Integrated Transcriptomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Mechanism of Poplar-Type Propolis on the Mouse Mastitis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Poplar-Type Propolis
2.3. Ethics Statement
2.4. Mice and Treatments
2.5. Hematoxylin−Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.6. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.8. Transcriptome Analysis
2.9. Network Pharmacology Analysis
2.10. Molecular Docking
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
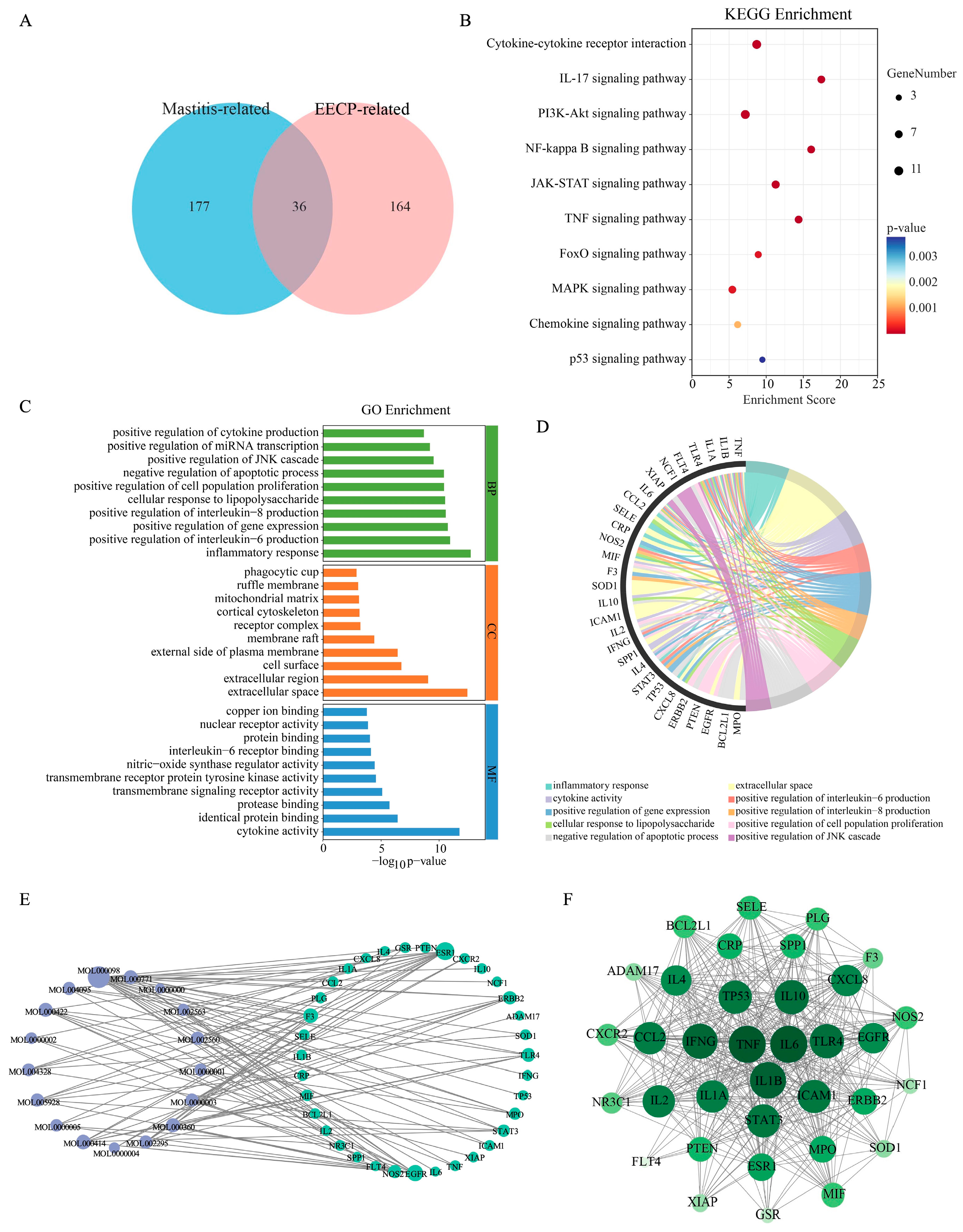
3.1. Network Pharmacological Analysis of EECP in the Treatment of Mastitis
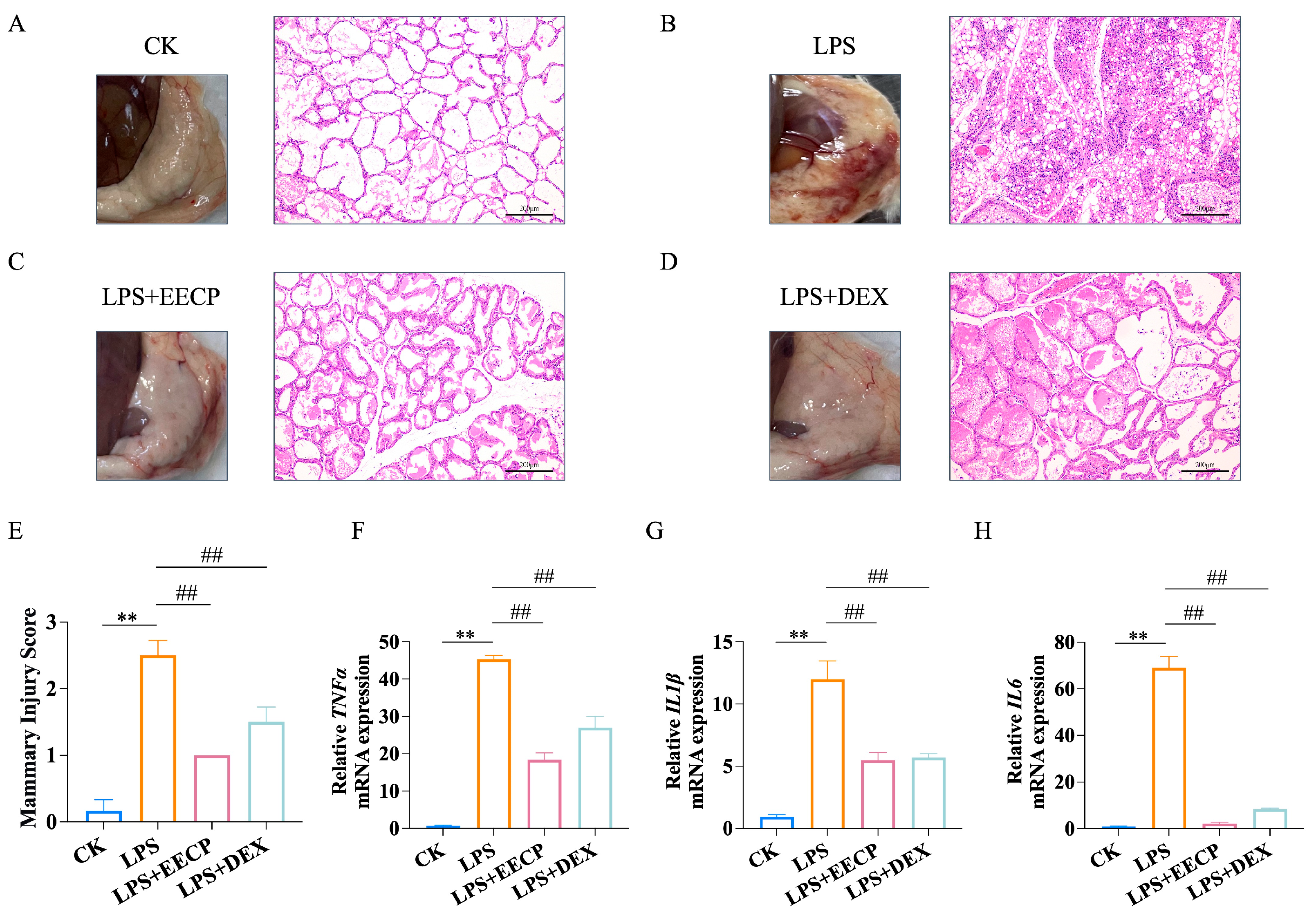
3.2. EECP Alleviates LPS-Induced Mammary Inflammatory Response
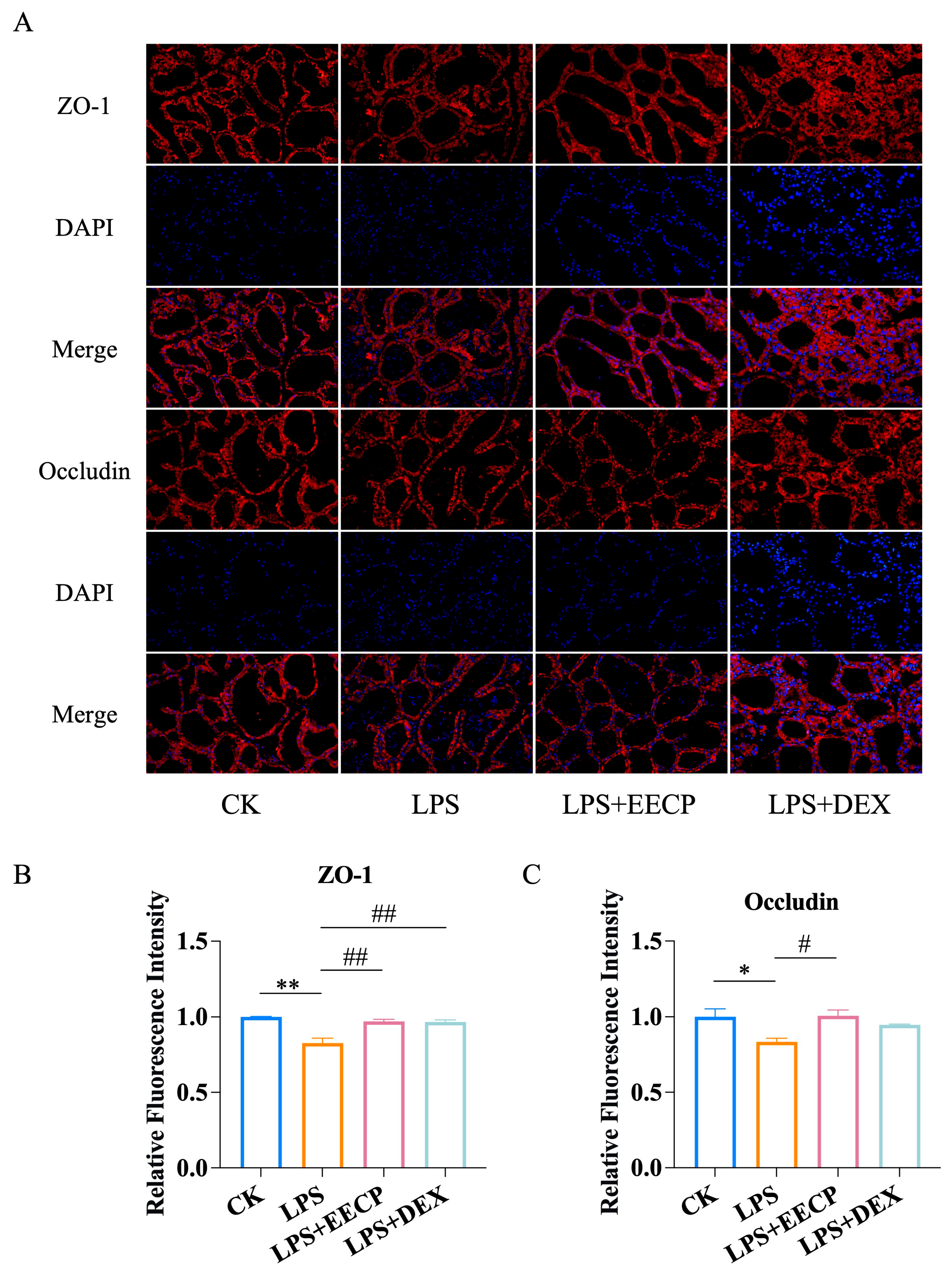
3.3. EECP Maintains Blood–Milk Barrier Integrity
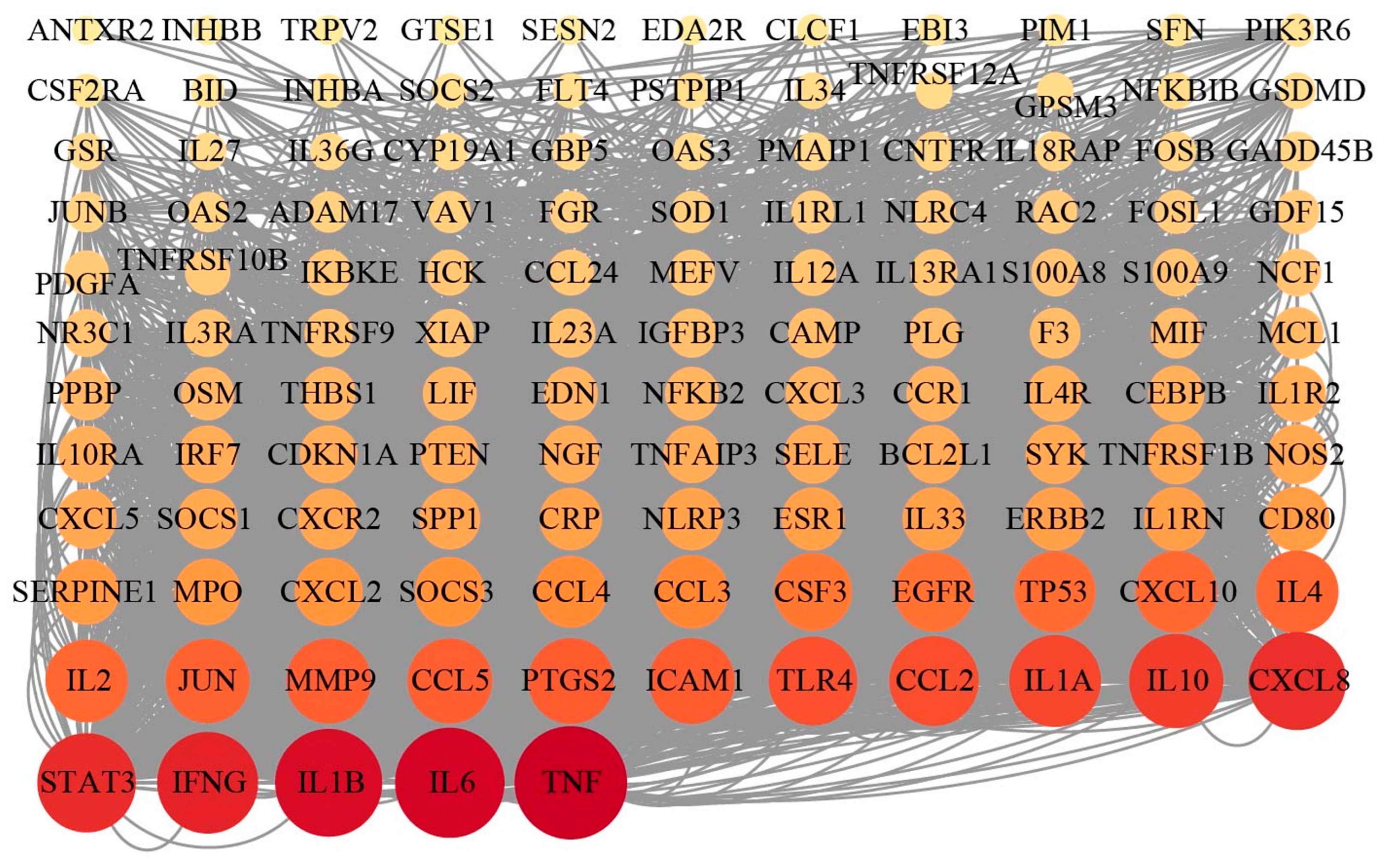
3.4. Transcriptomic Analysis of EECP Against Mammary Gland Injury
3.5. Integrated Analysis of RNA Sequencing and Network Pharmacology
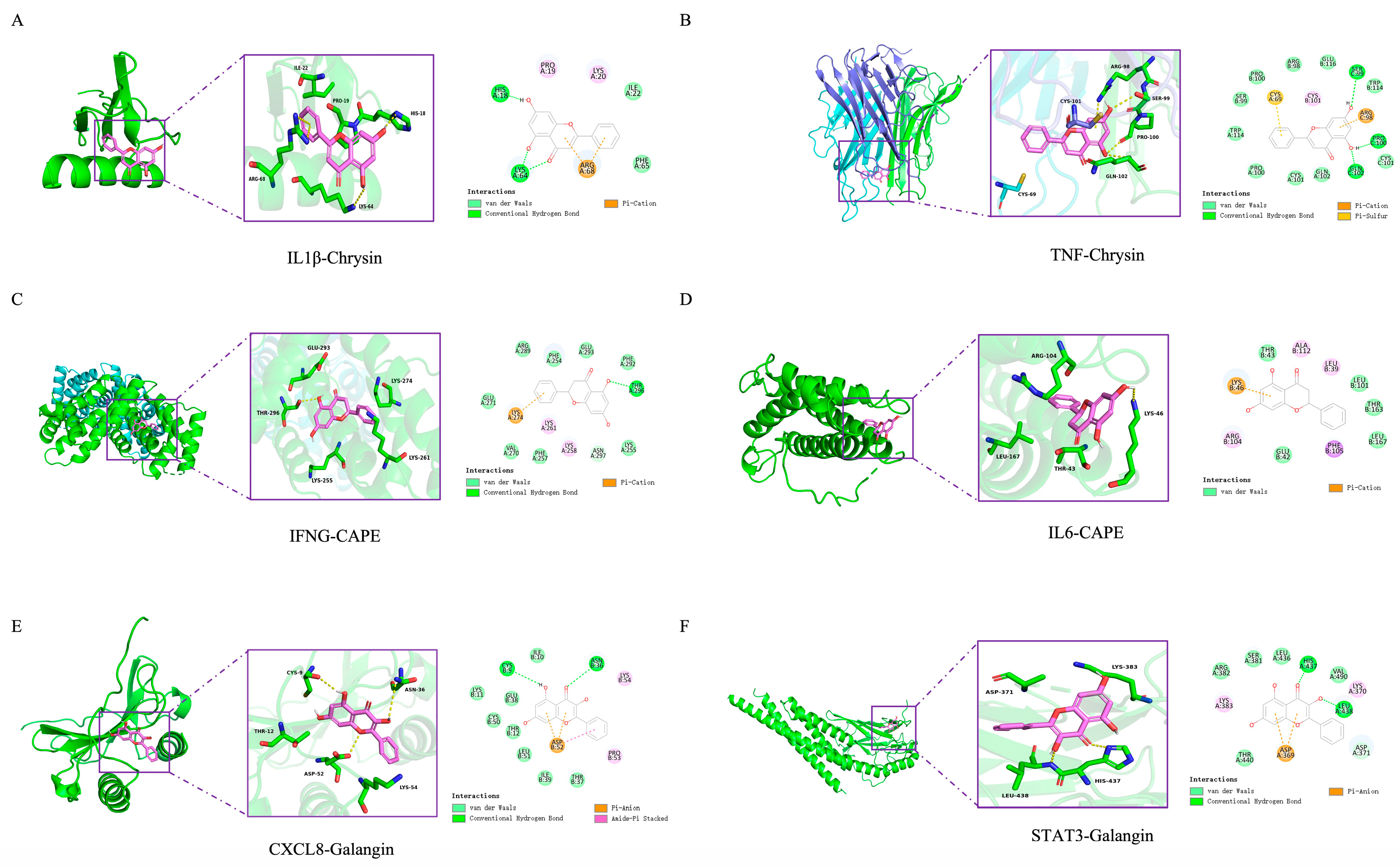
3.6. Molecular Docking of EECP’s Key Components and Key Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castro-Navarro, I.; Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Pace, C.D.W.; Kaur, H.; Piaskowski, J.; Aragon, A.; Rodriguez, J.M.; McGuire, M.A.; Fernandez, L.; et al. Immunological composition of human milk before and during subclinical and clinical mastitis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1532432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, D.; Huang, Y.; Ji, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, N.; Fan, C.; Song, H. Reshaping Intratumoral Mononuclear Phagocytes with Antibody-Opsonized Immunometabolic Nanoparticles. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2303298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Wang, F.; Su, J.; Ma, X.; et al. Generation of Anti-Mastitis Gene-Edited Dairy Goats with Enhancing Lysozyme Expression by Inflammatory Regulatory Sequence using ISDra2-TnpB System. