Nutritional Strategies to Address Malnutrition in Dialyses Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- -
- Controlled or randomised clinical trials.
- -
- Adult participants (≥18 years) on HD or PD.
- -
- Articles in English or Spanish.
- -
- Free full-text availability.
- -
- Publication between 2015 and 2025.
- -
- Interventions evaluating nutritional strategies (ONS, IDPN, or combined approaches).
- -
- Systematic reviews, meta-analyses, or non-experimental designs.
- -
- Animal or in vitro studies.
- -
- Articles without full-text access.
- -
- Duplicates or publications in languages other than English/Spanish.
- -
- Studies unrelated to nutrition in dialyses patients.
2.3. Outcomes of Interest
- -
- Changes in nutritional biomarkers (albumin, pre-albumin, transferrin).
- -
- Variations in muscle mass or body composition.
- -
- Improvement in Malnutrition–Inflammation Score (MIS).
- -
- Changes in health-related quality of life using validated questionnaires.
- -
- Secondary outcomes are as follows: Variations in inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6) and immunological parameters.
Null Hypothesis
2.4. Data Synthesis
3. Results
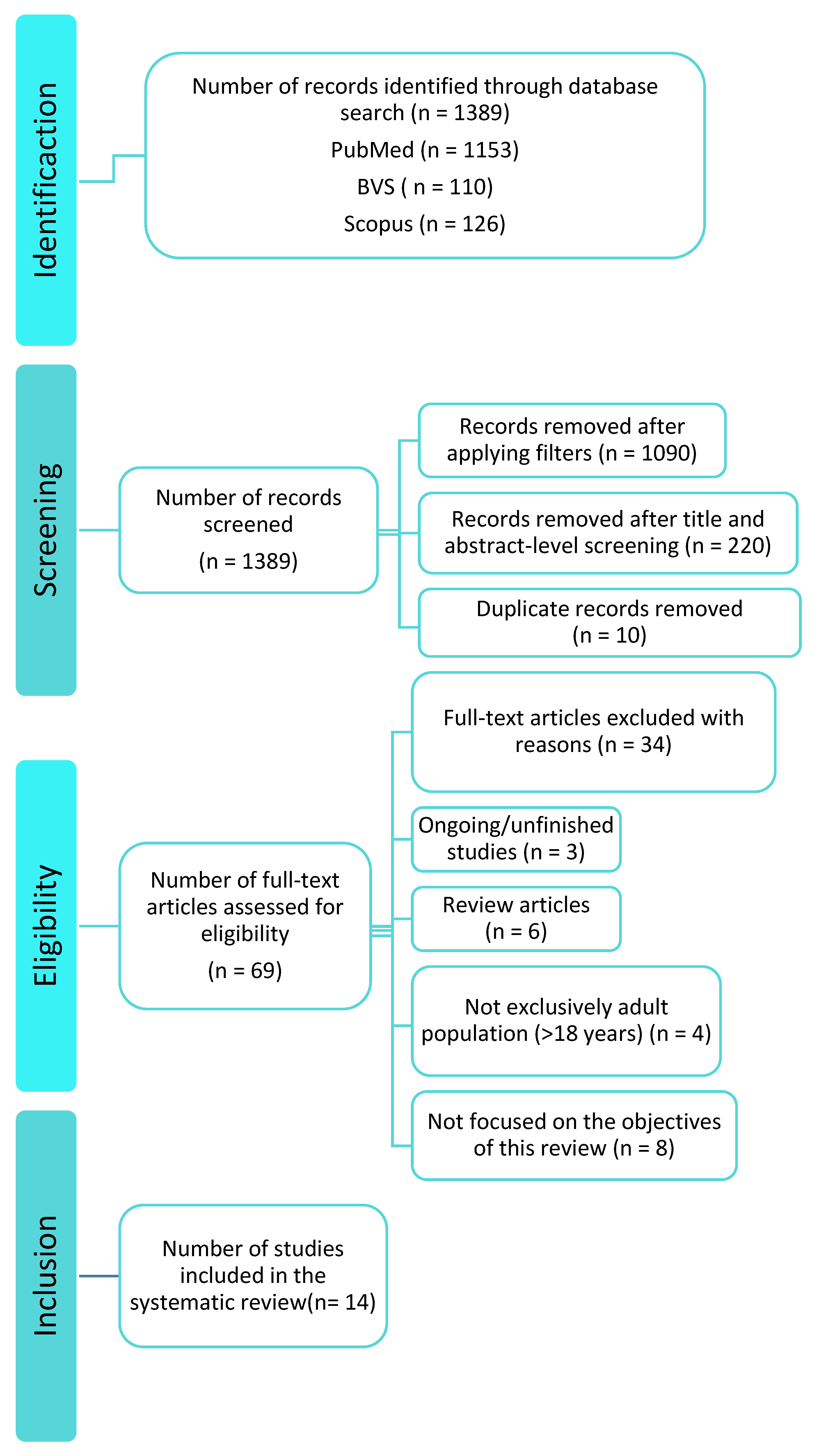
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Oral Nutritional Supplementation in Haemodialysis Patients
3.4. Intra-Dialytic Parenteral Nutrition
3.5. Nutritional Strategies in Peritoneal Dialyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| RRT | Renal replacement therapy |
| HD | Haemodialysis |
| PD | Peritoneal dialyses |
| PEW | Protein–energy wasting |
| ONS | Oral nutritional supplement |
| IDPN | Intra-dialytic parenteral nutrition |
| MIS | Malnutrition–inflammation score |
| SGA | Subjective global assessment |
| KDOQI | Kidney disease outcomes quality initiative |
| PRISMA | Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses |
| BVS | Biblioteca Virtual en Salud (virtual health library) |
| nPCR | Normalised protein catabolic rate |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| FFM | Fat-free mass |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | Tumour necrosis factor-alpha |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| Hb | Haemoglobin |
| BIVA | Bioelectrical impedance vector analysis |
| ESRD | End-stage renal disease |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| VLDL | Very low-density lipoprotein |
| PG-SGA | Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment |
References
- Llisterri, J.L.; Micó-Pérez, R.M.; Velilla-Zancada, S.; Rodríguez-Roca, G.C.; Prieto-Díaz, M.Á.; Martín-Sánchez, V.; Barquilla, A.; Polo-García, J.; Segura-Fragoso, A.; Cinza-Sanjurjo, S.; et al. Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease and Associated Factors in the Spanish Population Attended in Primary Care: Results of the IBERICAN Study. Med. Clin. 2021, 156, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador González, B.; Rodríguez Pascual, M.; Ruipérez Guijarro, L.; Ferré González, A.; Cunillera Puertolas, O.; Rodríguez Latre, L.M. Chronic kidney disease in Primary Health Care: Prevalence and associated risk factors. Aten. Primaria 2015, 47, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorostidi, M.; Sánchez-Martínez, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Graciani, A.; de la Cruz, J.J.; Santamaría, R.; Del Pino, M.D.