A Randomized Controlled Crossover Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Metabolic and Mental Health in Female Healthcare Night-Shift Workers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Participant Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Intervention
2.4. Body Composition
2.5. Phlebotomy
2.6. Fecal Microbiome Analysis
2.7. Serum Biomarker Analysis
2.8. Accelerometry
2.9. Subjective Data
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
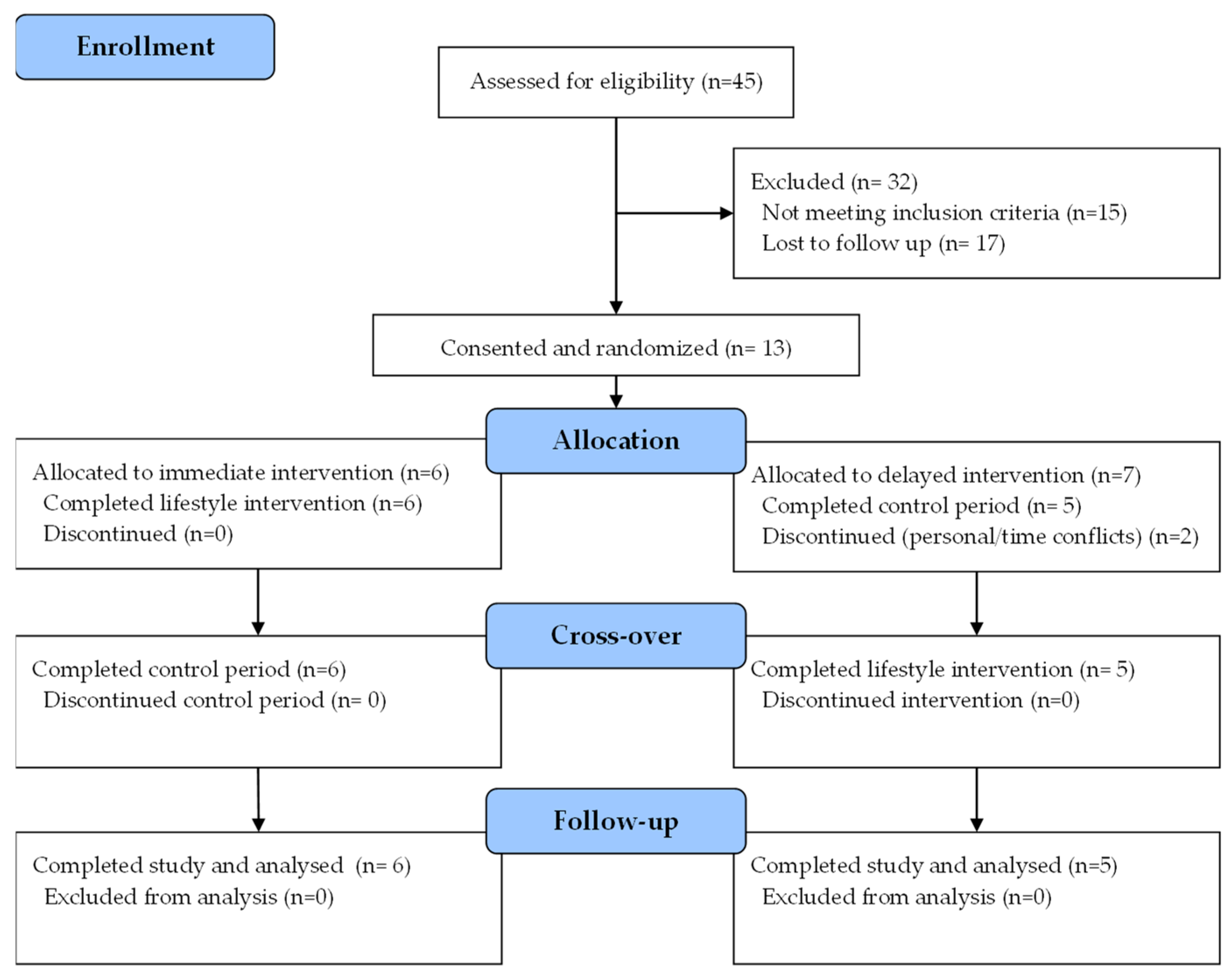
3.1. Participant Flow and Baseline Characteristics
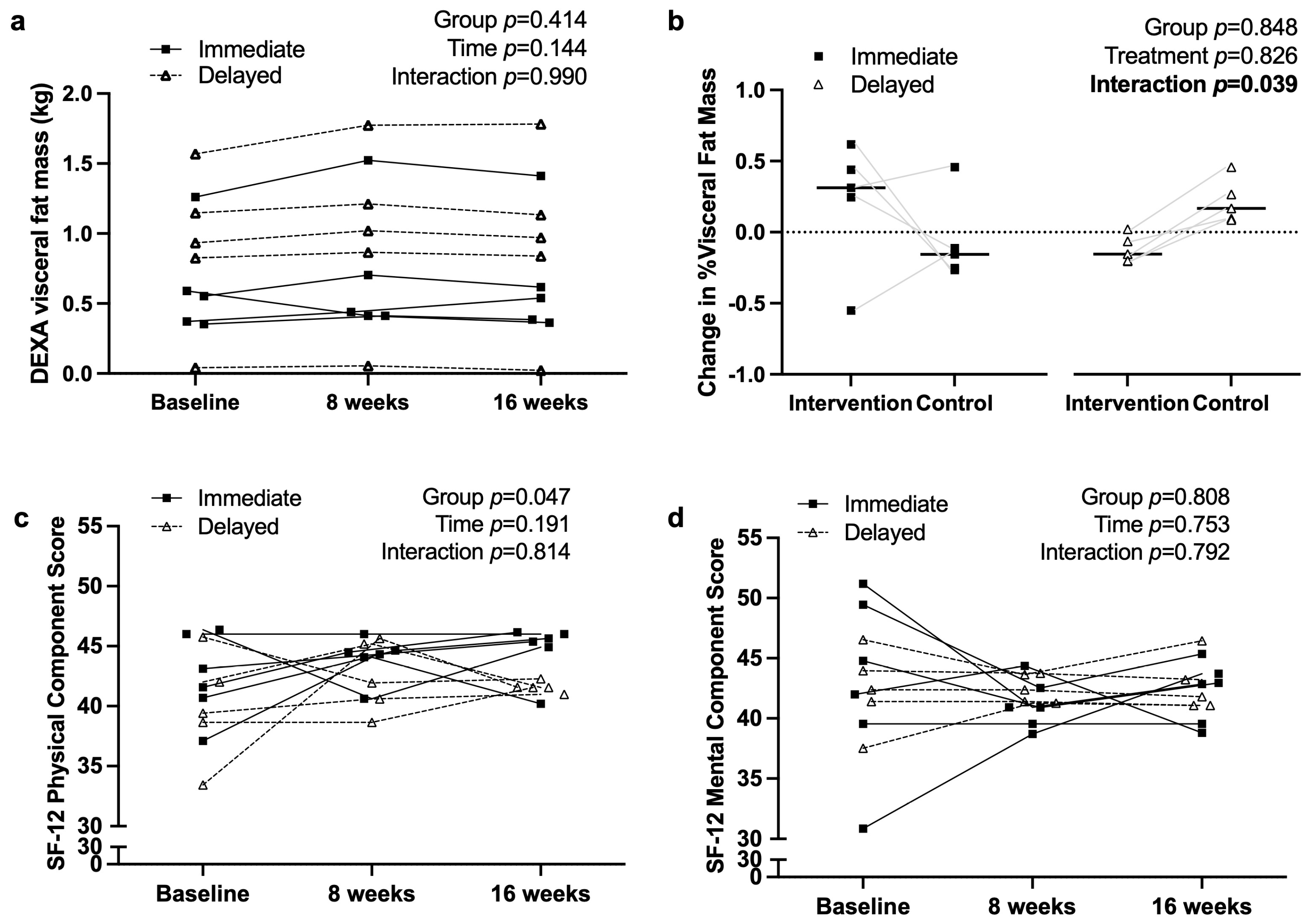
3.2. Anthropometry and Quality of Life Measures
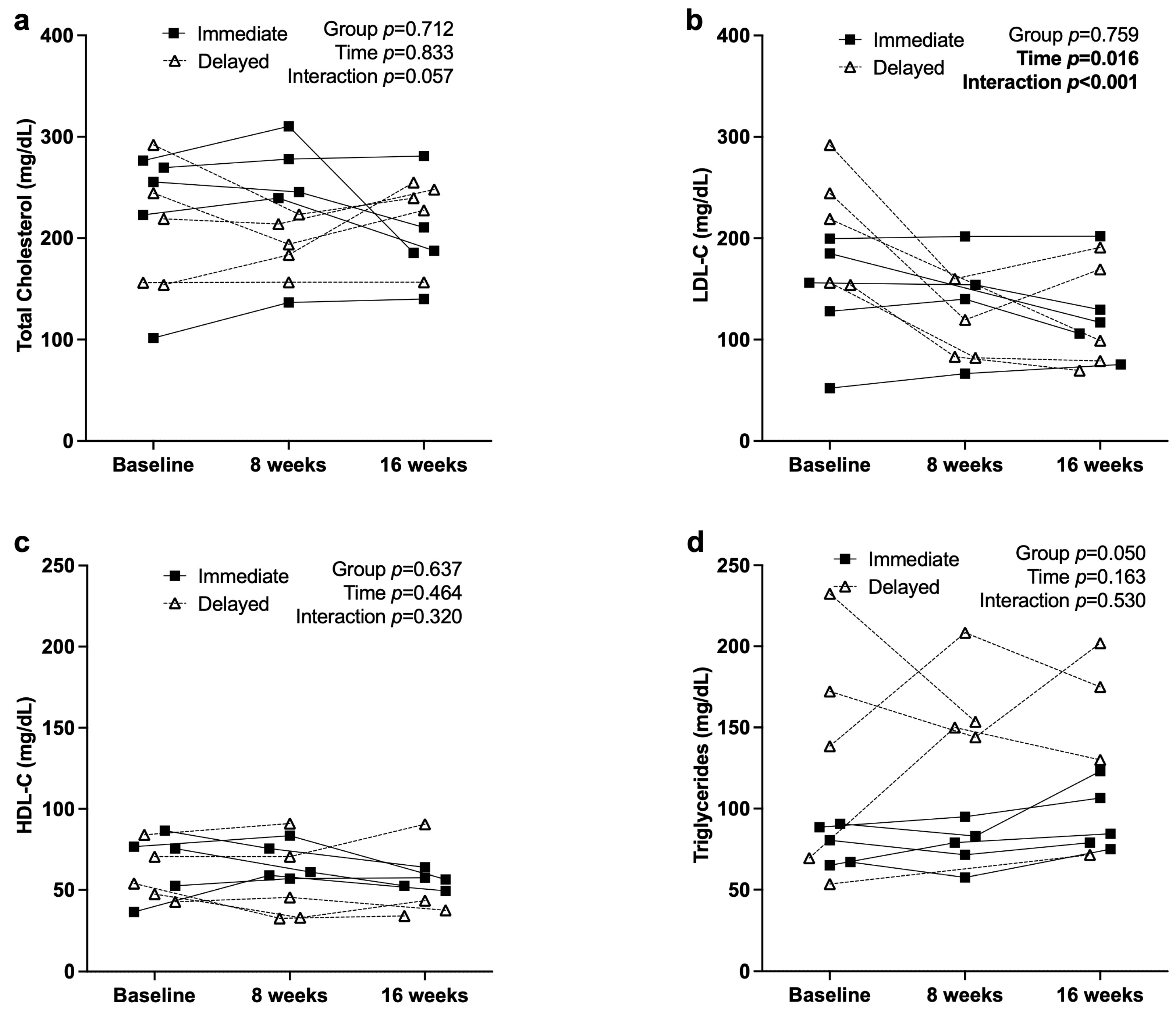
3.3. Metabolic and Inflammatory Markers
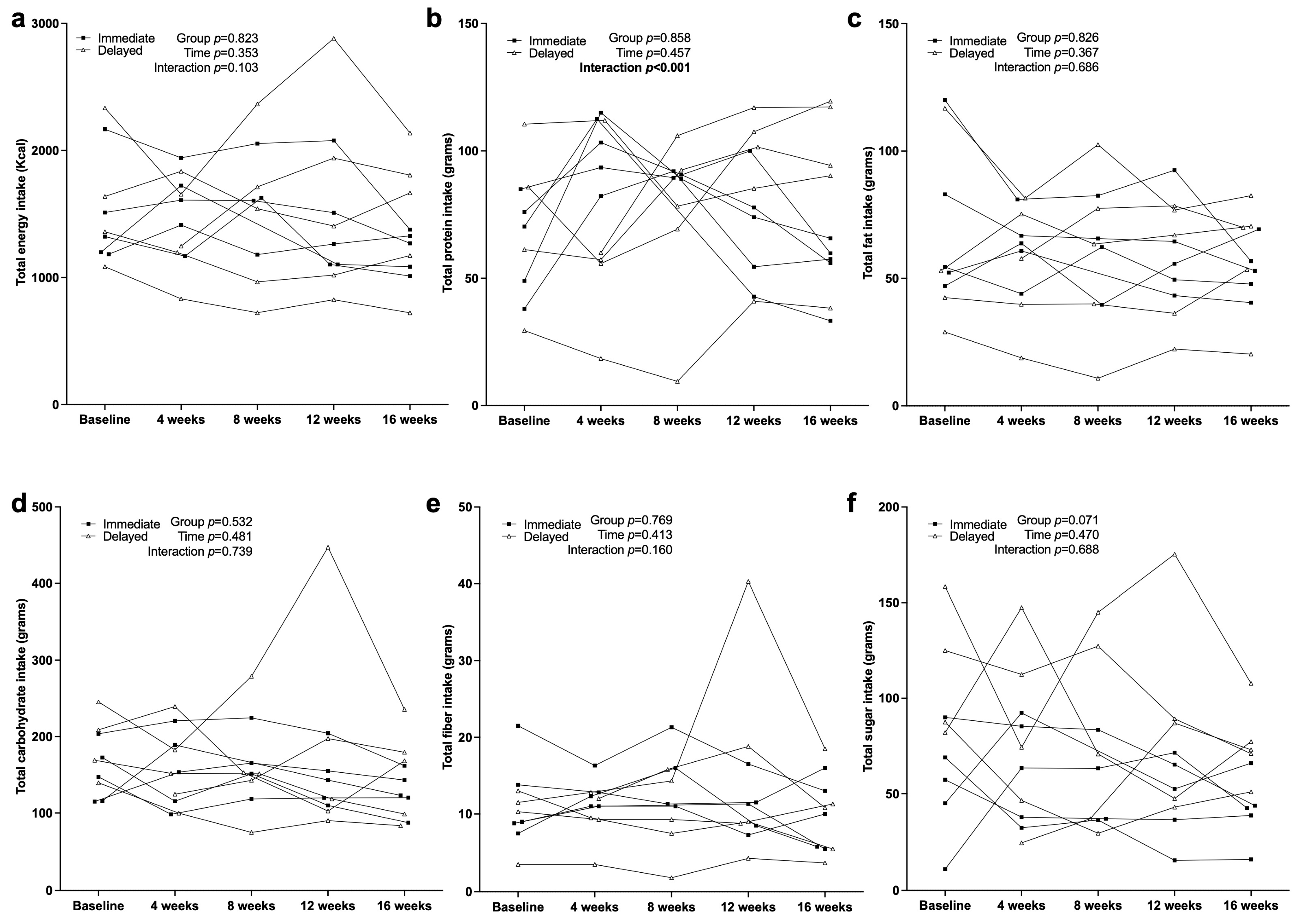
3.4. Dietary Intake Characteristics
