Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid from Different Sources on Prefrontal-Cortex Synaptic Plasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Lipid Extraction
2.5. Targeted Lipidomics Analysis Using LC-MS
2.6. Calculation and Normalization of Peak Area in Lipidomics
2.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.8. RNA Extraction and cDNA Conversion
2.9. Gene Expression Analysis Using Real-Time PCR
2.10. Protein Extraction and Analysis
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. PTDSS1 ELISA Kit
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
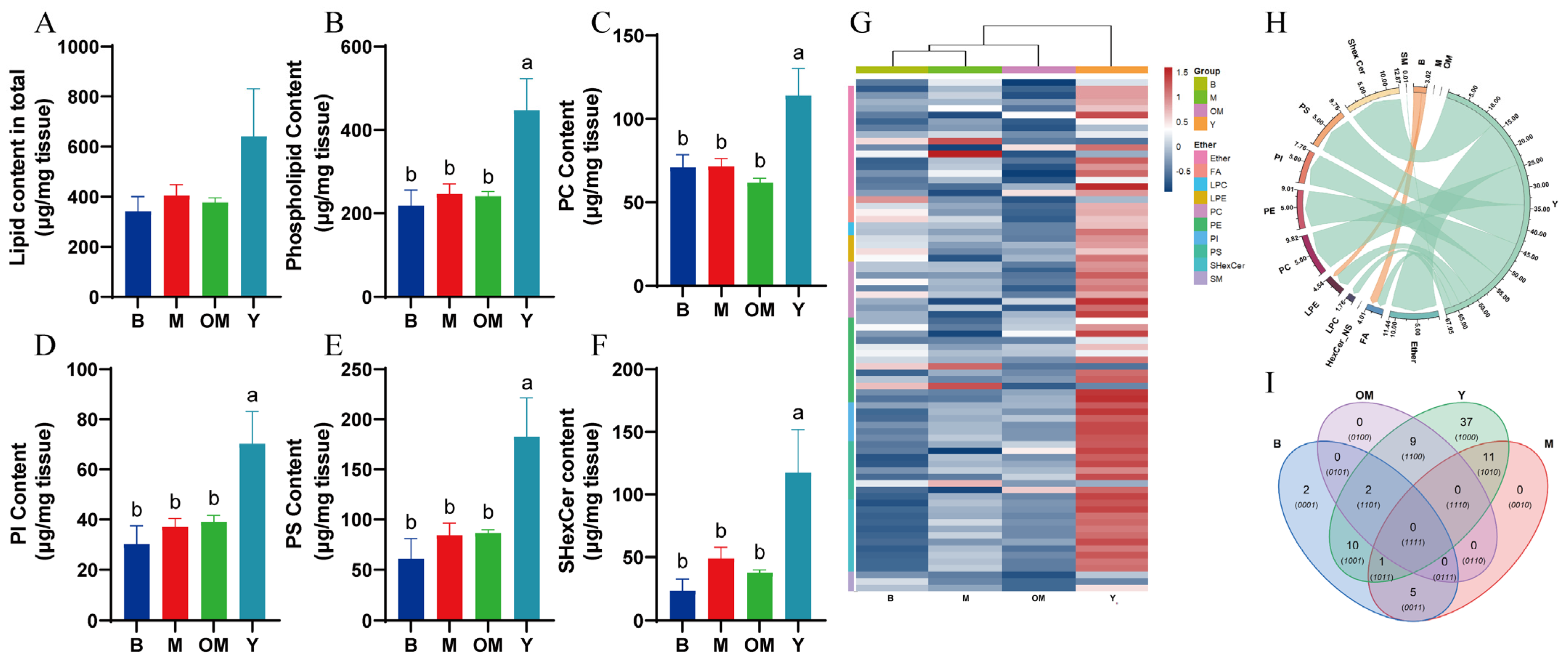
3.1. DHA Intervention from FO Significantly Changes the Content of Related PLs and Ceramide inPFC Tissue
3.2. Lipidomics Analysis Revealed That DHA Supplements Upregulated the Levels of PLs and Sphingomyelin in the PFC Tissue of Pigs
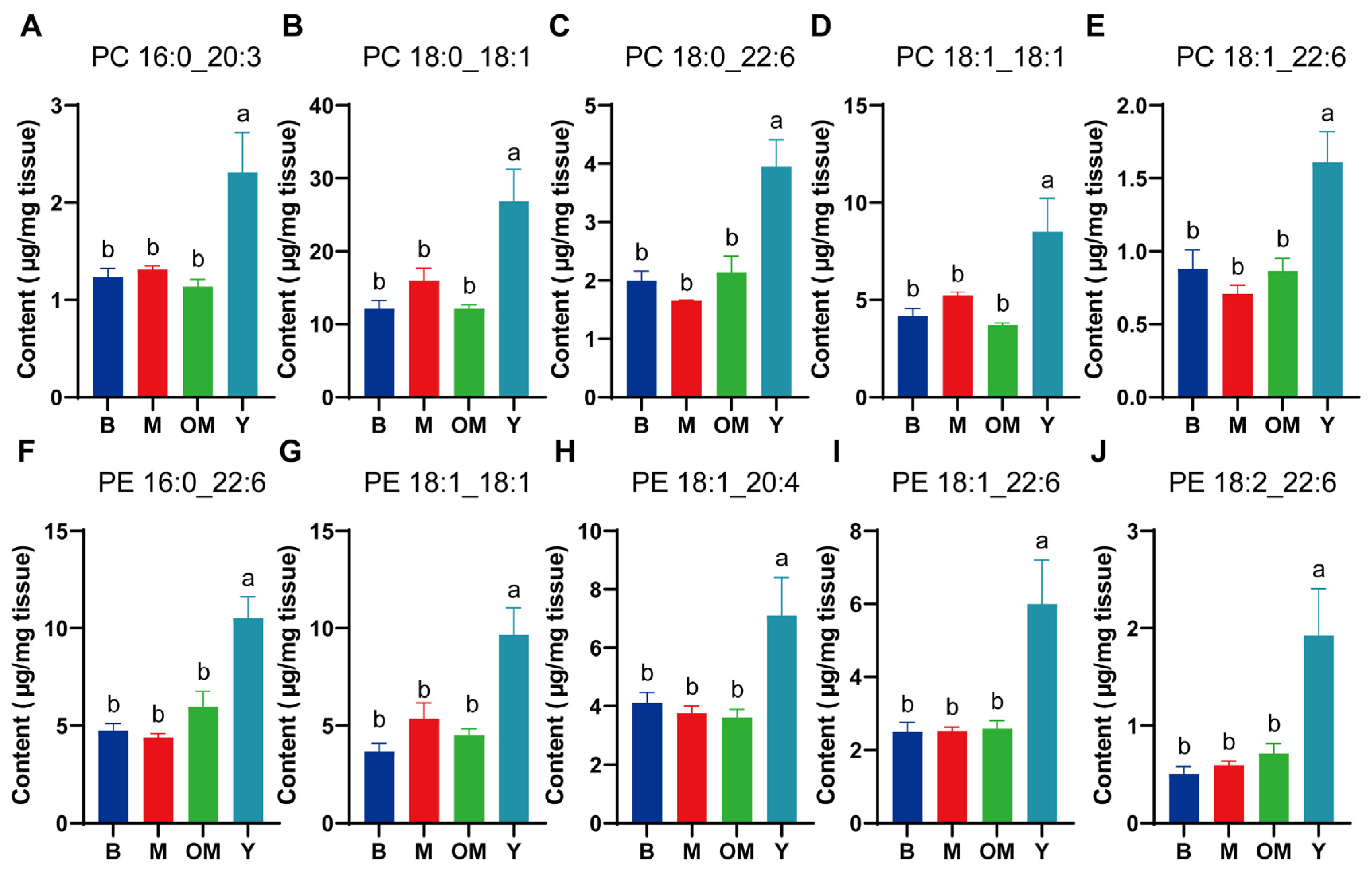
3.3. Changes in PC Content in PFC Tissue
3.4. Changes in PE Content in PFC Tissue
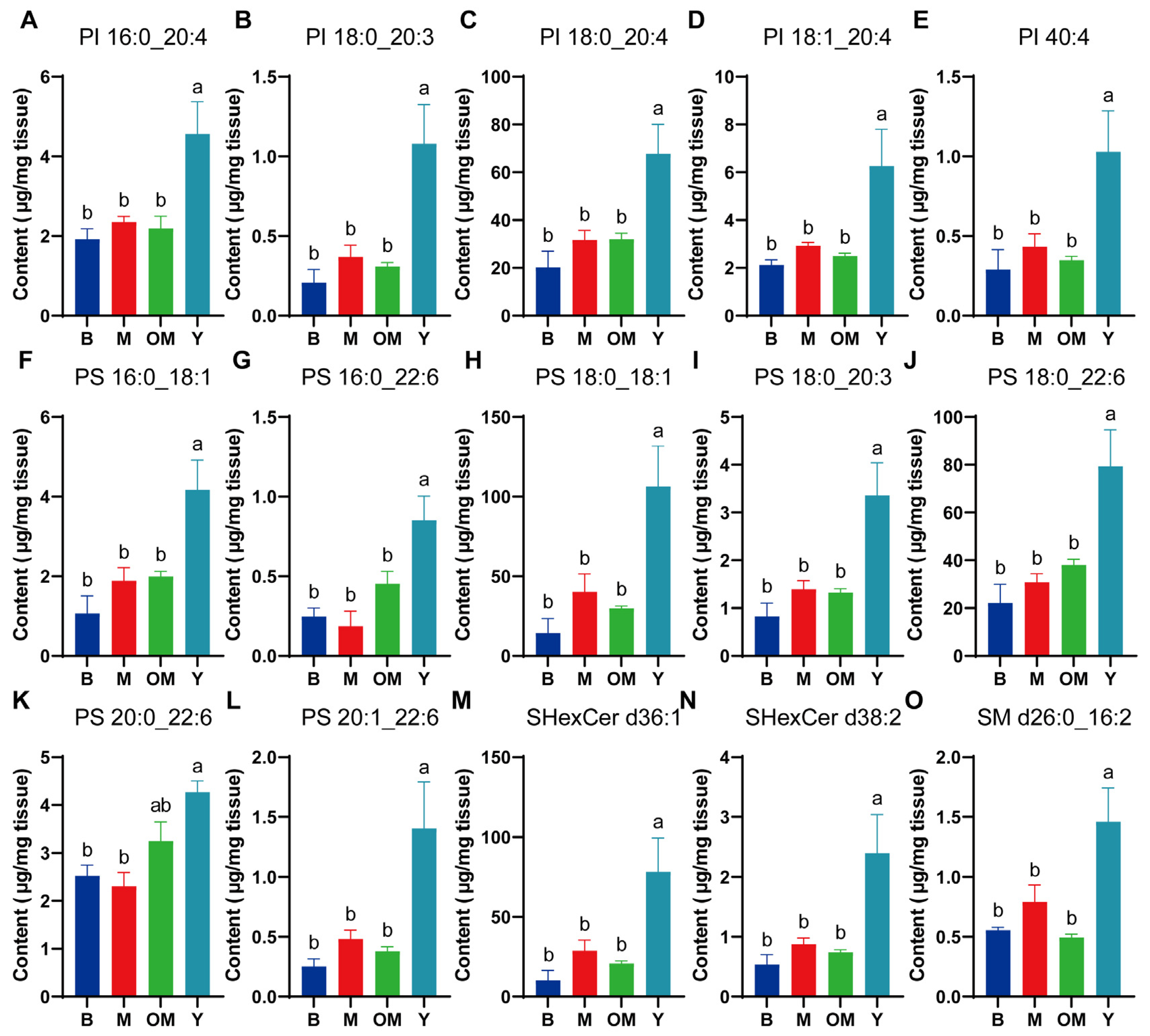
3.5. Changes in PI Content in PFC Tissue
3.6. Changes in PS Content in PFC Tissue
3.7. Changes in SHexCer Content in PFC Tissue
3.8. Changes in SM Content in PFC Tissue
3.9. Network Analysis of Differentially Expressed Lipids in PFC Tissue
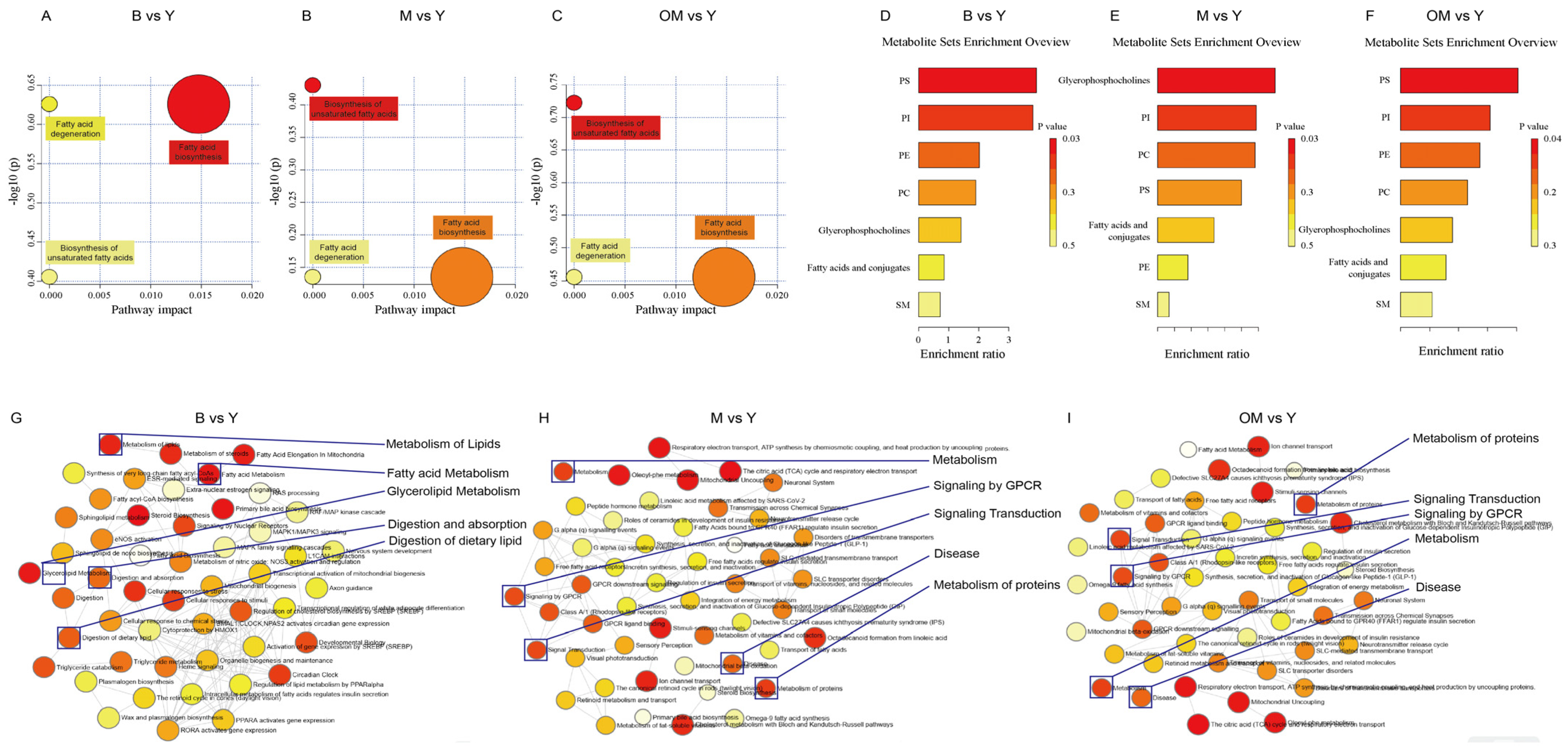
3.10. Pathway Analysis
3.11. Enrichment Analysis
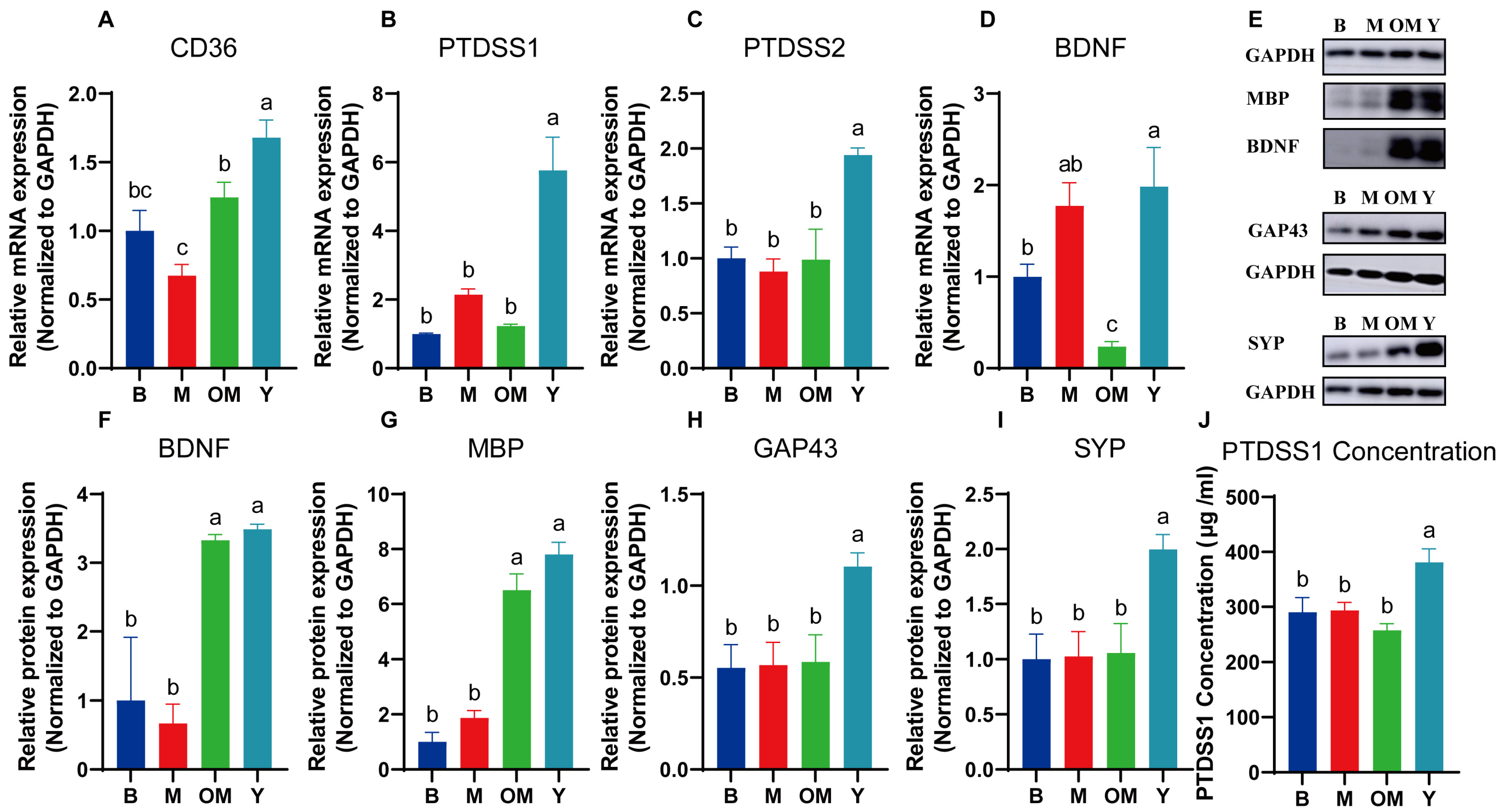
3.12. DHA Supplements Improved mRNA Expressions of Lipid Transportation and Metabolism in PFC Tissue
3.13. DHA Supplements Improved Synaptic Plasticity in PFC Tissue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Szeto, I.M.Y.; Liu, B.; Sinclair, A.; Li, D. Dietary intake of different ratios of ARA/DHA in early stages and its impact on infant development. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3259–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi Fard, S.; Loh, S.P.; Turchini, G.M.; Wang, B.; Elliott, G.; Sinclair, A.J. Microencapsulated Tuna Oil Results in Higher Absorption of DHA in Toddlers. Nutrients 2020, 12, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Jouhet, J.; Amato, A.; Marechal, E.; et al. Delta-5 elongase knockout reduces docosahexaenoic acid and lipid synthesis and increases heat sensitivity in a diatom. Plant Physiol. 2024, 10, 1356–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, J.; Sultan, S.; Rytz, A.; Steiner, P.; Schneider, N. A blend containing docosahexaenoic acid, arachidonic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin B9, iron and sphingomyelin promotes myelination in anin vitro model. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlAmmar, W.A.; Albeesh, F.H.; Ibrahim, L.M.; Algindan, Y.Y.; Yamani, L.Z.; Khattab, R.Y. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids and fish oil supplementation on multiple sclerosis: A systematic review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, B.E.; Abouleish, M.; Watters, K.E.; Vogel, S.; Ribic, A.; Schroeder, O.H.U.; Bader, B.M.; Biederer, T. Synaptic Connectivity and Cortical Maturation Are Promoted by the ω-3 Fatty Acid Docosahexaenoic Acid. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, J.; Kannan, S.; Govindasamy, A. Structured form of DHA prevents neurodegenerative disorders: A better insight into the pathophysiology and the mechanism of DHA transport to the brain. Nutr. Res. 2021, 85, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorve, J.; Hilvo, M.; Vihervaara, T.; Burri, L.; Bohov, P.; Tillander, V.; Bjorndal, B.; Suoniemi, M.; Laaksonen, R.; Ekroos, K.; et al. Fish oil and krill oil differentially modify the liver and brain lipidome when fed to mice. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, S.C.R.; Mason, R.P.; Libby, P.; Steg, P.G.; Bhatt, D.L. Do patients benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 119, 2884–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y. N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Elderly with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 99, S81–S95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaochen, H.; Jie, Z.; Shengqi, D.; Huiqiang, Z.; Nicholas, V.H.-L.; Linhong, Y. DHA and vitamin E antagonized the Aβ(25-35)-mediated neuron oxidative damage through activation of Nrf2 signaling pathways and regulation of CD36, SRB1 and FABP5 expression in PC12 cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Iwao, T.; Takata, F.; Matsumoto, J.; Aridome, H.; Yasunaga, M.; Yokoya, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Dohgu, S. Aging decreases docosahexaenoic acid transport across the blood-brain barrier in C57BL/6J mice. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Liu, Z.-K.; Xiao, G.; Shi, J.-W.; Liu, B.-L.; Xiao, N.; Sun, Z.-L. Simultaneous DHA and organic selenium production by Schizochytrium sp.: A theoretical basis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jian, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Mao, J.; Wei, W.