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; de Álvaro, F.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease in Spain: Prevalence and Impact of Accumulation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Nefrologia 2018, 38, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Okpechi, I.G.; Caskey, F.J.; Yang, C.-W.; Tonelli, M.; Jha, V. Perspectives on Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease: The Facts, the Questions, and a Proposed Framework for 2023 and Beyond. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorostidi, M.; Santamaría, R.; Alcázar, R.; Fernández-Fresnedo, G.; Galcerán, J.M.; Goicoechea, M.; Oliveras, A.; Portolés, J.; Rubio, E.; Segura, J.; et al. Spanish Society of Nephrology Document on KDIGO Guidelines for the Assessment and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nefrologia 2014, 34, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sezer, S.; Bal, Z.; Tutal, E.; Uyar, M.E.; Acar, N.O. Long-Term Oral Nutrition Supplementation Improves Outcomes in Malnourished Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Hemodialysis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2014, 38, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinig, C.E.; Moraes, T.; Ribeiro, S.; Riella, M.C.; Olandoski, M.; Martins, C.; Pecoits-Filho, R. Predictive Value of Malnutrition Markers for Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. J. Ren. Nutr. 2011, 21, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Iguacel, C.; González-Parra, E.; Pérez-Gómez, M.V.; Mahíllo, I.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A.; Carrero, J.J. Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome and Its Association with Mortality in Haemodialysis Patients in a Centre in Spain. Nefrología 2013, 33, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.M.; Elkazaz, A.M. The effect of different timings of protein supplementation on variable outcomes in hemodialysis patients: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2025, 29, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotiadou, E.; Georgianos, P.I.; Chourdakis, M.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Liakopoulos, V. Eating during the Hemodialysis Session: A Practice Improving Nutritional Status or a Risk Factor for Intradialytic Hypotension and Reduced Dialysis Adequacy? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A. Optimal Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2013, 20, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Iguacel, C.; González-Parra, E.; Mahillo, I.; Ortiz, A. Criteria for Classification of Protein-Energy Wasting in Dialysis Patients: Impact on Prevalence. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahathevan, S.; Khor, B.-H.; Ng, H.