Interaction Between First-Trimester Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Educational Level on the Risk of Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters: A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
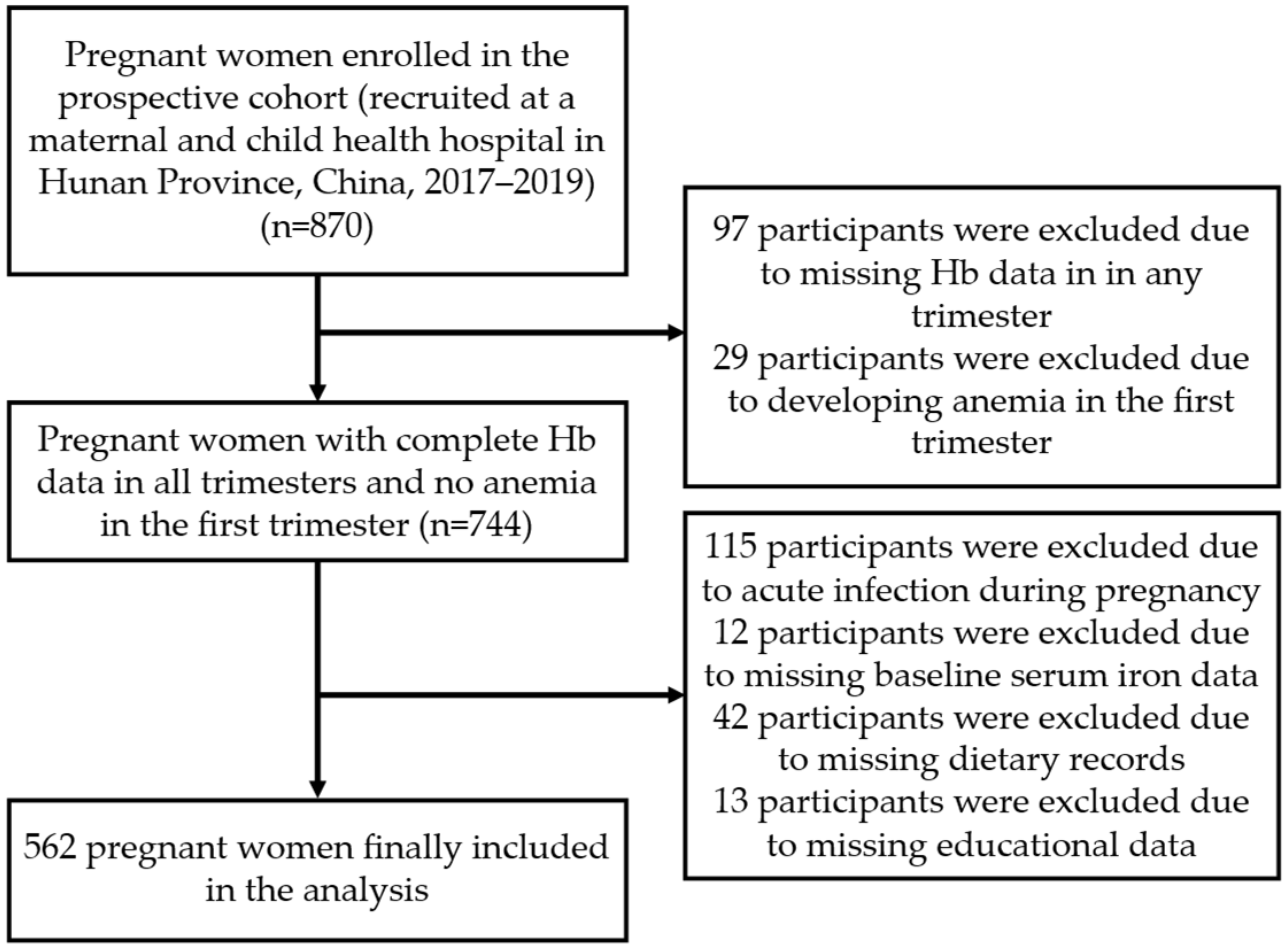
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Calculation of E-DII
2.5. Variable Definition
- (1)
- Age: Maternal age was categorized into two groups consisting of under 35 years and 35 years or older, with the latter classified as advanced maternal age [48].