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, P. Choline and Fish Oil Can Improve Memory of Mice through Increasing Brain DHA Level. Foods 2023, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotarescu, R.D.; Mathur, M.; Bejoy, A.M.; Anderson, G.H.; Metherel, A.H. Serum measures of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) synthesis underestimates whole body DHA synthesis in male and female mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 131, 109689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Yu, W.; Chen, S.; Ying, J.; Hua, F. Lipid metabolism and storage in neuroglia: Role in brain development and neurodegenerative diseases. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.-Q.; Wang, X.-D.; Pang, X.-Y.; Zhang, S.-W.; Lu, J.; Lu, J.-P.; Su, S.-C.; Wang, J.-F. Comparison of the stability of fatty acids in the storage period of goat dairy products with original ecology and artificial addition of docosahexaenoic acid. Shipin Kexue/Food Sci. 2022, 43, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, M.; Marotta, B.; Xu, H.; Geraert, P.-A.; Kaushik, S.; Montero, D.; Izquierdo, M. Complete replacement of fish oil by three microalgal products rich in n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in early weaning microdiets for gilthead sea bream (Sparu aurata). Aquaculture 2022, 558, 738354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipa-Silva, A.; Marques, A.; Salgado, M.A.; Abreu, H.; Dias, J.; Valente, L.M.P. Exploring alternative marine lipid sources as substitutes for fish oil in Farmed Sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and their influence on organoleptic, chemical, and nutritional properties during cold storage. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1224370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate, R.; el Jaber-Vazdekis, N.; Tejera, N.; Perez, J.A.; Rodriguez, C. Significance of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in human health. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurowska, A.; Ziemichod, W.; Herbet, M.; Piatkowska-Chmiel, I. The Role of Diet as a Modulator of the Inflammatory Process in the Neurological Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, K.B.; Ryan, A.S.; Forsyth, S.; Gautier, S.; Salem, N., Jr. The Essentiality of Arachidonic Acid in Infant Development. Nutrients 2016, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, A.S.; Place, R.; Starrett, M.J.; Chrastil, E.R.; Nitz, D.A. Rethinking retrosplenial cortex: Perspectives and predictions. Neuron 2023, 111, 150–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordt, M.; Gomez, J.; Natu, V.S.; Rezai, A.A.; Finzi, D.; Kular, H.; Grill-Spector, K. Longitudinal development of category representations in ventral temporal cortex predicts word and face recognition. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ma, L.; Yang, G.; Gan, W.-B. REM sleep selectively prunes and maintains new synapses in development and learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, A.C.; Chen, B.; Olson, L.; Ibarra, C.; Fong, C.; Reynolds, S.; Apostol, M.; Kinnear, M.; Muller, R.-A.; Fishman, I. Sleep Problems in Preschoolers with Autism Spectrum Disorder Are Associated With Sensory Sensitivities and Thalamocortical Overconnectivity. Biol. Psychiatry-Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2023, 8, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliz, E.; Shin, J.; Syme, C.; Black, S.; Seshadri, S.; Paus, T.; Pausova, Z. Thickness of the cerebral cortex shows positive association with blood levels of triacylglycerols carrying 18-carbon fatty acids. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, A. Synaptic plasticity during systems memory consolidation. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 183, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelerin, H.; Jouin, M.; Lallemand, M.-S.; Alessandri, J.-M.; Cunnane, S.C.; Langelier, B.; Guesnet, P. Gene expression of fatty acid transport and binding proteins in the blood-brain barrier and the cerebral cortex of the rat: Differences across development and with different DHA brain status. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2014, 91, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Xiang, W.; Chen, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, X.; Lu, S.; Zuo, Y.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Li, X. DHA Ameliorates Cognitive Ability, Reduces Amyloid Deposition, and Nerve Fiber Production in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 852433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xiang, H.; Zhang, P.; Zheng, C.; Fu, J.; Xie, X.; Chen, M.; Tang, X.; Xiao, M.; He, D. Effect of soybean formulated oil containing DHA algae oil on morphological structures of cerebral cortex and retina of SD rat. China Oils Fats 2017, 42, 124–149. [Google Scholar]
