Epidemiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure in Spain: Data from the REPAFI Registry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Data Collection Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIF | Chronic intestinal failure |
| HPN | Home parenteral nutrition |
| SBS | Short bowel syndrome |
| CE | Congenital enteropathies |
| ICV | Ileocecal valve |
| RBL | Residual bowel length |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| IF | Intestinal failure |
| SENPE | Spanish Society of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism |
| SEGHNP | Spanish Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition |
| REDCap | Research Electronic Data Capture |
| SMD | Severe motility disorder |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| PN | Parenteral nutrition |
| BW | Body weight |
| GA | Gestational age |
References
- Goulet, O.; Ruemmele, F. Causes and management of intestinal failure in children. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S16–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, A.; Capriati, T.; Gandullia, P.; Di Leo, G.; Lezo, A.; Lacitignola, L.; Spagnuolo, M.; Gatti, S.; D’antiga, L.; Verlato, G.; et al. Pediatric Chronic Intestinal Failure in Italy: Report from the 2016 Survey on Behalf of Italian Society for Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (SIGENP). Nutrients 2017, 9, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antiga, L.; Goulet, O. Intestinal failure in children: The European view. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiagarajah, J.R.; Kamin, D.S.; Acra, S.; Goldsmith, J.D.; Roland, J.T.; Lencer, W.I.; Muise, A.M.; Goldenring, J.R.; Avitzur, Y.; Martín, M.G.; et al. Advances in Evaluation of Chronic Diarrhea in Infants. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 20145–20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Goulet, O.; Buchman, A.; Messing, B.; Gabe, S.; Candusso, M.; Bond, G.; Gupte, G.; Pertkiewicz, M.; Steiger, E.; et al. Outcome on home parenteral nutrition for benign intestinal failure: A review of the literature and benchmarking with the European prospective survey of ESPEN. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrón Giner, C.; Cuervas-Mons Vendrell, M.; Galera Martínez, R.; López, L.G.; Muñoz, P.G.; Terradillos, I.I.; Costa, C.M.; Villares, J.M.M.; Maristany, C.P.-P.; Del Río, M.T.P.; et al. Pediatric parenteral nutrition: Clinical practice guidelines from the Spanish Society of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SENPE), the Spanish Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (SEGHNP) and the Spanish Society of Hospital Pharmacy (SEFH). Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 745–758. [Google Scholar]
- Duggan, C.P.; Jaksic, T. Pediatric Intestinal Failure. N. Eng. J. Med. 2017, 377, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.A.; Cohran, V.C.; Cole, C.R.; Corkins, M.R.; Dimmitt, R.A.; Duggan, C.; Hill, S.; Horslen, S.; Lim, J.D.; Mercer, D.F.; et al. Outcomes from a 12-week, open-label, multicenter clinical trial of teduglutide in pediatric short bowel syndrome. J. Pediatr. 2017, 181, 102–111.