Comparison of Metabolic Control, Dietary Habits, Activity, and Psychological Condition in Children and Adolescents Treated with Personal Insulin Pumps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants, Recruitment and Study Design
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. Clinical and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data
2.4. Food Preferences and Activity Data
2.5. Psychological Data
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Group
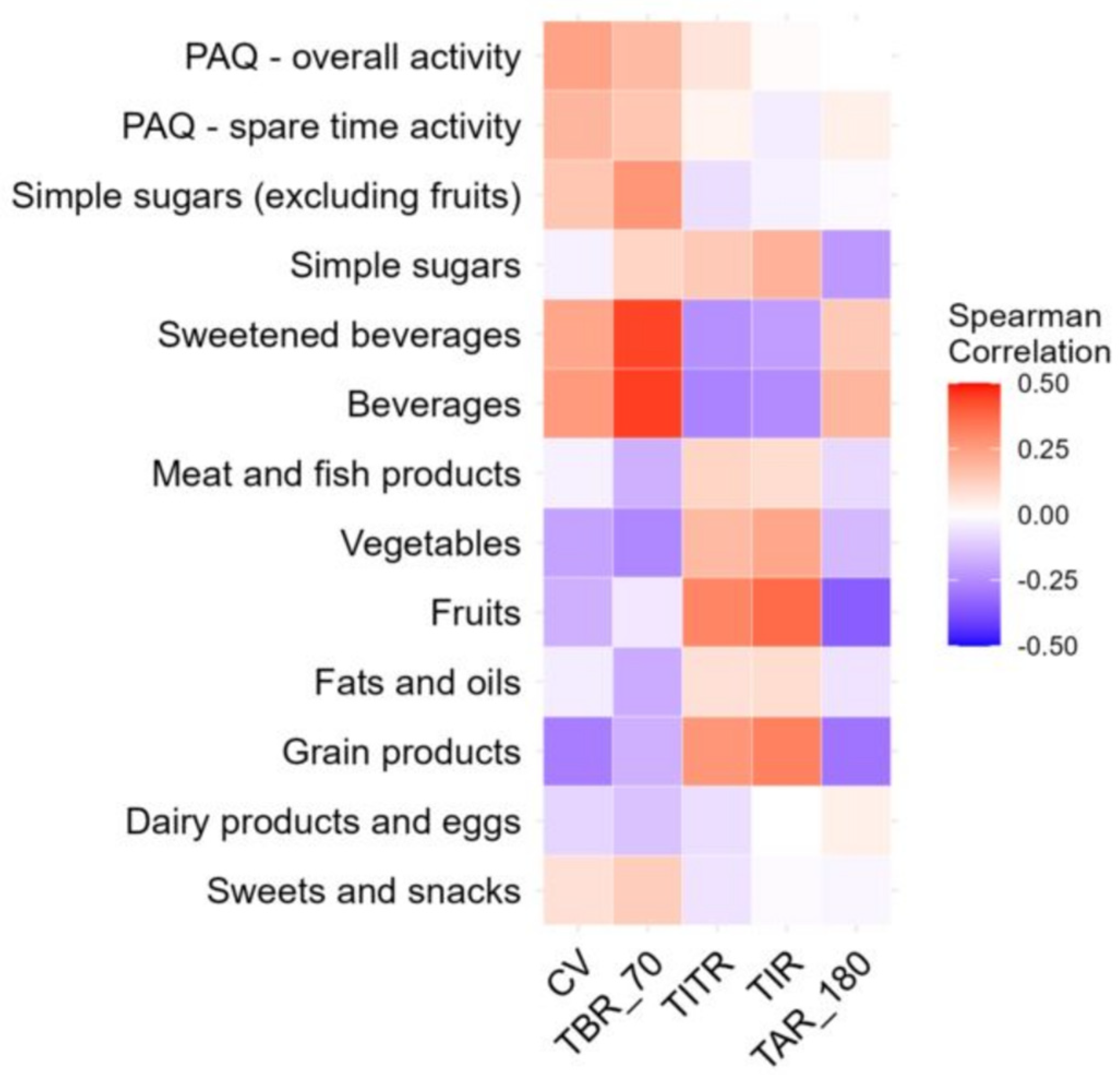
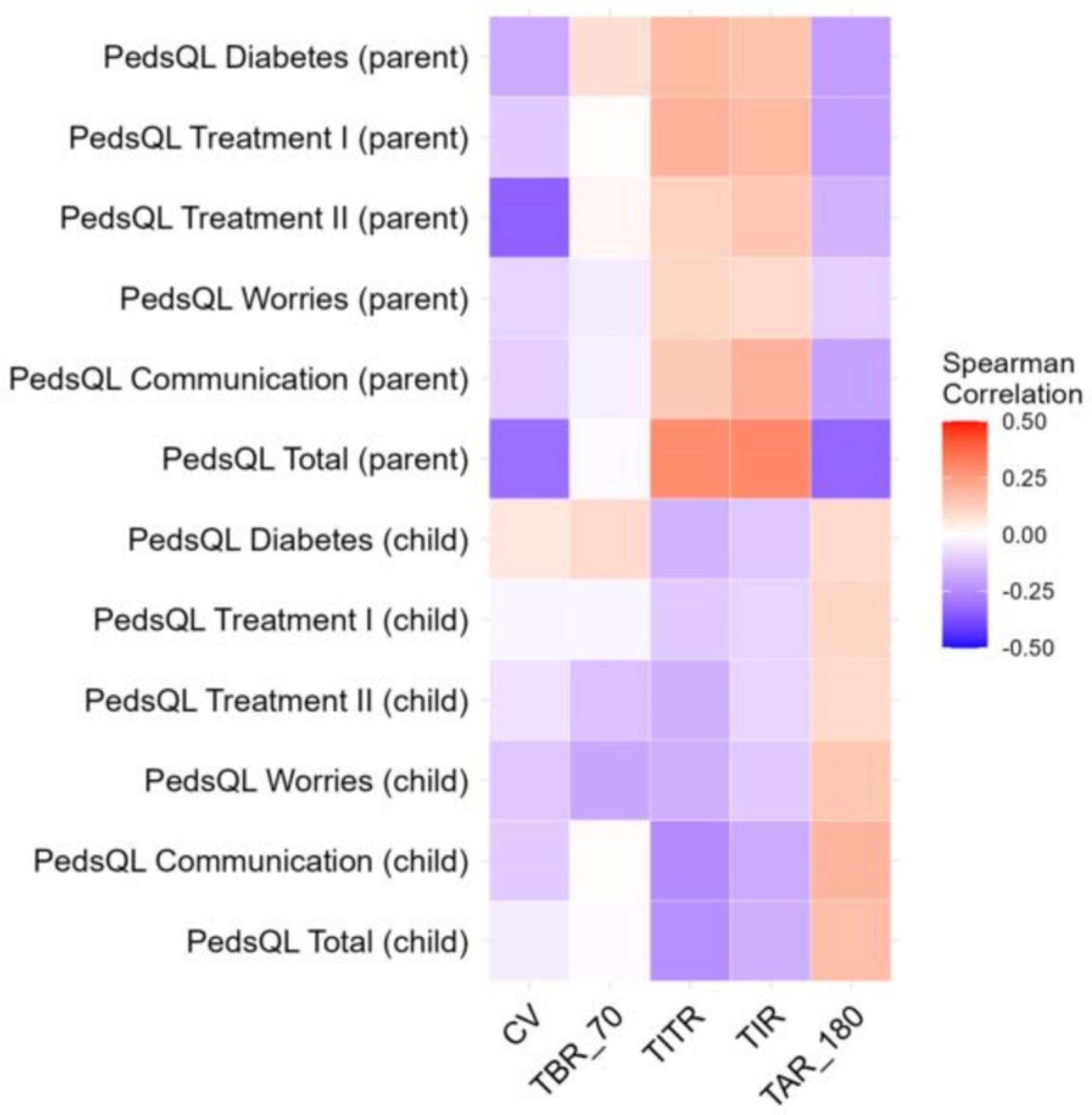
3.2. Association Between Glycemic Variability and Eating Habits, Activity, and Mental Health
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cockcroft, E.J.; Clarke, R.; Dias, R.P.; Lloyd, J.; Mann, R.H.; Narendran, P.; Reburn, C.; Smith, B.; Smith, J.R.; Andrews, R.C. Effectiveness of Educational and Psychoeducational Self-Management Interventions in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Diabetes 2024, 2024, 2921845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoi, A.; Marques, I.R.; Padrão, E.M.H.; Mahesh, A.; Hespanhol, L.C.; Júnior, J.E.R.L.; de Souza, I.A.F.; Moreira, V.C.S.; Silva, C.H.; Miyawaki, I.A.; et al. Glucose control and psychosocial outcomes with use of automated insulin delivery for 12 to 96 weeks in type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabia, M.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R.; Socha, K. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Possibilities of Prevention and Treatment: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 2019. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Szalecki, M.; Wysocka-Mincewicz, M.; Ramotowska, A.; Mazur, A.; Lisowicz, L.; Beń-Skowronek, I.; Sieniawska, J.; Klonowska, B.; Charemska, D.; Nawrotek, J.; et al. Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in Polish children: A multicentre cohort study. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, P.; Hanas, R.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Dovc, K.; Jendle, J. Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: A Narrative Review. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 19322968241248404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffini, R.; Deodati, A.; Nicoletti, M.C.; Carducci, C.; Ciampalini, P.; Lorubbio, A.; Matteoli, M.C.; Pampanini, V.; Patera, I.P.; Rapini, N.; et al. Comparison of two advanced hybrid closed loop in a pediatric population with type 1 diabetes: A real-life observational study. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jendle, J.H.; Riddell, M.C. Editorial: Physical Activity and Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafipour, F.; Mobasseri, M.; Yavari, A.; Nadrian, H.; Aliasgarzedeh, A.; Abbasi, N.M.; Niafar, M.; Gharamaleki, J.H.; Sadra, V. Effect of regular exercise training on changes in HbA1c, BMI and VO2max among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An 8-year trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2017, 5, e000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.; Guarino, M.; Tripodi, R.; Giannini, C.; Chiarelli, F.; Blasetti, A. Diet and Glycemic Index in Children with Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyem, R.; Zakarneh, S.; Al-Jayyousi, G.F. Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Uribe, N.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Izquierdo, M.; García-Hermoso, A. Association Between Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior and Physical Fitness and Glycated Hemoglobin in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canha, M.; Ferreira, S.; Santos Silva, R.; Azevedo, A.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Castro-Correia, C. Glycemic Control and Metabolic Parameters in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Cureus 2023, 15, e43416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, D.; Wardell, J.; Harrison, A.; Mizokami-Stout, K.; Hirschfeld, E.; Garrity, A.; Thomas, I.; Lee, J. Screening for diabetes distress and depression in routine clinical care for youth with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. Psychol. 2024, 49, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collyns, O.J.; Meier, R.A.; Betts, Z.L.; Chan, D.S.; Frampton, C.; Frewen, C.M.; Hewapathirana, N.M.; Jones, S.D.; Roy, A.; Grosman, B.; et al. Improved glycemic outcomes with medtronic minimed advanced hybrid closed-loop delivery: Results from a randomized crossover trial comparing automated insulin delivery