Isorhamnetin Exhibits Hypoglycemic Activity and Targets PI3K/AKT and COX-2 Pathways in Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical and Histological Analyses
2.4. Untargeted Metabolomics
2.5. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Cell-Based Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Prespecified Endpoints and Dose Rationale
3. Results
3.1. ISO Improves Glycemic Control, Lipid Profile, and Islet Integrity in T1DM Mice
3.2. ISO Modulates Metabolic Profiles and Key Pathways in T1DM
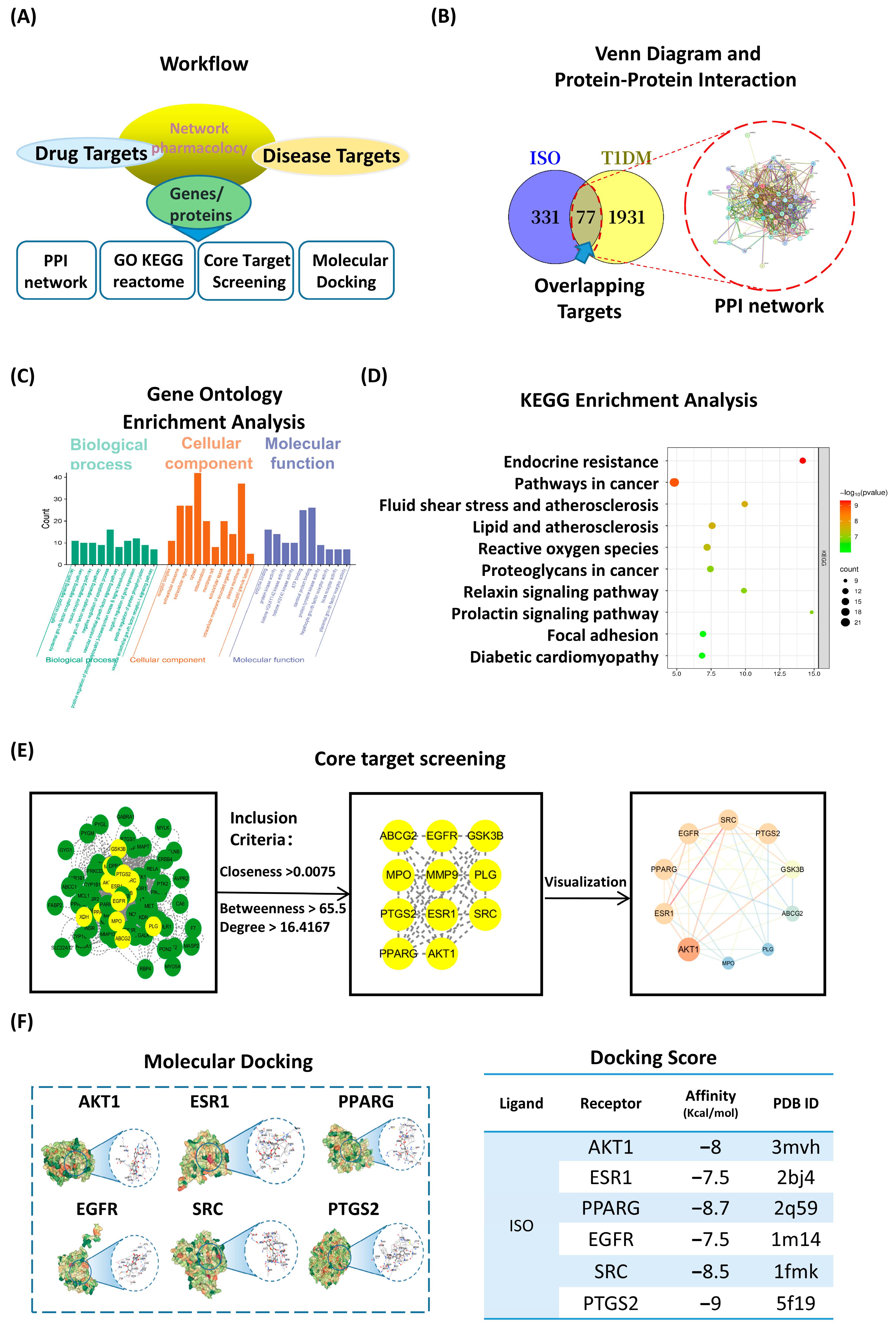
3.3. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Highlight PI3K/AKT as a Central ISO Target
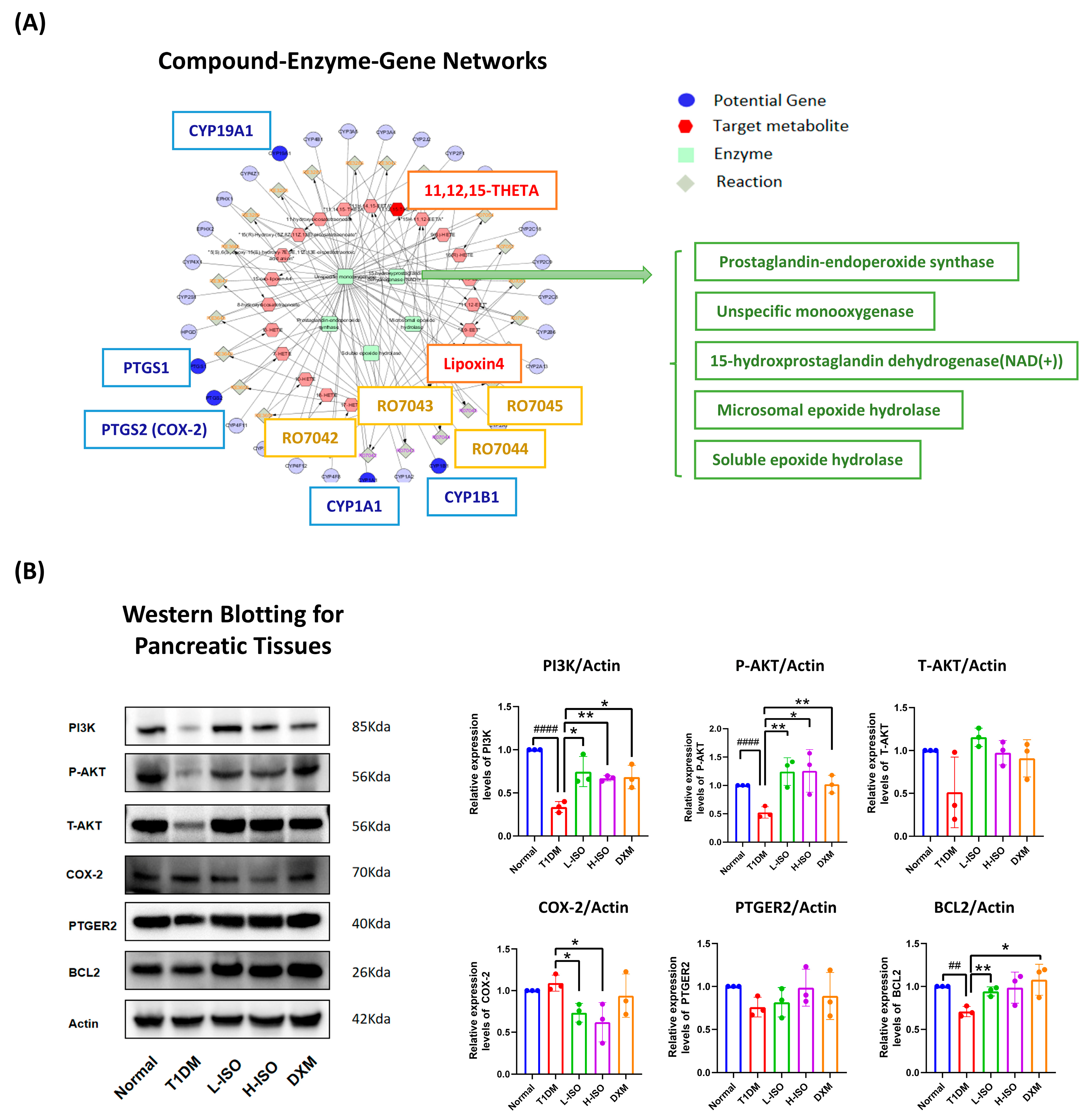
3.4. ISO Coordinates Gene–Metabolite Networks to Regulate Inflammation and Cell Survival
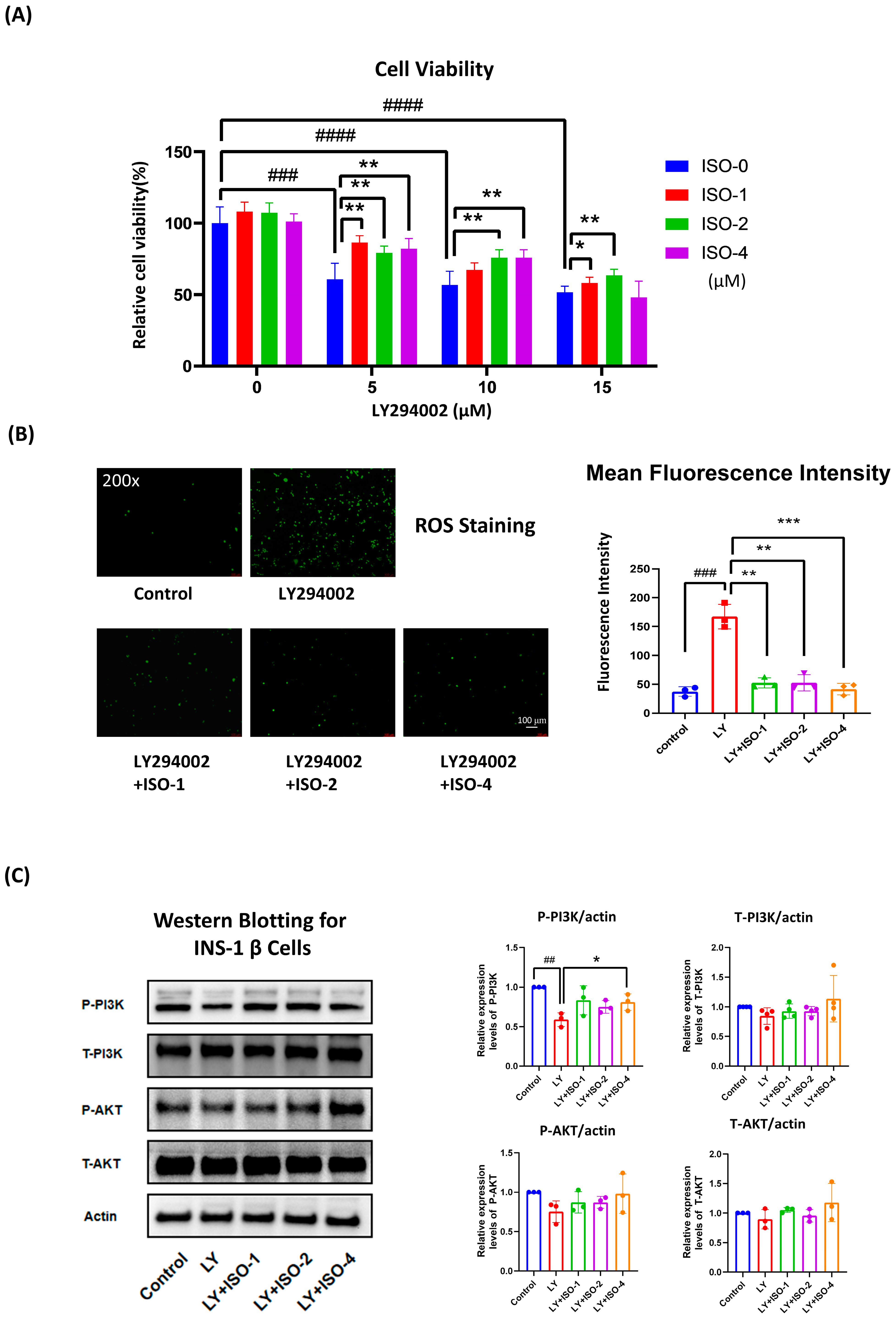
3.5. ISO Protects INS-1 β Cells from LY294002-Induced Dysfunction by Enhancing Viability, Reducing ROS, and Supporting PI3K/AKT Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| CV-ANOVA | cross-validation analysis of variance |
| DCFH-DA | 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| DXM | dexamethasone |
| EP | E-prostanoid (prostaglandin E2 receptor) |
| ESI | electrospray ionization |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GSK-3β | glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta |
| HDL-C | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1 |
| ISO | isorhamnetin |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| LC–MS | liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| LDL-C | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| OPLS-DA | orthogonal partial least squares–discriminant analysis |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PGE2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| PTGER2 | prostaglandin E receptor 2 (EP2) |
| QC-RSD | quality-control relative standard deviation |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| STZ | streptozotocin |
| T1DM | type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| UPLC | ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Ogle, G.D.; Wang, F.; Haynes, A.; Gregory, G.A.; King, T.W.; Deng, K.; Dabelea, D.; James, S.; Jenkins, A.J.; Li, X.; et al. Global Type 1 Diabetes Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality Estimates 2025: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Atlas, 11th Edition, and the T1D Index Version 3.0. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2025, 225, 112277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhou, S.; Luan, X.; Zhang, H. Isorhamnetin: A Review of Pharmacological Effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Taveira, M.; Pereira, D.M.