The Impact of Glomerular Disease on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients Treated with Dialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
2.2. Patient Data
2.3. Measures of Dyslipidemia
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Comparisons
3.2. Linear Analysis of Lipid Parameters
3.3. Categorical Analysis of Lipid Parameters Using NHLBI Definitions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CAKUT | Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CKD-MBD | Chronic Kidney Disease–Mineral Bone Disorder |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| ESKD | End Stage Kidney Disease |
| FSGS | Focal Segmental Glomerular Sclerosis |
| HDL-C | High density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HUS | Hemolytic uremic syndrome |
| JAML | Junctional adhesion molecule-like protein |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes |
| LDL-C | Low density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| NHLBI | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute |
| USRDS | United States Renal Disease Systems |
References
- Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Herzog, C.A.; Ishani, A.; Israni, A.K.; Ku, E.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; et al. US Renal Data System 2021 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, A8–A12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echefu, G.; Stowe, I.; Burka, S.; Basu-Ray, I.; Kumbala, D. Pathophysiological Concepts and Screening of Cardiovascular Disease in Dialysis Patients. Front. Nephrol. 2023, 3, 1198560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saland, J.M.; Kupferman, J.C.; Pierce, C.B.; Flynn, J.T.; Mitsnefes, M.M.; Warady, B.A.; Furth, S.L. Change in Dyslipidemia with Declining Glomerular Filtration Rate and Increasing Proteinuria in Children with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, H.G.; Choi, H.J.; Cheong, H.I.; Ha, I.S.; Han, K.H.; Cho, H.Y.; Shin, J.I.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Dyslipidemia in Pediatric CKD Patients: Results from Know-PEDCKD (Korean Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients with Pediatric CKD). Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, H.S.; Park, M.J.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, H.G.; Ahn, Y.H.; Han, K.H.; Cho, H.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, J.I.; et al. Association between Serum Total Cholesterol and Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Children: Results from the Know-PEDCKD. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 4101–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita-Cruz, J.N.; Villasís-Keever, M.Á.; Serret-Montoya, J.; Barbosa-Cortés, L.; Zepeda-Martínez, C.D.; Alegría-Torres, G.; Barradas-Vázquez, A.S.; Alonso-Flores, S.; Hernández-Hernández, C.; Manuel-Apolinar, L.; et al. The Leptin/Adiponectin Ratio as Prognostic Marker for Dyslipidemia during 1 Year of Follow-up in Pediatric Patients Receiving Kidney Replacement Therapy. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonthuis, M.; van Stralen, K.J.; Jager, K.J.; Baiko, S.; Jahnukainen, T.; Laube, G.F.; Podracka, L.; Seeman, T.; Tyerman, K.; Ulinski, T.; et al. Dyslipidaemia in Children on Renal Replacement Therapy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 29, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ashoor, I.F.; Mansfield, S.A.; O’Shaughnessy, M.M.; Parekh, R.S.; Zee, J.; Vasylyeva, T.L.; Kogon, A.J.; Sethna, C.B.; Glenn, D.A.; Chishti, A.S.; et al. Prevalence of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Childhood Glomerular Diseases. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, R.; Hamasaki, Y.; Okuda, Y.; Hamada, R.; Ishikura, K. Epidemiology of Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease/Kidney Failure: Learning from Registries and Cohort Studies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 37, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents: Summary Report. Pediatrics 2011, 128 (Suppl. S5), S213–S256. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.H.; Kim, S.W. Dyslipidemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Updated Overview. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, A.K.; Singh, J.; Jain, A.; Bhamra, R.; Rathi, V. The Mechanistic Role of Different Mediators in the Pathophysiology of nephropathy: A Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2023, 24, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Hou, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Tang, W.; Zhen, J.; et al. Elevation of JAML Promotes Diabetic Kidney Disease by Modulating Podocyte Lipid Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 1052–1062.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanner, C.; Tonelli, M. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Lipid Management in CKD: Summary of Recommendation Statements and Clinical Approach to the Patient. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, T.M.; Schneider, M.F.; Flynn, J.T.; Cox, C.; Samuels, J.; Saland, J.; White, C.T.; Furth, S.; Warady, B.A.; Mitsnefes, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Children with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, P.L.; Khandelwal, P.; Lakshmy, R.; Sinha, A.; Bagga, A.; Hari, P. Short-Term Safety and Efficacy of Escalating Doses of Atorvastatin for Dyslipidemia in Children with Predialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 2–5. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 2763–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, M.J.; Skinner, A.C.; Perrin, E.M. Fasting Might Not Be Necessary before Lipid Screening: A Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study. Pediatrics 2011, 128, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudio, P.; Gabriella, M. Nephrotic Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Consequences. J. Nephrol. 2023, 36, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
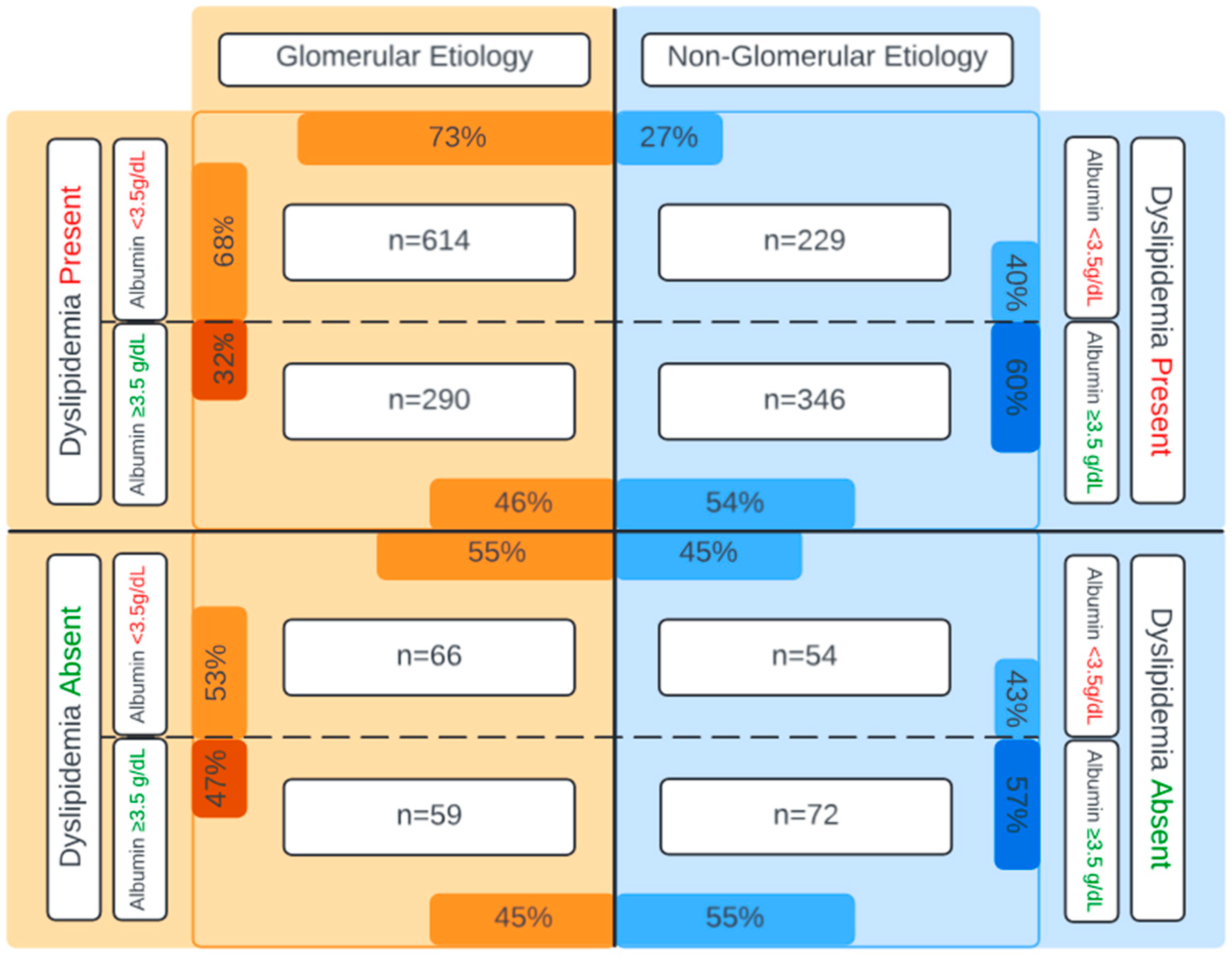
| Glomerular Etiology, n (%) | Non-Glomerular Etiology, n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 1029 | 701 | |
| Age, years | 17.7 (14.5, 19.7) | 15.2 (10.6, 18.7) | <0.0001 |
| Sex, n (%) | 0.0002 | ||
| Male | 523 (50.8%) | 419 (59.8%) | |
| Female | 506 (49.2%) | 282 (40.2%) | |
| Race, n (%) | <0.0001 | ||
| White | 294 (28.6%) | 318 (45.4%) | |
| Black | 335 (32.6%) | 140 (20.0%) | |
| Hispanic | 331 (32.2%) | 211 (30.1%) | |
| Asian | 43 (4.2%) | 19 (2.7%) | |
| Other/Unknown/Native American | 26 (2.5%) | 13 (1.9%) | |
| Modality, n (%) | 1 | ||
| HD | 750 (73.2%) | 506 (73.0%) | |
| PD | 275 (26.8%) | 187 (27.0%) | |
| Insurance, n (%) | 0.002 | ||
| Uninsured | 108 (10.5%) | 44 (6.3%) | |
| Public | 546 (53.1%) | 428 (61.1%) | |
| Private | 260 (25.3%) | 160 (22.8%) | |
| Unknown | 115 (11.2%) | 69 (9.8%) | |
| Height, cm | 162.0 (151.0, 170.2) | 151.0 (126.0, 163.0) | <0.0001 |
| Weight, kg | 59.0 (46.0, 77.0) | 47.0 (30.0, 63.0) | <0.0001 |
| BMI | 22.4 (18.8, 27.8) | 19.9 (16.9, 25.1) | <0.0001 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.1 (2.4, 3.7) | 3.7 (3.2, 4.1) | <0.0001 |
| Lipid Parameter | Glomerular Etiology, Median mg/dL (IQR) | Non-Glomerular Etiology, Median mg/dL (IQR) | p-Value | Linear Regression Models (ref = Non-Glomerular) % Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | 183 (146, 232) | 162 (130, 192) | <0.0001 | +19% (+14.7%, +23.8%) p < 0.0001 |
