Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ln4 Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparations of Bacterial Samples
2.2. Mouse Models and Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical Analysis of Serum Samples
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Obesity-Related Protein Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
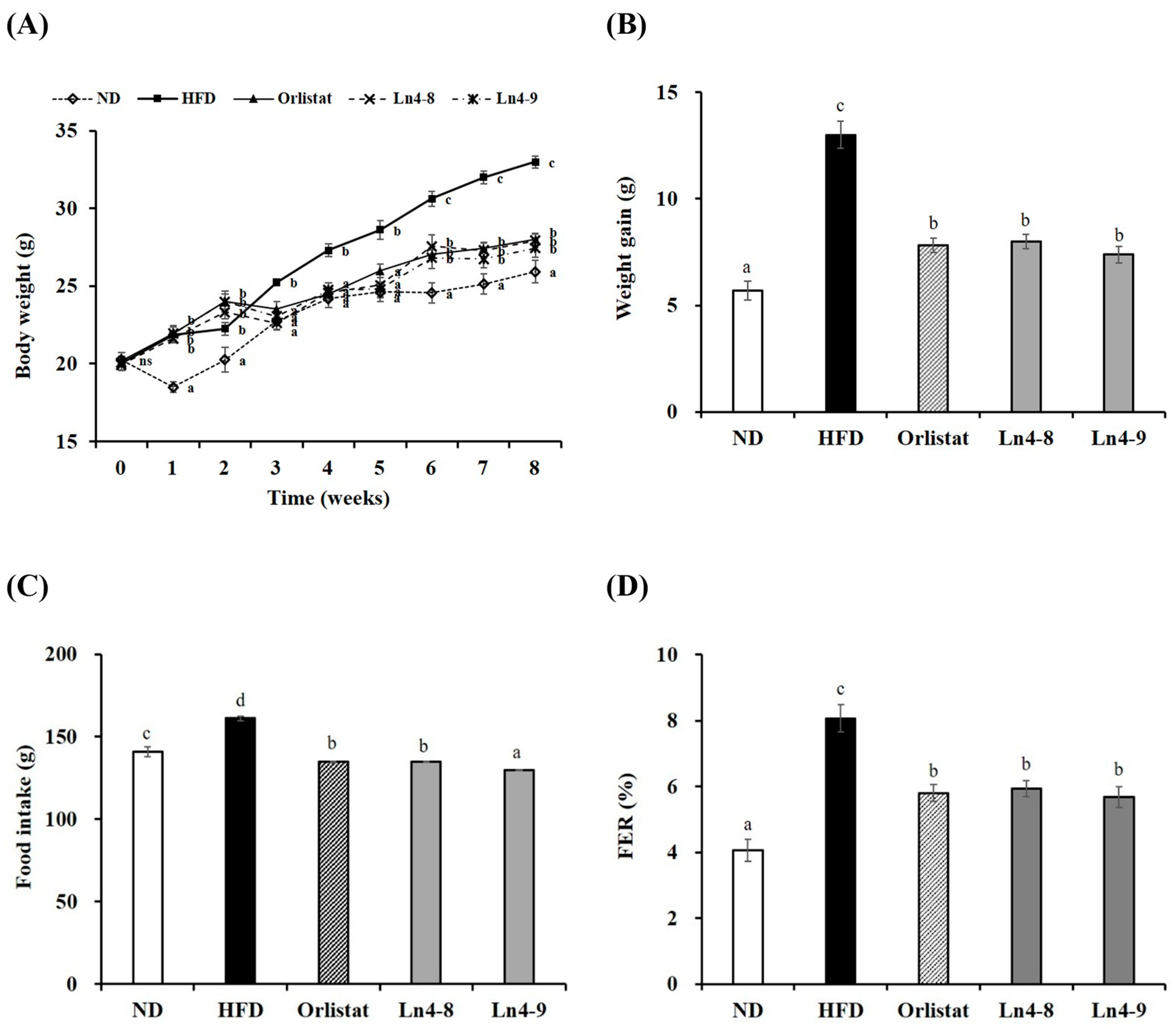
3.1. Effect of Ln4 on Body Weight and Body Fat Weight in Mice
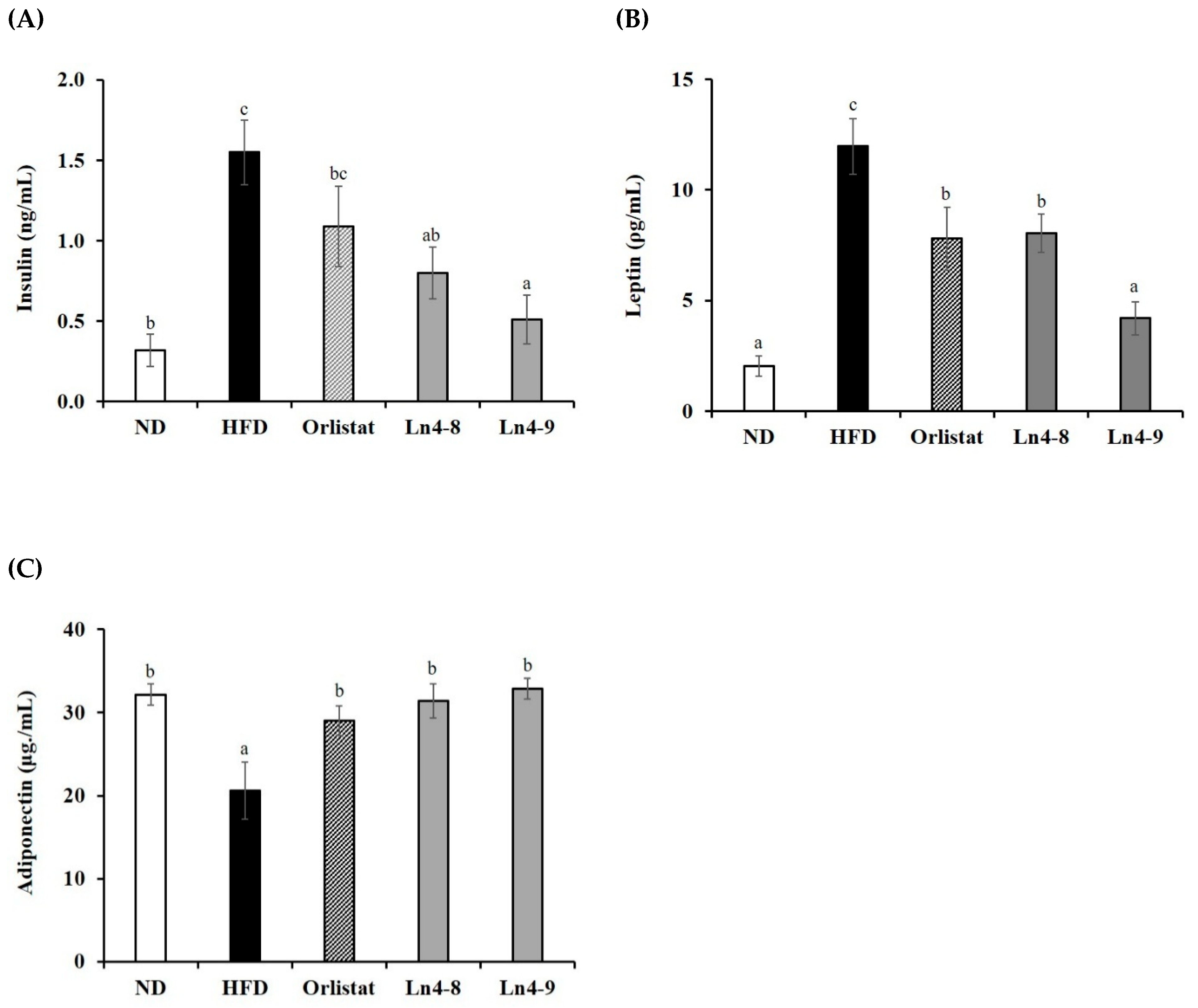
3.2. Effects of Ln4 on Serum Lipids in Mice
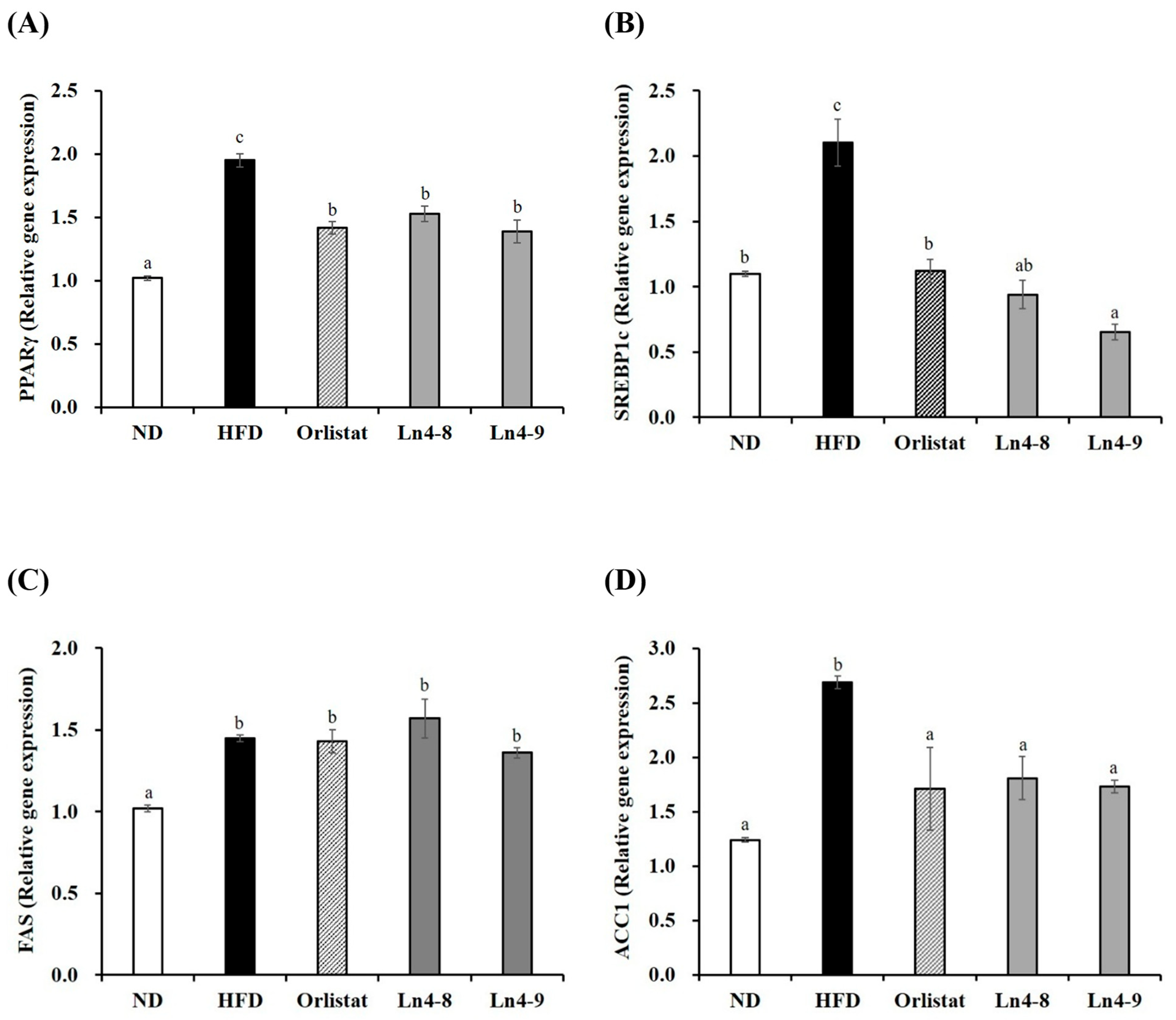
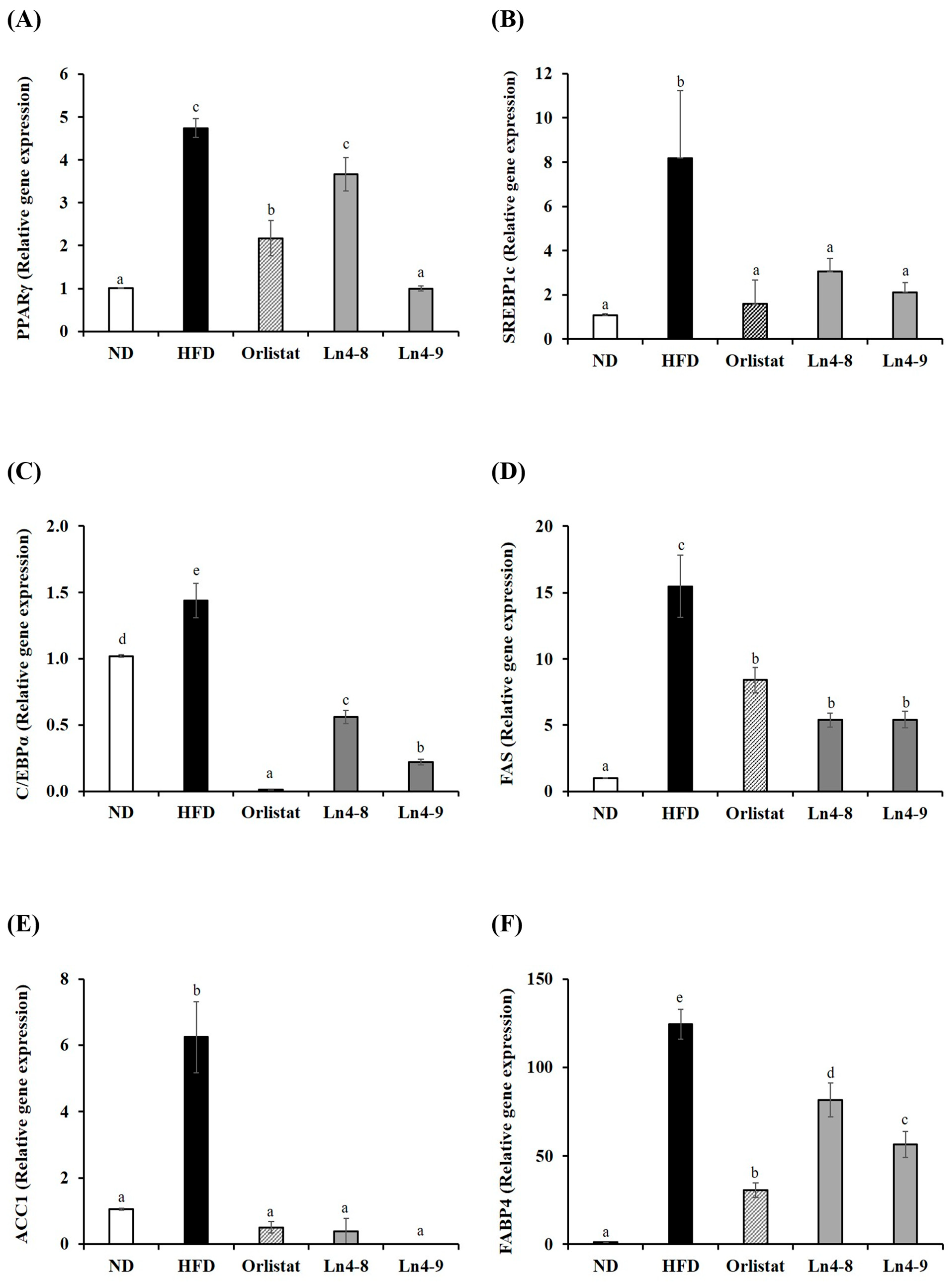