- (2)
- Pre-pregnancy BMI: It was classified as underweight (<18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5–24.0 kg/m2), or overweight/obesity (≥24.0 kg/m2) [49].
- (3)
- Pre-pregnancy regular physical activity: Exercise more than three times a week for more than 30 min each time.
- (4)
- Sleep quality: It was assessed using the PSQI, a 19-item instrument evaluating seven sleep components. The global PSQI score ranges from 0 to 21, with total scores categorized as very good (≤5), good (6–10), or poor (≥11) [32].
- (5)
- Depression: Depressive symptoms were assessed using the EPDS, which comprises 10 items rated on a 4-point scale. Total scores range from 0 to 30, with a score ≤ 12 indicating no clinically significant symptoms and a score ≥ 13 indicating clinically significant depressive symptoms [50].
- (6)
- First-trimester E-DII: This refers to the E-DII calculated from both dietary and supplemental nutrient intakes. It was the primary exposure variable in this study, representing the overall inflammatory potential of total nutrient intake. It was employed as a continuous variable, in tertiles (T1–T3) for association analyses, and as a binary variable for interaction analysis.
- (7)
- First-trimester E-DII excluding supplements: This was a supplementary exposure variable, calculated from dietary sources only. It was used to assess the inflammatory potential inherent to the habitual diet, independent of supplement use, and was also analyzed in tertiles (T1–T3).
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Participants
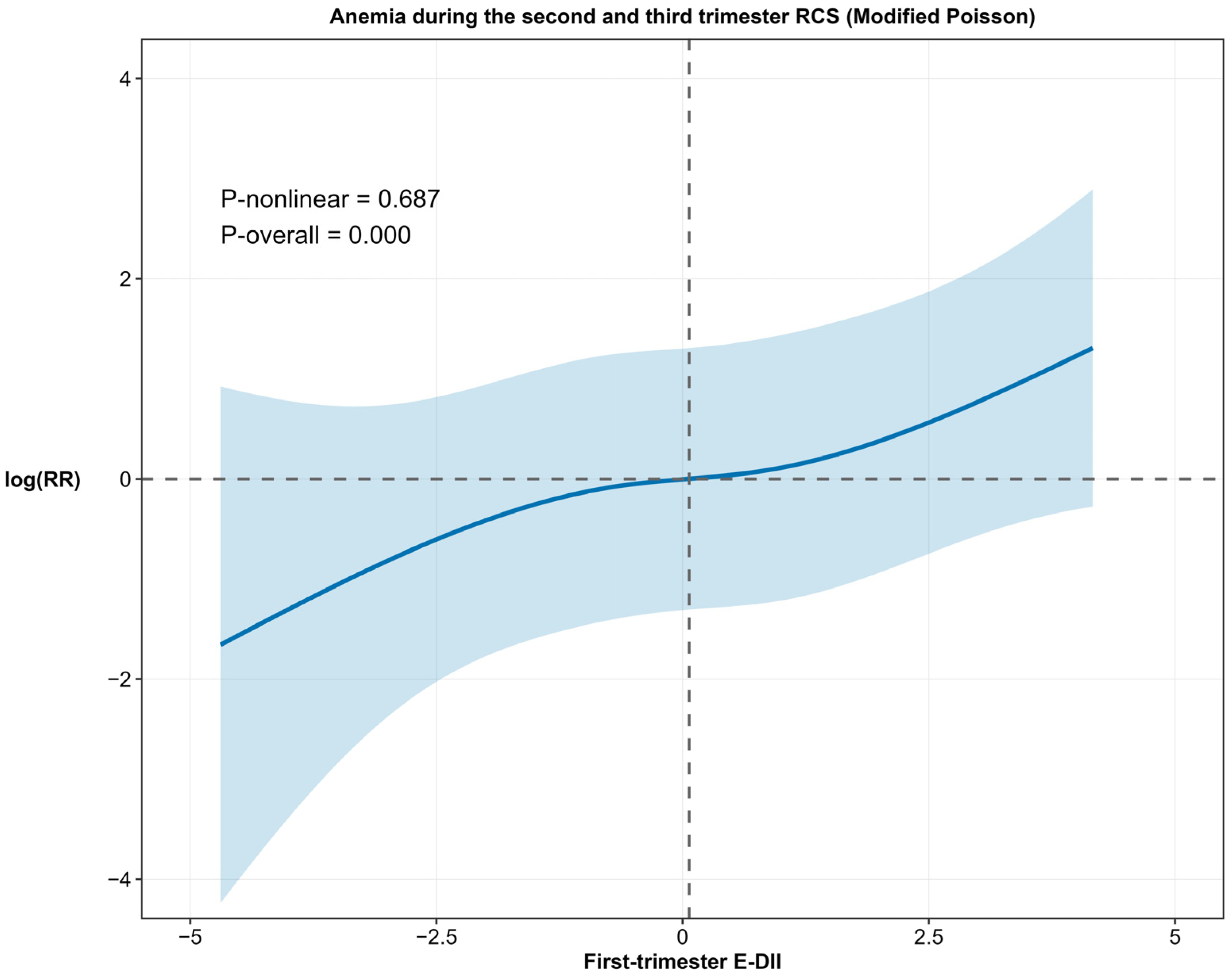
3.2. Relationship Between First-Trimester E-DII and Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters
3.3. Relationship Between Educational Level and Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters
3.4. The Interaction Between First-Trimester E-DII and Educational Level on Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ataide, R.; Fielding, K.; Pasricha, S.R.; Bennett, C. Iron deficiency, pregnancy, and neonatal development. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2023, 162 (Suppl. S2), 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradkar, M.N.; Mejia, I.; Abraheem, R.; Marroquín León, E.; Firdous, A.; Barroso, M.J.; Sampathkumar, D.K.; Morani, Z. Assessing the Impact of Hematological Changes in Pregnancy on Maternal and Fetal Death: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e66982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Ye, W.; Shi, H.; Peng, Y.; Wen, Z.; Narayan, A.; Huang, X.; Chang, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. The Prevalence of Anemia among Pregnant Women in China: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.F.; Liu, H.; Hao, Y.H.; Hu, H.T.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Zou, K.X.; Liu, X.M.; Sheng, J.Z.; Ding, G.L.; Huang, H.F. Association between gestational anemia in different trimesters and neonatal outcomes: A retrospective longitudinal cohort study. World J. Pediatr. 2021, 17, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, S.L.; Schmiegelow, C.; Larsen, L.G.; Nielsen, K.; Msemo, O.A.; Lusingu, J.P.A.; Minja, D.T.R.; Theander, T.G.; Bygbjerg, I.C.; Nyengaard, J.R. Anemia in late pregnancy induces an adaptive response in fetoplacental vascularization. Placenta 2019, 80, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruk, S.; Sanusi, K.O.; Ibrahim, K.G.; Abubakar, B.; Malami, I.; Bello, M.B.; Abubakar, M.B.; Abbas, A.Y.; Imam, M.U. Age and sex-based impacts of maternal iron deficiency on offspring’s cognitive function and anemia: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 78, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansda, R.; Tirkey, S.; Trivedi, K.; Singh, P.; Prakash, J. Study on types of anaemia and foetomaternal outcome in antenatal patients. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 3040–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Takekoshi, H.; Nakano, M. Chlorella pyrenoidosa supplementation reduces the risk of anemia, proteinuria and edema in pregnant women. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Ewald, M. Anemia in pregnancy. Review. Investig. Clin. 1991, 32, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel, E.P.; Yardley, D.A. Clinical and laboratory features and sequelae of deficiency of folic acid (folate) and vitamin B12 (cobalamin) in pregnancy and gynecology. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 14, 1079–1100, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Navais, P.; Salat-Batlle, J.; Cavallé-Busquets, P.; Fernandez-Ballart, J.; Ueland, P.M.; Ballesteros, M.; Ornosa-Martín, G.; Inglès-Puig, M.; Colomina, J.M.; Murphy, M.M. Early pregnancy folate-cobalamin interactions and their effects on cobalamin status and hematologic variables throughout pregnancy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zec, M.; Roje, D.; Matovinović, M.; Antičević, V.; Librenjak Škare, L.; Jerončić, A.; Puljak, L.; Madunić, S.; Meštrović, Z. Vitamin B12 Supplementation in Addition to Folic Acid and Iron Improves Hematological and Biochemical Markers in Pregnancy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abioye, A.I.; Park, S.; Ripp, K.; McDonald, E.A.; Kurtis, J.D.; Wu, H.; Pond-Tor, S.; Sharma, S.; Ernerudh, J.; Baltazar, P.; et al. Anemia of Inflammation during Human Pregnancy Does Not Affect Newborn Iron Endowment. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonewardene, M.; Shehata, M.; Hamad, A. Anaemia in pregnancy. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2012, 26, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hurley, T.G.; Hébert, J.R. Association between the dietary inflammatory index (DII) and telomere length and C-reactive protein from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey-1999–2002. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Hébert, J.R. Designing and developing a literature-derived, population-based dietary inflammatory index. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Wirth, M.D.; Hussey, J.R.; Hurley, T.G. Perspective: The Dietary Inflammatory Index (DII)-Lessons Learned, Improvements Made, and Future Directions. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Quan, L. Association between dietary inflammatory index and energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index and constipation in US adults. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024, 24, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanser, L.; Fuchs, D.; Kurz, K.; Weiss, G. Physiology and Inflammation Driven Pathophysiology of Iron Homeostasis-Mechanistic Insights into Anemia of Inflammation and Its Treatment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Guillet, R.; Cooper, E.M.; Westerman, M.; Orlando, M.; Pressman, E.; O’Brien, K.O. Maternal inflammation at delivery affects assessment of maternal iron status. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geta, T.G.; Gebremedhin, S.; Omigbodun, A.O. Prevalence and predictors of anemia among pregnant women in Ethiopia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Scott, S.; Avula, R.; Tran, L.M.; Menon, P. Trends and drivers of change in the prevalence of anaemia among 1 million women and children in India, 2006 to 2016. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e001010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaj, M.; Henson, C.A.; Aronsson, A.; Aravkin, A.; Beck, K.; Degail, C.; Donadello, L.; Eikemo, K.; Friedman, J.; Giouleka, A.; et al. Effects of education on adult mortality: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2024, 9, e155–e165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.E.; Lo, J.O.; Caughey, A.B. Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia During Pregnancy-Opportunities to Optimize Perinatal Health and Health Equity. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2429151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Pelikan, J.; Slonska, Z.; Brand, H. Health literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmon, N.; Drewnowski, A. Does social class predict diet quality? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, M.L.; Chantaprasopsuk, S.; Islami, F.; Rees-Punia, E.; Um, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Leach, C.R.; Sullivan, K.R.; Patel, A.V. Association of Socioeconomic and Geographic Factors With Diet Quality in US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2216406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, L.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Allès, B.; Touvier, M.; Srour, B.; Hercberg, S.; Buscail, C.; Julia, C. Association Between Ultraprocessed Food Consumption and Risk of Mortality Among Middle-aged Adults in France. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canny, S.P.; Orozco, S.L.; Thulin, N.K.; Hamerman, J.A. Immune Mechanisms in Inflammatory Anemia. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megli, C.J.; Coyne, C.B. Infections at the maternal-fetal interface: An overview of pathogenesis and defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. In Guideline on Haemoglobin Cutoffs to Define Anaemia in Individuals and Populations; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollayeva, T.; Thurairajah, P.; Burton, K.; Mollayeva, S.; Shapiro, C.M.; Colantonio, A. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index as a screening tool for sleep dysfunction in clinical and non-clinical samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2016, 25, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Holden, J.M.; Sagovsky, R. Detection of postnatal depression. Development of the 10-item Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale. Br. J. Psychiatry 1987, 150, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.I. Predictive validity of the Edinburgh postnatal depression scale and other tools for screening depression in pregnant and postpartum women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2023, 307, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Qiu, X.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, M.; Yi, N.; Xiong, G.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Hao, L.; et al. Reproducibility and relative validity of a semi-quantitative food frequency questionnaire for Chinese pregnant women. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Marcos, A.; Diaz, L.E.; Gomez, S.; Nova, E.; Michels, N.; Arouca, A.; González-Gil, E.; Frederic, G.; et al. Association between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the HELENA study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivappa, N.; Steck, S.E.; Hurley, T.G.; Hussey, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Ockene, I.S.; Tabung, F.; Hébert, J.R. A population-based dietary inflammatory index predicts levels of C-reactive protein in the Seasonal Variation of Blood Cholesterol Study (SEASONS). Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, D.; He, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, J. Dietary inflammatory index, and depression and mortality risk associations in U.S. adults, with a special focus on cancer survivors. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1034323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurig, A.C.; Thorand, B.; Fischer, B.; Heier, M.; Koenig, W. Association between the intake of vitamins and trace elements from supplements and C-reactive protein: Results of the MONICA/KORA Augsburg study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, L.C.; Bandera, E.V.; Qin, B.; Guertin, K.A.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Abbott, S.E.; Alberg, A.J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.; Bondy, M.; et al. Dietary inflammatory index and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in African American women. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhong, Z.; Xia, F.; He, J.; Ma, Y.; Liu, C.; Tan, H.; et al. Association Between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Depression in Mid-Pregnancy: Mediating Effect of Sleep Quality. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, H.; Askari, M.J.; Rouhani, H.; Nikbakht, M.H.; Shirban, F.; Bagherniya, M.; Askari, G. The Associate between Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Periodontal Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2024, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, M.; Liu, F.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, L. Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index Is Associated With 5-Year All Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality Among Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 899004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary inflammatory index and mental health: A cross-sectional analysis of the relationship with depressive symptoms, anxiety and well-being in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karataş, E.; Taştekin, F.; Yargucu Zihni, F.; Barutçuoğlu, B.; Karabulut, G. Association of the energy-adjusted dietary inflammatory index and Sjögren’s syndrome: A cross-sectional study. Br. J. Nutr. 2025, 133, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDiarmid, K.P.; Wood, L.G.; Upham, J.W.; MacDonald-Wicks, L.K.; Shivappa, N.; Hebert, J.R.; Scott, H.A. The Impact of Meal Dietary Inflammatory Index on Exercise-Induced Changes in Airway Inflammation in Adults with Asthma. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrampour, H.; Heaman, M. Advanced maternal age and the risk of cesarean birth: A systematic review. Birth 2010, 37, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, F.C. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, N.; Li, J.; Jiang, H. Research Progress of Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale in Screening of Perinatal Depression. Chin. J. Mod. Nurs. 2021, 27, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Hosseinikia, M.; Ghaffarian-Bahraman, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Davies, I.G.; Yousefi Rad, E.; Saboori, S. Dietary inflammatory index and elevated serum C-reactive protein: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 5786–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.M.; Shivappa, N.; Hébert, J.R.; Perry, I.J. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Biomarkers of Lipoprotein Metabolism, Inflammation and Glucose Homeostasis in Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viatte, L.; Vaulont, S. Hepcidin, the iron watcher. Biochimie 2009, 91, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, I.; Lo, E.; Ward, D.M.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin-induced internalization of ferroportin requires binding and cooperative interaction with Jak2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3800–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.B.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004, 306, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.; Zhong, Z.; Ma, Y.; Huang, X.; Xia, F.; Tan, H.; Deng, J.; Chen, M. First-Second-Trimester Dietary Inflammatory Index and Anemia Risk in the Third Trimester: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, I.; Sakane, N.; Suganuma, A.; Nagai, N. Association of a pro-inflammatory diet and gestational diabetes mellitus with maternal anemia and hemoglobin levels during pregnancy: A prospective observational case-control study. Nutr. Res. 2023, 115, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Di, J.; Yin, L.; Huang, A.; Zhao, W.; Hu, H.; Chen, S. Prevalence and influencing factors of anemia among pregnant women across first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy in monitoring areas, from 2016 to 2020: A population-based multi-center cohort study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas-Costa, N.C.; Carrilho, T.R.B.; Normando da Costa, P.; Constante, H.M.; Fujimori, E.; Sayuri Sato, A.P.; Kac, G. Hemoglobin Concentrations and Prevalence of Anemia During Pregnancy: Results from the Brazilian Maternal and Child Nutrition Consortium. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2025, 9, 107458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczmarski, M.F.; Adams, E.L.; Cotugna, N.; Pohlig, R.T.; Beydoun, M.A.; Zonderman, A.B.; Evans, M.K. Health Literacy and Education Predict Nutrient Quality of Diet of Socioeconomically Diverse, Urban Adults. J. Epidemiol. Prev. Med. 2016, 2, 13000115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Owais, A.; Goyena, E.A.; Merritt, C.E.; Lee, C.; Rattan, P.; Maniego, M.L.V.; Arias, F.P.S.; Azaña, G.P.; Desnacido, J.P.; et al. Drivers of anemia reduction among women of reproductive age in the Philippines: A country case study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 121 (Suppl. S1), S57–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Second- and Third-Trimester Non-Anemia Group (n = 480) | Second- and Third-Trimester Anemia Group (n = 82) | Overall (n = 562) | Statistical Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.006 | 0.938 | |||
| <35 | 420 (87.50) | 72 (87.80) | 492 (87.54) | ||
| ≥35 | 60 (12.50) | 10 (12.20) | 70 (12.46) | ||
| Ethnicity | 1.400 | 0.237 | |||
| Han ethnic group | 457 (95.21) | 81 (98.78) | 538 (95.73) | ||
| Other | 23 (4.79) | 1 (1.22) | 24 (4.27) | ||