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) Seeds: New Flavonols and Cytotoxic Effect. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2854–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Croft, K.D.; Ashida, H. Quercetin and Its Metabolite Isorhamnetin Promote Glucose Uptake through Different Signalling Pathways in Myotubes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Zha, Y.; Zang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y. Isorhamnetin Improves Diabetes-Induced Erectile Dysfunction in Rats through Activation of the PI3K/AKT/eNOS Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Shin, B.Y.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, M.G.; Wi, J.E.; Kim, Y.W.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C.; Shin, S.M.; Ki, S.H. Isorhamnetin Protects against Oxidative Stress by Activating Nrf2 and Inducing the Expression of Its Target Genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 274, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, S.C.; Ku, S.K.; Ki, S.H.; Shin, S.M. The Antioxidant Effects of Isorhamnetin Contribute to Inhibit COX-2 Expression in Response to Inflammation: A Potential Role of HO-1. Inflammation 2014, 37, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqudah, A.; Qnais, E.Y.; Wedyan, M.A.; Altaber, S.; Bseiso, Y.; Oqal, M.; AbuDalo, R.; Alrosan, K.; Alrosan, A.Z.; Bani Melhim, S.; et al. Isorhamnetin Reduces Glucose Level, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin Diabetic Mice Model. Molecules 2023, 28, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yang, J.; Bao, C.; Lu, F.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Lv, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, N.; et al. Isorhamnetin: What Is the In Vitro Evidence for Its Antitumor Potential and Beyond? Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1309178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camaya, I.; Donnelly, S.; O’Brien, B. Targeting the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic β-Cells to Enhance Their Survival and Function: An Emerging Therapeutic Strategy for Type 1 Diabetes. J. Diabetes 2022, 14, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Wang, M.-H. Eicosanoids, β-Cell Function, and Diabetes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, R.L.; Gill, N.S.; Pugh, W.; Lee, J.P.; Koeberlein, B.; Furth, E.E.; Polonsky, K.S.; Naji, A.; Birnbaum, M.J. Regulation of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Growth and Survival by the Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase Akt1/PKBα. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Wen, W.; Stahlhut, S.; Welling, C.M.; Permutt, M.A. Islet β-Cell Expression of Constitutively Active Akt1/PKBα Induces Striking Hypertrophy, Hyperplasia, and Hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, K.; Ueki, K.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Okamoto, M.; Awazawa, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Ohsugi, M.; Inabe, K.; Umehara, T.; et al. Class IA Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in Pancreatic β Cells Controls Insulin Secretion by Multiple Mechanisms. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Ohsugi, M.; Permutt, M.A. Glucose Promotes Pancreatic Islet β-Cell Survival through a PI 3-Kinase/Akt-Signaling Pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 283, E784–E793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalai, F.Z.; Boulaaba, M.; Ferdousi, F.; Isoda, H. Effects of Isorhamnetin on Diabetes and Its Associated Complications: A Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and a Post Hoc Transcriptome Analysis of Involved Molecular Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zheng, W.; Song, C.; Zhou, H.; Yao, J. Protective Effects of Food-Derived Kaempferol on Pancreatic β-Cells in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Foods 2024, 13, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimple, M.E.; Keller, M.P.; Rabaglia, M.R.; Pasker, R.L.; Neuman, J.C.; Truchan, N.A.; Brar, H.K.; Attie, A.D. Prostaglandin E2 Receptor, EP3, Is Induced in Diabetic Islets and Negatively Regulates Glucose- and Hormone-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carboneau, B.A.; Allan, J.A.; Townsend, S.E.; Kimple, M.E.; Breyer, R.M.; Gannon, M. Opposing Effects of Prostaglandin E2 Receptors EP3 and EP4 on Mouse and Human β-Cell Survival and Proliferation. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shridas, P.; Zahoor, L.; Forrest, K.J.; Layne, J.D.; Webb, N.R. Group X Secretory Phospholipase A2 Regulates Insulin Secretion through a Cyclooxygenase-2-Dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27410–27417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchan, N.A.; Fenske, R.J.; Sandhu, H.K.; Weeks, A.M.; Patibandla, C.; Wancewicz, B.; Pabich, S.; Reuter, A.; Harrington, J.M.; Brill, A.L.; et al. Human Islet Expression Levels of Prostaglandin E2 Synthetic Enzymes, But Not Prostaglandin EP3 Receptor, Are Positively Correlated with Markers of β-Cell Function and Mass in Nondiabetic Obesity. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennemann, A.; Gerstner, A.; Kern, N.; Ferreiros Bouzas, N.; Narumiya, S.; Maruyama, T.; Nüsing, R.M. PTGS-2–PTGER2/4 Signaling Pathway Partially Protects from Diabetogenic Toxicity of Streptozotocin in Mice. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui-Kato, M.; Patlada, S.; Yokode, M.; Kamei, K.; Minami, M. EP4 Signalling Is Essential for Controlling Islet Inflammation by Causing a Shift in Macrophage Polarization in Obesity/Type 2 Diabetes. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 2020, 17, 1479164120945675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin Vázquez, E.; Cobo-Vuilleumier, N.; Araujo Legido, R.; Marín-Cañas, S.; Nola, E.; Dorronsoro, A.; López Bermudo, L.; Crespo, A.; Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; García-Fernández, M.; et al. NR5A2/LRH-1 Regulates the PTGS2–PGE2–PTGER1 Pathway Contributing to Pancreatic Islet Survival and Function. iScience 2022, 25, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, J.C.; Reuter, A.; Carbajal, K.A.; Schaid, M.D.; Kelly, G.; Connors, K.; Kaiser, C.; Krause, J.; Hurley, L.D.; Olvera, A.; et al. The Prostaglandin E2 EP3 Receptor Has Disparate Effects on Islet Insulin Secretion and Content in β-Cells in a High-Fat Diet–Induced Mouse Model of Obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E567–E576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagishita, Y.; Fukutomi, T.; Sugawara, A.; Kawamura, H.; Takahashi, T.; Pi, J.; Uruno, A.; Yamamoto, M. Nrf2 Protects Pancreatic β-Cells from Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress in Diabetic Model Mice. Diabetes 2014, 63, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumel-Alterzon, S.; Katz, L.S.; Brill, G.; Jean-Pierre, C.; Li, Y.; Tse, I.; Biswal, S.; Garcia-Ocaña, A.; Scott, D.K. Nrf2 Regulates β-Cell Mass by Suppressing β-Cell Death and Promoting β-Cell Proliferation. Diabetes 2022, 71, 989–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. GSK-3β Acts Upstream of Fyn Kinase in Regulation of Nuclear Export and Degradation of NF-E2–Related Factor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16502–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lei, S.; Dong, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, B.; Tan, L.; Wu, J.; Yu, S.; et al. GSK-3β Downregulates Nrf2 in Cultured Cortical Neurons and in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Tang, S.; Wan, F.; Zhong, R.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. The PI3K/Akt–Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Mitophagy Synergistically Mediate Hydroxytyrosol to Alleviate Intestinal Oxidative Damage. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 4258–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé-Ubieto, R.; Estévez-Vázquez, O.; Ramadori, P.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Guidelines and Considerations for Metabolic Tolerance Tests in Mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, L.; Ehrlich, A.; Iversen, J.; Ashcroft, S.P.; Trošt, K.; Moritz, T.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Treebak, J.T.; Zierath, J.R.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Oral and Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Tests in Mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rijjal, D.; Wheeler, M.B. A Protocol for Studying Glucose Homeostasis and Islet Function in Mice. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, C. Botanical Flavonoids: Efficacy, Absorption, Metabolism and Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology for Improving Bioavailability. Molecules 2025, 30, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Description | ESI Mode | m/z | Retention Time (min) | HMDB ID | KEGG ID | PubChem ID | AUC | p Value | Fold Change (log2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porphobilinogen | positive | 227.1048 | 1.28 | HMDB0000245 | C00931 | 1021 | 0.97 | 0.00026 | −2.5903 |
| 20-Carboxy-leukotriene B4 | negative | 365.1983 | 0.92 | HMDB0006059 | C05950 | 5280877 | 0.91 | 0.00138 | 1.2271 |
| Cinnamic acid | positive | 149.0590 | 0.77 | HMDB0000567 | C10438 | 5372954 | 0.91 | 0.00000 | −0.4465 |
| Sphinganine | positive | 302.3061 | 1.80 | HMDB0000269 | C00836 | 91486 | 0.90 | 0.00007 | 0.5605 |
| 6-keto-prostaglandin F1α | positive | 371.2367 | 3.47 | HMDB0002886 | C05961 | 5280888 | 0.89 | 0.00001 | −0.8282 |
| Tetrahydrobiopterin | positive | 242.1202 | 1.45 | HMDB0000027 | C00272 | 44257 | 0.88 | 0.00133 | −2.8345 |
| 3-(Methylthio)-1-propanol | positive | 107.0510 | 1.08 | HMDB0031716 | C08249 | 10448 | 0.86 | 0.00023 | 0.4962 |
| Glycerol 3-phosphate | negative | 171.0070 | 0.80 | HMDB0000126 | C00093 | 439162 | 0.85 | 0.00243 | −0.7937 |
| Citric acid | negative | 191.0201 | 0.75 | HMDB0000094 | C00158 | 311 | 0.85 | 0.00003 | 0.5885 |
| Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate | positive | 248.0350 | 1.13 | HMDB0001491 | C00018 | 1051 | 0.85 | 0.00007 | −0.9147 |
| 15-Deoxy-d-12,14-PGJ2 | positive | 317.2095 | 3.24 | HMDB0005079 | C14717 | 5311211 | 0.84 | 0.00001 | −2.1549 |
| PE(20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)/18:0) | negative | 766.5385 | 4.30 | HMDB0009387 | C00350 | 52924644 | 0.84 | 0.00154 | −0.3945 |