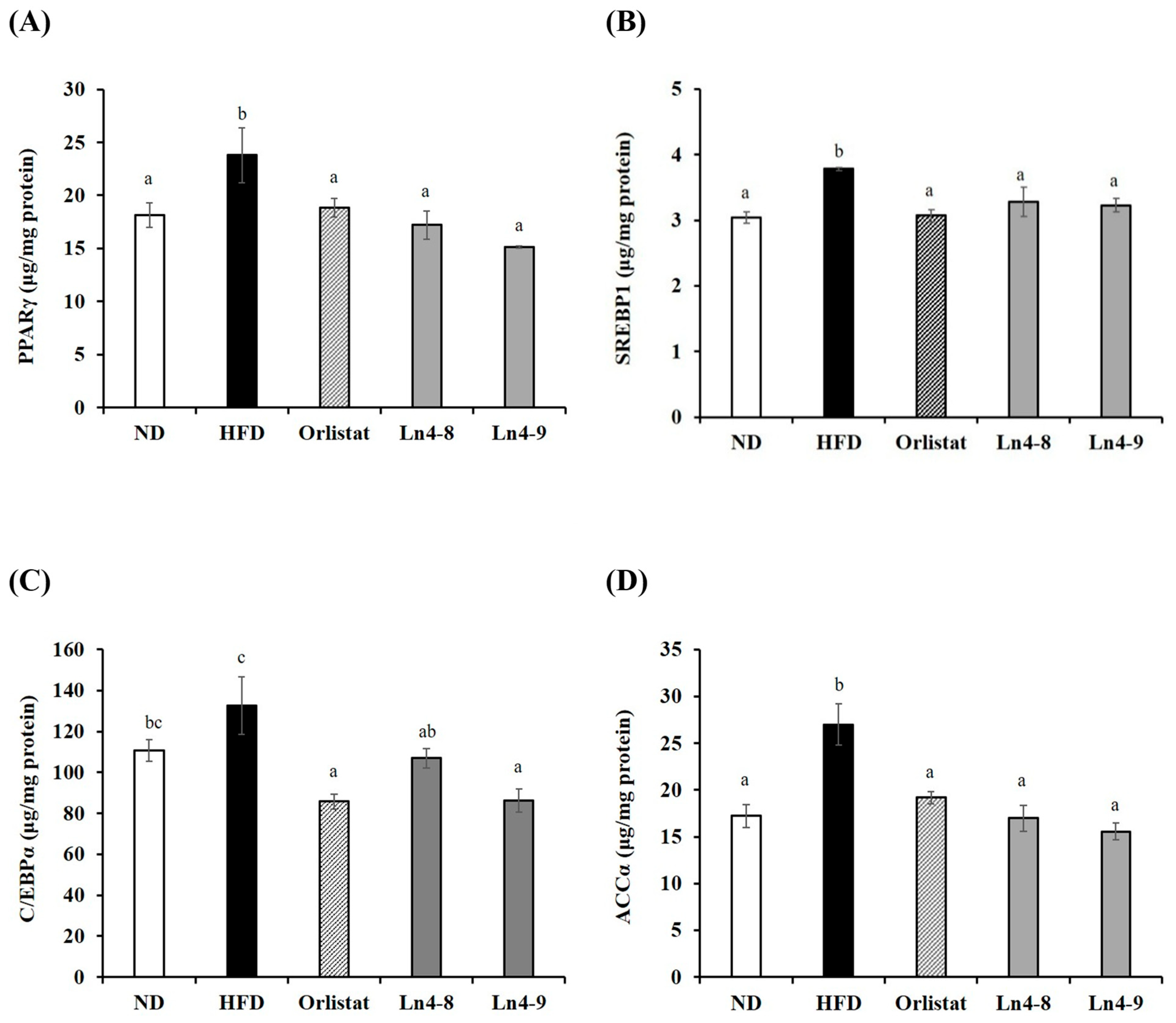
3.3. Effects of Ln4 on Adipocyte Differentiation and Lipid Synthesis in Livers and Epididymal Fat in Mice
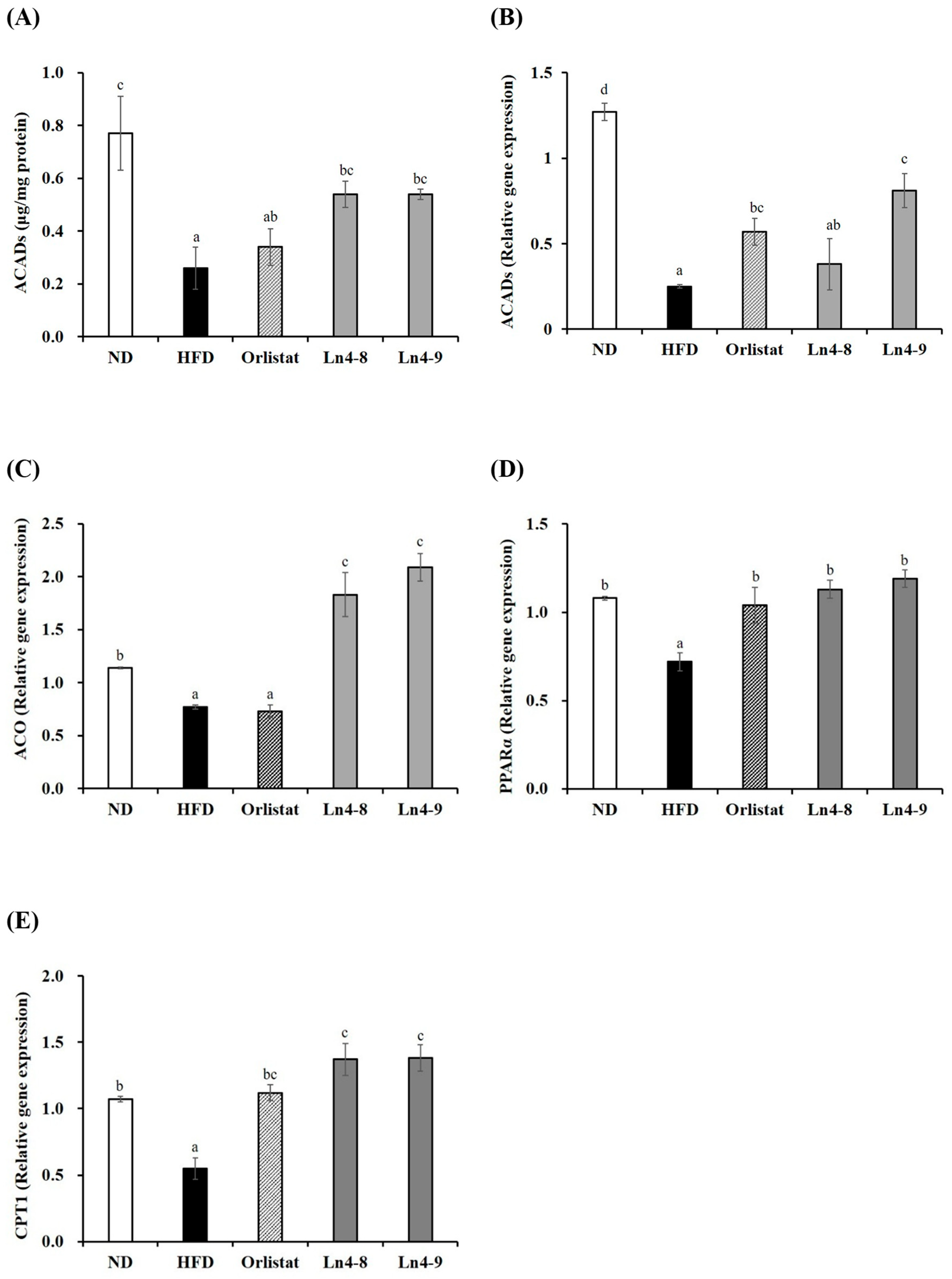
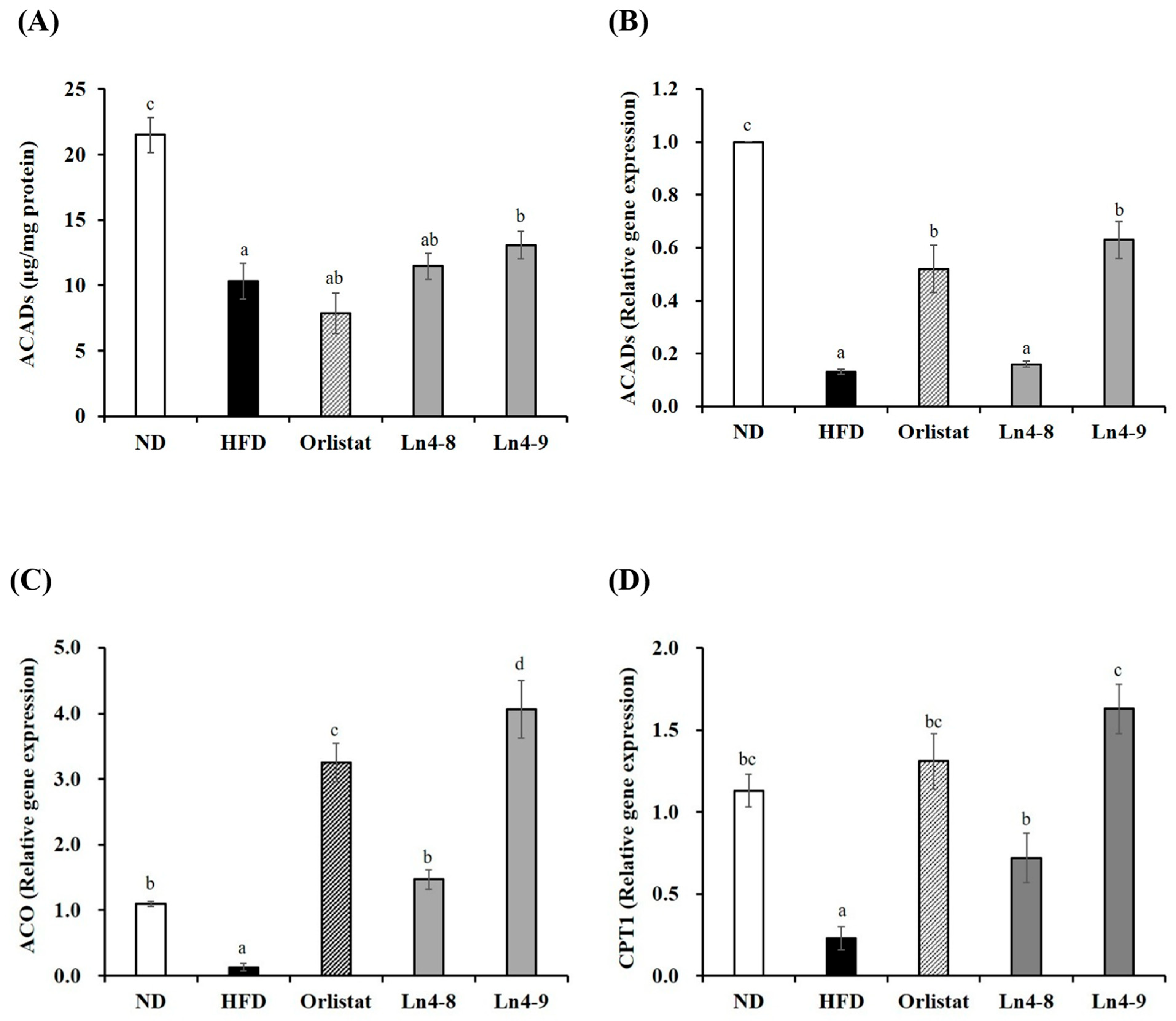
3.4. Effects of Ln4 on Lipolysis and Fatty Acid Oxidation in Livers and Epididymal Fat in Mice
