospective study. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 3806–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, R.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; Caponi, A.; Gibiino, G.; Eusebi, L.H.; Azzaroli, F.; Brighi, N.; Altimari, G.; Bazzoli, F. Severe hypernatremia as a predictor of mortality after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) placement. Dig. Liver. Dis. 2017, 49, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Tuck, J.; Hennessy, E.M.A. Comparison of mid upper arm circumference, body mass index and weight loss as indices of undernutrition in acutely hospitalized patients. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barosa, R.; Roque Ramos, L.; Santos, C.A.; Pereira, M.; Fonseca, J. Mid upper arm circumference and Powell-Tuck and Hennessy’s equation correlate with body mass index and can be used sequentially in gastrostomy fed patients. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas Deza, D.; Monzón Baez, R.M.; Lamuela Calvo, L.J.; Betoré Glaria, E.; Montil Miguel, E.; Julián Gomara, B.; Vicente Lidón, R. Complications and survival following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2024, 116, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peláez, R.B.; Segurola, H.G.; Lesmes, I.B. Nutritional support in stroke patients. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 29, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ojo, O.; Brooke, J. The Use of Enteral Nutrition in the Management of Stroke. Nutrients 2016, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.M. Nutritional Support in Stroke. ESPEN LLL Programme 2021. Module 25.2. Available online: https://www.espen.org/education/lll-programme (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Rowat, A. Enteral tube feeding for dysphagic stroke patients. Br. J. Nurs. 2015, 24, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavan, J. Update on management options for dysphagia after stroke. Br. J. Neurosci. Nurs. 2015, 11, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R. Nutritional Support in Dementia. ESPEN LLL Programme 2021. Module 25.4. Available online: https://www.espen.org/education/lll-programme (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Van Damme, P.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Andersen, P.M.; Chiò, A.; Couratier, P.; de Carvalho, M.; Hardiman, O.; Kuzma-Kozakiewicz, M.; Ludolph, A.; McDermott, C.J.; et al. European Academy of Neurology (EAN) guideline on the management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in collaboration with European Reference Network for Neuromuscular Diseases (ERN EURO-NMD). Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, e16264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Viggiani, M.T.; Introna, A.; D’errico, E.; Scarafino, A.; Iannone, A.; Di Leo, A.; Simone, I.L. Nutritional prognostic factors for survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients undergone percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, H.D.; Benatar, M. Enteral tube feeding for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011, 1, CD004030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Sun, L.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, X. Therapeutic effects of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy on survival in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, R. Nutritional Support in Chronic Neurological Conditions. ESPEN LLL Programme 2021. Module 25.3. Available online: https://www.espen.org/education/lll-programme (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Marshall, K.M.; Loeliger, J.; Nolte, L.; Kelaart, A.; Kiss, N.K. Prevalence of malnutrition and impact on clinical outcomes in cancer services: A comparison of two time points. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.; Givi, B.; Moore, M.G. AHNS Series—Do you know your guidelines?: Assessment and management of malnutrition in patients with head and neck cancer: Review of the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines In Oncology (NCCN Guidelines). Head Neck 2019, 41, 577–583. [Google Scholar]
