Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rats
2.2. Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance
2.3. Cinnamaldehyde on Glycogen Content in Insulin-Resistant Rats
2.4. Signaling Pathway of Cinnamaldehyde on Glucose Uptake in Insulin-Resistant Rats
2.5. Action of Cinnamaldehyde on 14C-Glucose Uptake in Insulin-Resistant Rats
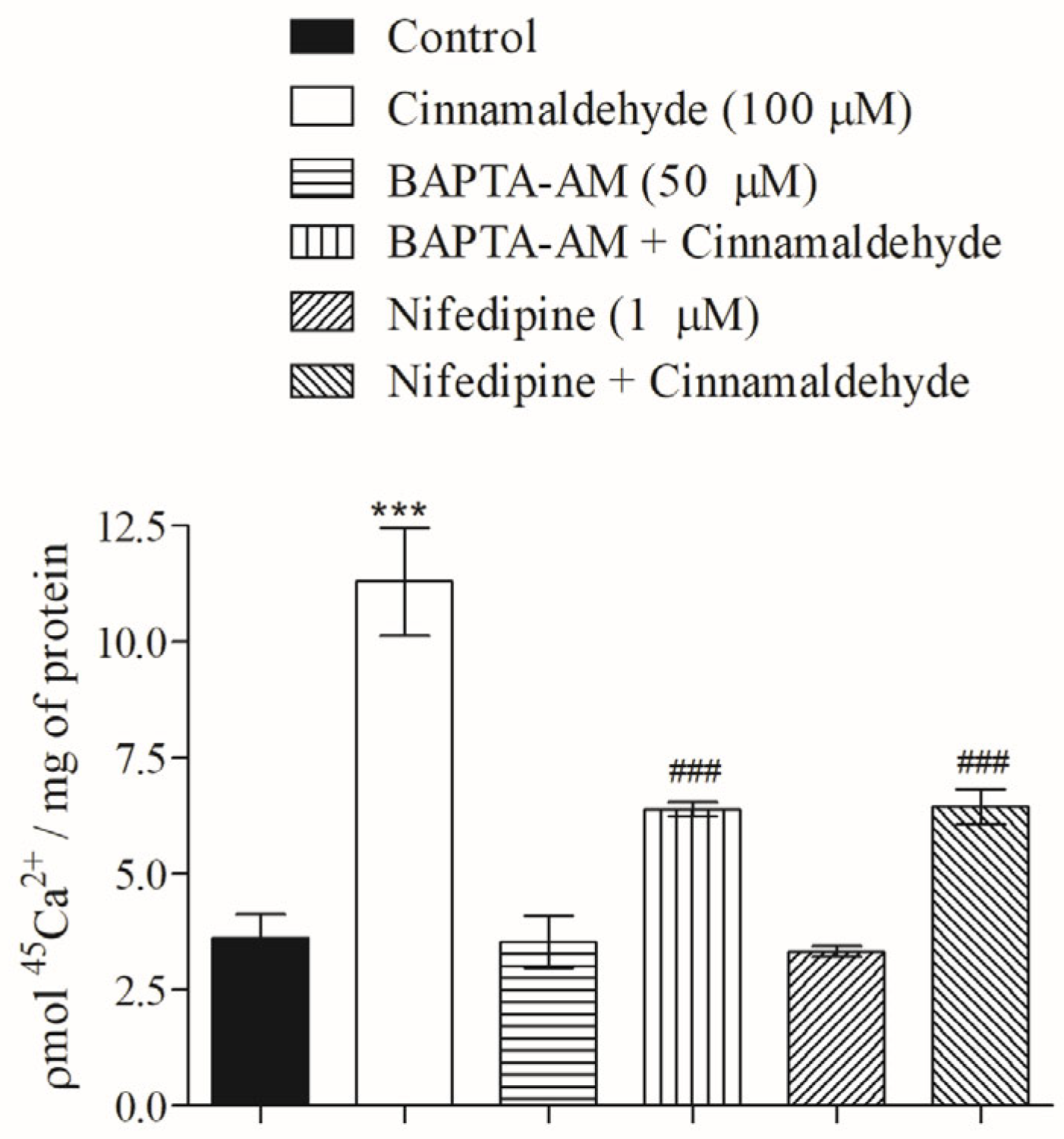
2.6. Role of Cinnamaldehyde on 45Ca2+ Influx
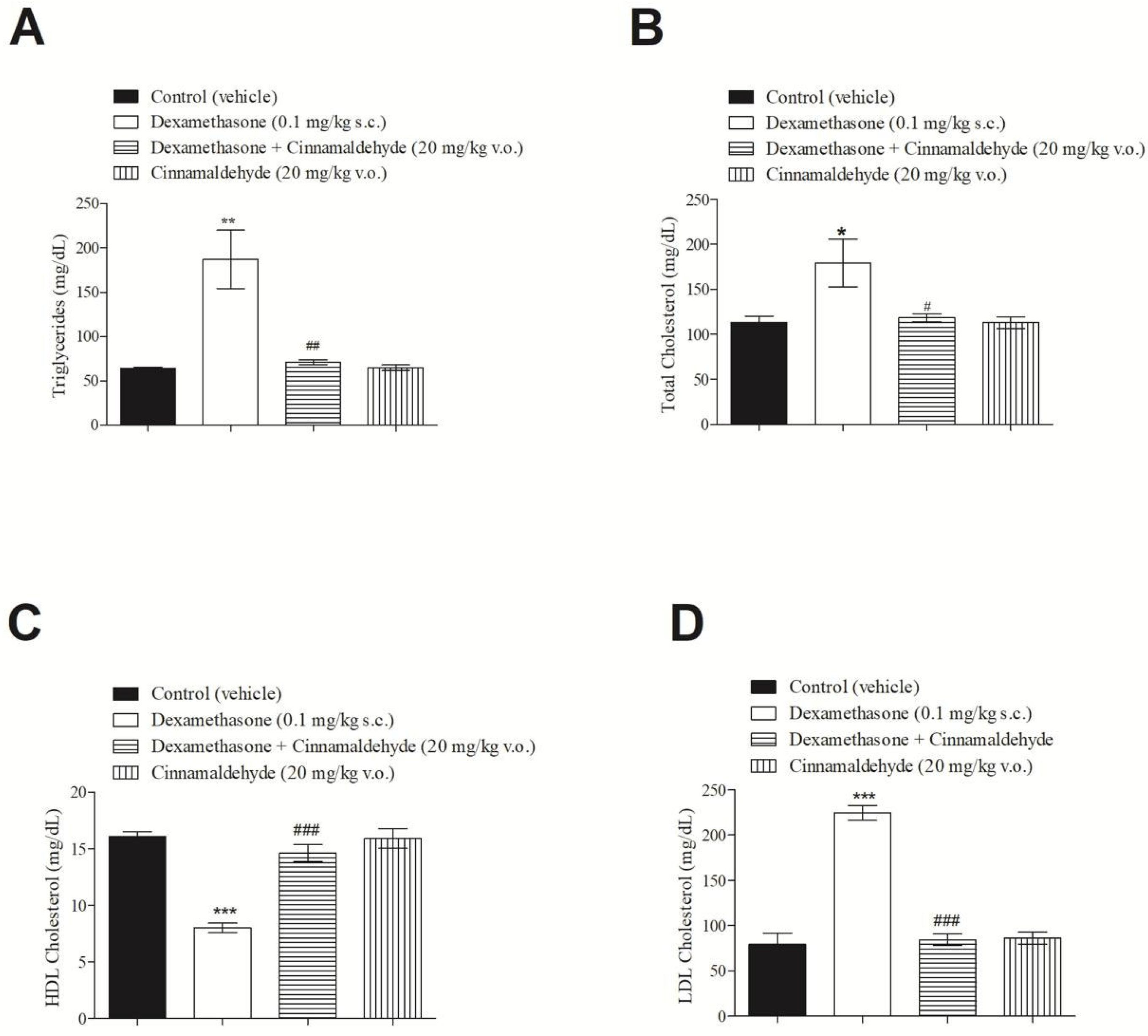
2.7. Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Serum Lipid Profile of Insulin-Resistant Rats
2.8. Role of Cinnamaldehyde on the Oral Triglyceride Tolerance Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
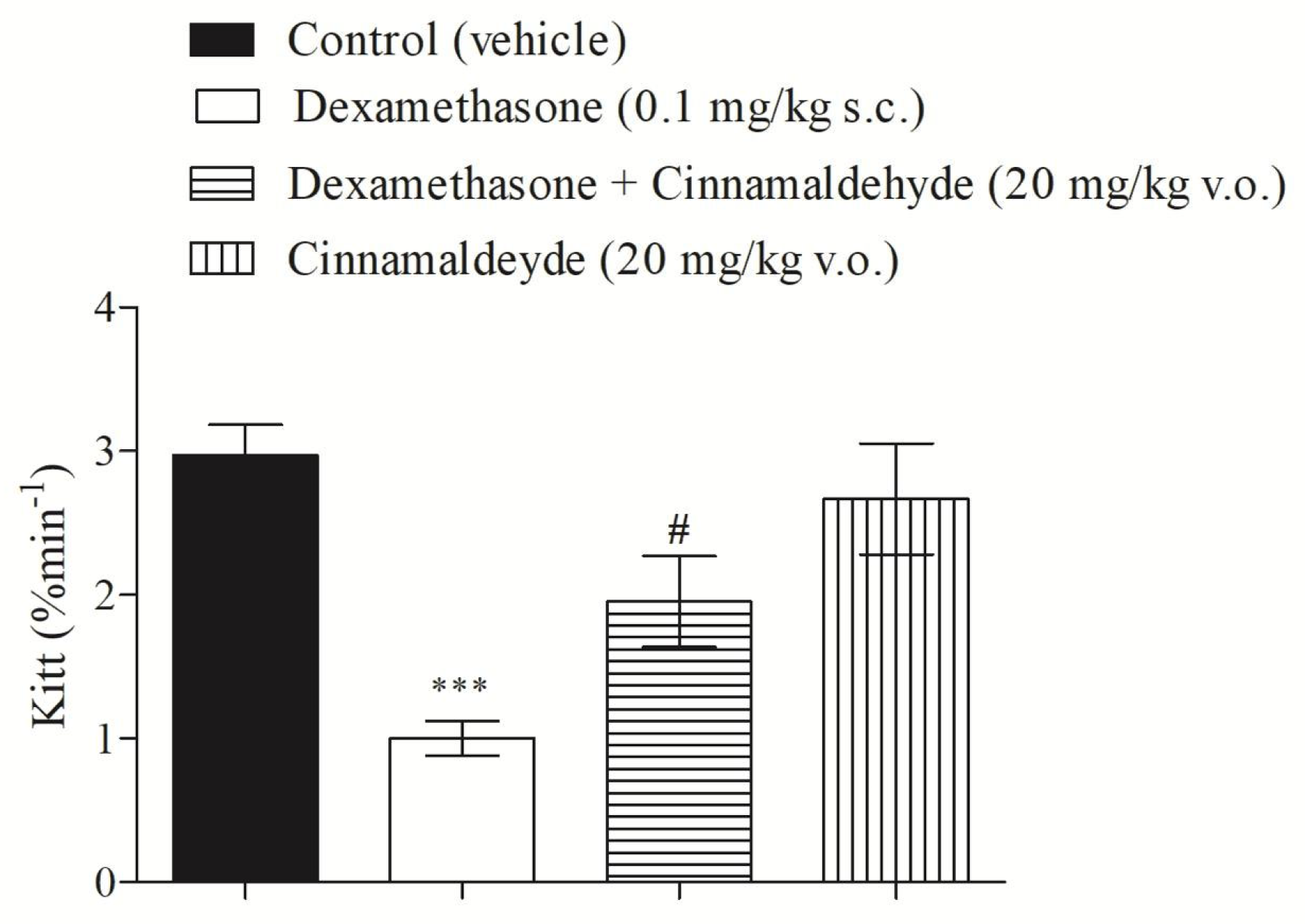
3.1. Cinnamaldehyde and Insulin Tolerance
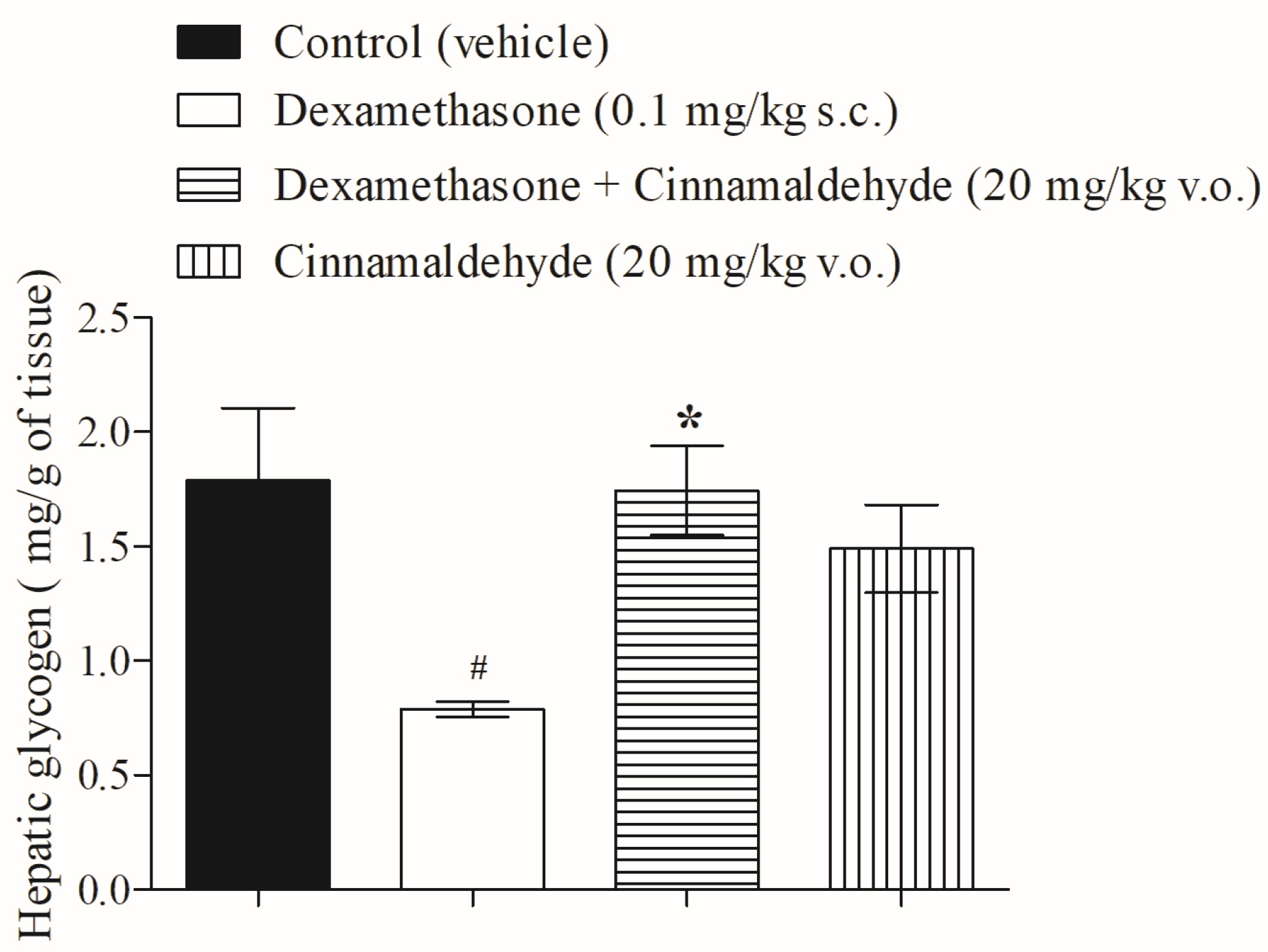
3.2. Cinnamaldehyde on Hepatic Glycogen Accumulation
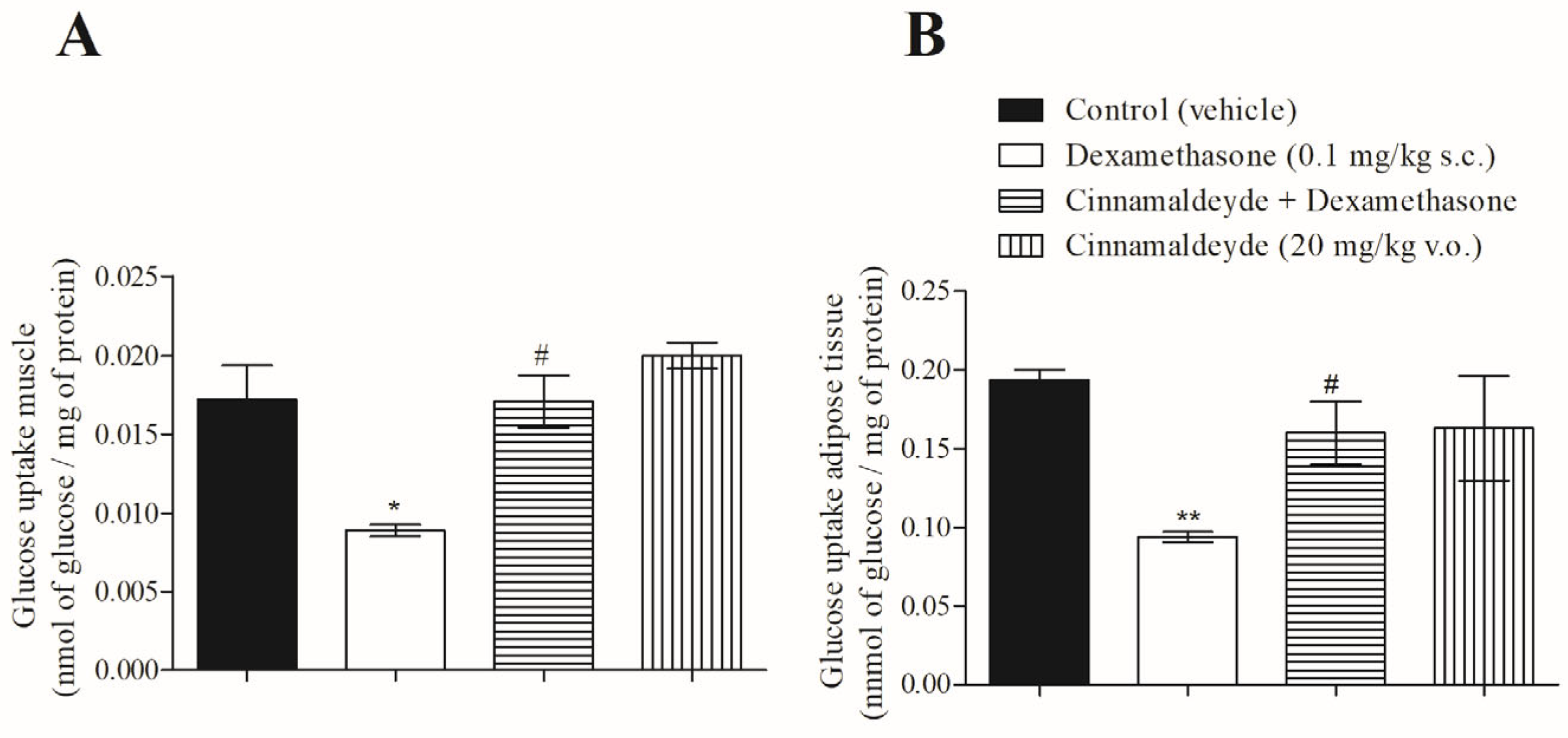
3.3. Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on 14C-Glucose Uptake
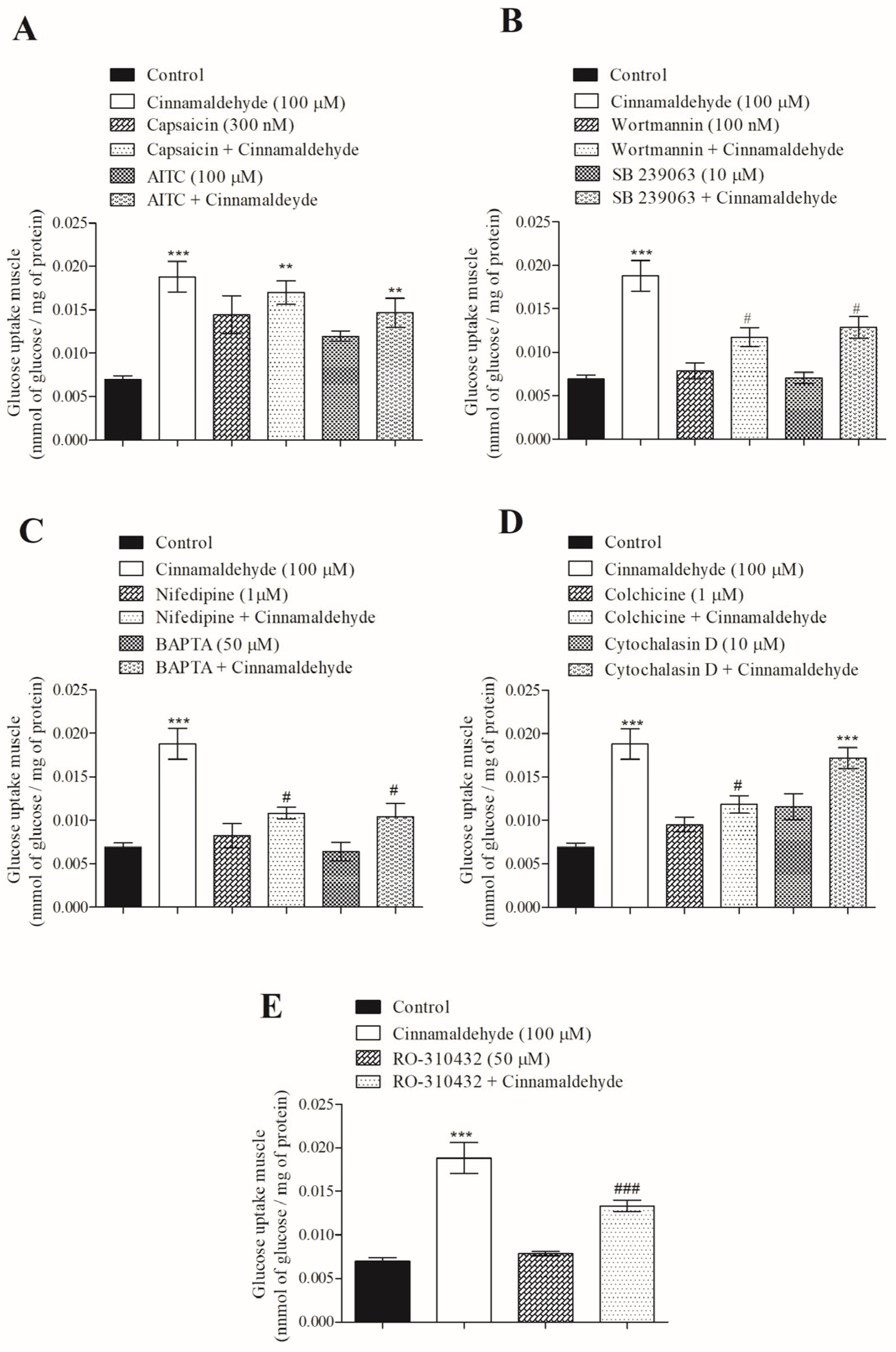
3.4. Mechanism of Action of Cinnamaldehyde on 14C-Glucose Uptake