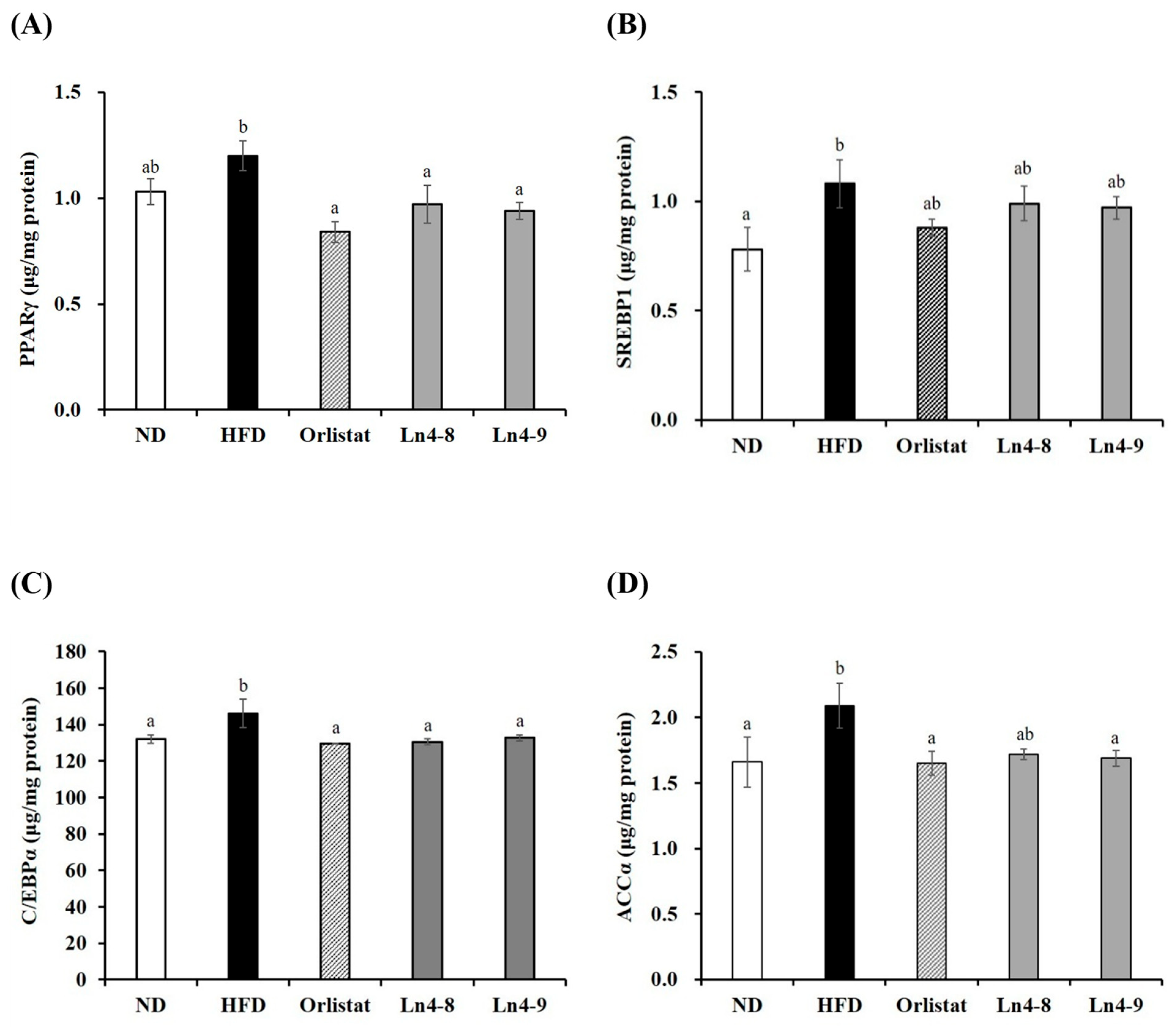
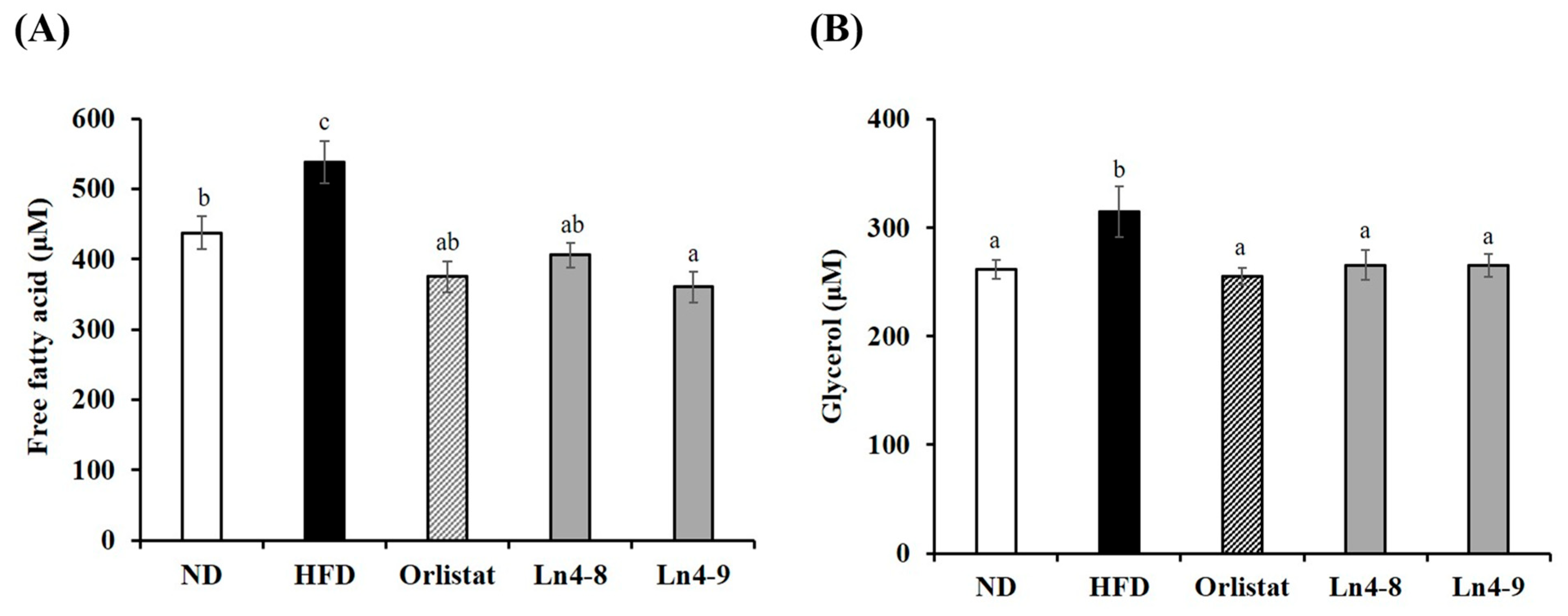
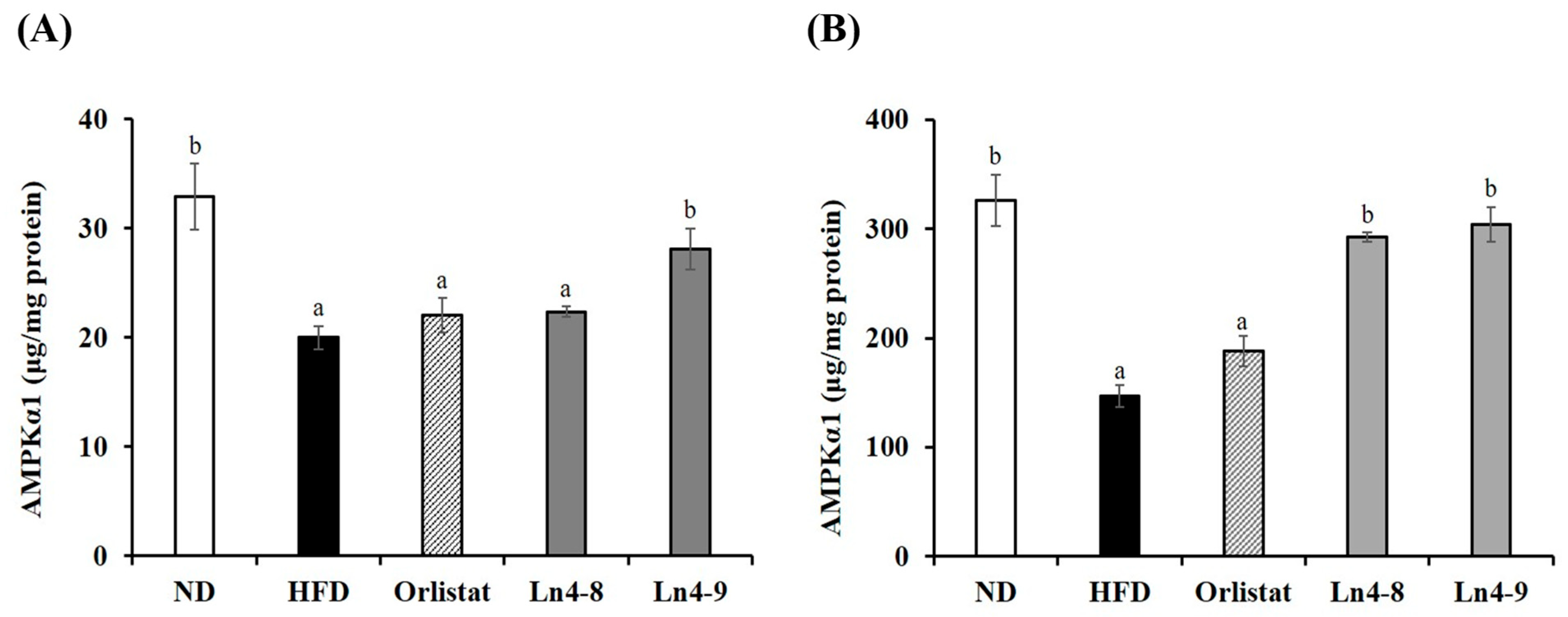
3.5. Effects of Ln4 on Lipolytic Indicators in Livers and Epididymal Fat in Mice
3.6. Effects of Ln4 on Energy Metabolism in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACADs | Acyl-CoA dehydrogenases |
| ACCα | Acetyl CoA carboxylase alpha |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| CPT-1 | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 |
| FAS | Fatty acid synthase |
| PPARα | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha |
| SREBP1c | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c |
| ACC1 | Acetyl CoA carboxylase 1 |
| ACO | Acyl-CoA oxidase |
| C/EBPα | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha |
| FABP4 | Fatty acid-binding protein 4 |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
References
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 18 July 2025).
