Gastrointestinal Survivability of a BSH-Positive Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VB4 Strain and Its Effect on Bile Acid Deconjugation in a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. BSH-Positive L. rhamnosus VB4 Strain
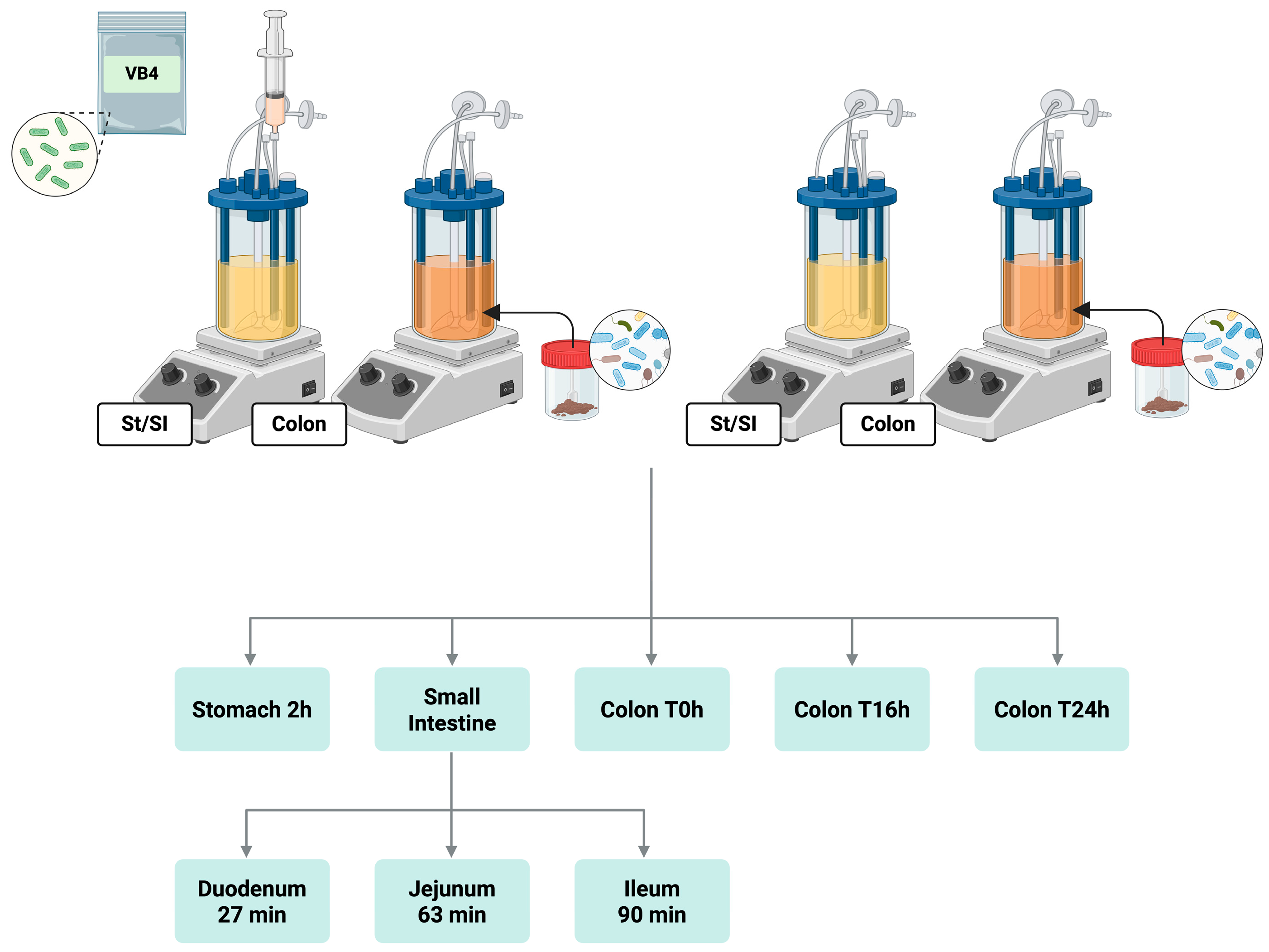
2.2. SHIME® Experiment Set-Up
2.3. Fecal Slurry Preparation and Colonic Incubation
2.4. Detection of Viability by Culture-Dependent Method
2.5. Detection of Gene Expression of BSH-Positive VB4 Strain2
2.5.1. RNA Extraction
2.5.2. RT-PCR and RT-qPCR Assays
2.6. Detection of BAs from SHIME® Samples
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
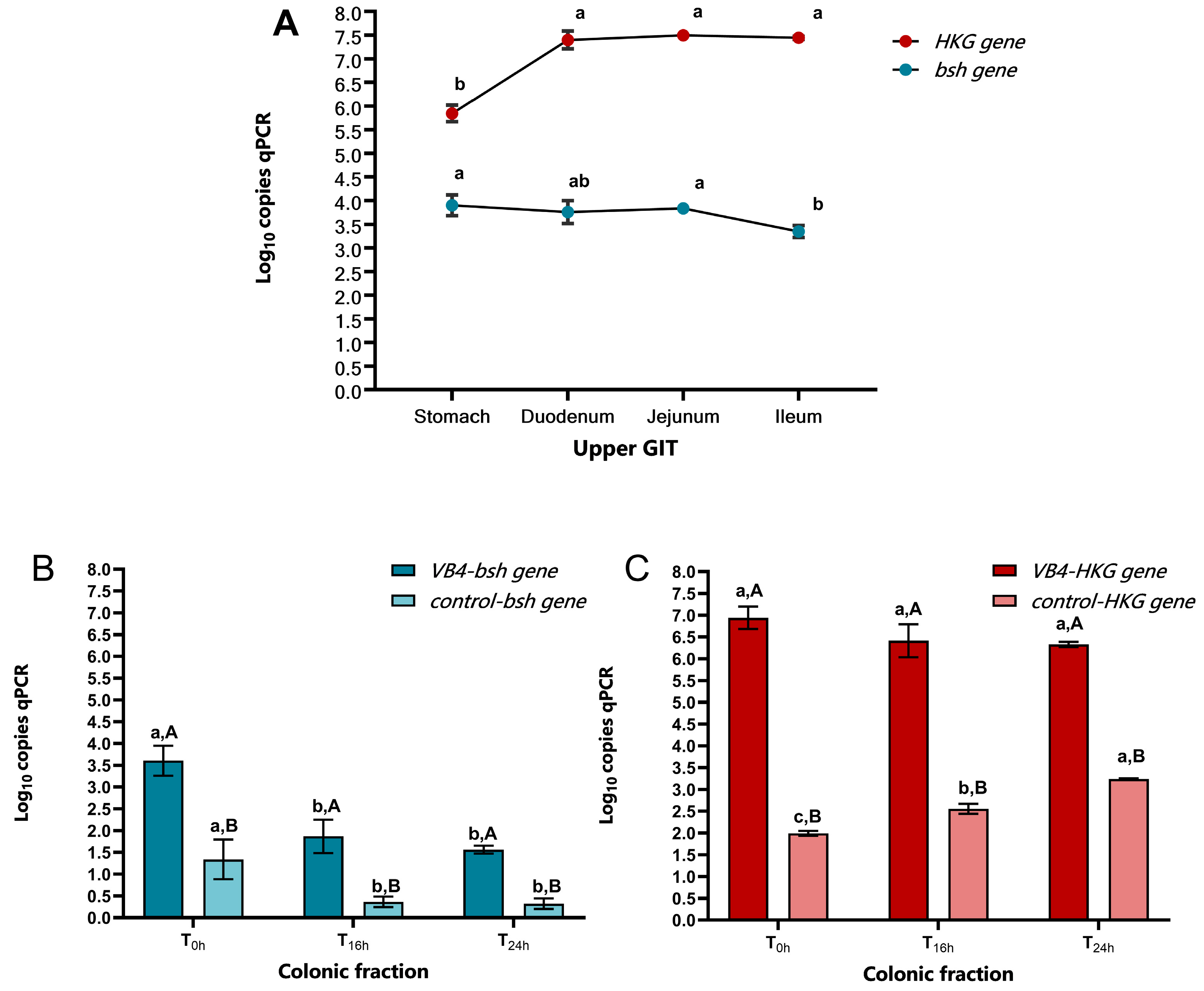
3.1. L. rhamnosus VB4 Strain Viability in Stomach/Small Intestine
3.2. Bsh Gene Detection Through qPCR Analysis
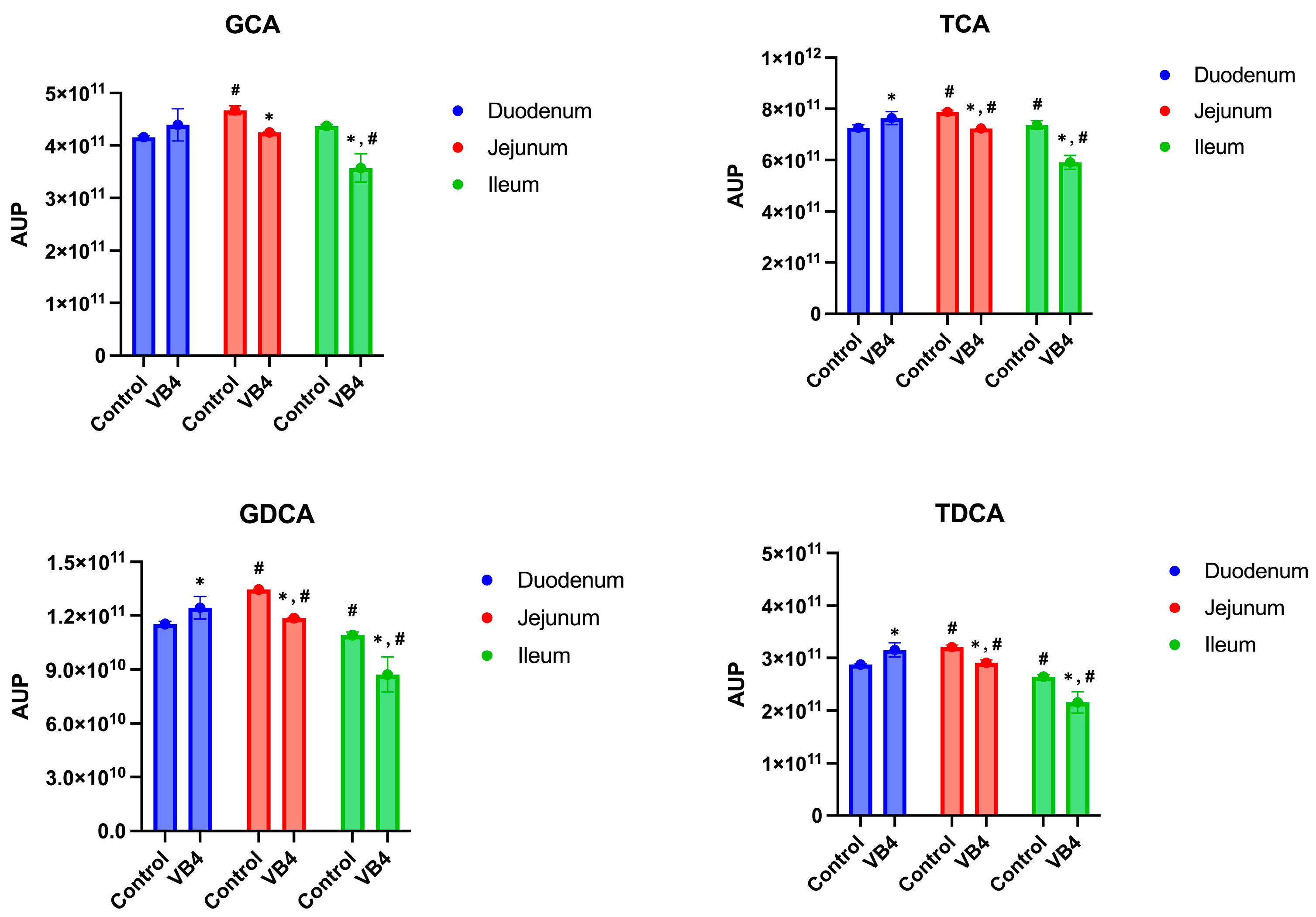
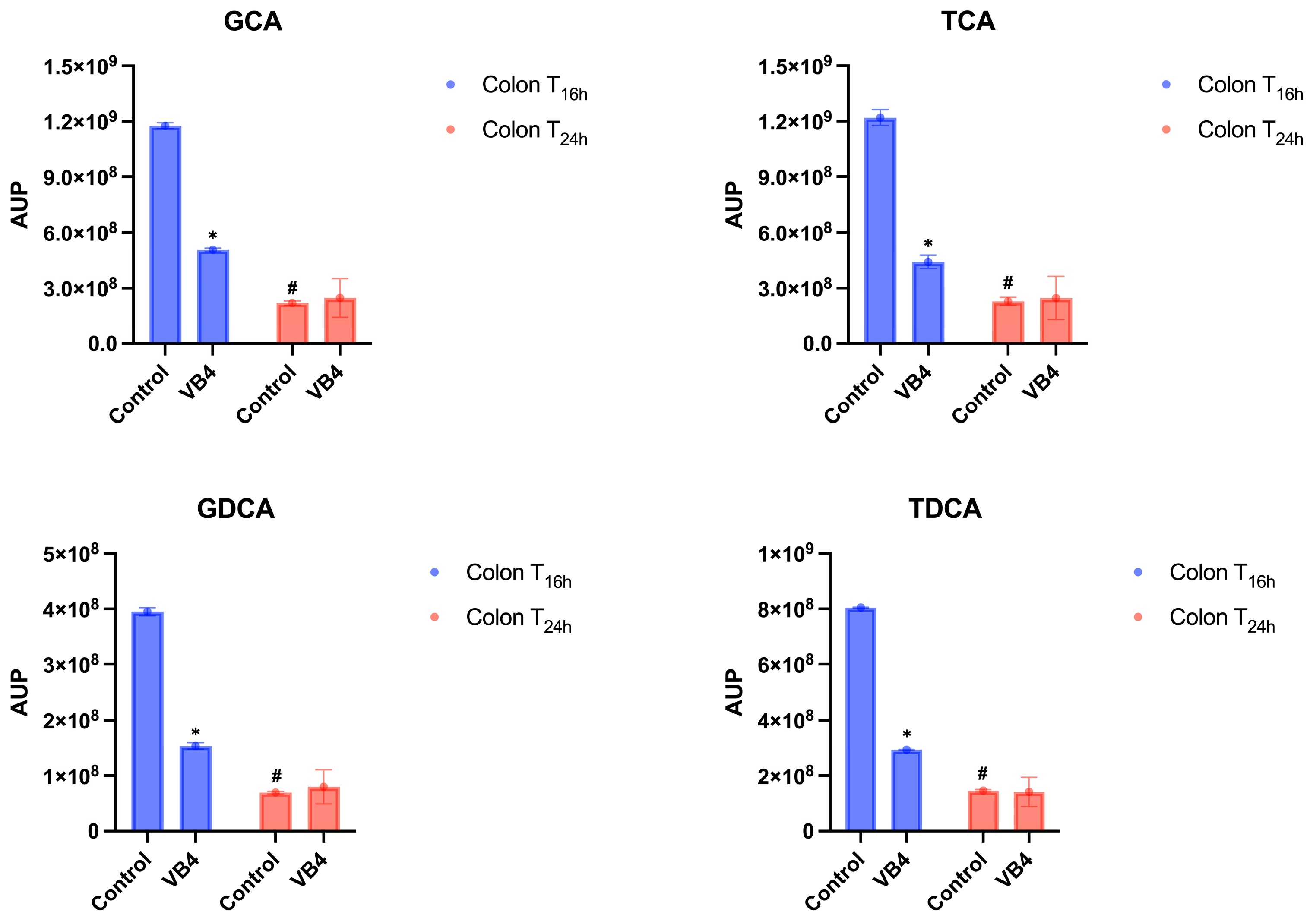
3.3. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of BAs in Small Intestine and Colon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, M.; Nagpal, R.; Kumar, R.; Hemalatha, R.; Verma, V.; Kumar, A.; Chakraborty, C.; Singh, B.; Marotta, F.; Jain, S.; et al. Cholesterol-Lowering Probiotics as Potential Biotherapeutics for Metabolic Diseases. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 902917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, S.A.; MacSharry, J.; Casey, P.G.; Kinsella, M.; Murphy, E.F.; Shanahan, F.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G. Regulation of Host Weight Gain and Lipid Metabolism by Bacterial Bile Acid Modification in the Gut. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agolino, G.; Pino, A.; Vaccalluzzo, A.; Cristofolini, M.; Solieri, L.; Caggia, C.; Randazzo, C.L. Bile Salt Hydrolase: The Complexity behind Its Mechanism in Relation to Lowering-Cholesterol Lactobacilli Probiotics. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 120, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Pan, J.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z.Y. Effect of Gut Microbiota on Blood Cholesterol: A Review on Mechanisms. Foods 2023, 12, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boever, P.; Wouters, R.; Verschaeve, L.; Berckmans, P.; Schoeters, G.; Verstraete, W. Protective Effect of the Bile Salt Hydrolase-Active Lactobacillus reuteri against Bile Salt Cytotoxicity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 53, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chiang, J.Y. Bile Acids as Metabolic Regulators. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flaherty, S.; Briner Crawley, A.; Theriot, C.M.; Barrangou, R. The Lactobacillus Bile Salt Hydrolase Repertoire Reveals Niche-Specific Adaptation. mSphere 2018, 3, e00108-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusada, H.; Morinaga, K.; Tamaki, H. Identification of Bile Salt Hydrolase and Bile Salt Resistance in a Probiotic Bacterium Lactobacillus gasseri JCM1131T. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lao, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, J. Taxonomic Profiling and Populational Patterns of Bacterial Bile Salt Hydrolase (BSH) Genes Based on Worldwide Human Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhou, X.; Song, Z.; Li, J.; Li, P. Taxonomic Identification of Bile Salt Hydrolase-Encoding Lactobacilli: Modulation of the Enterohepatic Bile Acid Profile. iMeta 2023, 2, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duysburgh, C.