-M.; Gafor, A.H.A.; Mat Daud, Z.A.; Mafra, D.; Karupaiah, T. Understanding Development of Malnutrition in Hemodialysis Patients: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, V.H.; López-Guerra, E.A.; Rodríguez-Castellanos, F.E. Association between Peritoneal Protein Excretion, Peritonitis and D/P Phosphate, in Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis. Nefrología 2013, 33, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrero, J.J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Axelsson, J.; Avesani, C.M.; Suliman, M.E.; Kato, S.; Bárány, P.; Snaedal-Jonsdottir, S.; Alvestrand, A.; Heimbürger, O.; et al. Comparison of Nutritional and Inflammatory Markers in Dialysis Patients with Reduced Appetite. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.D.; Humphreys, M.H.; Block, G. Comparing Outcome Predictability of Markers of Malnutrition-Inflammation Complex Syndrome in Haemodialysis Patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, M.C.C.; Vogt, B.P.; Martin, L.C.; Caramori, J.C.T. Malnutrition Inflammation Score Cut-off Predicting Mortality in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2017, 17, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado García de Polavieja, M.; Escribano Loma, S.; Manso de Real, P.; Sánchez Tocino, M.L.; Arenas Jiménez, M.D. ¿Qué novedades aportan en la práctica clínica las guías KDOQI de nutrición después de 20 años? Nefrología 2022, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tapiawala, S.; Vora, H.; Patel, Z.; Badve, S.; Shah, B. Subjective Global Assessment of Nutritional Status of Patients with Chronic Renal Insufficiency and End Stage Renal Disease on Dialysis. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2006, 54, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Santin, F.G.; Bigogno, F.G.; Dias Rodrigues, J.C.; Cuppari, L.; Avesani, C.M. Concurrent and Predictive Validity of Composite Methods to Assess Nutritional Status in Older Adults on Hemodialysis. J. Ren. Nutr. 2016, 26, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.-J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, A.C.B.; Schincaglia, R.M.; Candow, D.G.; Pimentel, G.D. Effect of Creatine Supplementation on Body Composition and Malnutrition-Inflammation Score in Hemodialysis Patients: An Exploratory 1-Year, Balanced, Double-Blind Design. Nutrients 2024, 16, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieves-Anaya, I.; Várgas, M.B.; García, O.P.; Biruete, A.; Kistler, B.; Atilano-Carsi, X. Effect of Oral Nutritional Supplementation Combined with Impedance Vectors for Dry Weight Adjustment on the Nutritional Status, Hydration Status and Quality of Life in Patients on Chronic Hemodialysis: A Pilot Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 54, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satirapoj, B.; Apiyangkool, T.; Thimachai, P.; Nata, N.; Supasyndh, O. Intradialytic Oral Nutrition Effects on Malnourished Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, M.S.; Nazeih, M.S.; El Said, T.W. Effect of Intradialytic Oral Nutritional Supplementation on Nutritional Markers in Malnourished Chronic Hemodialysis Patients: Prospective Randomized Trial. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtas, S.; Reggiardo, G.; Contu, R.; Cadeddu, M.; Secci, R.; Putzu, P.; Mocco, C.; Leoni, M.; Gigante Maria, V.; Marras, C.; et al. Replacement of the Massive Amino Acid Losses Induced by Hemodialysis: A New Treatment Option Proposal for a Largely Underestimated Issue. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 63, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo Ortiz, B.O.; Fuentes Preciado, A.R.; Ramírez Emiliano, J.; Martínez Garza, S.; Ramos Rodríguez, E.; de Alba Macías, L.A. Recovery of Bone and Muscle Mass in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Iron Overload on Hemodialysis and Taking Combined Supplementation with Curcumin and Resveratrol. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, A.C.B.; Motobu, R.D.; Freitas, A.T.V.; Mota, J.F.; Wall, B.T.; Pichard, C.; Laviano, A.; Pimentel, G.D. Short-Term Creatine Supplementation May Alleviate the Malnutrition-Inflammation Score and Lean Body Mass Loss in Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2020, 44, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsen, T.A.; Beer, J.; Mann, H.; German IDPN-Trial Group. Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients Suffering from Protein-Energy Wasting. Results of a Multicenter, Open, Prospective, Randomized Trial. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2017, 36, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabasawa, H.; Hosojima, M.; Kanda, E.; Nagai, M.; Murayama, T.; Tani, M.; Kamoshita, S.; Kuroda, A.; Kanno, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition Using ENEFLUID® in Malnourished Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis: An Exploratory, Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittiskulnam, P.; Banjongjit, A.; Metta, K.; Tiranathanagul, K.; Avihingsanon, Y.; Praditpornsilpa, K.; Tungsanga, K.; Eiam-Ong, S. The Beneficial Effects of Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients with Protein Energy Wasting: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, F.; Guo, L.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Shu, P. Effect of Multidisciplinary Medical Nutrition Therapy on the Nutrition Status of Patients Receiving Peritoneal Dialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2025, 40, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, L.; Dai, B.; Lin, B.; Lin, S.; Lin, E. Effects of Probiotics on Malnutrition and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Ren. Nutr. 2021, 31, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahathevan, S.; Se, C.-H.; Ng, S.; Khor, B.-H.; Chinna, K.; Goh, B.L.; Gafor, H.A.; Bavanandan, S.; Ahmad, G.; Karupaiah, T. Clinical Efficacy and Feasibility of Whey Protein Isolates Supplementation in Malnourished Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A Multicenter, Parallel, Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 25, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaccadori, E.; Sabatino, A.; Barazzoni, R.; Carrero, J.J.; Cupisti, A.; De Waele, E.; Jonckheer, J.; Singer, P.; Cuerda, C. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in Hospitalized Patients with Acute or Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2021, 40, 1644–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yao, X.; Ren, S.; Feng, Y. Oral Nutritional Supplement Helps to Improve Nutritional Status of Dialysis Dependent Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1294064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, C.; Bonilla, D.A.; Almendra-Pegueros, R.; Pérez-López, A.; Gamero, A.; dos Santos Duarte Junior, M.A.; Peterman-Rocha, F.; Lozano-Lorca, M.; Camacho-López, S.; Kammar-García, A.; et al. Evaluación de La Ingesta Alimentaria: Una Reflexión Que Nos Acerque al Futuro. Rev. Esp. Nutr. Humana Dietética 2021, 25, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordos, M.; Martu, M.A.; Vlad, C.E.; Toma, V.; Ciubotaru, A.D.; Badescu, M.C.; Goriuc, A.; Foia, L. Early Detection of Inflammation and Malnutrition and Prediction of Acute Events in Hemodialysis Patients through PINI (Prognostic Inflammatory and Nutritional Index). Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tocino, M.L.; Miranda-Serrano, B.; Gracia-Iguacel, C.; de-Alba-Peñaranda, A.M.; Mas-Fontao, S.; López-González, A.; Villoria-González, S.; Pereira-García, M.; Ortíz, A.; González-Parra, E. Sarcopenia Assessed by 4-Step EWGSOP2 in Elderly Hemodialysis Patients: Feasibility and Limitations. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gracia-Iguacel, C.; González-Parra, E.; Barril-Cuadrado, G.; Sánchez, R.; Egido, J.; Ortiz-Arduán, A.; Carrero, J.J. Defining Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: Prevalence and Clinical Implications. Nefrología 2014, 34, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieuwlaat, R.; Wilczynski, N.; Navarro, T.; Hobson, N.; Jeffery, R.; Keepanasseril, A.; Agoritsas, T.; Mistry, N.; Iorio, A.; Jack, S.; et al. Interventions for Enhancing Medication Adherence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD000011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, R.B.; Ackloo, E.; Sahota, N.; McDonald, H.P.; Yao, X. Interventions for Enhancing Medication Adherence. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2008, CD000011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, N.J.M.; Aparicio, M.; Brunori, G.; Carrero, J.J.; Cianciaruso, B.; Fiaccadori, E.; Lindholm, B.; Teplan, V.; Fouque, D.; Guarnieri, G.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Adult Renal Failure. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2009, 28, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ash, S.; Campbell, K.L.; Bogard, J.; Millichamp, A. Nutrition Prescription to Achieve Positive Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2014, 6, 416–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A. Intradialytic Nutrition and Exercise: Convenience versus Efficacy. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Nutrition in Cancer Patients. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Alhazzani, W.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo, J.C.; Pichard, C.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2019, 38, 48–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejos, O.P.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M. Probiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Microbial Modulation and Therapeutic Prospects. Trends Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