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Nayebi, N.; Larijani, B.; Abdollahi, M. A Systematic Review of the Efficacy and Safety of Herbal Medicines Used in the Treatment of Obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3073–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An Obesity-Associated Gut Microbiome with Increased Capacity for Energy Harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.; Chu, H. The Critical Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1025706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejtahed, H.S.; Angoorani, P.; Soroush, A.R.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Siadat, S.D.; Larijani, B. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in Obesity: A Systematic Review. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2020, 39, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterberg, K.L.; Boutagy, N.E.; McMillan, R.P.; Stevens, J.R.; Frisard, M.I.; Kavanaugh, J.W.; Davy, B.M.; Davy, K.P.; Hulver, M.W. Probiotic Supplementation Attenuates Increases in Body Mass and Fat Mass during High-Fat Diet in Healthy Young Adults. Obesity 2015, 23, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Seo, E.; Oh, S.; Seo, M.; Byun, K.; Kim, B.Y. Anti-Obesity Effects of Multi-Strain Probiotics in Mice with High-Carbohydrate Diet-Induced Obesity and the Underlying Molecular Mechanisms. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Ilyas, Z.; Giacosa, A.; Gasparri, C.; Peroni, G.; Faliva, M.A.; Rigon, C.; Naso, M.; Riva, A.; Petrangolini, G.; et al. Is Probiotic Supplementation Useful for the Management of Body Weight and Other Anthropometric Measures in Adults Affected by Overweight and Obesity with Metabolic Related Diseases? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, M.; Pakmehr, A.; Pourghazi, F.; Kami, A.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.; Hasani-Ranjbar, S.; Larijani, B. The Anti-Obesity Effects of Postbiotics: A Systematic Review of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 64, 370–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Liu, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shi, D.; Ruan, G.; Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Xu, C. A Meta-Analysis of Microbial Therapy Against Metabolic Syndrome: Evidence from Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 775216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasaei, N.; Heidari, M.; Esmaeili, F.; Khosravi, S.; Baeeri, M.; Tabatabaei-Malazy, O.; Emamgholipour, S. The Effects of Prebiotic, Probiotic or Synbiotic Supplementation on Overweight/Obesity Indicators: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1277921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Paraprobiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KU15122 in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Ln4 Showing Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effect Against Streptococcus mutans KCTC 5124 Causing Dental Caries. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Jung, S.R.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D.; Lim, S.I. Lactobacillus plantarum Strain Ln4 Attenuates Diet-Induced Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Changes in Hepatic mRNA Levels Associated with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2018, 10, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.J.; Dong, H.J.; Jeong, H.U.; Ryu, D.W.; Song, S.M.; Kim, Y.R.; Jung, H.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, Y.H. Lactobacillus plantarum LMT1-48 Exerts Anti-Obesity Effect in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice by Regulating Expression of Lipogenic Genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Lim, S.D. The Inhibitory Effect of L. plantarum Q180 on Adipocyte Differentiation in 3T3-L1 and Reduction of Adipocyte Size in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.J.; Yu, H.; Kim, J.I.; Seo, H.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, H.S.; Cheon, H.G. Anti-Obesity Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum SKO-001 in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.I.; Cho, I.H.; Han, S.H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Choi, J.G.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.H. Anti-Obesity Effects of Salvia plebeia R. Br. Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Back, S.; Yang, S.B.; Yang, Y.M. Atractylodes lancea and Its Constituent, Atractylodin, Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease via AMPK Activation. Biomol. Ther. 2024, 32, 778–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Q. Evaluation of Gut Microbiota Alterations Following Orlistat Administration in Obese Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 15, 1337245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, P.; Behl, T.; Chigurupati, S.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.S.; Das, S.; Palnimuthu, V.R.; et al. Exploring the Effect of Crinum latifolia in Obesity: Possible Role of Oxidative, Angiogenic, and Inflammatory Pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29130–29140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Syndrome: Connecting and Reconciling Cardiovascular and Diabetes Worlds. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Wadden, T.A. Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Management of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhang, J.; Niu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ji, B.; Qu, L.; et al. Anti-Obesity Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZNFL-1 by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet-Induced Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2025, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.J.; Eom, J.I.; Park, S.J.; Shin, C.H.; Kim, S.M.; Pan, C.H.; Lee, J.K. Synergistic Anti-Obesity Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Q180 and Phaeodactylum tricornutum (CKDB-322) in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.L.; Tachon, S. Probiotic Strain Functionality and Adaptation to the Gut Microbiota Environment. J. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Oh, D.N.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, D.P.; Yoon, S.J.; Jang, W.J.; Han, S.