Exploring Obesity Subtypes: Cluster Analysis of Eating Behaviors, Food Addiction, and Psychopathology in Turkish Adults Seeking Obesity Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Assessment and Measures
2.2.1. Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ-R18)
2.2.2. Night Eating Questionnaire (NEQ)
2.2.3. Yale Food Addiction Scale (YFAS)
2.2.4. Symptom Check List (SCL-90-R)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Scale Scores of the Study Sample
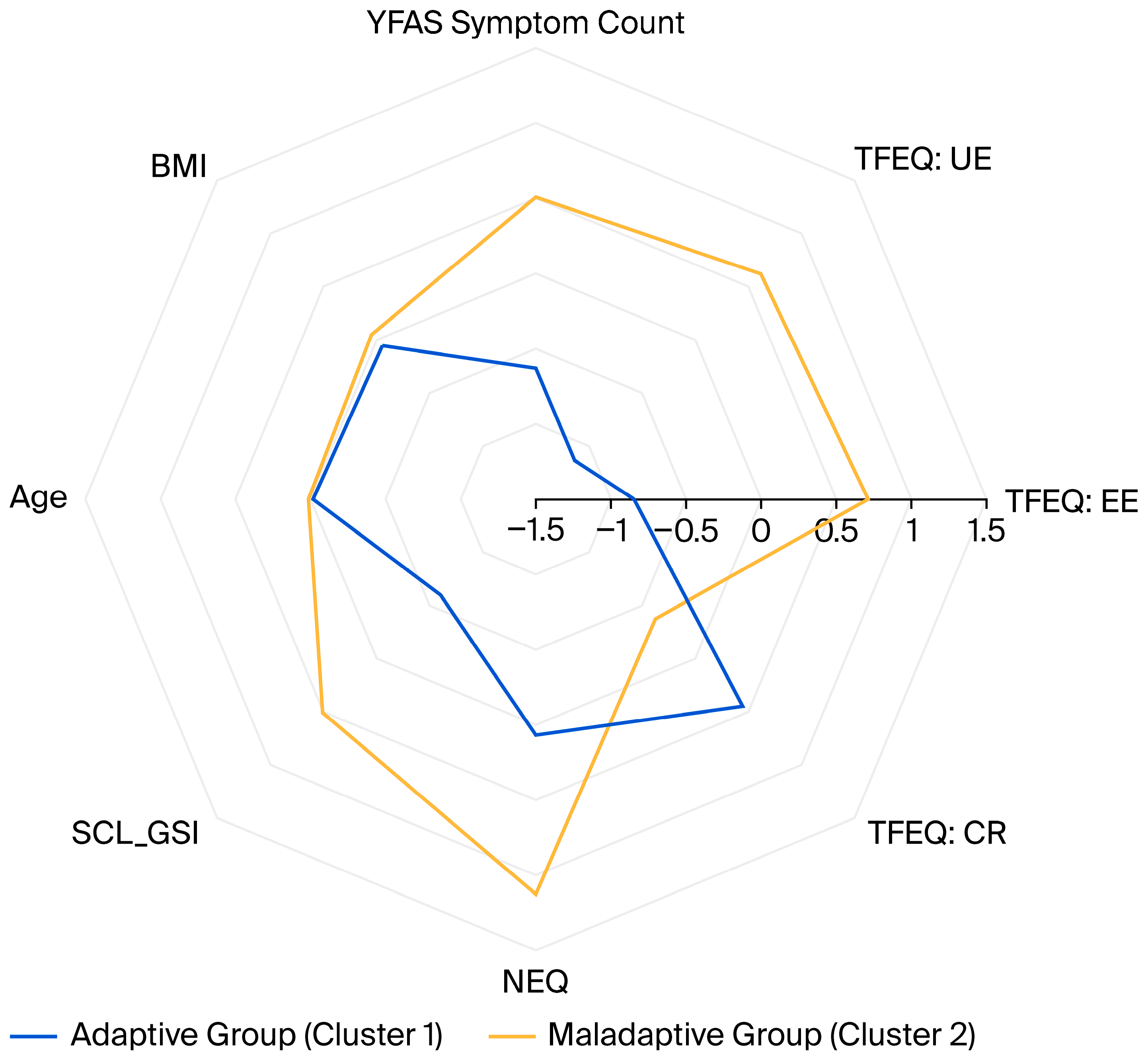
3.2. Cluster Analysis Results
3.2.1. Inter-Cluster Comparison of Sociodemographic Properties, Food Addiction, and Clinical Data
3.2.2. Comparison of Groups in Terms of Scale Scores and Sociodemographic Numerical Data
| Cluster 1 (Adaptive) | Cluster 2 (Maladaptive) | F | p | d | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||
| Age (years) | 39.86 | 11.65 | 40.21 | 11.06 | 0.048 | 0.827 | 0.03 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 42.73 | 5.57 | 43.30 | 5.35 | 0.550 | 0.459 | 0.10 |
| Height (m) | 1.64 | 0.08 | 1.63 | 0.10 | 1.137 | 0.288 | 0.15 |
| Weight (kg) | 115.36 | 19.84 | 114.75 | 18.19 | 0.051 | 0.822 | 0.03 |
| YFAS symptom score (0–7) | 3.16 | 1.50 | 5.15 | 1.41 | 93.261 | <0.001 * | 1.36 |
| TFEQ-R18: UE | 26.25 | 16.43 | 60.17 | 20.11 | 167.965 | <0.001 * | 1.83 |
| TFEQ-R18: EE | 23.91 | 21.72 | 75.66 | 20.33 | 304.826 | <0.001 * | 2.47 |
| TFEQ-R18: CR | 61.11 | 19.54 | 44.90 | 16.73 | 40.358 | <0.001 * | 0.90 |
| NEQ: Total Score | 12.42 | 5.85 | 22.40 | 9.54 | 76.561 | <0.001 * | 1.24 |
| SCL90-R: GSI | 0.61 | 0.40 | 1.33 | 0.64 | 87.594 | <0.001 * | 1.32 |
| SCL90-R: Somatization | 0.88 | 0.68 | 1.61 | 0.88 | 42.351 | <0.001 * | 0.92 |
| SCL90-R: Obsessive Compulsive | 0.80 | 0.54 | 1.64 | 0.74 | 82.61 | <0.001 * | 1.29 |
| SCL90-R: Interpersonal Sensitivity | 0.81 | 0.66 | 1.66 | 0.95 | 53.4 | <0.001 * | 1.03 |
| SCL90-R: Depressive | 0.70 | 0.53 | 1.55 | 0.83 | 72.461 | <0.001 * | 1.20 |
| SCL90-R: Anxiety | 0.40 | 0.34 | 1.05 | 0.70 | 65.363 | <0.001 * | 1.14 |
| SCL90-R: Hostility | 0.48 | 0.46 | 1.07 | 0.76 | 42.444 | <0.001 * | 0.92 |
| SCL90-R: Phobic Anxiety | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 35.784 | <0.001 * | 0.84 |
| SCL90-R: Paranoia | 0.55 | 0.49 | 1.27 | 0.79 | 59.279 | <0.001 * | 1.09 |
| SCL90-R: Psychoticism | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 44.905 | <0.001 * | 0.95 |
| SCL90-R: PST | 32.51 | 18.63 | 54.34 | 18.79 | 68.112 | <0.001 * | 1.17 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Courcoulas, A.P.; King, W.C.; Belle, S.H.; Berk, P.; Flum, D.R.; Garcia, L.; Gourash, W.; Horlick, M.; Mitchell, J.E.; Pomp, A.; et al. Seven-year weight trajectories and health outcomes in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery (LABS) study. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, V.M.; Breen, D.M.; Fortin, J.-P.; Liou, A.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Loomis, A.K.; Rives, M.-L.; Shah, B.; Carpino, P.A. Latest approaches for the treatment of obesity. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Camargo, C.A.; Ogino, S. The merits of subtyping obesity: One size does not fit all. JAMA 2013, 310, 2147–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.M.; Utzinger, L.M.; Pisetsky, E.M. Eating disorders and problematic eating behaviours before and after bariatric surgery: Characterization, assessment and association with treatment outcomes. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2015, 23, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, K.H.; Kramer, M.S.; Oken, E.; Timpson, N.J.; Skugarevsky, O.; Patel, R.; Bogdanovich, N.; Vilchuck, K.; Davey Smith, G.; Thompson, J.; et al. Prospective associations between problematic eating attitudes in midchildhood and the future onset of adolescent obesity and high blood pressure. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, A.; Lundgren, J.; Drapeau, V. The night-eating syndrome and obesity. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, J.M.; Hinman, N.; Koball, A.; Hoffmann, D.A.; Carels, R.A. Food addiction in adults seeking weight loss treatment. Implications for psychosocial health and weight loss. Appetite 2013, 60, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niego, S.H.; Kofman, M.D.; Weiss, J.J.; Geliebter, A. Binge eating in the bariatric surgery population: A review of the literature. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2007, 40, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Agüera, Z.; Paslakis, G.; Munguia, L.; Granero, R.; Sánchez-González, J.; Sánchez, I.; Riesco, N.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Dieguez, C.; et al. Food Addiction in Eating Disorders and Obesity: Analysis of Clusters and Implications for Treatment. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezaj, V.; Wiedemann, A.A.; Grilo, C.M. Food addiction and bariatric surgery: A systematic review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero Perez, F.; Sánchez-González, J.; Sánchez, I.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Granero, R.; Simó-Servat, A.; Ruiz, A.; Virgili, N.; López-Urdiales, R.; Montserrat-Gil de Bernabe, M.; et al. Food addiction and preoperative weight loss achievement in patients seeking bariatric surgery. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2018, 26, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, E.C.; Gould, E. New evidence linking obesity and food addiction. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Vainik, U.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Dagher, A. Overlapping neural endophenotypes in addiction and obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, B.A.; Cassin, S.E. Disordered eating among individuals with excess weight: A review of recent research. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, A. Emergence of bariatric psychiatry as a new subspecialty. World J. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.A.; Hawkins, M.A.; Duncan, J.; Rummell, C.M.; Perkins, S.; Crowther, J.H. Maladaptive eating behavior assessment among bariatric surgery candidates: Evaluation of the Eating Disorder Diagnostic Scale. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2017, 13, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, M.D.; Andris, D. Maladaptive eating patterns after weight-loss surgery. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2007, 22, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podina, I.R.; Fodor, L.A.; Cosmoiu, A.; Boian, R. An evidence-based gamified mHealth intervention for overweight young adults with maladaptive eating habits: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. The role of obesity in type 2 diabetes mellitus—An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.; Karg, R.S.; Spitzer, R.L. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Disorders: SCID-5-CV Clinician Version; American Psychiatric Association Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, J.; Persson, L.O.; Sjostrom, L.; Sullivan, M. Psychometric properties and factor structure of the Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (TFEQ) in obese men and women. Results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2000, 24, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Messick, S. The three-factor eating questionnaire to measure dietary restraint, disinhibition and hunger. J. Psychosom. Res. 1985, 29, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kıraç, D.; Kaspar, E.