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2404408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.; Woodd, S.L.; Benova, L. Incidence of and Risk Factors for Lactational Mastitis: A Systematic Review. J. Hum. Lact. 2020, 36, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevzner, M.; Dahan, A. Mastitis While Breastfeeding: Prevention, the Importance of Proper Treatment, and Potential Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalwadi, P.; Nathani, N.; Chauhan, K.; Mansuri, J.; Koringa, P.; Bhatt, V.; Kunjadiya, A.P. Whole-genome sequencing of bacteria accountable for lactational mastitis in humans combined with an examination of their antibiotic resistance profiles. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 3827–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforcin, J.M. Biological Properties and Therapeutic Applications of Propolis. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasote, D.; Bankova, V.; Viljoen, A.M. Propolis: Chemical diversity and challenges in quality control. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 1887–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.I.; Fedoruk, L.; Fisher, N.; Liu, A.X.; Khanna, S.; Naylor, K.; Gong, Z.; Celentano, A.; Alrashdan, M.S.; Cirillo, N. Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Agents in the Prevention of Chemoradiation-Induced Mucositis: A Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.C.D.; Vieira, D.S.; Yamamoto, S.M.; Costa, M.M.; Sá, M.C.A.; Silva, E.M.S.; Silva, T.M.S. Antimicrobial activity of propolis extract fractions against Staphylococcus spp. isolated from goat mastitis. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2019, 39, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.S.d.; Campanholi, K.d.S.S.; Bispo, A.S.; Caetano, W.; Pozza, M.S.d.S.; Perez, H.L.; Bruschi, M.L. Emulgels Containing Propolis and Curcumin for the Treatment of Mastitis and Umbilical Cord Healing. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2024, 67, e24230951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Yu, M.; Mao, Y.; Liu, M.; Guan, L.; Liu, L. Unraveling the alkaloid diversity and pharmacological potential of Ocimum: Integrated UPLC-MS/MS, network pharmacology, and transcriptomic insights for functional food and drug discovery. Food Res. Int. 2025, 219, 116985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Advancing Traditional Chinese Medicine Research through Network Pharmacology: Strategies for Target Identification, Mechanism Elucidation and Innovative Therapeutic Applications. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2025, 53, 2021–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Bao, J.; Liang, P.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Hu, F. Extraction of flavonoids and phenolic acids from poplar-type propolis: Optimization of maceration process, evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. LWT 2025, 233, 118481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Yin, Y.; Kan, X.; Gong, Q.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; et al. Licochalcone A Protects the Blood-Milk Barrier Integrity and Relieves the Inflammatory Response in LPS-Induced Mastitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kismet, K.; Ozcan, C.; Kuru, S.; Gencay Celemli, O.; Celepli, P.; Senes, M.; Guclu, T.; Sorkun, K.; Hucumenoglu, S.; Besler, T. Does propolis have any effect on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Liang, Y.; Yang, L.; Hu, S.