3.5. Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on 45Ca2+ Influx in Skeletal Muscle
3.6. In Vivo Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Serum Lipid Profile
3.7. Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Oral Triglyceride Tolerance Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punthakee, Z.; Goldenberg, R.; Katz, P. Definition, Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes, Prediabetes and Metabolic Syndrome. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42 (Suppl. 1), S10–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duckworth, W.; Abraira, C.; Moritz, T.; Reda, D.; Emanuele, N.; Reaven, P.D.; Zieve, F.J.; Marks, J.; Davis, S.N.; Hayward, R.; et al. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.I.; Yazdi, Z.S.; Beitelshees, A.L. Pharmacological treatment of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodhi, R.K.; Kumar, H.; Singh, R.; Bansal, Y.; Singh, Y.; Kondepudi, K.K.; Bishnoi, M.; Kuhad, A. Allyl isothiocyanate, a TRPA1 agonist, protects against olanzapine-induced hypothalamic and hepatic metabolic aberrations in female mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista, D.M.; Movahed, P.; Hinman, A.; Axelsson, H.E.; Sterner, O.; Högestätt, E.D.; Julius, D.; Jordt, S.-E.; Zygmunt, P.M. Pungent products from garlic activate the sensory ion channel TRPA1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12248–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, D.M.; Jordt, S.-E.; Nikai, T.; Tsuruda, P.R.; Read, A.J.; Poblete, J.; Yamoah, E.N.; Basbaum, A.I.; Julius, D. TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell 2006, 124, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederico, M.J.S.; Cipriani, A.; Heim, J.B.A.; Mendes, A.K.B.; Aragón, M.; Gaspar, J.M.; De Alencar, N.M.N.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Electrophilic Agonists Modulate the Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin-1 Channels Mediated by Insulin and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Secretion for Glucose Homeostasis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; Chung, J.-J.; Tsai, J.-C.; Chen, Y.-I.; Hsu, T.-H.; Lin, J.-G.; Lee, K.-R.; Chang, S.