- Arends, J. Malnutrition in cancer patients: Causes, consequences and treatment options. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 50, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, M.; Gkolfakis, P.; Despott, E.J.; Ballarin, A.; Beyna, T.; Boeykens, K.; Elbe, P.; Gisbertz, I.; Hoyois, A.; Mosteanu, O.; et al. Endoscopic management of enteral tubes in adult patients—Part 1: Definitions and indications. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowell, N.P. Tumor implantation following percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy insertion for head and neck and oesophageal cancer: Review of the literature. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellrichmann, M.; Sergeev, P.; Bethge, J.; Arlt, A.; Topalidis, T.; Ambrosch, P.; Wiltfang, J.; Fritscher-Ravens, A. Prospective evaluation of malignant cell seeding after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in patients with oropharyngeal/esophageal cancers. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenberg, K.; Eriksson, A.; Odensten, C.; Darehed, D. Mortality and complications after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: A retrospective multicentre study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamran, U.; Lee, P.C.; Coupland, B. Improving 30-day mortality after PEG tube placement in England from 2007 to 2019: A retrospective national cohort analysis of 87,862 patients. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 96, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
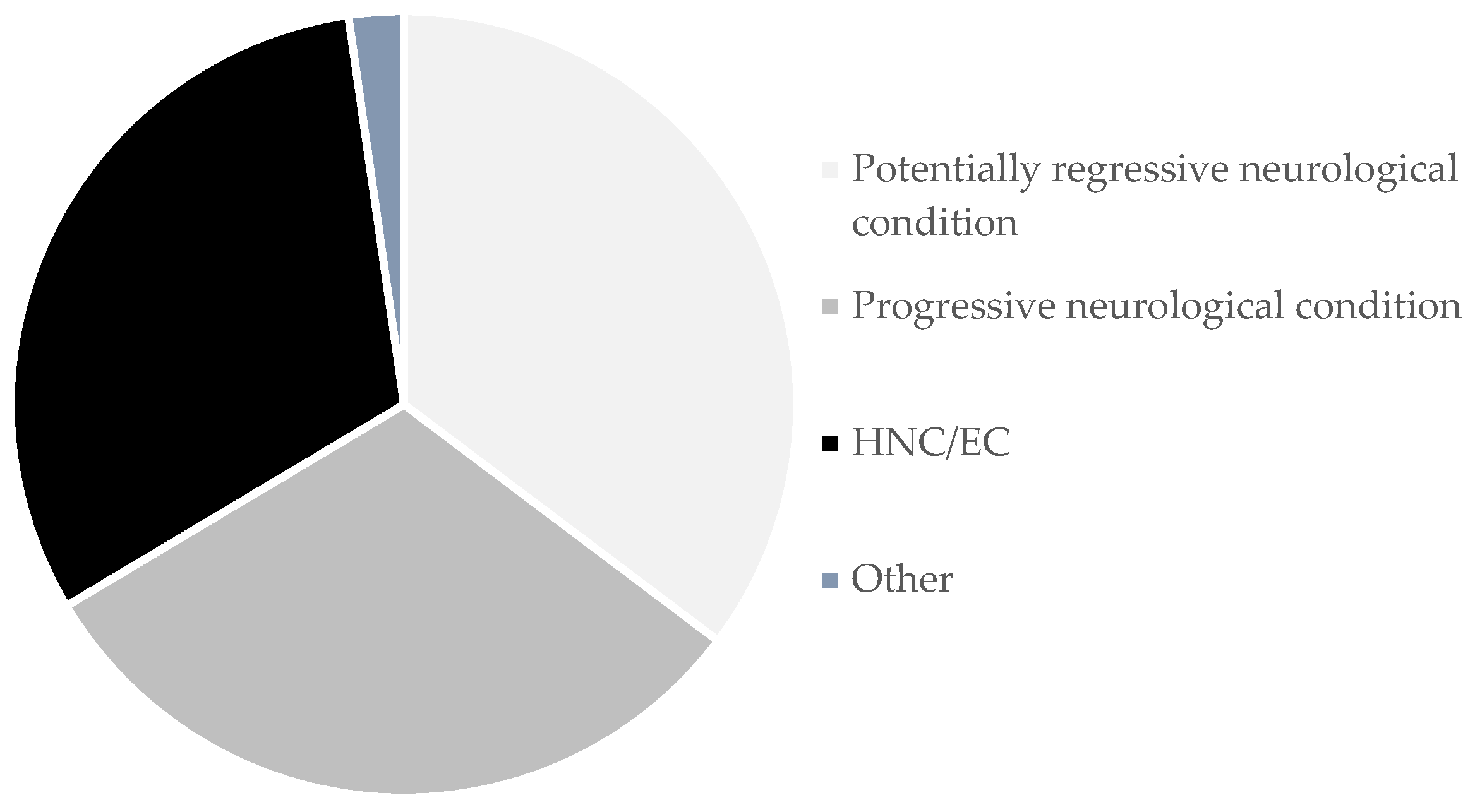
| Total: n (%) | Male: n (%) | Female: n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Potentially regressive neurological condition | 499 (35.3) | 273 (54.7) | 226 (45.3) |
| Post-stroke dysphagia | 361 (25.5) | 177 (49.0) | 184 (51.0) |
| Traumatic brain injury | 78 (5.5) | 55 (70.5) | 23 (29.5) |
| Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy | 33 (2.3) | 23 (69.7) | 10 (30.3) |
| Cerebral palsy | 10 (0.7) | 6 (60.0) | 4 (40.0) |
| Other | 17 (1.2) | 12 (70.6) | 5 (29.4) |
| Progressive neurological condition | 441 (31.2) | 193 (43.8) | 248 (56.2) |
| Dementia | 155 (11.0) | 61 (39.4) | 94 (60.6) |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis | 153 (10.8) | 76 (49.7) | 77 (50.3) |
| Parkinsonian syndromes | 39 (2.8) | 18 (46.2) | 21 (53.8) |
| Cerebral neoplasm | 39 (2.8) | 15 (38.5) | 24 (61.5) |
| Huntington’s disease | 13 (0.9) | 5 (38.5) | 8 (61.5) |
| Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy | 11 (0.8) | 5 (45.5) | 6 (54.5) |
| Other | 31 (2.2) | 13 (41.9) | 18 (58.1) |
| Head and neck cancer/Esophageal cancer | 443 (31.3) | 388 (87.6) | 55 (12.5) |
| Laryngeal cancer | 135 (9.5) | 127 (94.1) | 8 (5.9) |
| Pharyngeal cancer | 132 (9.3) | 118 (89.4) | 14 (10.6) |
| Oral cavity cancer | 98 (6.9) | 85 (86.7) | 13 (13.3) |
| Esophageal cancer | 54 (3.8) | 46 (85.2) | 8 (14.8) |
| Other | 24 (1.7) | 12 (50.0) | 12 (50.0) |
| Other conditions | 32 (2.3) | 20 (62.5) | 12 (37.5) |
| Total: n (%) | |
|---|---|
| BMI (n = 1251) | |
| Underweight | 623 (49.8) |
| Normal | 494 (39.5) |
| Overweight | 82 (6.6) |
| Obesity | 52 (4.2) |
| Albumin (n = 1297) | |
| Low (<3.5 g/dL) | 560 (43.2) |
| Normal (≥3.5 g/dL) | 737 (56.8) |
| Transferrin (n = 1253) | |
| Low (<200 mg/dL) | 779 (62.2) |
| Normal (≥200 mg/dL) | 474 (37.8) |
| Total cholesterol (n = 1243) | |
| Low (<160 mg/dL) | 622 (50.0) |
| Normal (≥160 mg/dL) | 621 (50.0) |
| Survival | 95% CI | Log-Rank (Mantel–Cox) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Months) | Std. Error | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Chi-Square | p-Value | |