- Akihiro, G.; Yasunori, H. Offline neuronal activity and synaptic plasticity during sleep and memory consolidation. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 189, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Mallick, R.; Duttaroy, A.K. Maternal Docosahexaenoic Acid Status during Pregnancy and Its Impact on Infant Neurodevelopment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtman, R.J.; Cansev, M.E.H.M.E.T.; Ulus, I.H. Synapse formation is enhanced by oral administration of uridine and DHA, the circulating precursors of brain phosphatides. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, F.; Feng, R.; Wang, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. ATP11B deficiency leads to impairment of hippocampal synaptic plasticity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Phosphatidylserine in the brain: Metabolism and function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Fleuriot, L.; Janel, S.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, D.; Morel, C.; Mettouchi, A.; Debayle, D.; Dallongeville, S.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Antonny, B.; et al. DHA-containing phospholipids control membrane fusion and transcellular tunnel dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 2022, 135, jcs.259119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; He, T.; Mu, Y.; Mu, P.; Ao, J.; Lin, X.; Ruan, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, D.; et al. The genome of a hadal sea cucumber reveals novel adaptive strategies to deep-sea environments. Iscience 2022, 25, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Molecular and Signaling Mechanisms for Docosahexaenoic Acid-Derived Neurodevelopment and Neuroprotection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.-T.; Hu, J.-Q.; Qi, Z.-Y.; Xie, Q.-C.; Ou, J.; Pan, Y.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.-Q. Analysis of the value of nutritional fortification in food based on bioavailability: Taking DHA as an example. China Oils Fats 2023, 48, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- GB149250–2010; Laboratory Animal Requirement of Environment and Housing Facilities. National Standardization Administration: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Kusy, B.; Parzecka, K.; Kucharczyk, P.; Szczepanik, K. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and brain functions—Literature review. Wiad. Lek. 2024, 77, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha, E.; Balbo, I.; Parolisi, R.; Audano, M.; Montarolo, F.; Ravera, F.; Guglielmotto, M.; Muratori, L.; Raimondo, S.; DiGregorio, E.; et al. Elovl5 is required for proper action potential conduction along peripheral myelinated fibers. Glia 2021, 69, 2419–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Mallick, R.