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Marzorati, M. SHIME®: An Advanced In Vitro Technology Platform for Studying the Mode-of-Action of Probiotics in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Nutrafoods 2018, 17, 213–217. Available online: https://www.nutrafoods.eu/index.php/nutra/article/view/42 (accessed on 4 October 2025). [CrossRef]
- Rudzka, A.; Patloka, O.N.D.; Plecha, M.; Królikowski, T.; Oczkowski, M.; Zborowski, M.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D.; Zielinska, D. Changes in the Microbiome of a Human and in the Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®) in Response to a Diet and Probiotic Supplementation. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2023, 30, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Wiele, T.; Van den Abbeele, P.; Ossieur, W.; Possemiers, S.; Marzorati, M. The Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®). In The Impact of Food Bioactives on Health: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Models; Verhoeckx, K., Cotter, P., López-Expósito, I., Mackie, T.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Chapter 27; pp. 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agolino, G.; Cristofolini, M.; Vaccalluzzo, A.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Cattivelli, A.; Pino, A.; Caggia, C.; Solieri, L.; Randazzo, C.L. Genome Mining and Characterization of Two Novel Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probiotic Candidates with Bile Salt Hydrolase Activity. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzorati, M.; Calatayud, M.; Rotsaert, C.; Van Mele, M.; Duysburgh, C.; Durkee, S.; White, T.; Fowler, K.; Jannin, V.; Bellamine, A. Comparison of Protection and Release Behavior of Different Capsule Polymer Combinations Based on L. acidophilus Survivability and Function and Caffeine Release. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannin, V.; Duysburgh, C.; Gonzalez, V.; Govaert, M.; Agisson, M.; Marzorati, M.; Madit, N. In Vitro Evaluation of the Gastrointestinal Delivery of Acid-Sensitive Pancrelipase in a Next Generation Enteric Capsule Using an Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Disease Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 630, 122441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, M.H.; O’Flaherty, S.; Allen, G.; Rivera, A.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Barrangou, R.; Theriot, C.M. Lactobacillus Bile Salt Hydrolase Substrate Specificity Governs Bacterial Fitness and Host Colonization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017709118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y.; Huan, H. Bile Salt Hydrolase Can Improve Lactobacillus plantarum Survival in Gastrointestinal Tract by Enhancing Their Adhesion Ability. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgin, M.; Kriaa, A.; Mkaouar, H.; Mariaule, V.; Jablaoui, A.; Maguin, E.; Rhimi, M. Bile Salt Hydrolases: At the Crossroads of Microbiota and Human Health. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaert, M.; Rotsaert, C.; Vannieuwenhuyse, C.; Duysburgh, C.; Medlin, S.; Marzorati, M.; Jarrett, H. Survival of Probiotic Bacterial Cells in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract and the Effect of the Surviving Population on the Colonic Microbial Community Activity and Composition. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duary, R.K.; Batish, V.K.; Grover, S. Relative gene expression of bile salt hydrolase and surface proteins in two putative indigenous Lactobacillus plantarum strains under in vitro gut conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2541–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Dong, W.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Dicaffeoylquinic Acids Is Associated with the Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 72, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Hagey, L.R. Bile Acids: Chemistry, Pathochemistry, Biology, Pathobiology, and Therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2461–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yue, T.L.; Guo, C.F. Bile Acid Patterns in Commercially Available Oxgall Powders Used for the Evaluation of the Bile Tolerance Ability of Potential Probiotics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyaert, S.; Moens, F.; Pirovano, W.; van den Bogert, B.; Klaassens, E.S.; Marzorati, M.; Van den Abbeele, P. Development of a Reproducible Small Intestinal Microbiota Model and Its Integration into the SHIME®-System, a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1054061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, R.M.; Cariello, M.; Crudele, L.; Moschetta, A. Bile Salt Hydrolase-Competent Probiotics in the Management of IBD: Unlocking the “Bile Acid Code”. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Bile Salt Biotransformations by Human Intestinal Bacteria. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaccalluzzo, A.; Agolino, G.; Pino, A.; Cristofolini, M.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Cattivelli, A.; Caggia, C.; Solieri, L.; Randazzo, C.L. Gastrointestinal Survivability of a BSH-Positive Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VB4 Strain and Its Effect on Bile Acid Deconjugation in a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193179
Vaccalluzzo A, Agolino G, Pino A, Cristofolini M, Tagliazucchi D, Cattivelli A, Caggia C, Solieri L, Randazzo CL. Gastrointestinal Survivability of a BSH-Positive Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VB4 Strain and Its Effect on Bile Acid Deconjugation in a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model. Nutrients. 2025; 17(19):3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193179
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaccalluzzo, Amanda, Gianluigi Agolino, Alessandra Pino, Marianna Cristofolini, Davide Tagliazucchi, Alice Cattivelli, Cinzia Caggia, Lisa Solieri, and Cinzia Lucia Randazzo. 2025. "Gastrointestinal Survivability of a BSH-Positive Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VB4 Strain and Its Effect on Bile Acid Deconjugation in a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model" Nutrients 17, no. 19: 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193179
APA StyleVaccalluzzo, A., Agolino, G., Pino, A., Cristofolini, M., Tagliazucchi, D., Cattivelli, A., Caggia, C., Solieri, L., & Randazzo, C. L. (2025). Gastrointestinal Survivability of a BSH-Positive Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus VB4 Strain and Its Effect on Bile Acid Deconjugation in a Dynamic In Vitro Gut Model. Nutrients, 17(19), 3179. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17193179