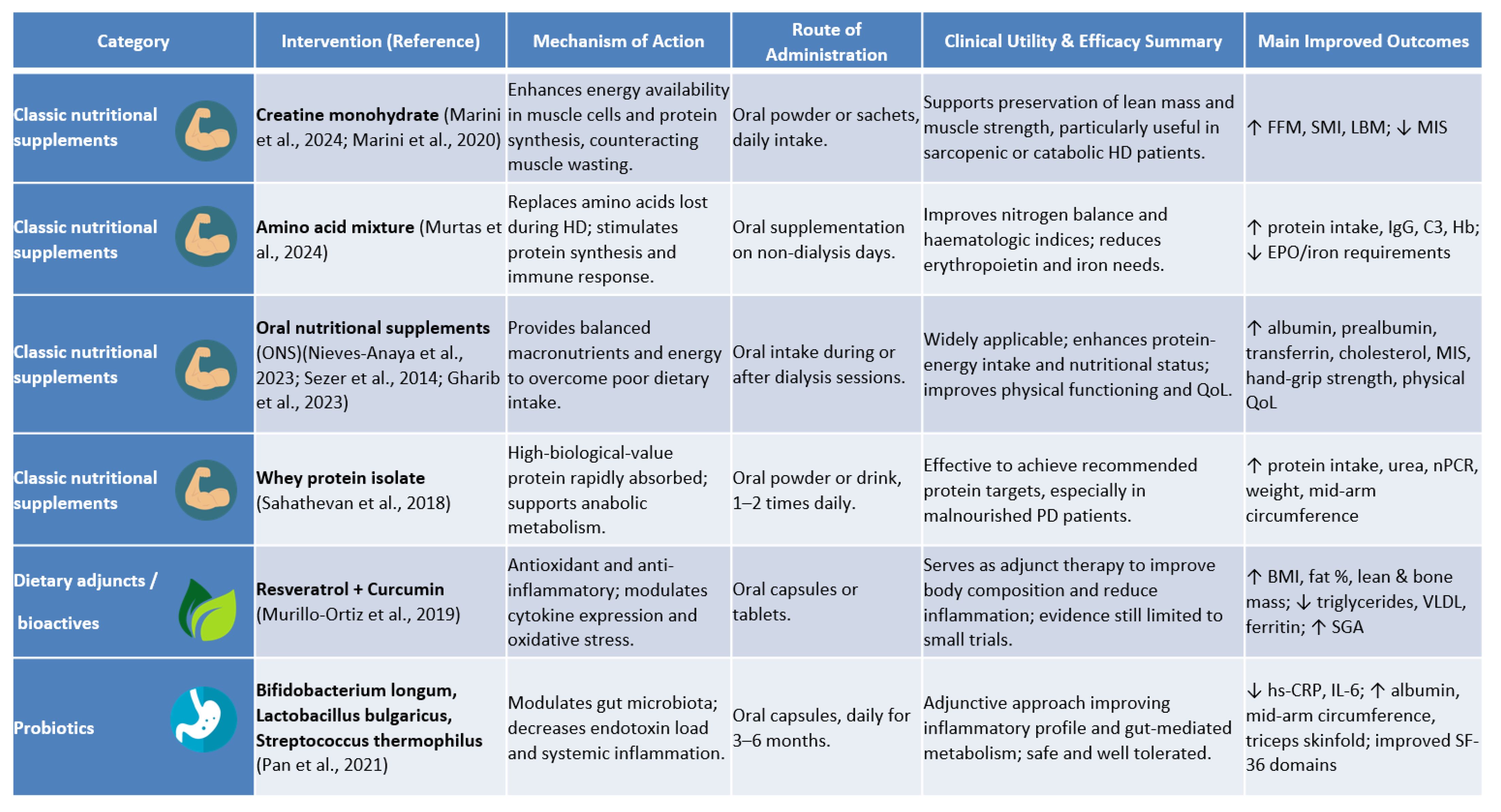
| Authors and Year | Study Design | Sample and Intervention | Methodology | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marini et al., 2024 [24] | Balanced randomised double-blind controlled trial | n = 40 HD; intervention (n = 21): oral sachets containing 5 g creatine monohydrate + 5 g maltodextrin daily; control (n = 19): 10 g maltodextrin daily | Body composition and MIS assessed at baseline, 6 months, and 12 months | ↑ in fat-free mass, skeletal muscle mass index, intracellular water, total body water, and body weight in intervention group (all p < 0.05). MIS unchanged in both groups. |
| Nieves-Anaya et al., 2023 [25] | Pilot randomised study | n = 32 chronic HD; intervention: personalised diet + ONS (Enterex DBT) + 5.6 g protein powder; control: personalised diet only | Baseline and post-intervention assessments | Intervention reduced moderate malnutrition by 48%, whereas severe malnutrition rose by 13% in controls (p < 0.04). ↑ in hand-grip strength, serum albumin, transferrin, and quality of life in intervention group. |
| Satirapoj et al., 2024 [26] | Randomised controlled trial | n = 32 ESRD on HD; intra-dialytic ONS (n = 16; 370 kcal Once Dialyze) vs. inter-dialytic ONS (n = 16) | 12-month follow-up | Both groups ↓ in MIS, greater reduction with intra-dialytic ONS. No significant differences in albumin, dietary intake, or anthropometry. |
| Sezer et al., 2014 [6] | Prospective trial | n = 58 HD; intervention: ONS (Nutrena) + dietary counselling (n = 29); control: increased dietary intake + counselling (n = 29) | 6-month assessment | Intervention ↑ in serum albumin, LDL-cholesterol, triceps skinfold thickness, and dry weight; ↓ in EPO requirement. Controls showed ↓ in BMI and FFM and ↑ in MIS. |
| Gharib et al., 2023 [27] | Prospective randomised trial | n = 60 malnourished HD; intervention: powder ONS (NEO-MUNE) + counselling; control: counselling only | Pre-/post-comparison | Intervention ↑ in albumin, pre-albumin, cholesterol, albumin-to-surface area ratio, and PEW score; ↓ in hs-CRP (p ≤ 0.016). |
| Murtas et al., 2024 [28] | Double-blind randomised trial | n = 30 HD; intervention: 5.4 g amino acid mixture on inter-dialytic days; control: no supplement | 3-month follow-up | Intervention ↑ in protein intake, serum IgG, complement C3, and haemoglobin; ↓ in EPO and IV iron needs (p < 0.05). Controls ↓ in body fat. |
| Murillo Ortiz et al., 2019 [29] | Randomised clinical trial | n = 40 CKD; intervention: 500 mg resveratrol + 500 mg curcumin daily; control: placebo | 12-week assessment | Intervention ↑ in BMI, fat %, and lean and bone mass; ↓in triglycerides, VLDL, and ferritin; ↑ in SGA score. No change in oxidative stress markers. |
| Marini et al., 2020 [30] | Placebo-controlled randomised trial | n = 30 HD; intervention: creatine + maltodextrin; control: maltodextrin | 4-week study | Intervention ↓ in MIS, ↑ in lean body mass (p < 0.05). 28.6% of controls lost lean mass vs. 14.4% in intervention. |
| Marsen et al., 2017 [31] | Multicentre open randomised trial | n = 107 HD with PEW; intervention: IDPN (aa/glucose/lipids/vitamins) 3×/week + standard counselling; control: counselling only | 16 weeks | Intervention ↑ in serum pre-albumin (41% achieved ≥15% rise by week 4 vs. 20.5% controls). Greater response in moderate malnutrition (SGA B). |