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Maternal Supply of Both Arachidonic and Docosahexaenoic Acids Is Required for Optimal Neurodevelopment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gsoellpointner, M.; Thanhaeuser, M.; Eibensteiner, F.; Ristl, R.; Jilma, B.; Fuiko, R.; Brandstetter, S.; Berger, A.; Haiden, N. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake during Complementary Feeding and Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Li, W.; Deng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, N. Assessment of lipid composition and eicosapentaenoic acid/docosahexaenoic acid bioavailability in fish oil obtained through different enrichment methods. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1136490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, J.; He, Q.; Xia, Y.; Tian, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, C.; Loor, J.J. Docosahexaenoic Acid Alters Lipid Metabolism Processes via H3K9ac Epigenetic Modification in Dairy Goat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8527–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasamatsu, A.; Tachimoto, H.; Urashima, M. Impact of Maternal Fish Consumption on Serum Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) Levels in Breastfed Infants: A Cross-Sectional Study of a Randomized Clinical Trial in Japan. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.-C.; Yin, F.-W.; Zhong, X.; Liu, H.-L.; Song, L.; Zhao, G.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhou, D.-Y. Effects of different antioxidants and their combinations on the oxidative stability of DHA algae oil and walnut oil. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 2804–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.-y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, H.-m.; Lyu, X.; Chen, H.; Wei, F. Comprehensive lipidomics and volatile compounds profiling reveals correlation of lipids and flavors in DHA-enriched egg yolk. Oil Crop Sci. 2023, 8, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwall, C.B.; Sasaki, Y.; Strickland, A.; Summers, D.W.; Bloom, A.J.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J. Suppressing phagocyte activation by overexpressing the phosphatidylserine lipase ABHD12 preserves sarmopathic nerves. Biorxiv Prepr. Serv. Biol. 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Li, Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Xue, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhang, T.