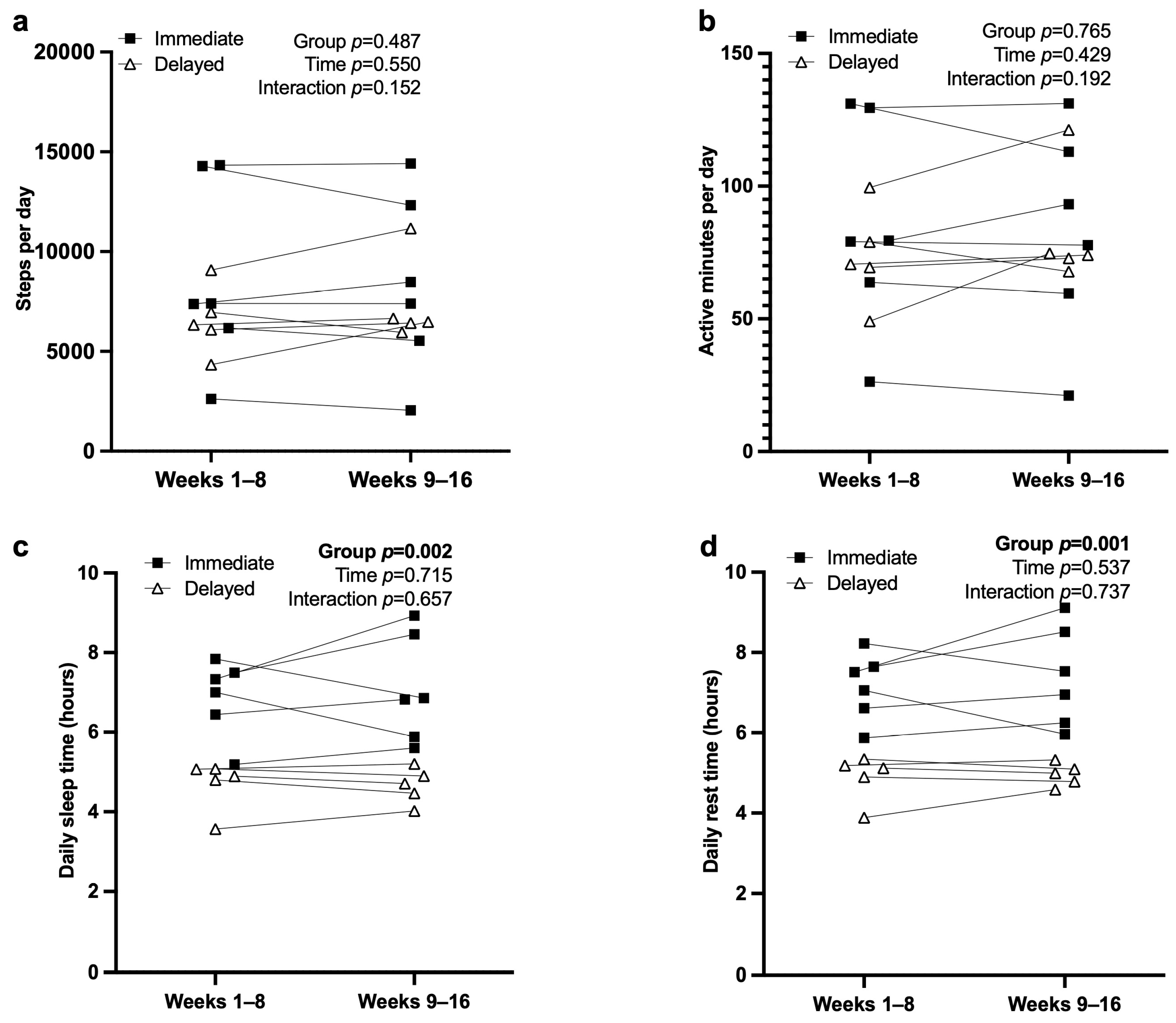
3.5. Actigraphy and Sleep
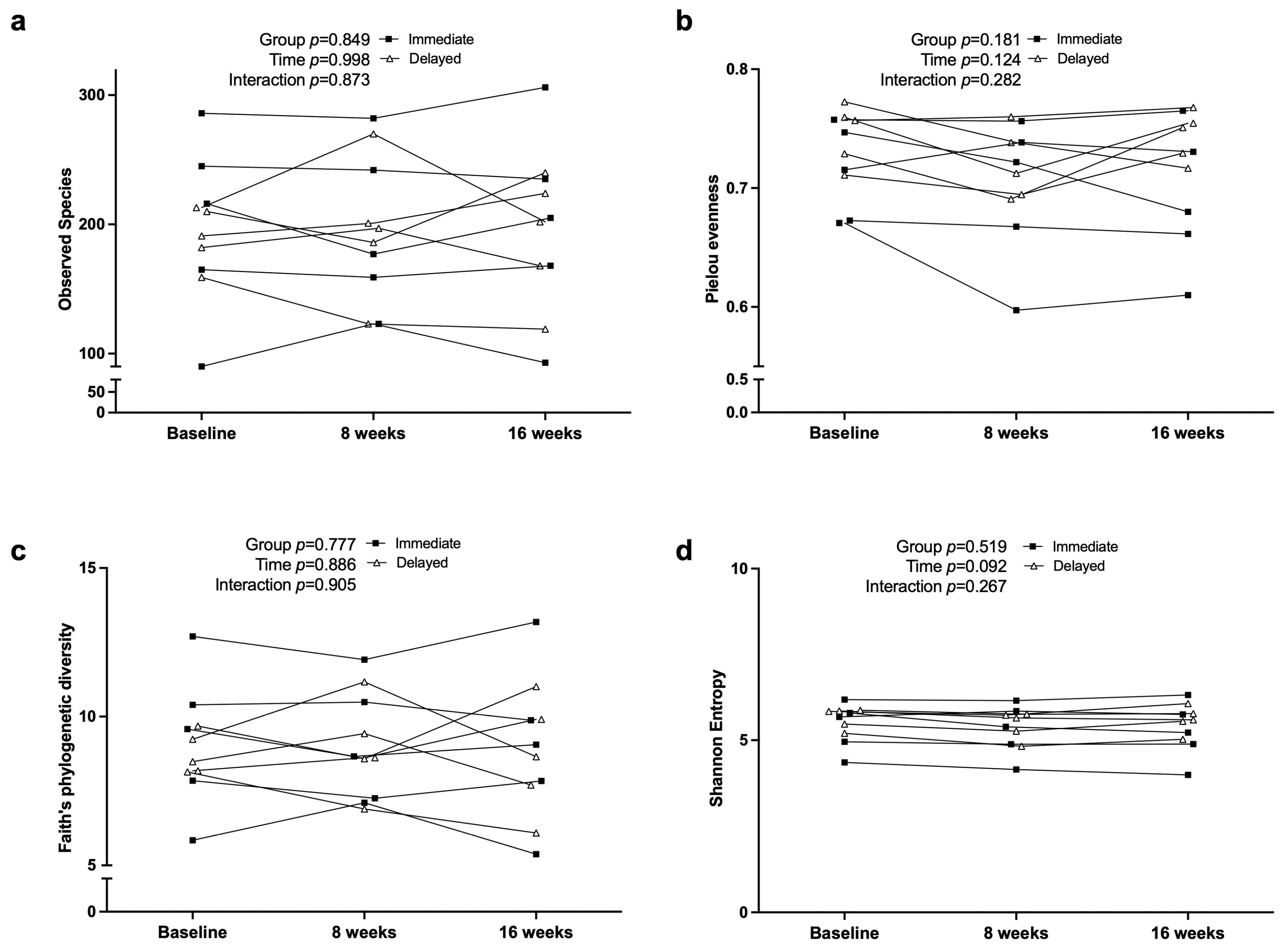
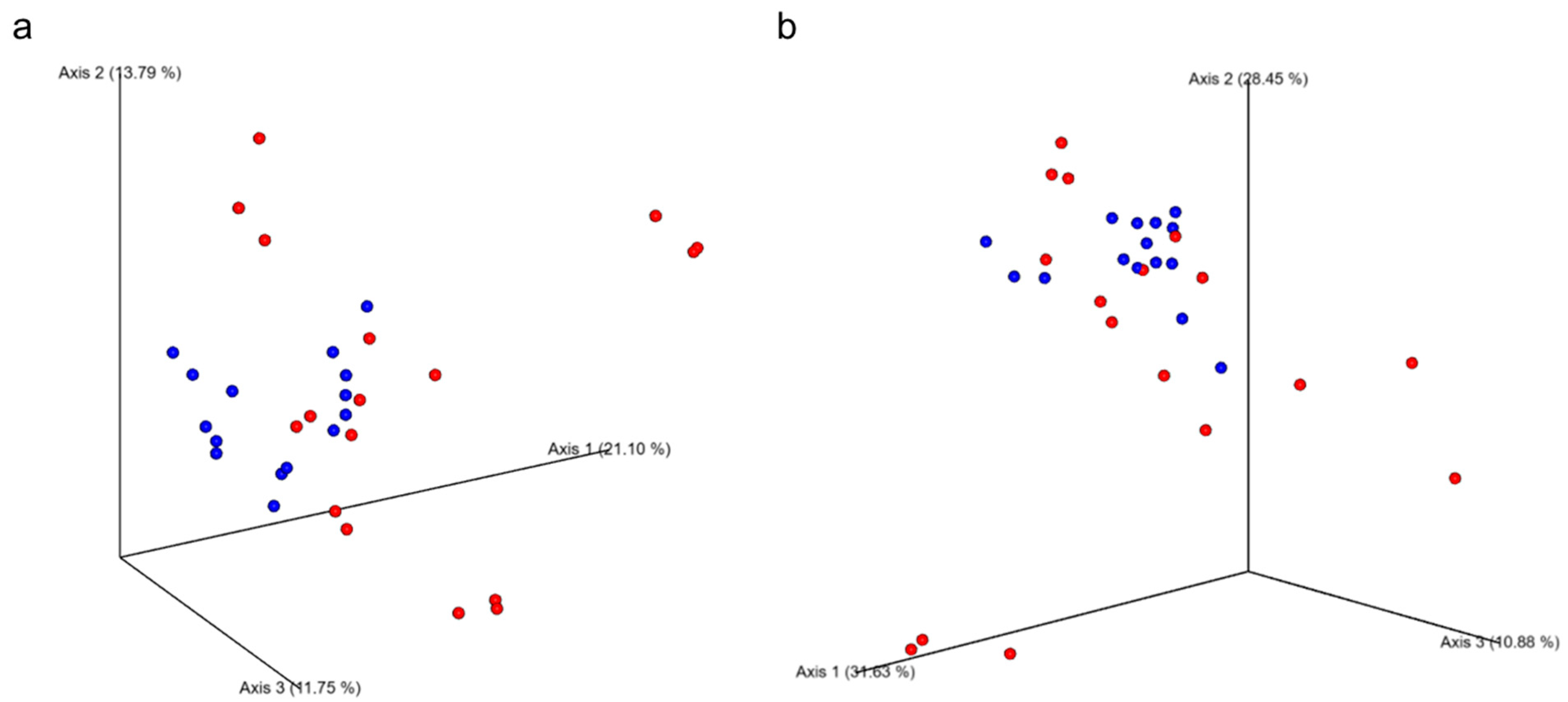
3.6. Fecal Microbiome Diversity and Composition
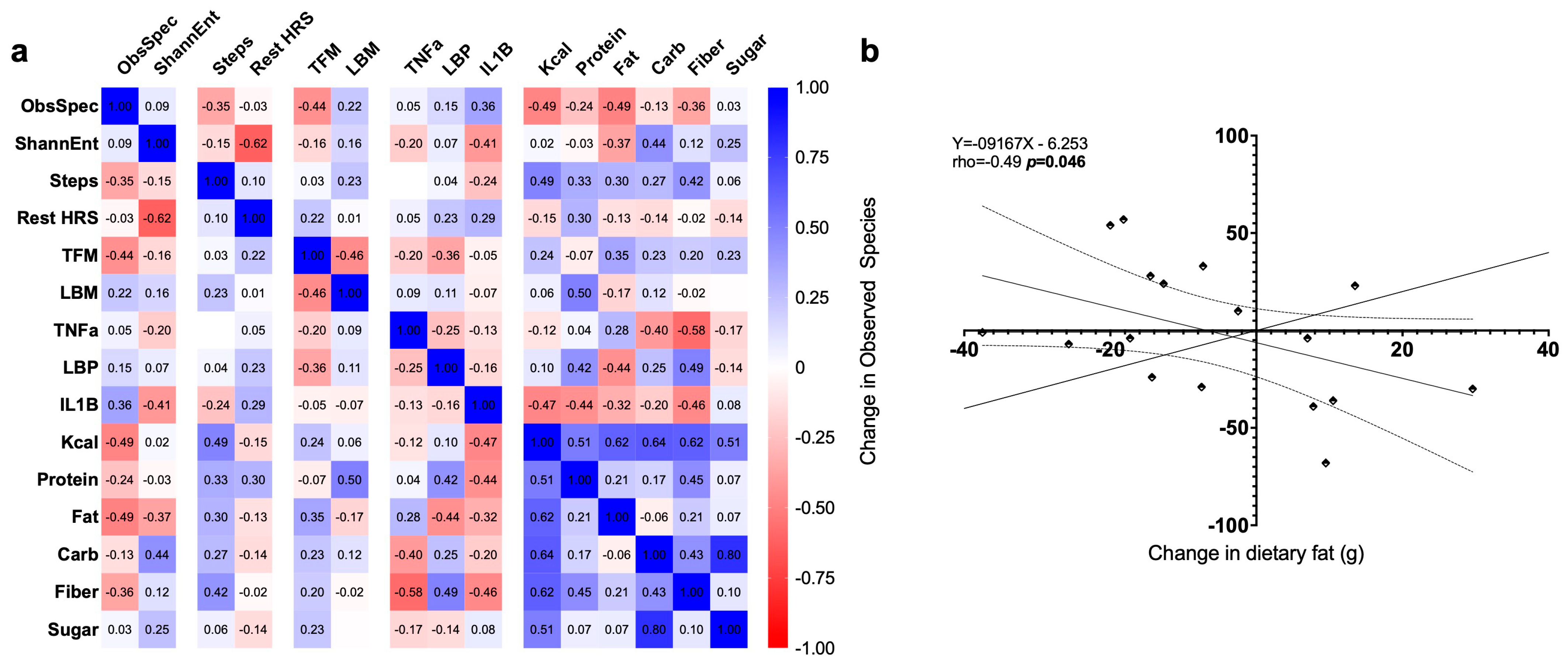
3.7. Exploratory Correlations
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolic and Inflammatory Responses
4.2. Dietary Intake and Macronutrient Distribution
4.3. Impact on Body Composition and Physical Health
4.4. Quality of Life and Mental Health
4.5. Gut Microbiome Outcomes
4.6. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonham, M.P.; Bonnell, E.K.; Huggins, C.E. Energy Intake of Shift Workers Compared to Fixed Day Workers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chronobiol. Int. 2016, 33, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Feng, W.; Wang, F.