Ç.; Avcılar, T.; Çakır, Ö.K.; Ulucan, K.; Kurtel, H.; Deyneli, O.; Güney, A.İ. Obeziteyle ilişkili beslenme alışkanlıklarının araştırılmasında yeni bir yöntem “Üç faktörlü beslenme anketi”. Clin. Exp. Health Sci. 2015, 5, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, K.C.; Lundgren, J.D.; O’Reardon, J.P.; Martino, N.S.; Sarwer, D.B.; Wadden, T.A.; Crosby, R.D.; Engel, S.G.; Stunkard, A.J. The Night Eating Questionnaire (NEQ): Psychometric properties of a measure of severity of the Night Eating Syndrome. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atasoy, N.; Saraçlı, Ö.; Konuk, N.; Ankaralı, H.; Güriz, O.; Akdemir, A.; Sevinçer, G.M.; Atik, L. Gece Yeme Anketi-Türkçe Formunun psikiyatrik ayaktan hasta popülasyonunda geçerlilik ve güvenilirlik çalışması. Anadolu Psikiyatr. Derg. 2014, 15, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhardt, A.N.; Corbin, W.R.; Brownell, K.D. Preliminary validation of the Yale food addiction scale. Appetite 2009, 52, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevinçer, G.M.; Konuk, N.; Bozkurt, S.; Saraçlı, Ö.; Coşkun, H. Psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the Yale Food Addiction Scale among bariatric surgery patients. Anatol. J. Psychiatry 2015, 16, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derogatis, L.R.; Savitz, K.L. The SCL-90-R, Brief Symptom Inventory, and Matching Clinical Rating Scales. In The Use of Psychological Testing for Treatment Planning and Outcomes Assessment, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 679–724. [Google Scholar]
- Dağ, I. Belirti Tarama Listesi (Scl-90-R)’nin Üniversite Öğrencileri için güvenirliği ve geçerliği. [Reliability and validity of the Symptom Check List (SCL-90-R) for university students.]. Türk Psikiyatr. Derg. 1991, 2, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fraley, C.; Raftery, A.E. How many clusters? Which clustering method? Answers via model-based cluster analysis. Comput. J. 1998, 41, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylund, K.L.; Asparouhov, T.; Muthén, B.O. Deciding on the Number of Classes in Latent Class Analysis and Growth Mixture Modeling: A Monte Carlo Simulation Study. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 2007, 14, 535–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, A.E.; Inge, T.H.; Belle, S.H.; Johnson, G.S.; Wahed, A.S.; Pories, W.J.; Spaniolas, K.; Mitchell, J.E.; Pomp, A.; Dakin, G.F.; et al. Association of Obesity Subtypes in the Longitudinal Assessment of Bariatric Surgery Study and 3-Year Postoperative Weight Change. Obesity 2018, 26, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, E.A.; Rania, M.; D’Onofrio, E.; Quirino, D.; De Filippis, R.; Rotella, L.; Aloi, M.; Fiorentino, V.T.; Murphy, R.; Segura-Garcia, C. The Greater the Number of Altered Eating Behaviors in Obesity, the More Severe the Psychopathology. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroleo, M.; Primerano, A.; Rania, M.; Aloi, M.; Pugliese, V.; Magliocco, F.; Fazia, G.; Filippo, A.; Sinopoli, F.; Ricchio, M.; et al. A real world study on the genetic, cognitive and psychopathological differences of obese patients clustered according to eating behaviours. Eur. Psychiatry 2018, 48, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leombruni, P.; Rocca, G.; Fassino, S.; Gastaldi, F.; Nicotra, B.; Siccardi, S.; Lavagnino, L. An exploratory study to subtype obese binge eaters by personality traits. Psychother. Psychosom. 