-T. A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons. Marine Drugs 2023, 21, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Tachibana, N.; Nagao, K.; Tamura, T.; Hamachi, I. Organelle-selective click labeling coupled with flow cytometry allows pooled CRISPR screening of genes involved in phosphatidylcholine metabolism. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen-Jing, X.; Qian, L.; Lin, D.; Hao-Hao, S.; Chang-Hu, X.; Xiang-Zhao, M.; Yu-Ming, W.; Tian-Tian, Z. A comparative study of the effects of phosphatidylserine rich in DHA and EPA on Aβ-induced Alzheimer’s disease using cell models. Food Funct 2021, 12, 4411–4423. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T.; Li, D.; Vale, G.; Jiang, Y.; Schmiege, P.; Yang, Z.J.; McDonald, J.G.; Li, X. Molecular insights into human phosphatidylserine synthase 1 reveal its inhibition promotes LDL uptake. Cell 2024, 187, 5665–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisio, H.; Krishnan, A.; Marq, J.-B.; Soldati-Favre, D. Toxoplasma gondii phosphatidylserine flippase complex ATP2B-CDC50.4 critically participates in microneme exocytosis. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; He, Y.; Phan, K.; Bhatia, S.; Pickford, R.; Wu, P.; Dzamko, N.; Halliday, G.M.; Kim, W.S. Increased unsaturated lipids underlie lipid peroxidation in synucleinopathy brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.Y.; Cui, F.; Kim, H.K.; Nawaz, H.; Kang, S.; Kim, H.; Jang, J.; Go, G.-W. Effect of phosphatidylserine on cognitive function in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 54, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
| Name | Calorie (kcal/100 mL) | Protein (g/100 mL) | Carbohydrate (g/100 mL) | Fat (g/100 mL) | DHA (mg/100 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milk without DHA (Group B) | 73.8 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 4.4 | 0 |
| Model milk (Group M) | 73.8 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 4.4 | 0 |
| Naturally supplemented milk (Group OM) | 71.2 | 3.6 | 4.8 | 4.2 | 20 |
| FO-supplemented milk (Group Y) | 73.8 | 3.6 | 5.0 | 4.4 | 20 |
| Name | Core (%) | Soybean Meal (%) | Premix (%) | DHA | Calorie (kcal/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feed | 76 | 20 | 4 | 0 | 3270 |
| Time (min) | %A | %B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 60 | 40 |
| 1.5 | 15 | 85 |
| 10.5 | 15 | 85 |
| 14 | 15 | 85 |
| 14.1 | 0 | 100 |
| 15.1 | 0 | 100 |
| 15.3 | 60 | 40 |
| Setting Items | Setting Value |
|---|---|
| Ion Source | Point Jet Ionization Interface |
| Drying Machine Temperature | 300 °C |
| Nebulizer Pressure | 35 psig |
| Sheath Temperature | 35 °C |
| Sheath Flow Rate | 12 L/min |