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Tse, G.; Vlaanderen, J.; Vermeulen, R.; Tse, L.A. Meta-Analysis on Shift Work and Risks of Specific Obesity Types. Obes. Rev. 2018, 19, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, A.E.; Coakley, E.H.; Must, A.; Spadano, J.L.; Laird, N.; Dietz, W.H.; Rimm, E.; Colditz, G.A. Impact of Overweight on the Risk of Developing Common Chronic Diseases during a 10-Year Period. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, M.D.; Burch, J.; Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Vena, J.E.; Hébert, J.R. Dietary Inflammatory Index Scores Differ by Shift Work Status: NHANES 2005 to 2010. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2014, 56, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiola, F.; Minh, N.L.; Preitner, N.; Kornmann, B.; Fleury-Olela, F.; Schibler, U. Restricted Feeding Uncouples Circadian Oscillators in Peripheral Tissues from the Central Pacemaker in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, E.; Ramsey, K.M.; Bass, J. Circadian rhythms and metabolic syndrome: From experimental genetics to human disease. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Mota, S.; Zhang, B. Circadian clock regulation on lipid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Lipid Transf. Lipoprotein Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 1276, 53–66. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, L.C.; Levandovski, R.; Dantas, G.; Caumo, W.; Hidalgo, M.P. Obesity and Shift Work: Chronobiological Aspects. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itani, O.; Kaneita, Y.; Murata, A.; Yokoyama, E.; Ohida, T. Association of Onset of Obesity with Sleep Duration and Shift Work among Japanese Adults. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacaro, V.; Ballesio, A.; Cerolini, S.; Vacca, M.; Poggiogalle, E.; Donini, L.M.; Lucidi, F.; Lombardo, C. Sleep Duration and Obesity in Adulthood: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 14, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoi, Y.Y.; Keogh, J.B. Dietary Interventions for Night Shift Workers: A Literature Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellappa, S.L.; Qian, J.; Vujovic, N.; Morris, C.J.; Nedeltcheva, A.; Nguyen, H.; Rahman, N.; Heng, S.W.; Kelly, L.; Kerlin-Monteiro, K.; et al. Daytime Eating Prevents Internal Circadian Misalignment and Glucose Intolerance in Night Work. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gannon, M.C.; Nuttall, F.Q.; Saeed, A.; Jordan, K.; Hoover, H. An Increase in Dietary Protein Improves the Blood Glucose Response in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.B. Night Shift Work, Sleep Quality, and Obesity. J. Lifestyle Med. 2013, 3, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, K.M.; Johnson, R.K.; Soultanakis, R.P.; Matthews, D.E. In-Person vs Telephone-Administered Multiple-Pass 24-Hour Recalls in Women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2000, 100, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medline. Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP): MedlinePlus Medical Test [updated 2025/03/24]. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/comprehensive-metabolic-panel-cmp/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Jiang, L.; Bokulich, N.A.; McDonald, D.; González, A.; Kosciolek, T.; Martino, C.; Zhu, Q.; Birmingham, A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; et al. QIIME 2 enables comprehensive end-to-end analysis of diverse microbiome data and comparative studies with publicly available data. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Pol, W.J.; Kumar, R.; Morrow, C.D.; Blanchard, E.E.; Taylor, C.M.; Martin, D.H.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Muzny, C.A. In silico and experimental evaluation of primer sets for species-level resolution of the vaginal microbiota using 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholestech LDX™ Lipid Profile Cassettes [Cited 2024 March]. Available online: https://www.globalpointofcare.abbott/us/en/product-details/cholestech-lipid-profile-cassettes.html (accessed on 21 October 2025).