| Kabasawa et al., 2024 [32] | Multicentre open randomised trial | n = 34 maintenance HD with mild–moderate malnutrition; intervention: IDPN with ENEFLUID® 550 mL 3×/week; control: no IDPN | 12-month follow-up | No difference in serum transthyretin; intervention ↑ in protein intake, blood urea nitrogen, and nPCR; controls ↓ in protein intake. |
| Kittiskulnam et al., 2022 [33] | Prospective randomised controlled trial | n = 38 HD with PEW intolerant to ONS; intervention: 3-in-1 fish-oil IDPN for 3 months; control: intensive dietary counselling | Baseline, 3, and 6 months | Intervention ↑ in serum albumin, body weight, MIS, and spontaneous intake; ↑ in leptin in controls. |
| Authors and Year | Study Design | Sample and Intervention | Methodology | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liang et al., 2025 [34] | Randomised controlled trial | n = 81 PD; intervention: multidisciplinary medical nutrition therapy (MNT) (n = 41) vs. standard care (n = 40) | 6-month follow-up | Intervention ↑ in serum albumin, calcium, iron, Hb, mid-arm circumference, triceps skinfold, hand-grip strength, and protein and energy intake; ↓ in CRP, NLR, and PLR. |
| Pan et al., 2021 [35] | Randomised controlled trial | n = 116 PD; intervention: probiotic capsules (B. longum, L. bulgaricus, S. thermophilus) (n = 58) vs. no probiotics (n = 58) | Pre-/post-assessment | Intervention ↓ in hs-CRP and IL-6; ↑ in serum albumin, arm circumference, and triceps skinfold; improved selected SF-36 domains. |
| Sahathevan et al., 2018 [36] | Multicentre open randomised trial | n = 126 malnourished PD; intervention: whey protein isolate sachets + dietary counselling (n = 65); control: counselling only (n = 61) | 6-month follow-up | 59.5% of intervention achieved adequate protein intake vs. 16.2% controls (p < 0.001); ↑ in serum urea, nPCR, weight, and arm circumference in responders; controls ↓ in quality of life. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arroyo-Serrano, P.; Alonso-Dominguez, R.; Mas-Fontao, S.; Gonzalez-Parra, E.; Sánchez-Tocino, M.L. Nutritional Strategies to Address Malnutrition in Dialyses Patients: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213478
Arroyo-Serrano P, Alonso-Dominguez R, Mas-Fontao S, Gonzalez-Parra E, Sánchez-Tocino ML. Nutritional Strategies to Address Malnutrition in Dialyses Patients: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213478
Chicago/Turabian StyleArroyo-Serrano, Paula, Rosario Alonso-Dominguez, Sebastián Mas-Fontao, Emilio Gonzalez-Parra, and María Luz Sánchez-Tocino. 2025. "Nutritional Strategies to Address Malnutrition in Dialyses Patients: A Systematic Review" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213478
APA StyleArroyo-Serrano, P., Alonso-Dominguez, R., Mas-Fontao, S., Gonzalez-Parra, E., & Sánchez-Tocino, M. L. (2025). Nutritional Strategies to Address Malnutrition in Dialyses Patients: A Systematic Review. Nutrients, 17(21), 3478. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213478