| LDL-C | 108 (78, 140) | 87 (65, 111) | <0.0001 | +21% (+14.8%, +26.6%) p < 0.0001 |
| TG | 169 (116, 242) | 147 (102, 223) | <0.0001 | +22.3% (+15.5%, +29.5%) p < 0.0001 |
| HDL-C | 38 (30, 49) | 38 (30, 50) | 0.3 | −1.4% (−5.4%, +2.7%) p = 0.5 |
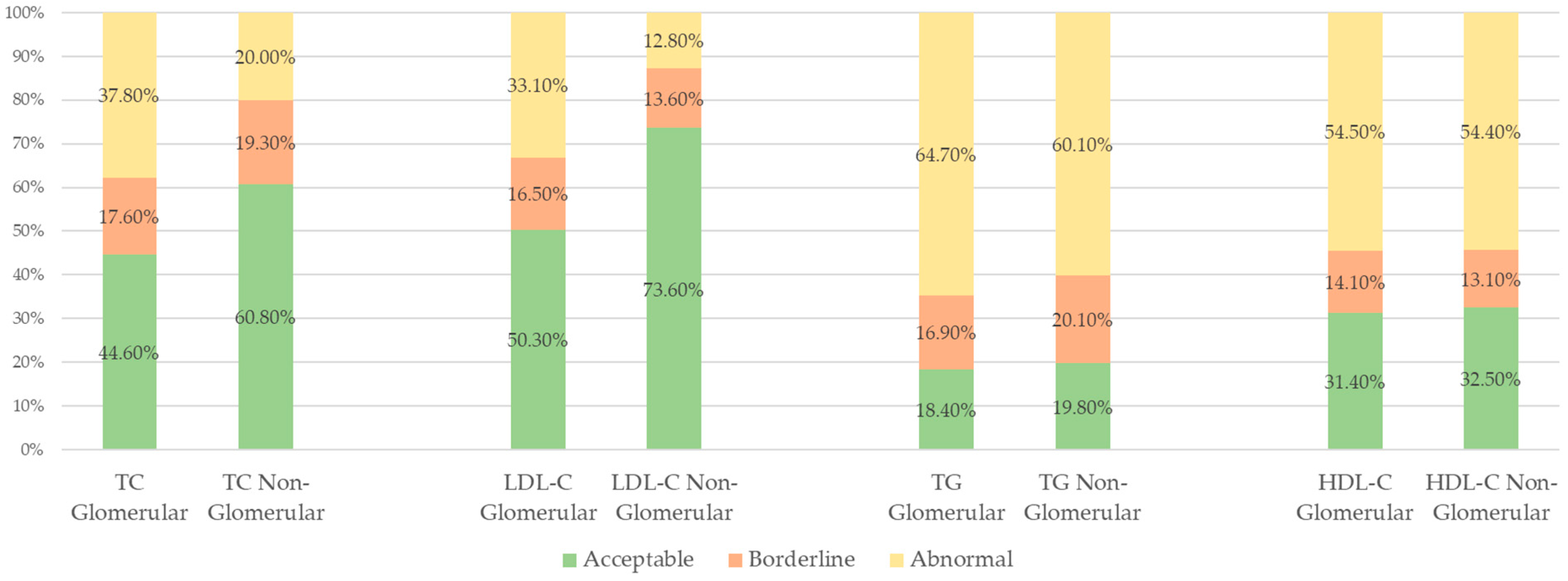
| Entire Cohort n (%) | Glomerular Etiology n (%) | Non-Glomerular Etiology n (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any lipid parameter | 1479/1730 (85.5%) | 904/1029 (87.9%) | 575/701 (82.0%) |
| TC | 529/1730 (30.6%) | 389/1029 (37.8%) | 140/701 (20.0%) |
| LDL-C | 431/1730 (24.9%) | 341/1029 (33.1%) | 90/701 (12.8%) |
| TG | 1087/1730 (62.8%) | 666/1029 (64.7%) | 421/701 (60.1%) |
| HDL-C | 942/1730 (54.5%) | 561/1029 (54.5%) | 381/701 (54.4%) |
| Glomerular Etiology, n (%) | Non-Glomerular Etiology, n (%) | p-Value | Logistic Regression Models (ref = Non-Glomerular) OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC | <0.0001 | 3.0 (2.4, 3.9) p < 0.0001 | ||
| Acceptable/Borderline | 640 (62.2%) | 561 (80%) | ||
| Abnormal | 389 (37.8%) | 140 (20%) | ||
| LDL-C | <0.0001 | 3.8 (2.8, 5.0) p < 0.0001 | ||
| Acceptable/Borderline | 688 (66.9%) | 611 (87.2%) | ||
| Abnormal | 341 (33.1%) | 90 (12.8%) | ||
| TG | 0.049 | 1.9 (1.5, 2.4) p < 0.0001 | ||
| Acceptable/Borderline | 363 (35.3%) | 280 (40.0%) | ||
| Abnormal | 666 (64.7%) | 421 (60.0%) | ||
| HDL-C | 1 | 0.9 (0.7, 1.1) p = 0.4 | ||
| Acceptable/Borderline | 468 (45.5%) | 320 (45.6%) | ||
| Abnormal | 561 (54.5%) | 381 (54.4%) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zitnik, E.; Streja, E.; Laster, M. The Impact of Glomerular Disease on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients Treated with Dialysis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030459
Zitnik E, Streja E, Laster M. The Impact of Glomerular Disease on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients Treated with Dialysis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030459
Chicago/Turabian StyleZitnik, Edward, Elani Streja, and Marciana Laster. 2025. "The Impact of Glomerular Disease on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients Treated with Dialysis" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030459
APA StyleZitnik, E., Streja, E., & Laster, M. (2025). The Impact of Glomerular Disease on Dyslipidemia in Pediatric Patients Treated with Dialysis. Nutrients, 17(3), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030459