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Q.; Tian, S.; Ding, Y. Gastrodin Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Through Activation of the Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway. Hepatology 2021, 74, 3074–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, C.T.K.; Hu, Y.H.; Tsoi, B.; Wong, F.N.; Hau, P.T.; Tam, E.W.T.; Mok, D.K.W.; Kwan, Y.W.; Leung, G.P.H.; Lee, S.M.Y.; et al. water extract ameliorates mastitis by suppressing bacterial internalization and inflammation via MAPKs signaling in vitro and in vivo. Food Front. 2025, 6, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Ke, Y.; Amona, F.M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; et al. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside mitigates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis by suppressing inflammatory responses and Ferroptosis mediated by SESN2/Nrf2. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 159, 114868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Gorecka, A.; Keskin, S.; Bobis, O.; Felitti, R.; Gorecki, M.; Otreba, M.; Stojko, J.; Olczyk, P.; Kolayli, S.; Rzepecka-Stojko, A. Comparison of the Antioxidant Activity of Propolis Samples from Different Geographical Regions. Plants 2022, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Hu, B.; Qu, X. Effects of propolis intake on endurance exercise and molecular signaling related to inflammation and oxidative stress. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1539701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pu, D.; Meng, F.; Shi, G.; Li, J. Alterations in Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Granulomatous Lobular Mastitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2025, 18, 9185–9197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, S.; He, F.; Li, K.; Hu, G.; Guo, W. Phytic Acid Maintains the Integrity of the Blood-Milk Barrier by Regulating Inflammatory Response and Intestinal Flora Structure. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xiang, Q.; Mao, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Protective Effects of Microbiome-Derived Inosine on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Damage and Inflammation in Mice via Mediating the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7619–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, W.; Wu, T.; Lu, R.; Shi, B. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses in human gingival fibroblasts via NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 794, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Ge, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin on LPS-induced mastitis in lactating SD rats through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cytokine 2025, 191, 156944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, H. Tanshinone IIA Promoted Autophagy and Inhibited Inflammation to Alleviate Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 2709–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitropoulou, G.; Stavropoulou, E.; Vaou, N.; Tsakris, Z.; Voidarou, C.; Tsiotsias, A.; Tsigalou, C.; Taban, B.M.; Kourkoutas, Y.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Insights into Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Applications of Plant Bioactive Compounds. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yin, P.; Gong, P.; Lv, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F. 8-Methoxypsoralen protects bovine mammary epithelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory injury via suppressing JAK/STAT and NF-κB pathway. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 63, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ran, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Hou, S.; Yang, Z.; Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Hu, G.; Guo, W. Evodiamine Relieve LPS-Induced Mastitis by Inhibiting AKT/NF-κB p65 and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation 2022, 45, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellnitz, O.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Invited review: The role of the blood-milk barrier and its manipulation for the efficacy of the mammary immune response and milk production. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 6376–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Hu, X.; Qiu, M.; Bao, L.; Wu, K.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, L.; Duan, S.; He, Y.; et al. Sialic acid exacerbates gut dysbiosis-associated mastitis through the microbiota-gut-mammary axis by fueling gut microbiota disruption. Microbiome 2023, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V.; Chai, Y.L.; Poh, L.; Selvaraji, S.; Fann, D.Y.; Jo, D.G.; De Silva, T.M.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Arumugam, T.V.; et al. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: A critical feature in unravelling the etiology of vascular cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Shi, C.X.; Min, S.N.; Li, B.Y.; Lu, Y.; Cao, B.H.; Su, H.W.; He, Y. Recent advances in flavonoids benefiting intestinal homeostasis. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 165, 105311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbottom, E.F.; Ban, Y.G.; Sun, X.D.; Capobianco, A.J.; Marsit, C.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Karagas, M.R.; Robbins, D.J. Transcriptome-wide analysis of changes in the fetal placenta associated with prenatal arsenic exposure in the New Hampshire Birth Cohort Study. Environ. Health Glob. 2019, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Laurent-Rolle, M.; Grove, T.L.; Hsu, J.C.C. Interferon-Stimulated Genes and Immune Metabolites as Broad-Spectrum Biomarkers for Viral Infections. Viruses 2025, 17, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Sense Primer (5′-3′) | Antisense Primer (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mouse TNFα | CATCTTCTCAAAATTCGAGTGACAA | TGGGAGTAGACAAGGTACAACCC |