| Crusher Voltage | 140 V |
| Capillary Voltage | 3500 V |
| Collection Rate | 3 Spectrum/s |
| Scanning Rate | 100–1700 m/z |
| Name | Oligo | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F | TCGGAGTGAACGGATTTGGC |
| R | TGACAAGCTTCCCGTTCTCC | |
| PTDSS1 | F | TCAGCCTCATGTACTTCGCC |
| R | AGTTCACAGCATACTCCATTGGG | |
| PTDSS2 | F | GAACACCTTCTTCTGGCGGG |
| R | CTCTTGGTGTTGTAGGCCGT | |
| BDNF | F | GAGTCTGGGGATTTCGGGG |
| R | CTCACCTGGTGGAACTTTTCAG | |
| CD36 | F | TGACCCAGCACTTGAAGCAA |
| R | TCCAAGAGGTATGCTTCTTTTCCA |
| Name | Body Weight (kg) | Brain Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|
| Group B | 15.70 ± 1.06 | 63.66 ± 3.49 |
| Group M | 14.12 ± 1.51 | 56.09 ± 8.87 |
| Group OM | 15.14 ± 0.97 | 60.09 ± 2.45 |
| Group Y | 14.15 ± 3.11 | 58.13 ± 6.59 |
| B vs. Y | M vs. Y | OM vs. Y | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | Degree | Node | Degree | Node | Degree |
| PI 18:0_20:3 | 9 | PE 18:0_22:4 | 7 | SHexCer d36:1 | 9 |
| SM d36:1 | 7 | PS 18:0_20:3 | 7 | SHexCer d38:2 | 8 |
| PS 20:1_22:6 | 7 | PC 16:0_18:1 | 6 | PC 18:0_18:1 | 7 |
| PE 18:0_22:4 | 6 | SHexCer d38:2 | 6 | PE 18:1_22:6 | 6 |
| PS 18:0_20:3 | 6 | PI 18:0_20:4 | 6 | PS 18:0_20:3 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Z.; Xiong, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Sun, Y. Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid from Different Sources on Prefrontal-Cortex Synaptic Plasticity. Nutrients 2025, 17, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030457
He Z, Xiong W, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Li B, Wang F, Li Y, Wang R, Sun Y. Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid from Different Sources on Prefrontal-Cortex Synaptic Plasticity. Nutrients. 2025; 17(3):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030457
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Zude, Wei Xiong, Yue Yang, Yifan Zhang, Boying Li, Fuqing Wang, Yixuan Li, Ran Wang, and Yanan Sun. 2025. "Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid from Different Sources on Prefrontal-Cortex Synaptic Plasticity" Nutrients 17, no. 3: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030457
APA StyleHe, Z., Xiong, W., Yang, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, B., Wang, F., Li, Y., Wang, R., & Sun, Y. (2025). Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid from Different Sources on Prefrontal-Cortex Synaptic Plasticity. Nutrients, 17(3), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17030457