2014, 83, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsager, C.; Færk, E.; Lauritsen, M.B.; Østergaard, S.D. Food addiction comorbid to mental disorders: A nationwide survey and register-based study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, L.G.; Stroebele, N.; Wyatt, H.R.; Catenacci, V.A.; Peters, J.C.; Stuht, J.; Wing, R.R.; Hill, J.O. Cluster analysis of the national weight control registry to identify distinct subgroups maintaining successful weight loss. Obesity 2012, 20, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Strong, M.; Razak, F.; Subramanian, S.; Relton, C.; Bissell, P. Who are the obese? A cluster analysis exploring subgroups of the obese. J. Public Health 2016, 38, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Claes, L.; Wilderjans, T.F.; De Zwaan, M. Temperament subtypes in treatment seeking obese individuals: A latent profile analysis. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2014, 22, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho-Barcia, L.; Lucas, I.; Miranda-Olivos, R.; Jimenez-Murcia, S.; Fernandez-Aranda, F. Applying psycho-behavioural phenotyping in obesity characterization. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuschl, R.J. From dietary restraint to binge eating: Some theoretical considerations. Appetite 1990, 14, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, R.M.; Alhazmi, A. Association between cognitive restraint, emotional eating, uncontrolled eating, and body mass index among health care professionals. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, I.; Bégin, C.; Maltais-Giguère, J.; Bédard, A.; Tchernof, A.; Lemieux, S. Impact of Experimentally Induced Cognitive Dietary Restraint on Eating Behavior Traits, Appetite Sensations, and Markers of Stress during Energy Restriction in Overweight/Obese Women. J. Obes. 2018, 2018, 4259389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.; Troop, N.; Connan, F.; Treasure, J.; Campbell, I.C. The effects of stress on body weight: Biological and psychological predictors of change in BMI. Obesity 2007, 15, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloi, M.; Liuzza, M.T.; Rania, M.; Carbone, E.A.; De Filippis, R.; Gearhardt, A.N.; Segura-Garcia, C. Using latent class analysis to identify different clinical profiles according to food addiction symptoms in obesity with and without binge eating disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2024, 13, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meule, A.; Gearhardt, A.N. Food addiction in the light of DSM-5. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3653–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauck, C.; Cook, B.; Ellrott, T. Food addiction, eating addiction and eating disorders. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, P.H.; Balodis, I.M.; Potenza, M.N. Binge-eating disorder: Clinical and therapeutic advances. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 182, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, T.; Menchon, J.M.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; Soriano-Mas, C.; Fernandez-Aranda, F. Neural network alterations across eating disorders: A narrative review of fMRI studies. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenaki, N.; Bacopoulou, F.; Kokkinos, A.; Nicolaides, N.C.; Chrousos, G.P.; Darviri, C. Impact of a stress management program on weight loss, mental health and lifestyle in adults with obesity: A randomized controlled trial. J. Mol. Biochem. 2018, 7, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Willem, C.; Gandolphe, M.C.; Doba, K.; Roussel, M.; Verkindt, H.; Pattou, F.; Nandrino, J.L. Eating in case of emotion dys-regulation, depression and anxiety: Different pathways to emotional eating in moderate and severe obesity. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.B.; Braga Tibães, J.R.; Sanches, M.; Jacka, F.; Berk, M.; Teixeira, A.L. Nutrition-based interventions for mood disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, W.; Moseley, G.; Berk, M.; Jacka, F. Nutritional psychiatry: The present state of the evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sysko, R.; Hildebrandt, T.; Wilson, G.T.; Wilfley, D.E.; Agras, W.S. Heterogeneity moderates treatment response among patients with binge eating disorder. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2010, 78, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO European Regional Obesity Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
| n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) (mean ± SD) | 43.03 ± 5.44 | |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 40.04 ± 11.30 | |
| Sex | Female | 163 (80.7) |
| Male | 39 (19.3) | |
| Education | Primary Education | 36 (17.8) |
| Lower Secondary Education | 40 (19.8) | |
| Upper Secondary Education | 68 (33.7) | |
| Higher Education | 58 (28.7) | |
| Diagnoses (DSM-5) | Major Depressive Disorder | 29 (14.4) |
| Anxiety Disorder | 20 (9.9) | |
| Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder | 5 (2.5) | |
| Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder | 2 (1) | |
| Adjustment Disorder | 9 (4.5) | |
| Panic Disorder | 2 (1) | |
| Eating and Feeding Disorders (DSM-5) | Pica | 2 (1) |
| Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder | 6 (3) | |
| Bulimia Nervosa | 3 (1.5) | |
| Binge-Eating Disorder | 38 (18.8) | |
| Food Addiction | 97 (48) | |
| Cluster 1 (Adaptive) n (%) | Cluster 2 (Maladaptive) n (%) | p | V | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 19 (20.7) | 20 (18.2) | 0.658 | 0.031 |
| Female | 73 (79.3) | 90 (81.8) | |||
| Education | Primary | 13 (14.1) | 23 (20.9) | 0.407 | 0.120 |
| Lower Secondary | 17 (18.5) | 23 (20.9) | |||
| Higher Secondary | 31 (33.7) | 37 (33.6) | |||
| Higher Education | 31 (33.7) | 27 (24.5) | |||
| Occupation | Unemployed | 7 (7.6) | 6 (5.5) | 0.865 | 0.097 |
| Student | 5 (5.4) | 19 (9.1) | |||
| Housewife | 43 (46.7) | 54 (49.1) | |||
| Worker | 16 (17.4) | 18 (16.4) | |||
| Retired | 5 (5.4) | 7 (6.4) | |||
| Self-employed | 16 (17.4) | 15 (13.6) | |||
| Anxiety Disorder | 6 (6.5) | 14 (12.7) | 0.141 | 0.103 | |
| MDD | 3 (3.3) | 26 (23.6) | <0.001 * | 0.289 | |
| BED | 10 (10.9) | 28 (25.5) | <0.01 * | 0.186 | |
| FA | 19 (20.7) | 78 (70.9) | <0.001 * | 0.501 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortaköylü, O.; Gündoğmuş, A.G.; Örsel, S. Exploring Obesity Subtypes: Cluster Analysis of Eating Behaviors, Food Addiction, and Psychopathology in Turkish Adults Seeking Obesity Treatment. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243823
Ortaköylü O, Gündoğmuş AG, Örsel S. Exploring Obesity Subtypes: Cluster Analysis of Eating Behaviors, Food Addiction, and Psychopathology in Turkish Adults Seeking Obesity Treatment. Nutrients. 2025; 17(24):3823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243823
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtaköylü, Orçun, Ayşe Gökçen Gündoğmuş, and Sibel Örsel. 2025. "Exploring Obesity Subtypes: Cluster Analysis of Eating Behaviors, Food Addiction, and Psychopathology in Turkish Adults Seeking Obesity Treatment" Nutrients 17, no. 24: 3823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243823
APA StyleOrtaköylü, O., Gündoğmuş, A. G., & Örsel, S. (2025). Exploring Obesity Subtypes: Cluster Analysis of Eating Behaviors, Food Addiction, and Psychopathology in Turkish Adults Seeking Obesity Treatment. Nutrients, 17(24), 3823. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17243823