| Pre-pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 20.84 ± 2.70 | 20.26 ± 2.25 | 20.75 ± 2.65 | 1.822 | 0.069 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI group | 4.846 | 0.089 | |||
| <18.5 | 93 (19.38) | 16 (19.51) | 109 (19.40) | ||
| 18.5–24.0 | 323 (67.29) | 62 (75.61) | 385 (68.50) | ||
| ≥24.0 | 64 (13.33) | 4 (4.88) | 68 (12.10) | ||
| Educational level | 13.350 | <0.001 *** | |||
| Bachelor’s degree and above | 353 (73.54) | 44 (53.66) | 397 (70.64) | ||
| Below bachelor’s degree | 127 (26.46) | 38 (46.34) | 165 (29.36) | ||
| Employment | 0.006 | 0.938 | |||
| Unemployed | 60 (12.50) | 10 (12.20) | 70 (12.46) | ||
| Employed | 420 (87.50) | 72 (87.80) | 492 (87.54) | ||
| Monthly household income (RMB) | 1.469 | 0.226 | |||
| ≤10,000 | 276 (57.50) | 53 (64.63) | 329 (58.54) | ||
| >10,000 | 204 (42.50) | 29 (35.37) | 233 (41.46) | ||
| Health insurance status | 0.067 | 0.796 | |||
| Uninsured | 33 (6.88) | 5 (6.10) | 38 (6.76) | ||
| Insured | 447 (93.12) | 77 (93.90) | 524 (93.24) | ||
| History of adverse pregnancy outcomes | 1.152 | 0.283 | |||
| No | 280 (58.33) | 53 (64.63) | 333 (59.25) | ||
| Yes | 200 (41.67) | 29 (35.37) | 229 (40.75) | ||
| Gravidity | 0.146 | 0.929 | |||
| 1 | 206 (42.92) | 37 (45.12) | 243 (43.24) | ||
| 2 | 142 (29.58) | 23 (28.05) | 165 (29.36) | ||
| ≥3 | 132 (27.50) | 22 (26.83) | 154 (27.40) | ||
| Parity | 0.007 | 0.934 | |||
| 0 | 295 (61.46) | 50 (60.98) | 345 (61.39) | ||
| ≥1 | 185 (38.54) | 32 (39.02) | 217 (38.61) | ||
| Baseline serum iron (mmol/L) | 8.75 ± 0.85 | 8.69 ± 0.82 | 8.74 ± 0.85 | 0.573 | 0.567 |
| Iron supplementation | 2.016 | 0.156 | |||
| Yes | 204 (42.5) | 28 (34.15) | 232 (41.28) | ||
| No | 276 (57.5) | 54 (65.85) | 330 (58.72) | ||
| Folic acid supplementation | 3.011 | 0.083 | |||
| Yes | 452 (94.17) | 73 (89.02) | 525 (93.42) | ||
| No | 28 (5.83) | 9 (10.98) | 37 (6.58) | ||
| Vitamin B12 supplementation | 2.943 | 0.086 | |||
| Yes | 182 (37.92) | 23 (28.05) | 205 (36.48) | ||
| No | 298 (62.08) | 59 (71.95) | 357 (63.52) | ||
| Vomiting(days) | 2.570 | 0.109 | |||
| <30 | 245 (51.04) | 34 (41.46) | 279 (49.64) | ||
| ≥30 | 235 (48.96) | 48 (58.54) | 283 (50.36) | ||
| Menstrual blood loss (ml) | 1.867 | 0.393 | |||
| <30 | 32 (6.67) | 3 (3.66) | 35 (6.23) | ||
| 30–80 | 434 (90.42) | 75 (91.46) | 509 (90.57) | ||
| >80 | 14 (2.91) | 4 (4.88) | 18 (3.2) | ||
| Pre-pregnancy regular physical activity | 0.389 | 0.533 | |||
| No | 347 (72.29) | 62 (75.61) | 409 (72.78) | ||
| Yes | 133 (27.71) | 20 (24.39) | 153 (27.22) | ||
| Pre-pregnancy smoking history | 0.008 | 0.928 | |||
| No | 470 (97.92) | 81 (98.78) | 551 (98.04) | ||
| Yes | 10 (2.08) | 1 (1.22) | 11 (1.96) | ||
| Pre-pregnancy alcohol consumption | <0.001 | 1.000 | |||
| No | 468 (97.50) | 80 (97.56) | 548 (97.51) | ||
| Yes | 12 (2.50) | 2 (2.44) | 14 (2.49) | ||
| Secondhand smoke exposure | 2.196 | 0.138 | |||
| No | 382 (79.58) | 71 (86.59) | 453 (80.6) | ||
| Yes | 98 (20.42) | 11 (13.41) | 109 (19.4) | ||
| Sleep quality (PSQI score classification) | 0.442 | 0.802 | |||
| Very good | 97 (20.21) | 15 (18.29) | 112 (19.93) | ||
| Good | 275 (57.29) | 46 (56.10) | 321 (57.12) | ||
| Poor | 108 (22.50) | 21 (25.61) | 129 (22.95) | ||
| Depression (EPDS score classification) | 0.015 | 0.901 | |||
| No | 418 (87.08) | 71 (86.59) | 489 (87.01) | ||
| Yes | 62 (12.92) | 11 (13.41) | 73 (12.99) | ||
| First-trimester E-DII score | 0.00 (2.36) | 0.74 (2.49) | 0.07 (2.33) | 24,452 | <0.001 *** |