-L. 15 Hz electroacupuncture at ST36 improves insulin sensitivity and reduces free fatty acid levels in rats with chronic dexamethasone-induced insulin resistance. Acupunct. Med. J. Br. Med. Acupunct. Soc. 2016, 34, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, V.D.; Pereira, D.F.; Cazarolli, L.H.; Guesser, S.M.; da Silva, C.H.B.; Schenkel, E.P.; Reginatto, F.G.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Short and long-term effects of Baccharis articulata on glucose homeostasis. Molecules 2012, 17, 6754–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisman, C.R. A method for the colorimetric estimation of glycogen with lodine. Anal. Biochem. 1962, 4, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Randall, R.J.; Farr, L. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, S.; Sjogren, C. Effect of estrogen treatment of calcium uptake by the rat uterine smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1983, 32, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, A.K.B.; Sulis, P.M.; Cavalari, F.C.; Padilla, D.P.R.; Aragón, M.; Gaspar, J.M.; Silva, F.R.M.B. 1α,25-(OH)2 Vitamin D3 prevents insulin resistance and regulates coordinated exocytosis and insulin secretion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 99, 108864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, D.; Sulis, P.M.; Fernandes, T.A.; Gonçalves, R.; Frederico, M.J.S.; Costa, G.M.; Aragon, M.; Ospina, L.F.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Astragalin augments basal calcium influx and insulin secretion in rat pancreatic islets. Cell Calcium 2019, 80, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concepción, B.D.l.C.; Cortez, Y.A.F.; Bonilla, M.I.B.; Bello, J.M.M.; Rojo, M.E. Insulin: A connection between pancreatic β cells and the hypothalamus. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yan, S.; Jiang, X.; Su, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xie, J.; Hao, E.; Yao, C. Advances in pharmacological effects and mechanism of action of cinnamaldehyde. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1365949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, R.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Niu, J.; Fu, M.; Zhang, D.; et al. Cinnamaldehyde in diabetes: A review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and safety. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 122, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, H.Q.; Smith, T.; Klorig, D.C.; Godwin, D.W. Protein kinase C epsilon-mediated modulation of T-type calcium channels underlies alcohol withdrawal hyperexcitability in the midline thalamus. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 48, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nmarneh, A.; Priel, A. TRPM5 activation depends on a synergistic effect of calcium and PKC phosphorylation. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Sabe, S.A.; Shi, G.; Harris, D.D.; Liu, Y.; Sellke, F.W.; Feng, J. Role of Protein Kinase C in Metabolic Regulation of Coronary Endothelial Small Conductance Calcium-Activated Potassium Channels. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2024, 13, e031028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninello, M.; Bean, C. Highly Specialized Mechanisms for Mitochondrial Transport in Neurons: From Intracellular Mobility to Intercellular Transfer of Mitochondria. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, J.W.; Vogan, J.M.; Buch, P.J.; Zhang, S.-S.; Fong, T.S.; Hong, T.-T.; Shaw, R.M. Actin Cytoskeleton rest stops regulate anterograde traffic of connexin 43 vesicles to the plasma membrane. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkes, M.; Landers, N.L.; Gramlich, M.W. Recently recycled synaptic vesicles use multi-cytoskeletal transport and differential presynaptic capture probability to establish a retrograde net flux during ISVE in central neurons. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1286915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, N.; Kazemi, A.; Saffari-Chaleshtori, J.; Samare-Najaf, M.; Mohammadi, V.; Clark, C.C. The effect of cinnamon supplementation on lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 55, 102571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.W.; Schwartzman, E.; Baker, W.L.; Coleman, C.I.; Phung, O.J. Cinnamon use in type 2 diabetes: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Fam. Med. 2013, 11, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-E.; Futawaka, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kasahara, M.; Tagami, T.; Liu, T.-H.; Moriyama, K. Cinnamaldehyde Contributes to Insulin Sensitivity by Activating PPARδ, PPARγ, and RXR. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frederico, M.J.S.; Sulis, P.M.; Pereira, L.L.; Rey, D.; Aragón, M.; Silva, F.R.M.B. Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020297
Frederico MJS, Sulis PM, Pereira LL, Rey D, Aragón M, Silva FRMB. Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. Nutrients. 2025; 17(2):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020297
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrederico, Marisa Jadna Silva, Paola Miranda Sulis, Landerson Lopes Pereira, Diana Rey, Marcela Aragón, and Fátima Regina Mena Barreto Silva. 2025. "Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis" Nutrients 17, no. 2: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020297
APA StyleFrederico, M. J. S., Sulis, P. M., Pereira, L. L., Rey, D., Aragón, M., & Silva, F. R. M. B. (2025). Potential Effect of Cinnamaldehyde on Insulin Resistance Is Mediated by Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis. Nutrients, 17(2), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17020297