- Shah, C.H.; Brown, J.D. Reliability and Validity of the Short-Form 12 Item Version 2 (SF−12v2) Health-Related Quality of Life Survey and Disutilities Associated with Relevant Conditions in the U.S. Older Adult Population. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kecklund, G.; Axelsson, J. Health Consequences of Shift Work and Insufficient Sleep. BMJ 2016, 355, i5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arble, D.M.; Bass, J.; Laposky, A.D.; Vitaterna, M.H.; Turek, F.W. Circadian Timing of Food Intake Contributes to Weight Gain. Obesity 2009, 17, 2100–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidy, H.J.; Clifton, P.M.; Astrup, A.; Wycherley, T.P.; Westerterp-Plantenga, M.S.; Luscombe-Marsh, N.D.; Woods, S.C.; Mattes, R.D. The Role of Protein in Weight Loss and Maintenance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 1320S–1329S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitting, K.M.; Vujovic, N.; Yuan, R.K.; Isherwood, C.M.; Medina, J.E.; Wang, W.; Buxton, O.M.; Williams, J.S.; Czeisler, C.A.; Duffy, J.F. Human Resting Energy Expenditure Varies with Circadian Phase. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3685–3690.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaeth, A.M.; Dinges, D.F.; Goel, N. Effects of Experimental Sleep Restriction on Weight Gain, Caloric Intake, and Meal Timing in Healthy Adults. Sleep 2013, 36, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, D.J.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Jebb, S.A.; Aveyard, P.; Behavioural Weight Management Review Group. Diet or exercise interventions vs combined behavioral weight management programs: A systematic review and meta-analysis of direct comparisons. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepper, M.J.; McAtee, J.R.; Chai, W. Effect of a workplace weight-loss program for overweight and obese healthcare workers. Am. J. Health Promot. 2021, 35, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, C.; Vogel, H.; Jonas, W.; Woting, A.; Blaut, M.; Schürmann, A.; Cedernaes, J. Gut microbiota and glucometabolic alterations in response to recurrent partial sleep deprivation in normal-weight young individuals. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Chao, Y.-P.; Huang, C.-M.; Lee, H.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Li, K.-W.; Hsu, A.-L.; Tung, Y.-T.; Wu, C.W. Impacts of night shift on medical professionals: A pilot study of brain connectivity and gut microbiota. Front. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1503176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaha, B.; Heddes, M.; Pilorz, V.; Niu, Y.; Gorbunova, E.; Gigl, M.; Kleigrewe, K.; Oster, H.; Haller, D.; Kiessling, S. Genetic and environmental circadian disruption induce weight gain through changes in the gut microbiome. Mol. Metab. 2022, 66, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Rao, M.C.; Chang, E.B. Gut microbiota as a transducer of dietary cues to regulate host circadian rhythms and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.E.G.; Lashinger, L.M.; Weinstock, G.M.; Bray, M.S. Circadian rhythms and the gut microbiome synchronize the host’s metabolic response to diet. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, T.K.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, D.; Root, K.M.; Regal, J.F.; Alejandro, E.U.; Cao, R. Circadian disruption across lifespan impairs glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in adult mice. Metabolites 2024, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measure | All (n = 11) | Immediate (n = 6) | Delayed (n = 5) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 32.6 (8.5) | 31.2 (10.0) | 34.4 (7.0) | 0.279 |
| Weekly Shifts | 3.3 (1) | 3.7 (1.2) | 2.8 (0.4) | 0.083 |
| Hours Worked Overnight | 11.6 (1.2) | 11.3 (1.6) | 12 (0.0) | 0.195 |
| Dual X-ray Absorptiometry | ||||
| Total Body Mass (kg) | 80.09 (12.12) | 78.51 (11.69) | 81.67 (13.7) | 1.000 |
| Lean Body Mass (kg) | 44.65 (3.63) | 44.9 (4.27) | 44.4 (3.36) | 0.996 |
| Total Fat Mass (kg) | 32.78 (9.68) | 32.15 (10.11) | 33.41 (10.38) | 1.000 |
| Accelerometry | ||||
| Daily Steps | 7725 (3659) | 8698 (4684) | 6558 (1709) | 0.347 |
| Daily Rest Time (hours) | 6.12 (1.37) | 7.15 (0.83) | 4.89 (0.58) | <0.001 |
| Average dietary intake | ||||
| Energy (Kcal) | 1534 (442) | 1477 (408) | 1284 (855) | 1.000 |
| Protein (g) | 67.3 (25.7) | 63.7 (19.5) | 57.4 (43.9) | 1.000 |
| Fat (g) | 66.5 (32.7) | 71.4 (30.6) | 48.3 (43.2) | 0.996 |
| Carbohydrate (g) | 168.5 (44.3) | 150.8 (38) | 152.5 (94.2) | 0.703 |
| Fiber (g) | 11 (5) | 12.1 (5.8) | 7.7 (5.6) | 1.000 |
| Sugar (g) | 80.6 (43.2) | 54.5 (29.4) | 90.6 (59.3) | 0.194 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robinson, L.A.; Lennon, S.; Pegel, A.R.; Strickland, K.P.; Feeley, C.A.; Watts, S.O.; J. Van Der Pol, W.; Roberts, M.D.; Greene, M.W.; Frugé, A.D. A Randomized Controlled Crossover Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Metabolic and Mental Health in Female Healthcare Night-Shift Workers. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213342
Robinson LA, Lennon S, Pegel AR, Strickland KP, Feeley CA, Watts SO, J. Van Der Pol W, Roberts MD, Greene MW, Frugé AD. A Randomized Controlled Crossover Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Metabolic and Mental Health in Female Healthcare Night-Shift Workers. Nutrients. 2025; 17(21):3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213342
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobinson, Laura A., Sarah Lennon, Alexandrea R. Pegel, Kelly P. Strickland, Christine A. Feeley, Sarah O. Watts, William J. Van Der Pol, Michael D. Roberts, Michael W. Greene, and Andrew D. Frugé. 2025. "A Randomized Controlled Crossover Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Metabolic and Mental Health in Female Healthcare Night-Shift Workers" Nutrients 17, no. 21: 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213342
APA StyleRobinson, L. A., Lennon, S., Pegel, A. R., Strickland, K. P., Feeley, C. A., Watts, S. O., J. Van Der Pol, W., Roberts, M. D., Greene, M. W., & Frugé, A. D. (2025). A Randomized Controlled Crossover Lifestyle Intervention to Improve Metabolic and Mental Health in Female Healthcare Night-Shift Workers. Nutrients, 17(21), 3342. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17213342