| First-trimester E-DII (groups) | 11.806 | 0.003 ** | |||
| T1 (≤−0.68) | 171 (35.63) | 17 (20.73) | 188 (33.46) | ||
| T2 (−0.68~0.81) | 162 (33.75) | 25 (30.49) | 187 (33.27) | ||
| T3 (≥ 0.81) | 147 (30.62) | 40 (48.78) | 187 (33.27) | ||
| First-trimester E-DII excluding supplements | 0.06 (2.16) | 0.26 (2.22) | 0.10 (2.17) | 21473 | 0.187 |
| First-trimester E-DII excluding supplements (groups) | 1.281 | 0.527 | |||
| T1 (≤−0.64) | 165 (34.38) | 23 (28.05) | 188 (33.46) | ||
| T2 (−0.64~0.87) | 158 (32.92) | 29 (35.37) | 187 (33.27) | ||
| T3 (≥0.87) | 157 (32.70) | 30 (36.58) | 187 (33.27) |
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95%CI) | p Value | RR (95%CI) | p Value | |
| First-trimester E-DII score | 1.25 (1.11, 1.41) | <0.001 *** | 1.27 (1.13, 1.42) | <0.001 *** |
| First-trimester E-DII (groups) | ||||
| T1 (≤−0.68) | 1 (Ref.) | - | 1 (Ref.) | - |
| T2 (−0.68~0.81) | 1.48 (0.83, 2.65) | 0.188 | 1.45 (0.80, 2.66) | 0.223 |
| T3 (≥0.81) | 2.37 (1.39, 4.02) | 0.001 ** | 2.30 (1.36, 3.90) | 0.002 ** |
| Variable | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RR (95%CI) | p Value | RR (95%CI) | p Value | |
| Educational level | ||||
| Bachelor’s degree and above | 1 (Ref.) | - | 1 (Ref.) | - |
| Below bachelor’s degree | 2.08 (1.40, 3.08) | <0.001 *** | 2.27 (1.52, 3.39) | <0.001 *** |
| Variable | Educational Level | RERI a | AP a | SI a | Multiplicative Scale a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bachelor’s Degree and Above | Below Bachelor’s Degree | Effect of Below Bachelor’s Degree Within the Strata of E-DII | |||||
| First-trimester E-DII (groups) | 4.64 (1.51, 11.34) * | 0.68 (0.26, 0.86) *** | 4.91 (1.16, 20.69) * | 2.69 (0.93, 7.78) | |||
| anti-inflammatory (≤0.07) | 1 (Ref.) | 1.63 (0.70, 3.80) | 1.63 (0.70, 3.80) | ||||
| pro-inflammatory (>0.07) | 1.56 (0.81, 3.00) | 6.83 (3.27, 14.26) *** | 4.39 (2.24, 8.61) *** | ||||
| Effect of pro-inflammatory within the strata of educational level | 1.56 (0.81, 3.00) | 4.19 (1.83, 9.56) *** | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, F.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; He, J.; Tan, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Deng, J. Interaction Between First-Trimester Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Educational Level on the Risk of Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203241
Xia F, Huang C, Zhang Z, He J, Tan H, Wang T, Chen L, Chen M, Deng J. Interaction Between First-Trimester Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Educational Level on the Risk of Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203241
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Fan, Cong Huang, Zhitan Zhang, Junwei He, Hongzhuan Tan, Tingting Wang, Lizhang Chen, Mengshi Chen, and Jing Deng. 2025. "Interaction Between First-Trimester Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Educational Level on the Risk of Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters: A Prospective Cohort Study" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203241
APA StyleXia, F., Huang, C., Zhang, Z., He, J., Tan, H., Wang, T., Chen, L., Chen, M., & Deng, J. (2025). Interaction Between First-Trimester Energy-Adjusted Dietary Inflammatory Index and Educational Level on the Risk of Anemia During the Second and Third Trimesters: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients, 17(20), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203241