with predictive low glucose suspend in peoplewithtype1diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnside, M.J.; Lewis, D.M.; Crocket, H.R.; Meier, R.A.; Williman, J.A.; Sanders, O.J.; Jefferies, C.A.; Faherty, A.M.; Paul, R.G.; Lever, C.S.; et al. Extended Use of an Open-Source Automated Insulin Delivery System in Children and Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The 24-Week Continuation Phase Following the CREATE Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2023, 25, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isganaitis, E.; Raghinaru, D.; Ambler-Osborn, L.; Pinsker, J.E.; Buckingham, B.A.; Wadwa, R.P.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Kudva, Y.C.; Levy, C.; Forlenza, G.P.; et al. Closed-Loop Insulin Therapy Improves Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults: Outcomes from the International Diabetes Closed-Loop Trial. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2021, 23, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejk, A.; Myśliwiec, K.; Michalak, A.; Pernak, B.; Fendler, W.; Myśliwiec, M. Comparison of Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents Treated with Insulin Pumps. Children 2024, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, P.; Gkiourtzis, N.; Christoforidis, A.; Kotanidou, E.P.; Galli-Tsinopoulou, A. The efficacy of automated insulin delivery systems in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes Mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 199, 110678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakami, T.; Terada, H.; Tanabe, S.; Mine, Y.; Aoki, M.; Aoki, R.; Suzuki, J.; Morioka, I. Clinical significance of coefficient of variation in continuous glucose monitoring for glycemic management in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitsi, E.; Livadas, S.; Angelopoulos, N.; Paparodis, R.D.; Raftopoulou, M.; Argyrakopoulou, G. A Nutritional Approach to Optimizing Pump Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dłużniak-Gołaska, K.; Panczyk, M.; Szypowska, A.; Sińska, B.; Szostak-Węgierek, D. Influence of two different methods of nutrition education on the quality of life in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus—A randomized study. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig./Ann. Natl. Inst. Hyg. 2020, 71, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Leelarathna, L.; Choudhary, P.; Wilmot, E.G.; Lumb, A.; Street, T.; Kar, P.; Ng, S.M. Hybrid Closed-loop Therapy: Where Are We in 2021? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, M.D.; Kanapka, L.G.; Beck, R.W.; Ekhlaspour, L.; Forlenza, G.P.; Cengiz, E.; Schoelwer, M.; Ruedy, K.J.; Jost, E.; Carria, L.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Closed-Loop Control in Children with Type 1 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, P.; Taplin, C.E.; Zaharieva, D.P.; Pemberton, J.; Davis, E.A.; Riddell, M.C.; McGavock, J.; Moser, O.; Szadkowska, A.; Lopez, P.; et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Exercise in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1341–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerc, A. Nutrition education to type 1 diabetes patients: Few changes over the time. Front. Clin. Diabetes Healthc. 2023, 4, 1243237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | HCL (N = 21) | PLGS (N = 16) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | 10.42 (9.13–12.13) | 9.78 (9.07–11.84) | 0.5959 |
| Weight [kg] | 37 (31.2–43.2) | 34.45 (29.25–38.5) | 0.3576 |
| Weight [z-score] | −0.08 (−1.1–0.78) | −0.22 (−0.77–0.49) | 0.5750 |
| Weight [percentile] | 46.89 (13.59–78.21) | 41.25 (22.64–68.76) | - |
| Height [cm] | 144.8 (136.4–151.1) | 133.8 (131–148.5) | 0.2761 |
| Height [z-score] | 0.11 (−0.88–0.67) | −0.49 (−0.74–0.04) | 0.2379 |
| Height [percentile] | 54.31 (19.03–74.88) | 31.17 (23–51.6) | - |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 16.89 (15.85–19.3) | 17.64 (15.73–18.82) | 0.8903 |
| BMI [z-score] | −0.25 (−0.61–0.56) | 0.29 (−0.72–0.56) | 0.9879 |
| BMI [percentile] | 39.99 (27.03–71.37) | 61.36 (23.88–71.31) | - |
| Disease duration [years] | 4.07 (2.8–6.31) | 3.34 (2.88–5.99) | >0.9999 |
| DDI [U/kg/day] | 0.73 (0.68–0.98) | 0.78 (0.67–0.83) | 0.9879 |
| Basal insulin [%] | 33 (28–40) | 35 (27.75–38) | 0.7872 |
| Variable | HCL (N = 21) | PLGS (N = 16) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
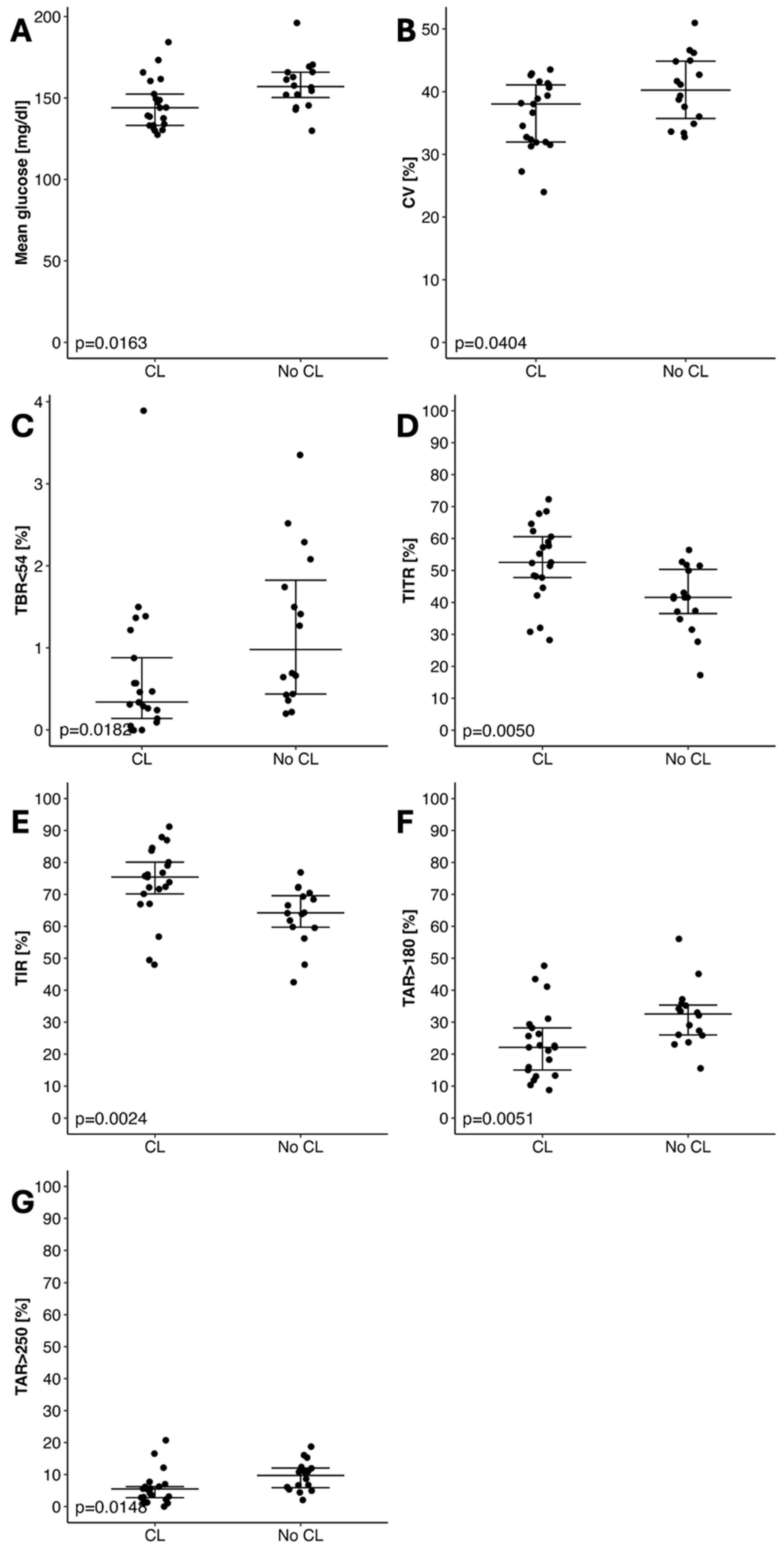
| Mean glucose [mg/dL] | 144.02 (133.17–152.43) | 157.06 (150.28–165.79) | 0.0193 |