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Candusso, M.; Biondo, A.; Bosco, A.; Castaldi, P.; Contaldo, F.; Finocchiaro, E.; Giannoni, A.; Mazzuoli, S.; Orlandoni, P.; et al. Prevalence of home artificial nutrition in Italy in 2005: A survey by the Italian Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (SINPE). Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beath, S.V.; Gowen, H.; Puntis, J.W.L. Trends in paediatric home parenteral nutrition and implications for service development. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelis, E.G.; Roskott, A.M.; Dijkstra, G.; Wanten, G.; Serlie, M.; Tabbers, M.; Damen, G.; Olthof, E.; Jonkers, C.; Kloeze, J.; et al. Presentation of a nationwide multicenter registry of intestinal failure and intestinal transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawinkel, M.B.; Scholz, D.; Busch, A.; Kohl, M.; Wessel, L.M.; Zimmer, K.P. Chronic intestinal failure in children. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2012, 109, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.; Breton, A.; Coste, M.E.; Dubern, B.; Ecochard-Dugelay, E.; Guimber, D.; Loras-Duclaux, I.; Abi Nader, E.; Marinier, E.; Peretti, N.; et al. Pediatric Home Parenteral Nutrition in France: A six years national survey. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5278–5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, H.; Nóbrega, S.; Correia, M.; Campos, A.P.; Silva, R.; Guerra, P.; Mourato, P.; Lopes, A.I.; Mansilha, H.; Tavares, M. Portuguese Prevalence of Pediatric Chronic Intestinal Failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A.R.; Henderson, P.; Gowen, H.; Puntis, J.; BIFS collaborators. The continued rise of paediatric home parenteral nutrition use: Implications for service and the improvement of longitudinal data collection. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanden-Berghe, C.; Virgili Casas, N.; Cuerda Compés, C.; Ramos Boluda, E.; Pereira Cunill, J.L.; Maíz Jiménez, M.I.; Peláez, R.B.; Candela, C.G.; Lázaro, M.Á.P.; Martos, E.Á.S.; et al. Nutrición parenteral domiciliaria en España, 2019: Informe del Grupo de Nutrición Artificial Domiciliaria y Ambulatoria NADYA [Home and Ambulatory Artificial Nutrition (NADYA) Group report: Home parenteral nutrition in Spain, 2019]. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Researcho electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNicholl, A.G.; Gisbert, J.P. Research to the N-Power: The Strengths of Networked Clinical Collaboration in Spain. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1761–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomb, V.; Dabbas-Tyan, M.; Taupin, P.; Talbotec, C.; Révillon, Y.; Jan, D.; De Potter, S.; Gorski-Colin, A.; Lamor, M.; Herreman, K.; et al. Long-term outcome of children receiving home parenteral nutrition: A 20-year single-center experience in 302 Patients. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 44, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gossum, A.; Vahedi, K.; Abdel, M. Clinical, social and rehabilitation status of long-term home parenteral nutrition patients: Results of a European multicenter survey. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, R.T.; Steiger, E. Early History of Home Parenteral Nutrition: From Hospital to Home. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2018, 33, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuera, I.; Garcia-Peris, P.; Camblor, M.; Bretón, I.; Velasco, C.; Romero, R.; Frias, L.; Cuerda, C. Outcomes of a general hospital-based home parenteral nutrition (HPN) program; report of our experience from a 26-year period. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- López Bermejo, A.; Moreno Villares, J.M.; Gomis Muñoz, P.; León Sanz, M.; Manzanares López, J. Nutrición parenteral domiciliaria: Experiencia inicial. An. Esp. Pediatr. 1996, 44, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guía de Nutrición Parenteral Domiciliaria en el Sistema Nacional de Salud. Ministerio de Sanidad y política Social 2009. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/prestacionesSanitarias/publicaciones/docs/guiaNPD.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Germán Díaz, M.; Ramos Boluda, E.; Moreno Villares, J.M. Los registros de pacientes pediátricos con nutrición artificial en el domicilio. La experiencia española [The registers of pediatric patients with home artificial nutrition. The Spanish experience]. Nutr. Hosp. 2024, 41, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gandullia, P.; Lugani, F.; Costabello, L.; Arrigo, S.; Calvi, A.; Castellano, E.; Vignola, S.; Pistorio, A.; Barabino, A.V. Long-term home parenteral nutrition in children with chronic intestinal failure: A 15-year experience at a single Italian centre. Dig. Liver Dis. 2011, 43, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanger, J.D.; Oliveira, C.; Blackmore, C.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W. The impact of multi-disciplinary intestinal rehabilitation programs on the outcome of pediatric patients with intestinal failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2013, 48, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
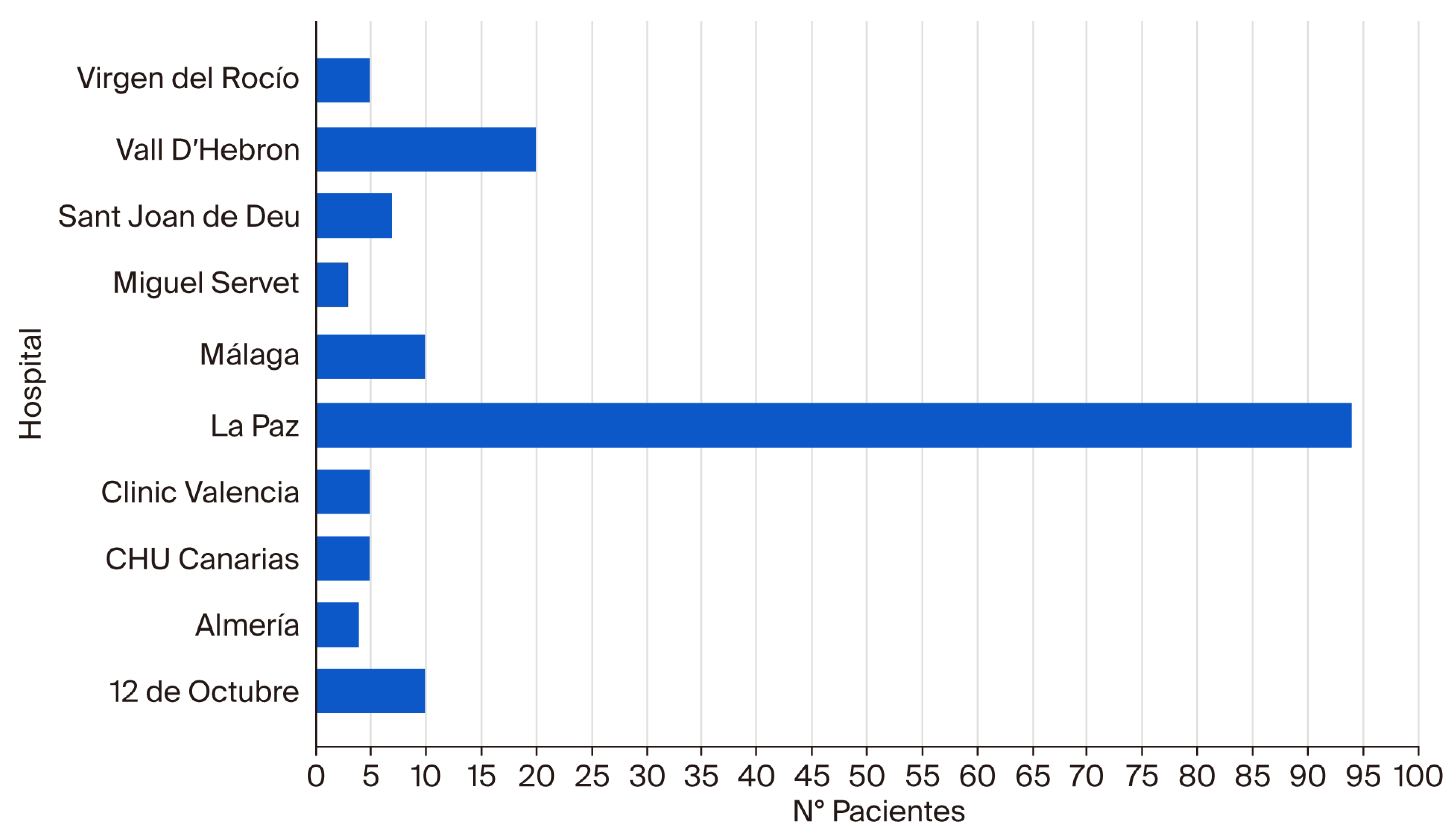

| N° Patients | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Short Bowel | 126 | 77.3 |
| Congenital Enteropathy | 9 | 5.5 |
| Severe Motility Disorder | 21 | 12.9 |
| Other (Immunodeficiencies, inflammatory bowel disease, cancer, cystic fibrosis…) | 7 | 4.3 |
| Total | 163 | 100.0 |
| N° Patients | Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Type | ||
| Type 1 (enterostomy) | 32 | 25.4 |
| Type 2 (jejuno-colic anastomosis) | 59 | 46.8 |
| Type 3 (jejuno-ileal anastomosis with ICV) | 34 | 27 |
| Classification According to RBL | ||
| <15 cm | 29 | 23 |
| 15–40 cm | 46 | 36.5 |
| >40 cm | 50 | 39.7 |
| Presence of ICV | ||
| No | 79 | 62.7 |
| Yes | 44 | 34.9 |
| Diagnosis | N° Patients |
|---|---|
| Severe Motility Disorders | 21 |
| Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction | 13 |
| Others | 8 |
| Congenital Enteropathies | 9 |
| Microvillus inclusion disease | 3 |
| Intestinal epithelial dysplasia | 3 |
| Trichohepatoenteric syndrome | 2 |
| Others | 1 |
| Other Causes | 7 |
| Syndromes | 2 |
| Cancer | 2 |
| Chylomicron retention disease | 1 |
| Short bowel resection with associated motility disorder | 1 |
| Sclerosing peritonitis | 1 |
| Year | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° patients | 11 | 8 | 8 | 20 | 23 | 17 | 22 | 23 | 16 | 15 |
| Sex (%) | ||||||||||
| Male | 81.8 | 50 | 62.5 | 40 | 65.2 | 47.1 | 40.9 | 65.2 | 43.8 | 60 |
| Female | 18.2 | 50 | 37.5 | 60 | 34.8 | 52.9 | 59.1 | 34.8 | 56.3 | 40 |
