Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design
- Control (C): received individualized dietary recommendations.
- ONS + placebo (SU-PL): received ONS and dietary recommendations.
- ONS+ probiotics (SU-PR): received ONS with probiotics and dietary recommendations.
2.2. Outcomes
2.2.1. Blood Biomarkers
2.2.2. Psychological Questionnaires
2.2.3. DNA Sequencing
2.2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
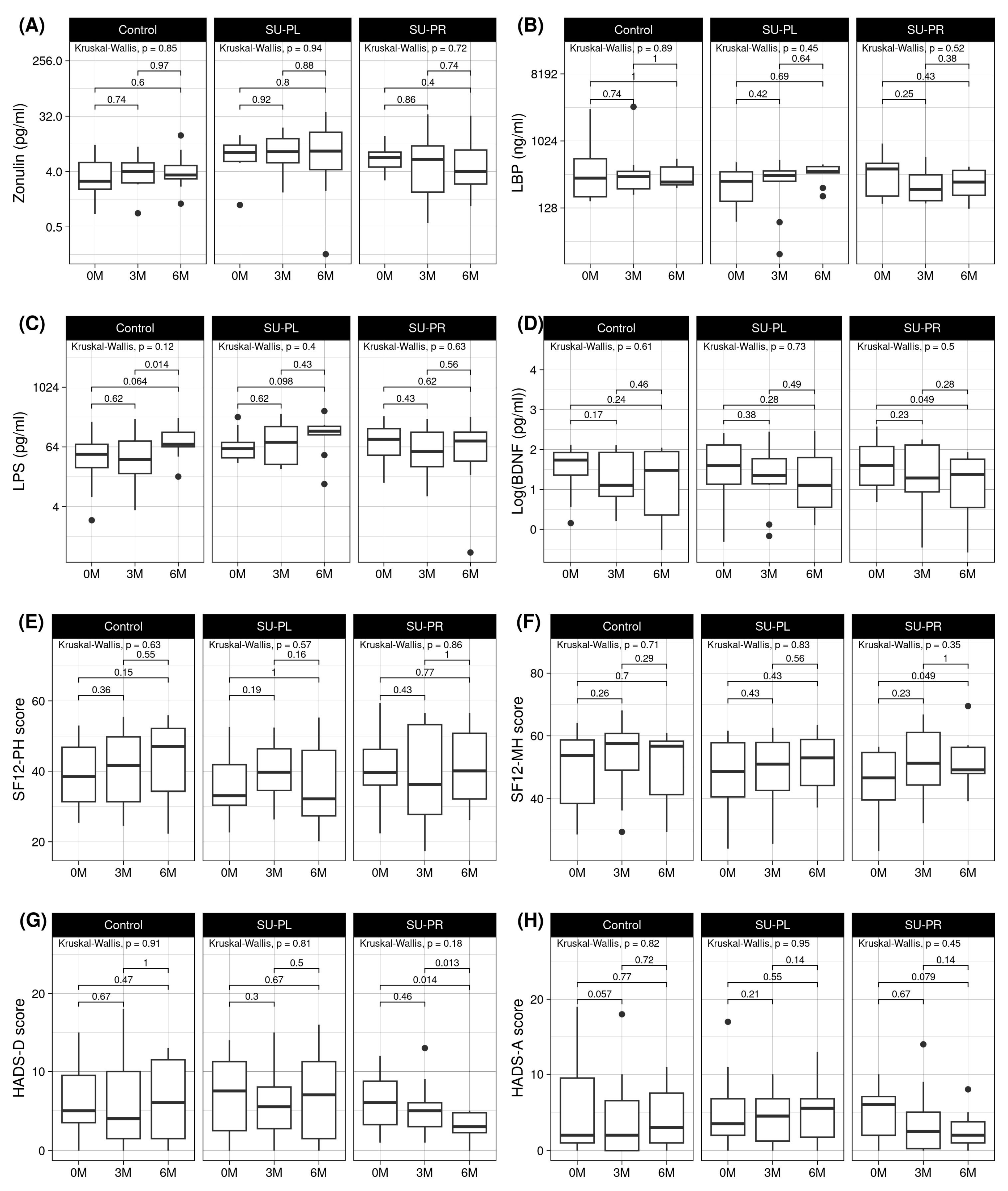
3.1. Effects on Clinical Parameters by Group
3.2. Effects on Mental Health Parameters by Group
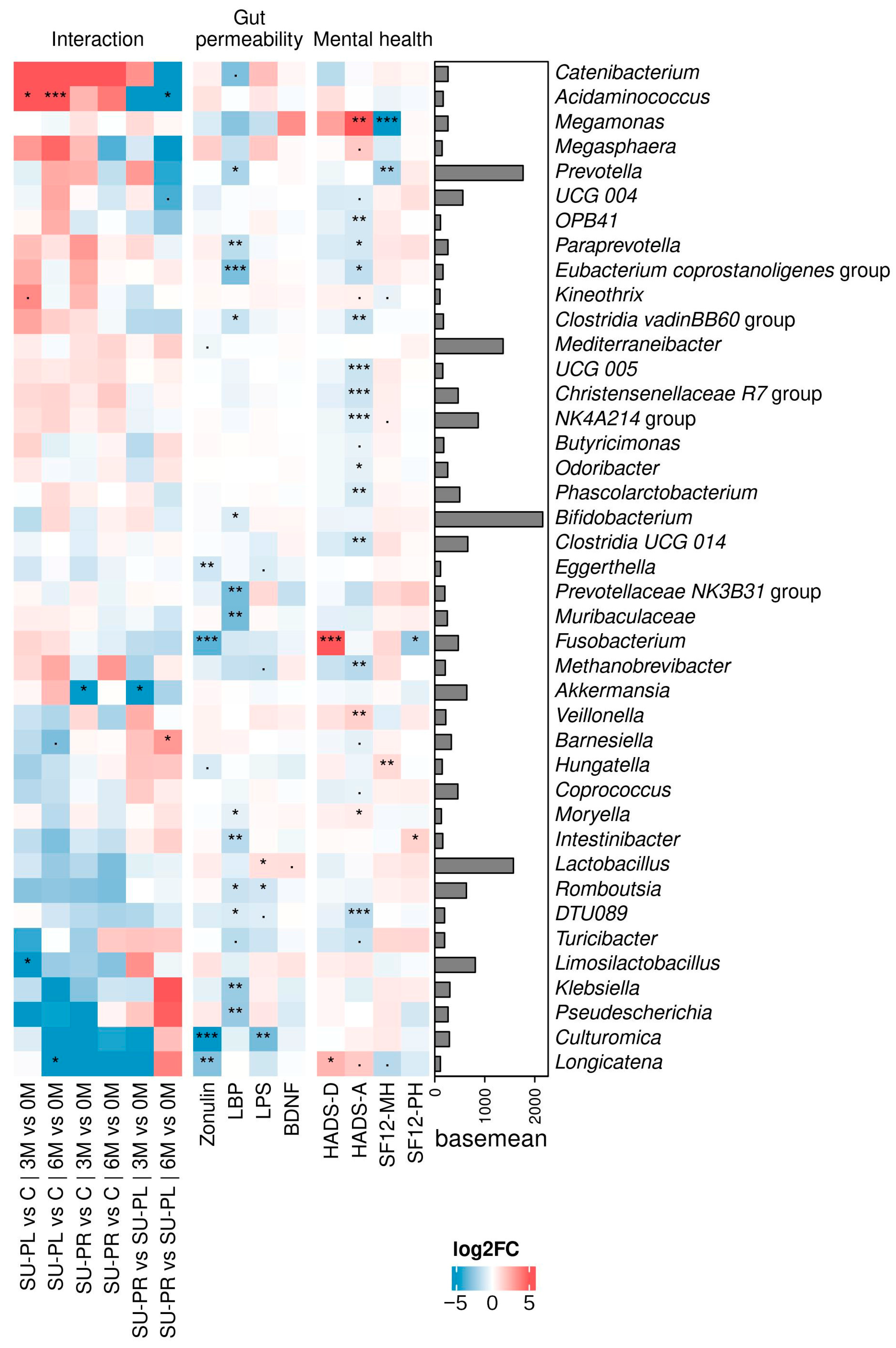
3.3. Effects on Gut Microbiota and Their Association with Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorostidi, M.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Graciani, A.; de la Cruz, J.J.; Santamaría, R.; Del Pino, M.D.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; de Álvaro, F.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; et al. Chronic kidney disease in Spain: Prevalence and impact of accumulation of cardiovascular risk factors. Nefrología 2018, 38, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schouten, R.W.; Haverkamp, G.L.; Loosman, W.L.; Chandie Shaw, P.K.; van Ittersum, F.J.; Smets, Y.F.C.; Vleming, L.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Honig, A.; Siegert, C.E.H. Anxiety Symptoms, Mortality, and Hospitalization in Patients Receiving Maintenance Dialysis: A Cohort Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Robles, E.; Lerma, A.; Calderón-Juárez, M.; Ibarra, A.; Pérez-Grovas, H.; Bermúdez-Aceves, L.A.; Bosques-Brugada, L.E.; Lerma, C. Assessment of Factors Related to Diminished Appetite in Hemodialysis Patients with a New Adapted and Validated Questionnaire. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, P.; Palmer, S.C.; Ruospo, M.; Saglimbene, V.M.; Rabindranath, K.S.; Strippoli, G.F. Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD004542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.; Vecchio, M.; Craig, J.C.; Tonelli, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Nicolucci, A.; Pellegrini, F.; Saglimbene, V.; Logroscino, G.; Fishbane, S.; et al. Prevalence of depression in chronic kidney disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, D.; Yu, H.; Shen, H.; Liu, H.; Meng, F.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X. The microbiota-gut-brain axis in pathogenesis of depression: A narrative review. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 260, 114056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis and Mental Health. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, K. Psychobiotics: Are they the future intervention for managing depression and anxiety? A literature review. Explore 2023, 19, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.; Merckelbach, E.; Noels, H.; Vohra, A.; Jankowski, J. Homeostasis in the Gut Microbiota in Chronic Kidney Disease. Toxins 2022, 14, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonali, S.; Ray, B.; Ahmed Tousif, H.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Sunanda, T.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Essa, M.M.; Qoronfleh, M.W.; Chidambaram, S.B.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into the Link between Gut Dysbiosis and Major Depression: An Extensive Review. Cells 2022, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevilla, F.; Padial, M.; Blanca, M.; Barril, G.; Jiménez-Salcedo, T.; Ramirez-Ortiz, M.; Nogueira, Á.; Gentile, A.; García-Escobar, E.; Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; et al. Effect on nutritional status and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidation of an oral nutritional supplement (with or without probiotics) in malnourished hemodialysis patients. A multicenter randomized clinical trial “Renacare Trial”. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedret, A.; Valls, R.M.; Calderon-Perez, L.; Llaurado, E.; Companys, J.; Pla-Paga, L.; Moragas, A.; Martin-Lujan, F.; Ortega, Y.; Giralt, M.; et al. Effects of daily consumption of the probiotic Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CECT 8145 on anthropometric adiposity biomarkers in abdominally obese subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amat-Bou, M.; Garcia-Ribera, S.; Climent, E.; Piquer-Garcia, I.; Corripio, R.; Sanchez-Infantes, D.; Villalta, L.; Elias, M.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C.; Chenoll, E.; et al. Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis (BPL1) Supplementation in Children and Adolescents with Prader-Willi Syndrome: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Gomez-Llorente, C.; Campana-Martin, L.; Matencio, E.; Ortuno, I.; Martinez-Silla, R.; Gomez-Gallego, C.; Periago, M.J.; Ros, G.; Chenoll, E.; et al. Safety and immunomodulatory effects of three probiotic strains isolated from the feces of breast-fed infants in healthy adults: SETOPROB study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushnell, B.; Rood, J.; Singer, E. BBMerge—Accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. cutPrimers: A New Tool for Accurate Cutting of Primers from Reads of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2′s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudzik, A.; Orzylowska, A.; Rola, R.; Stanisz, G.J. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Postbiotics on Mitigation of Depression Symptoms: Modulation of the Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.C.W.; Gorbovskaya, I.; Hahn, M.K.; Müller, D.J. The Gut Microbiome in Schizophrenia and the Potential Benefits of Prebiotic and Probiotic Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Shin, Y.C.; Kim, T.Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.N.; Eunju, O.; Kim, K.S.; Kweon, M.N. Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1892441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Kong, Q.; Zheng, N.; Ling, Z.; Hu, W. Akkermansia muciniphila in neuropsychiatric disorders: Friend or foe? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1224155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.S.; Seekatz, A.M.; Koropatkin, N.M.; Kamada, N.; Hickey, C.A.; Wolter, M.; Pudlo, N.A.; Kitamoto, S.; Terrapon, N.; Muller, A.; et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell 2016, 167, 1339–1353.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, N.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; et al. Predictive microbial feature analysis in patients with depression after acute ischemic stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintz-Buschart, A.; Pandey, U.; Wicke, T.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Janzen, A.; Sittig-Wiegand, E.; Trenkwalder, C.; Oertel, W.H.; Mollenhauer, B.; Wilmes, P. The nasal and gut microbiome in Parkinson’s disease and idiopathic rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, B.; Yang, Q.; Yin, J.; Tian, L.; Zhu, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y. Evaluation of depression status and its influencing factors in convalescent elderly patients with first-episode stroke. Asian J. Psychiatry 2022, 77, 103252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubeda, C.; Bucci, V.; Caballero, S.; Djukovic, A.; Toussaint, N.C.; Equinda, M.; Lipuma, L.; Ling, L.; Gobourne, A.; No, D.; et al. Intestinal microbiota containing Barnesiella species cures vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium colonization. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, L.; Khan, I.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lee, M.Y.S.; Leong, W.; Hsiao, W.L.W.; Zheng, Y. Fructo-oligosaccharides from Morinda officinalis remodeled gut microbiota and alleviated depression features in a stress rat model. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Martín-Hernández, D.; Virto, L.; MacDowell, K.S.; Montero, E.; González-Bris, Á.; Marín, M.J.; Ambrosio, N.; Herrera, D.; Leza, J.C.; et al. Periodontal diseases and depression: A pre-clinical in vivo study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 503–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Shang, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, S.; Xie, J. Gut microbiota and its relation to inflammation in patients with bipolar depression: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2023, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, S.G.; Goldenthal, A.R.; Uhlemann, A.C.; Mann, J.J.; Miller, J.M.; Sublette, M.E. Systematic Review of Gut Microbiota and Major Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith, M.R.B.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in Gut Microbiota Composition in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, W.T.; Chen, J.J. Multi-omics data reveals the important role of glycerophospholipid metabolism in the crosstalk between gut and brain in depression. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xie, P.; Xu, G.; et al. Discovery and validation of plasma biomarkers for major depressive disorder classification based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Song, Z.; Liu, A.; Dahmen, U.; Yang, X.; Fang, H. Effects of Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein (LBP) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) in Infections, Inflammatory Diseases, Metabolic Disorders and Cancers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 681810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Amersfoort, E.S.; Van Berkel, T.J.; Kuiper, J. Receptors, mediators, and mechanisms involved in bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 379–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.S.; Kim, M.J.; Ji, G.E. Assessment of lipopolysaccharide-binding activity of Bifidobacterium and its relationship with cell surface hydrophobicity, autoaggregation, and inhibition of interleukin-8 production. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Nie, Z.; Shu, H.; Kuang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Yu, S.; Liu, H. The Role of BDNF on Neural Plasticity in Depression. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranuh, R.; Athiyyah, A.F.; Darma, A.; Risky, V.P.; Riawan, W.; Surono, I.S.; Sudarmo, S.M. Effect of the probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 on BDNF and 5HT stimulation: Role of intestinal microbiota on the gut-brain axis. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
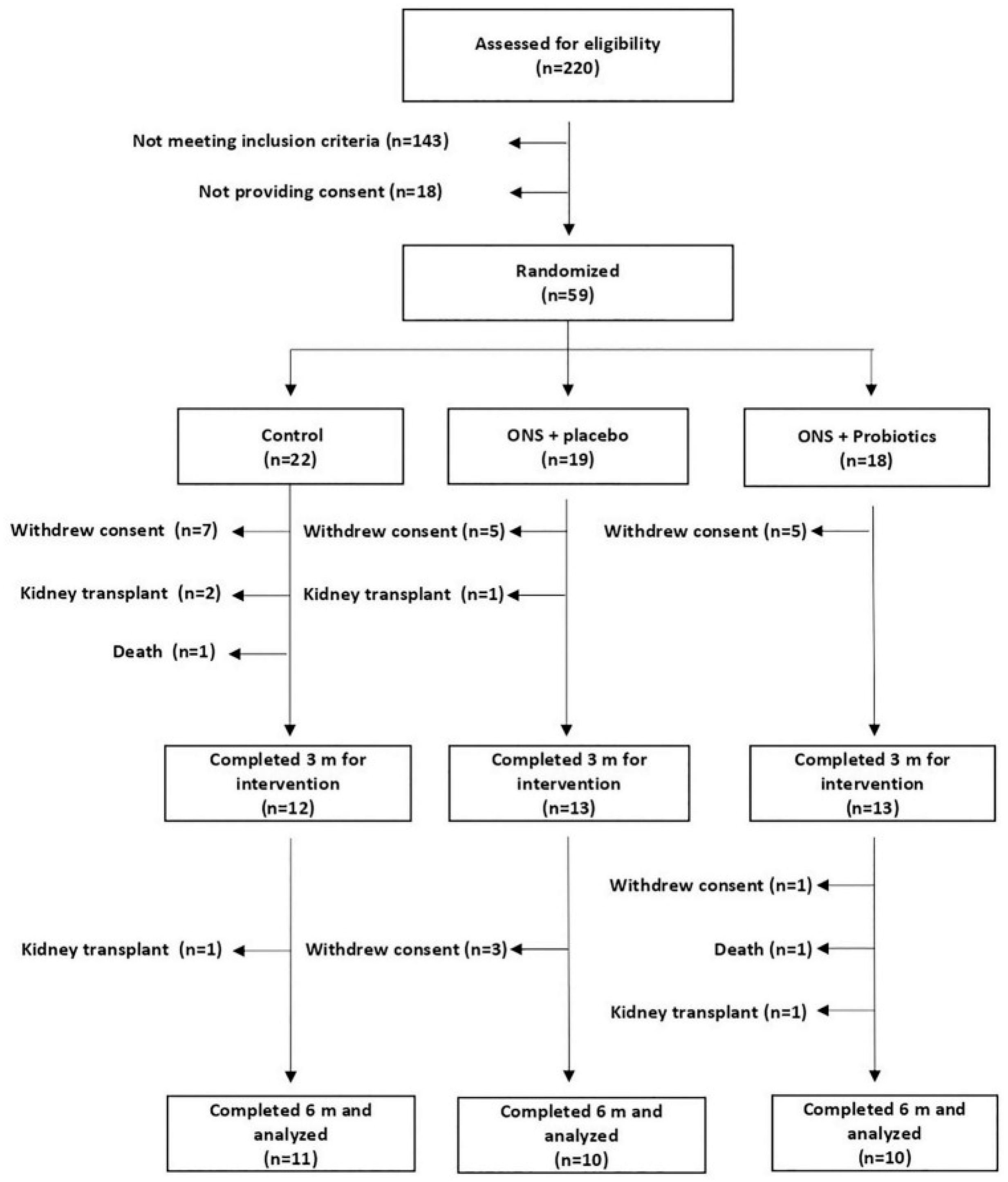
| Control | SU-PL | SU-PR | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 11) | (n = 10) | (n = 10) | ||
| Age (years) m ± ds | 76.3 ± 8.7 | 65.1 ± 18.4 | 66 ± 18.5 | ns |
| Sex, women % (n) | 27 (3) | 20 (2) | 30 (3) | ns |
| Diabetes mellitus % (n) | 36.4 (4) | 40 (4) | 30 (3) | ns |
| Antibiotic treatment in the last month | 9.1 (1) | 20 (2) | 10 (1) | ns |
| Consumption of yogurt or fermented milk in the last month % (n) | 63.6 (7) | 60 (6) | 60 (6) | ns |
| Charlson comorbidity index. m ± ds | 4 ± 2.31 | 5.1 ± 2.02 | 4.18 ± 2.6 | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Climent, E.; Hevilla, F.; Padial, M.; Barril-Cuadrado, G.; Blanca, M.; Jiménez-Salcedo, T.; López-Picasso, M.; Nogueira-Pérez, Á.; Olveira, G. Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients 2025, 17, 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040652
Climent E, Hevilla F, Padial M, Barril-Cuadrado G, Blanca M, Jiménez-Salcedo T, López-Picasso M, Nogueira-Pérez Á, Olveira G. Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients. 2025; 17(4):652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040652
Chicago/Turabian StyleCliment, Eric, Francisco Hevilla, Marina Padial, Guillermina Barril-Cuadrado, María Blanca, Tamara Jiménez-Salcedo, Maria López-Picasso, Ángel Nogueira-Pérez, and Gabriel Olveira. 2025. "Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial" Nutrients 17, no. 4: 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040652
APA StyleCliment, E., Hevilla, F., Padial, M., Barril-Cuadrado, G., Blanca, M., Jiménez-Salcedo, T., López-Picasso, M., Nogueira-Pérez, Á., & Olveira, G. (2025). Psychobiotic Protection of Nutritional Supplements and Probiotics in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis: A Randomized Trial. Nutrients, 17(4), 652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17040652