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.M. Anti-Obesity Potential through Regulation of Carbohydrate Uptake and Gene Expression in Intestinal Epithelial Cells by the Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum MGEL20154 from Fermented Food. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 33, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaumerova, B.; Rosolova, H. Obesity and Dyslipidemia. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2023, 25, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, H.S.; Kuan, C.Y.; Ewe, J.A.; Fung, W.Y.; Liong, M.T. The Improvement of Hypertension by Probiotics: Effects on Cholesterol, Diabetes, Renin, and Phytoestrogens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3755–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Chain, F.; Martín, R.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G.; Courau, S.; Langella, P. Beneficial Effects on Host Energy Metabolism of Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Vitamins Produced by Commensal and Probiotic Bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, S.R. Transcriptional Control of Adipocyte Formation. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.; Jung, A.H.; Suh, H.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, H. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K8-Based Paraprobiotics Prevent Obesity and Obesity-Induced Inflammatory Responses in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacouton, E.; Mondot, S.; Langella, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Impact of Oral Administration of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strain CNCM I-4459 on Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diet in Mice. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Choi, S.I. Schisandrin C Isolated from Schisandra chinensis Fruits Inhibits Lipid Accumulation by Regulating Adipogenesis and Lipolysis through AMPK Signaling in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, G. Obesity and Free Fatty Acids. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Xu, W.; He, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tao, X.; Qiu, L.; Wei, H. Amelioration of Hypercholesterolemia by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum GLPL02 via Regulating Intestinal Flora and Cholesterol Metabolism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 8206–8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, S. Integrated Physiology and Systems Biology of PPARα. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, O.; Proczko-Stepaniak, M.; Mika, A. Short-Chain Fatty Acids—A Product of the Microbiome and Its Participation in Two-Way Communication on the Microbiome–Host Mammal Line. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Targeted Gene | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| Sense | Antisense | |
| PPARγ | 5′-ccacactatgaagacattccat-3′ | 5′-gttctactttgatcgcactttg-3′ |
| SREBP1c, | 5′-gtgtgcaccgtagttctggg-3′ | 5′-aggtcagcttgtttgcgatg-3′ |
| C/EBPα | 5′-cactatcgcctggaggac-3′ | 5′-cgttctgtgagcctgtga-3′ |
| FABP4 | 5′-tttcccctagaaagcaatcc-3′ | 5′-agaaaatctgcacggtaagt-3′ |
| ACC1 | 5′-ccctacacttactgatgagc-3′ | 5′-gggaagcaataagaacctga-3′ |
| FAS | 5′-aagaaagtgctggaaaagga-3′ | 5′-cagcaattctcgggatgtat-3′ |
| ACADs | 5′-gattcaaaatagccatgcaa-3′ | 5′-gcatacttcacagcacaatc-3′ |
| ACO | 5′-attaagtcgccaccattctt-3′ | 5′-ggtccgttgttactgaatct-3′ |
| PPARα | 5′-gaatccacgaagcctacc-3′ | 5′-gccatacacaaggtatcc-3′ |
| CPT-1 | 5′-aagatcaatcggaccctaga-3′ | 5′-atagtcatgatgatcgaaac-3′ |
| Variable | ND | HFD | Orlistat | Ln4-8 | Ln4-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Adipose Tissue Weight (g/100 g BW) | |||||
| Brown fat | 0.31 ± 0.02 ns | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.26 ± 0.02 |
| Subcutaneous fat | 0.76 ± 0.09 a | 2.19 ± 0.18 b | 1.85 ± 0.18 b | 2.14 ± 0.13 b | 1.76 ± 0.16 b |
| Visceral fat | 1.68 ± 0.18 a | 6.94 ± 0.36 d | 5.27 ± 0.53 bc | 6.40 ± 0.50 cd | 4.69 ± 0.41 b |
| Epididymal fat | 0.99 ± 0.10 a | 3.83 ± 0.21 c | 3.06 ± 0.39 bc | 3.74 ± 0.33 c | 2.51 ± 0.29 b |
| Retroperitoneal fat | 0.23 ± 0.05 a | 1.29 ± 0.12 b | 0.99 ± 0.18 b | 1.20 ± 0.16 b | 1.05 ± 0.11 b |
| Perirenal fat | 0.12 ± 0.01 a | 0.47 ± 0.11 c | 0.28 ± 0.05 ab | 0.33 ± 0.04 bc | 0.21 ± 0.02 ab |
| Mesenteric fat | 0.35 ± 0.08 a | 1.35 ± 0.15 c | 0.94 ± 0.17 bc | 1.14 ± 0.10 bc | 0.91 ± 0.16 b |
| Variable | ND | HFD | Orlistat | Ln4-8 | Ln4-9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 131.27 ± 0.51 a | 133.50 ± 0.86 b | 132.17 ± 0.44 ab | 131.64 ± 0.40 a | 131.71 ± 0.55 a |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 41.93 ± 0.50 ab | 45.61 ± 0.82 c | 43.57 ± 0.63 bc | 44.76 ± 0.81 bc | 40.31 ± 1.56 a |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 6.02 ± 0.45 ns | 5.98 ± 0.32 | 6.46 ± 0.53 | 7.13 ± 0.34 | 7.04 ± 0.40 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 8.86 ± 0.76 a | 12.13 ± 0.34 c | 10.38 ± 0.42 b | 10.41 ± 0.33 b | 10.16 ± 0.46 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.; Lee, N.-K.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.-M.; Kim, H.; Paik, H.-D.; Park, E. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ln4 Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233668
Lee Y, Lee N-K, Kim N, Choi Y-M, Kim H, Paik H-D, Park E. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ln4 Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients. 2025; 17(23):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233668
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yunjung, Na-Kyoung Lee, Nayoung Kim, Yong-Min Choi, Haebom Kim, Hyun-Dong Paik, and Eunju Park. 2025. "Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ln4 Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice" Nutrients 17, no. 23: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233668
APA StyleLee, Y., Lee, N.-K., Kim, N., Choi, Y.-M., Kim, H., Paik, H.-D., & Park, E. (2025). Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Ln4 Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Lipid Metabolism and Adipogenesis in C57BL/6 Mice. Nutrients, 17(23), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17233668