| Gestational Age | ||||||||||
| Median (weeks) [IQR] | 36 [33.0–39.0] | 32 [29.5–38.8] | 34 [27.5–39.5] | 35 [27.8–38.0] | 35 [34.0–39.0] | 35 [27.0–39.0] | 38 [33.8–39.0] | 35 [33.0–36.3] | 36 [34.0–38.0] | 31 [28.0–37.0] |
| Birth Weight | ||||||||||
| Median (kg) | 2.5 | 2.16 | 2.09 | 2.01 | 2.14 | 2.5 | 2.82 | 2.21 | 2.52 | 1.67 |
| [IQR] | [2.0–2.8] | [1.2–3.3] | [1.1–3.1] | [0.9–2.8] | [1.7–2.9] | [1.0–3.0] | [1.9–3.1] | [1.6–3.0] | [1.7–3.2] | [1.0–2.5] |
| Length at Birth | ||||||||||
| Median (cm) | 45 | 44 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 45.5 | 47 | 44.5 | 46 | 42.5 |
| [IQR] | [41–49] | [35–50] | [35–49] | [35–49] | [40–47] | [35–50] | [45–50] | [42–48] | [44–49] | [35–46] |
| Cause of CIF (%) | ||||||||||
| SBS | 72.7 | 87.5 | 87.5 | 75 | 78.3 | 82.4 | 63.6 | 82.6 | 75 | 80 |
| CE | 9.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17.4 | 5.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
| SMD | 18.2 | 12.5 | 12.5 | 25 | 4.3 | 5.9 | 22.7 | 8.7 | 18.8 | 0 |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.9 | 13.6 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 0 |
| RBL | ||||||||||
| Median (cm) | 36 | 30 | 26 | 29 | 25 | 48 | 34 | 48 | 55 | 32 |
| [IQR] | [31.3–47.5] | [8.0–48.0] | [5.0–40.0] | [15.2–42.5] | [11.5–32.5] | [12.0–72.5] | [6.2–51.5] | [28.0–90.0] | [32.5–109.0] | [20.5–50.0] |
| Age at Start of HPN | ||||||||||
| Median (months) | 6 | 8.3 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.9 | 7.2 | 6.8 | 6.1 | 5.3 | 6.2 |
| [IQR] | [3.3–8.5] | [3.2–17.3] | [4.1–8.1] | [5.2–9.0] | [4.8–14.4] | [5.0–15.6] | [5.5–32.0] | [3.8–27.1] | [3.4–67.4] | [4.0–18.7] |
| Weight-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | ||||||||||
| Median | −3.6 | −3.7 | −3.9 | −4.3 | −3.9 | −3.6 | −2.8 | −2.6 | −3.3 | −3.9 |
| [IQR] | [−5.0–−2.3] | [−4.9–−2.6] | [−5.6–−2.6] | [−5.4–−1.6] | [−5.3–−2.7] | [−5.4–−2.2] | [−3.9–−1.6] | [−4.1–−1.3] | [−4.6–−1.8] | [−5.3–−3.1] |
| Length-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | ||||||||||
| Median | −2.6 | −1.8 | −2.3 | −4 | −3.7 | −3.4 | −1.8 | −2.3 | −2.6 | −3.8 |
| [IQR] | [−4.3–−2.0] | [−5.1–−1.5] | [−6.5–−0.7] | [−6.4–−2.2] | [−4.5–−2.0] | [−4.3–−1.9] | [−3.0–−0.3] | [−3.7–−0.7] | [−3.8–−0.4] | [−4.9–−2.7] |
| Body Mass Index (BMI)-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | ||||||||||
| Median | −2 | −3.3 | −2.7 | −1.8 | −2.7 | −2 | −2.2 | −1.6 | −2.2 | −2.4 |
| [IQR] | [−4.1–−1.4] | [−3.6–−0.5] | [−4.6–−2.3] | [−3.8–−1.1] | [−4.0–−1.4] | [−3.8–−1.2] | [−3.0–−0.8] | [−3.7–−0.5] | [−3.9–−1.2] | [−3.2–−1.2] |
| Type of PN administered (%) | ||||||||||
| Individually prepared by hospital pharmacy | 45.5 | 25 | 37.5 | 45 | 26.1 | 35.3 | 36.4 | 30.4 | 56.3 | 60 |
| Individually prepared by catering service | 54.5 | 75 | 62.5 | 55 | 73.9 | 64.7 | 63.6 | 69.6 | 43.8 | 40 |
| Standard | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Characteristics | Cause of CIF | Comparison by Groups (p-Value) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | SBS (1) | CE (2) | SMD (3) | Others (4) | p-Value | p 1–2 | p 1–3 | p 1–4 | p 2–3 | p 2–4 | p 3–4 | |
| N = 163 | N = 126 | N = 9 | N = 21 | N = 7 | ||||||||
| GA | <0.01 | 0.02 | <0.01 | 0.04 | 0.94 | 0.75 | 0.8 | |||||