| Uric acid | negative | 167.0216 | 0.73 | HMDB0000289 | C00366 | 1175 | 0.83 | 0.00010 | −0.6480 |
| N6,N6,N6-Trimethyl-L-lysine | positive | 189.1610 | 1.00 | HMDB0001325 | C03793 | 440120 | 0.81 | 0.00027 | 0.9815 |
| Suberic acid | negative | 173.0829 | 0.22 | HMDB0000893 | C08278 | 10457 | 0.81 | 0.00041 | −0.7202 |
| Retinoyl β-glucuronide | positive | 477.2401 | 0.84 | HMDB0003141 | C11061 | 5281877 | 0.81 | 0.00035 | −0.8292 |
| 12,13-DiHOME | negative | 313.2374 | 1.25 | HMDB0004705 | C14829 | 25320870 | 0.80 | 0.00025 | 0.64733 |
| Pathway Name | p Value | FDR | Pathway Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling | 8.22 × 10−14 | 7.88 × 10−11 | R-HSA-6785807 |
| Negative regulation of the PI3K/AKT network | 7.45 × 10−13 | 3.57 × 10−10 | R-HSA-199418 |
| PI3K/AKT Signaling in Cancer | 3.25 × 10−12 | 1.04 × 10−9 | R-HSA-2219528 |
| PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling | 5.30 × 10−12 | 1.27 × 10−9 | R-HSA-6811558 |
| Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling | 6.66 × 10−12 | 1.27 × 10−9 | R-HSA-9009391 |
| Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases | 2.10 × 10−11 | 3.33 × 10−9 | R-HSA-9006934 |
| ESR-mediated signaling | 2.14 × 10−10 | 2.94 × 10−8 | R-HSA-8939211 |
| PIP3 activates AKT signaling | 4.85 × 10−10 | 5.53 × 10−8 | R-HSA-1257604 |
| Intracellular signaling by second messengers | 5.21 × 10−10 | 5.53 × 10−8 | R-HSA-9006925 |
| Constitutive Signaling by Aberrant PI3K in Cancer | 7.75 × 10−10 | 7.36 × 10−8 | R-HSA-2219530 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Yao, J. Isorhamnetin Exhibits Hypoglycemic Activity and Targets PI3K/AKT and COX-2 Pathways in Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203201
Li L, Li J, Ren J, Yao J. Isorhamnetin Exhibits Hypoglycemic Activity and Targets PI3K/AKT and COX-2 Pathways in Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2025; 17(20):3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203201
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lijia, Jia Li, Jie Ren, and Jengyuan Yao. 2025. "Isorhamnetin Exhibits Hypoglycemic Activity and Targets PI3K/AKT and COX-2 Pathways in Type 1 Diabetes" Nutrients 17, no. 20: 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203201
APA StyleLi, L., Li, J., Ren, J., & Yao, J. (2025). Isorhamnetin Exhibits Hypoglycemic Activity and Targets PI3K/AKT and COX-2 Pathways in Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients, 17(20), 3201. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17203201