| CV (%) | 38.03 (31.96–41.07) | 40.24 (35.73–44.86) | 0.0404 |
| Time Below Target Range ≤ 54 mg/dL [%] | 0.34 (0.14–0.88) | 0.98 (0.44–1.82) | 0.0182 |
| Time in Tight Range 70–140 mg/dL [%] | 52.52 (47.78–60.56) | 41.57 (36.53–50.33) | 0.0050 |
| Time in Target Range 70–180 mg/dL [%] | 75.4 (70.16–80.06) | 64.2 (59.72–69.59) | 0.0024 |
| Time Above Range ≥ 180 mg/dL [%] | 22.12 (15.02–28.22) | 32.55 (25.98–35.34) | 0.0051 |
| Time Above Target Range ≥ 250 mg/dL [%] | 5.51 (2.8–6.23) | 9.74 (5.9–12.05) | 0.0148 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lejk, A.; Myśliwiec, K.; Chrzanowski, J.; Burzyński, J.; Michalak, A.; Musiał-Paździor, M.; Bandura, M.; Rutkowska-Kośmińska, J.; Drzewińska, K.; Grabowska, A.; et al. Comparison of Metabolic Control, Dietary Habits, Activity, and Psychological Condition in Children and Adolescents Treated with Personal Insulin Pumps. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203304
Lejk A, Myśliwiec K, Chrzanowski J, Burzyński J, Michalak A, Musiał-Paździor M, Bandura M, Rutkowska-Kośmińska J, Drzewińska K, Grabowska A, et al. Comparison of Metabolic Control, Dietary Habits, Activity, and Psychological Condition in Children and Adolescents Treated with Personal Insulin Pumps. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203304
Chicago/Turabian StyleLejk, Agnieszka, Karolina Myśliwiec, Jędrzej Chrzanowski, Jacek Burzyński, Arkadiusz Michalak, Malwina Musiał-Paździor, Marta Bandura, Jolanta Rutkowska-Kośmińska, Kinga Drzewińska, Aleksandra Grabowska, and et al. 2025. "Comparison of Metabolic Control, Dietary Habits, Activity, and Psychological Condition in Children and Adolescents Treated with Personal Insulin Pumps" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203304
APA StyleLejk, A., Myśliwiec, K., Chrzanowski, J., Burzyński, J., Michalak, A., Musiał-Paździor, M., Bandura, M., Rutkowska-Kośmińska, J., Drzewińska, K., Grabowska, A., Okonek, M., Herstowska, M., Hoffmann, M., & Fendler, W. (2025). Comparison of Metabolic Control, Dietary Habits, Activity, and Psychological Condition in Children and Adolescents Treated with Personal Insulin Pumps. Nutrients, 17(20), 3304. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203304