| Median (weeks) | 35 | 34 | 38 | 38 | 38 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [31.5–38.0] | [30.0–37.0] | [37.0–39.0] | [37.0–39.0] | [34.0–40.0] | |||||||
| BW | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.75 | |||||
| Median (kg) | 2.32 | 2.15 | 2.66 | 2.71 | 2.8 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [1.63–2.95] | [1.43–2.89] | [2.48–2.80] | [2.27–3.10] | [1.75–3.26] | |||||||
| Age at Start of HPN | 0.06 | 0.28 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.61 | |||||
| Median (months) | 6.6 | 6.1 | 8 | 25 | 17 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [4.60–15.00] | [4.40–9.50] | [6.20–14.40] | [5.10–105.80] | [11.90–101.00] | |||||||
| Weight-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.92 | |||||
| Median | −3.4 | −3.5 | −4.3 | −2.5 | −2.8 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [−5.00–−2.30] | [−5.10–−2.40] | [−4.90–−3.70] | [−3.70–−1.70] | [−3.20–−0.70] | |||||||
| Length-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.23 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.89 | |||||
| Median | −2.85 | −2.9 | −3.8 | −2 | −2.1 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [−4.50–−1.50] | [−4.60–−1.50] | [−4.50–−3.00] | [−3.00–−1.50] | [−3.60–−1.40] | |||||||
| Body Mass Index (BMI)-for-age Z-score at the start of HPN | 0.55 | 0.78 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.43 | 0.89 | |||||
| Median | −2.2 | −2.3 | −2.6 | −1.9 | −1.5 | |||||||
| [IQR] | [−3.70–−1.30] | [−3.70–−1.40] | [−3.90–−1.30] | [−3.10–0.10] | [−3.00–−1.10] | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Germán-Díaz, M.; González-Sacristán, R.; Cabello, V.; Blasco-Alonso, J.; Rodríguez, A.; de los Santos, M.; Arcos-Machancoses, J.V.; Murray-Hurtado, M.; García-Romero, R.; Galera-Martínez, R.; et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure in Spain: Data from the REPAFI Registry. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233768
Germán-Díaz M, González-Sacristán R, Cabello V, Blasco-Alonso J, Rodríguez A, de los Santos M, Arcos-Machancoses JV, Murray-Hurtado M, García-Romero R, Galera-Martínez R, et al. Epidemiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure in Spain: Data from the REPAFI Registry. Nutrients. 2025; 17(23):3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233768
Chicago/Turabian StyleGermán-Díaz, Marta, Rocío González-Sacristán, Vanessa Cabello, Javier Blasco-Alonso, Alejandro Rodríguez, Mariela de los Santos, José Vicente Arcos-Machancoses, Mercedes Murray-Hurtado, Ruth García-Romero, Rafael Galera-Martínez, and et al. 2025. "Epidemiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure in Spain: Data from the REPAFI Registry" Nutrients 17, no. 23: 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233768
APA StyleGermán-Díaz, M., González-Sacristán, R., Cabello, V., Blasco-Alonso, J., Rodríguez, A., de los Santos, M., Arcos-Machancoses, J. V., Murray-Hurtado, M., García-Romero, R., Galera-Martínez, R., Martín-Arriscado, C., Redecillas-Ferreiro, S., Moreno-Villares, J. M., & Ramos-Boluda, E. (2025). Epidemiological Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure in Spain: Data from the REPAFI Registry. Nutrients, 17(23), 3768. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233768