| Neurological regressive | 16.6 | 1.9 | 12.9 | 20.2 | - | - |
| Neurological progressive | 13.3 | 1.1 | 11.1 | 15.5 | 8.50 | 0.004 |
| HNC/EC | 6.6 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 7.7 | 37.91 | <0.001 |
| Others | 6.4 | 13.6 | 0.0 | 33.1 | 0.07 | 0.793 |
| Neurological progressive | 13.3 | 1.1 | 11.1 | 15.5 | - | - |
| HNC/EC | 6.6 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 7.7 | 13.23 | <0.001 |
| Others | 6.4 | 13.6 | 0.0 | 33.1 | 2.15 | 0.143 |
| HNC/EC | 6.6 | 0.6 | 5.4 | 7.7 | - | - |
| Others | 6.4 | 13.6 | 0.0 | 33.1 | 5.14 | 0.023 |
| Survival | 95% CI | Log-Rank (Mantel–Cox) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Months) | Std. Error | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Chi-Square | p-Value | |
| Female | 16.0 | 1.44 | 13.14 | 18.80 | - | - |
| Male | 8.2 | 0.74 | 6.79 | 9.67 | 20.84 | <0.001 |
| Correlation Coefficient (r) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.17 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.12 | <0.001 |
| Albumin | 0.24 | <0.001 |
| Transferrin | 0.23 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Adequate Survivors (mean ± s.d.) | Short Survivors (mean ± s.d.) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 67.8 ± 14.3 | 70.9 ± 13.6 | 0.008 |
| BMI | 20.8 ± 4.3 | 20.4 ± 4.6 | 0.331 |
| Albumin | 3.5 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | <0.001 |
| Transferrin | 186.6 ± 48.3 | 156.6 ± 46.3 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol | 164.0 ± 46.8 | 151.2 ± 51.0 | 0.003 |
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||
| Gender | 0.396 | 0.245 | 0.641 | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.020 | 1.015 | 1.025 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.963 | 0.946 | 0.981 | <0.001 |
| Albumin | 0.687 | 0.619 | 0.763 | <0.001 |
| Group of underlying condition | ||||
| Neurological progressive (ref.) vs. Neurological regressive | 0.791 | 0.670 | 0.935 | 0.006 |
| Neurological progressive (ref.) vs.HNC/EC | 1.391 | 1.169 | 1.656 | <0.001 |
| Neurological progressive (ref.) vs. Others | 0.730 | 0.451 | 1.183 | 0.202 |
| Neurological regressive (ref.) vs. HNC/EC | 1.758 | 1.483 | 2.084 | <0.001 |
| Neurological regressive (ref.) vs. Others | 0.923 | 0.572 | 1.489 | 0.743 |
| HNC/EC (ref.) vs. Others | 0.525 | 0.325 | 0.847 | 0.080 |
| Gender x BMI x Albumin | 1.008 | 1.002 | 1.015 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendes, I.; Vara-Luiz, F.; Palma, C.; Nunes, G.; Lima, M.J.; Oliveira, C.; Brito, M.; Santos, A.P.; Santos, C.A.; Meira, T.; et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in the 21st Century—An Overview of 1415 Consecutive Dysphagic Adult Patients. Nutrients 2025, 17, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050747
Mendes I, Vara-Luiz F, Palma C, Nunes G, Lima MJ, Oliveira C, Brito M, Santos AP, Santos CA, Meira T, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in the 21st Century—An Overview of 1415 Consecutive Dysphagic Adult Patients. Nutrients. 2025; 17(5):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050747
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendes, Ivo, Francisco Vara-Luiz, Carolina Palma, Gonçalo Nunes, Maria João Lima, Cátia Oliveira, Marta Brito, Ana Paula Santos, Carla Adriana Santos, Tânia Meira, and et al. 2025. "Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in the 21st Century—An Overview of 1415 Consecutive Dysphagic Adult Patients" Nutrients 17, no. 5: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050747
APA StyleMendes, I., Vara-Luiz, F., Palma, C., Nunes, G., Lima, M. J., Oliveira, C., Brito, M., Santos, A. P., Santos, C. A., Meira, T., Mascarenhas, P., & Fonseca, J. (2025). Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy in the 21st Century—An Overview of 1415 Consecutive Dysphagic Adult Patients. Nutrients, 17(5), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17050747