| Mouse IL1β | CCGTGGACCTTCCAGGATGA | GGGAACGTCACACACCAGCA |
| Mouse IL6 | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC |
| Mouse β-actin | GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA | GCCGGACTCATCGTACTCC |
| Protein | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pinocembrin | Pinobanksin | Chrysin | CAPE | Galangin | |
| TNF | −7.8 | −7.7 | −7.9 | −7.1 | −7.8 |
| IL6 | −7.4 | −7.2 | −7.0 | −7.5 | −7.0 |
| IL1β | −6.2 | −6.1 | −6.7 | −6.2 | −6.6 |
| IFNG | −7.4 | −7.6 | −7.5 | −7.7 | −7.6 |
| STAT3 | −6.8 | −6.9 | −6.8 | −6.2 | −7.0 |
| CXCL8 | −6.5 | −6.4 | −6.6 | −6.5 | −6.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Wei, R.; Yuan, B.; Li, S.; Hu, F. Integrated Transcriptomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Mechanism of Poplar-Type Propolis on the Mouse Mastitis Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233683
Zhu M, Wei R, Yuan B, Li S, Hu F. Integrated Transcriptomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Mechanism of Poplar-Type Propolis on the Mouse Mastitis Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(23):3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233683
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Meifei, Ruike Wei, Bin Yuan, Shanshan Li, and Fuliang Hu. 2025. "Integrated Transcriptomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Mechanism of Poplar-Type Propolis on the Mouse Mastitis Model" Nutrients 17, no. 23: 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233683
APA StyleZhu, M., Wei, R., Yuan, B., Li, S., & Hu, F. (2025). Integrated Transcriptomics and Network Pharmacology Reveal the Mechanism of Poplar-Type Propolis on the Mouse Mastitis Model. Nutrients, 17(23), 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233683






